Abstract
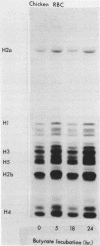
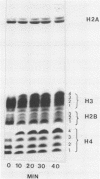
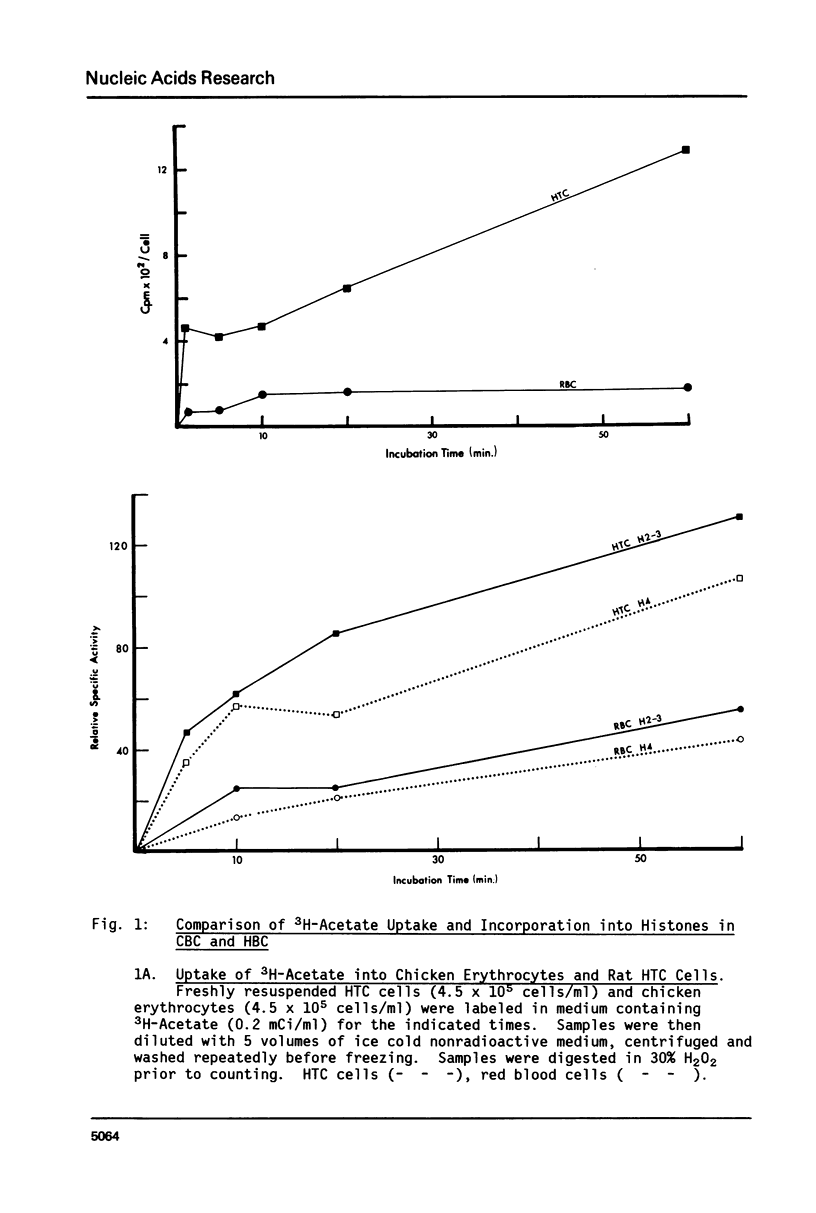
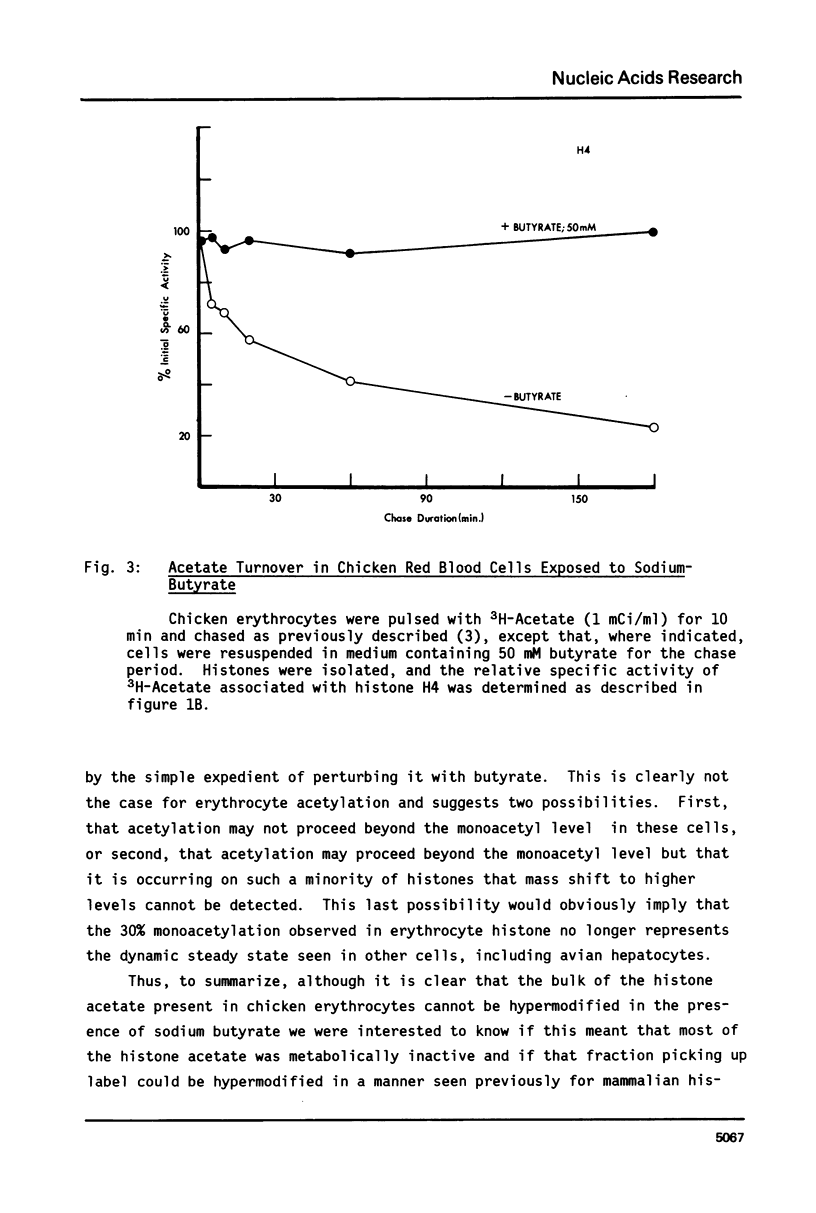
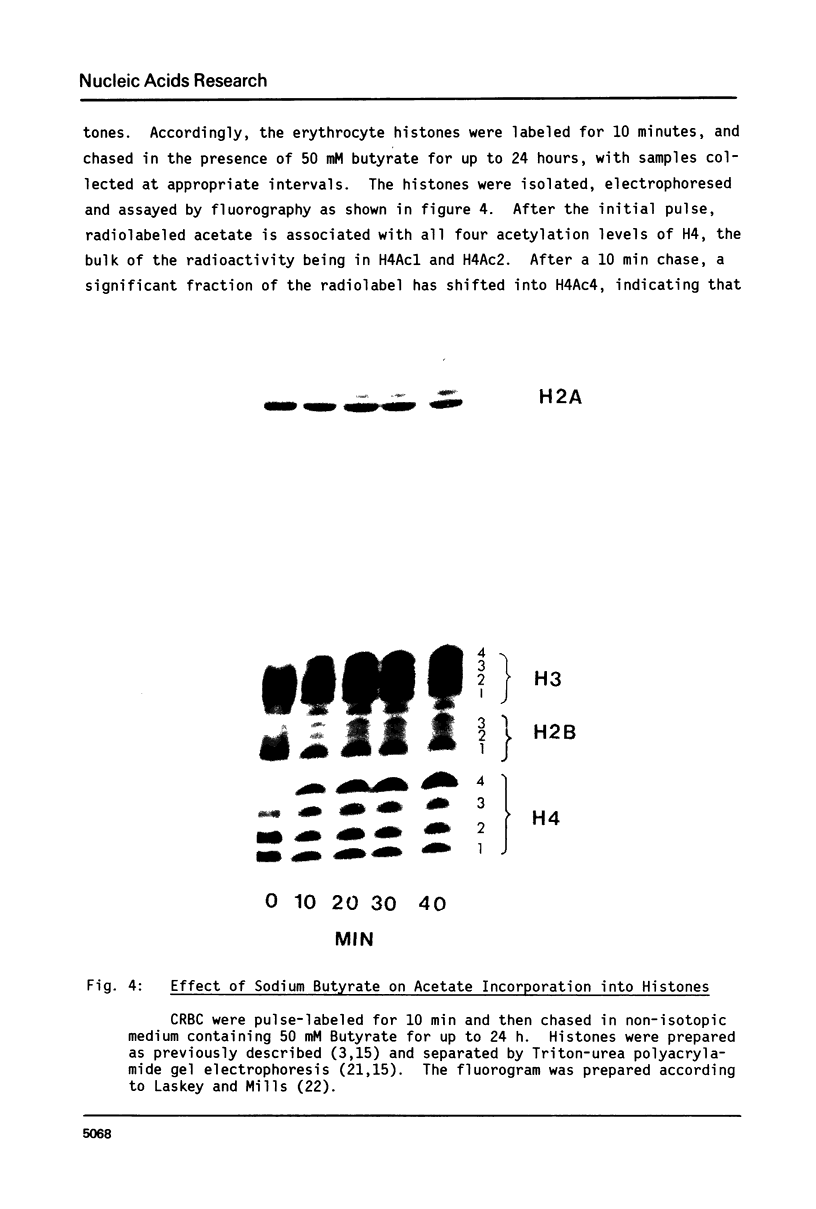
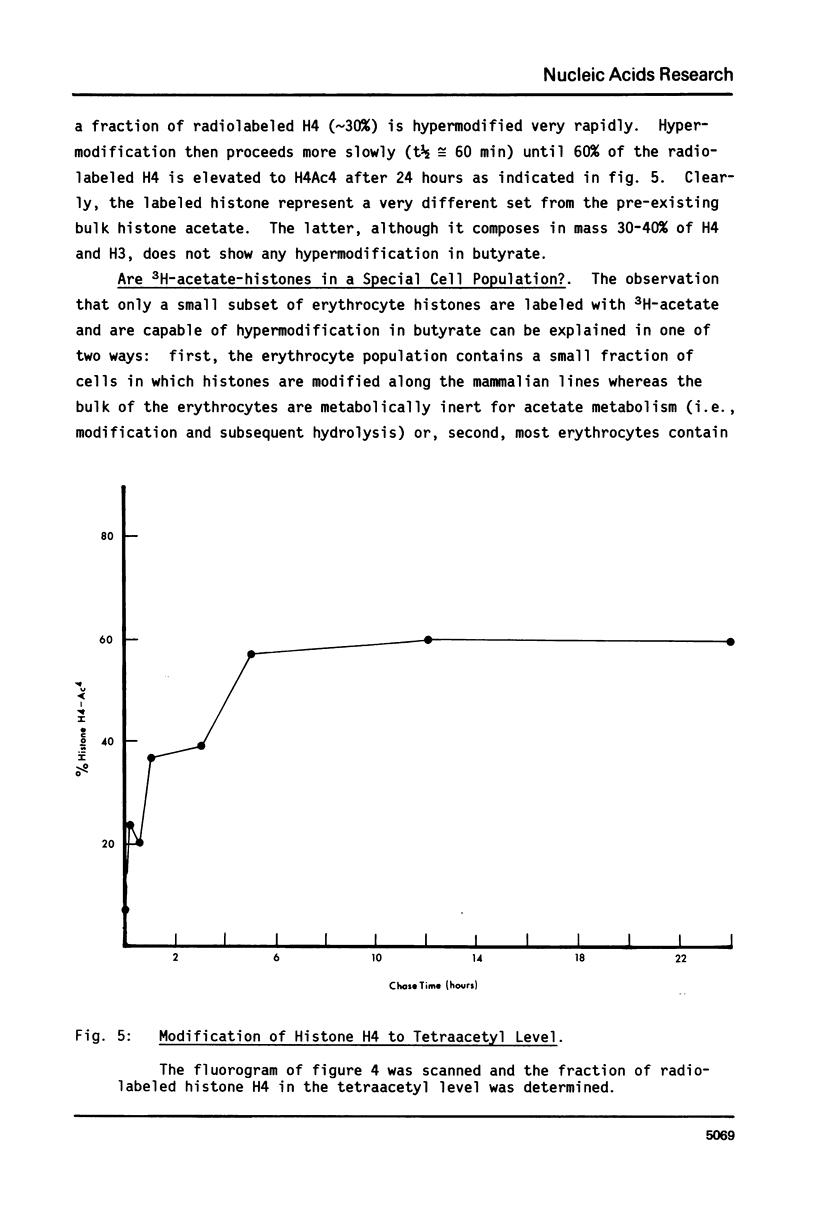
We have studied histone acetylation in chicken erythrocytes. We find that about 30% of the histone in these cells is acetylated, however the majority of these histones are not in a dynamic steady state typical of other chicken cells and of mammalian cells, but rather are frozen in this state of modification. A very small fraction of erythrocyte histones are being modified normally but cannot be detected as shifting to higher levels of acetylation upon treatment with butyrate because the amount of histone so modified is small. Nonetheless, chicken erythrocytes incorporate 3H-acetate into histones about 40% as well as seen in the dynamically active HTC cells. This is most likely due to the formation of very high specific activity Acetyl CoA pools in erythrocytes which have very low levels of coenzyme A. We conclude that these genetically inactive cells are involved in only a minor way with histone acetylation.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTER R. H., JANDL J. H. PLATELET SEQUESTRATION IN MAN. I. METHODS. J Clin Invest. 1964 May;43:843–855. doi: 10.1172/JCI104970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alfageme C. R., Zweidler A., Mahowald A., Cohen L. H. Histones of Drosophila embryos. Electrophoretic isolation and structural studies. