Abstract