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3729–3736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allred J. B., Guy D. G. Determination of coenzyme A and acetyl CoA in tissue extracts. Anal Biochem. 1969 May;29(2):293–299. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90312-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appels R., Wells J. R., Williams A. F. Characterization of DNA-bound histone in the cells of the avian erythropoietic series. J Cell Sci. 1972 Jan;10(1):47–59. doi: 10.1242/jcs.10.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billett M. A., Hindley J. A study of the quantitative variation of histones, and their relationship to RNA synthesis, during erythropoiesis in the adult chicken. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Aug 4;28(4):451–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns G. A., Ingram V. M. The erythroid cells and haemoglobins of the chick embryo. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Oct 25;266(877):225–305. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1973.0050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousens L. S., Gallwitz D., Alberts B. M. Different accessibilities in chromatin to histone acetylase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1716–1723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covault J., Chalkley R. The identification of distinct populations of acetylated histone. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9110–9116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson V., Shires A., Chalkley R., Granner D. K. Studies on highly metabolically active acetylation and phosphorylation of histones. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):4856–4863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D., Covault J., Chalkley R. Segregation of rapidly acetylated histones into a chromatin fraction released from intact nuclei by the action of micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 25;8(8):1745–1763. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.8.1745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble P. B., Cutts J. H. Separation of blood leukocytes by Ficoll gradient. Can Vet J. 1967 May;8(5):110–111. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogo B. G., Allfrey V. G., Mirsky A. E. RNA synthesis and histone acetylation during the course of gene activation in lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Apr;55(4):805–812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.4.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs M. G., Whittaker R. G., Neumann J. R., Ingram V. M. n-Butyrate causes histone modification in HeLa and Friend erythroleukaemia cells. Nature. 1977 Aug 4;268(5619):462–464. doi: 10.1038/268462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Carrillo A., Wangh L. J., Littau V. C., Allfrey V. G. Changes in histone acetyl content and in nuclear non-histone protein composition of avian erythroid cells at different stages of maturation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 25;249(22):7358–7368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders L. A., Schechter N. M., McCarty K. S. A comparative study of histone acetylation, histone deacetylation, and ribonucleic acid synthesis in avian reticulocytes and erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb 27;12(5):783–791. doi: 10.1021/bi00729a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. S., Benjamin T. L. Deficiency in histone acetylation in nontransforming host range mutants of polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1092–1096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealy L., Chalkley R. DNA associated with hyperacetylated histone is preferentially digested by DNase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jun;5(6):1863–1876. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.6.1863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealy L., Chalkley R. The effect of sodium butyrate on histone modification. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):115–121. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. V., Davies H. G. Erythropoiesis in the yolk sac of the early chick embryo: an electron microscope and microspectrophotometric study. Tissue Cell. 1972;4(3):341–378. doi: 10.1016/s0040-8166(72)80015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweidler A. Resolution of histones by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in presence of nonionic detergents. Methods Cell Biol. 1978;17:223–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]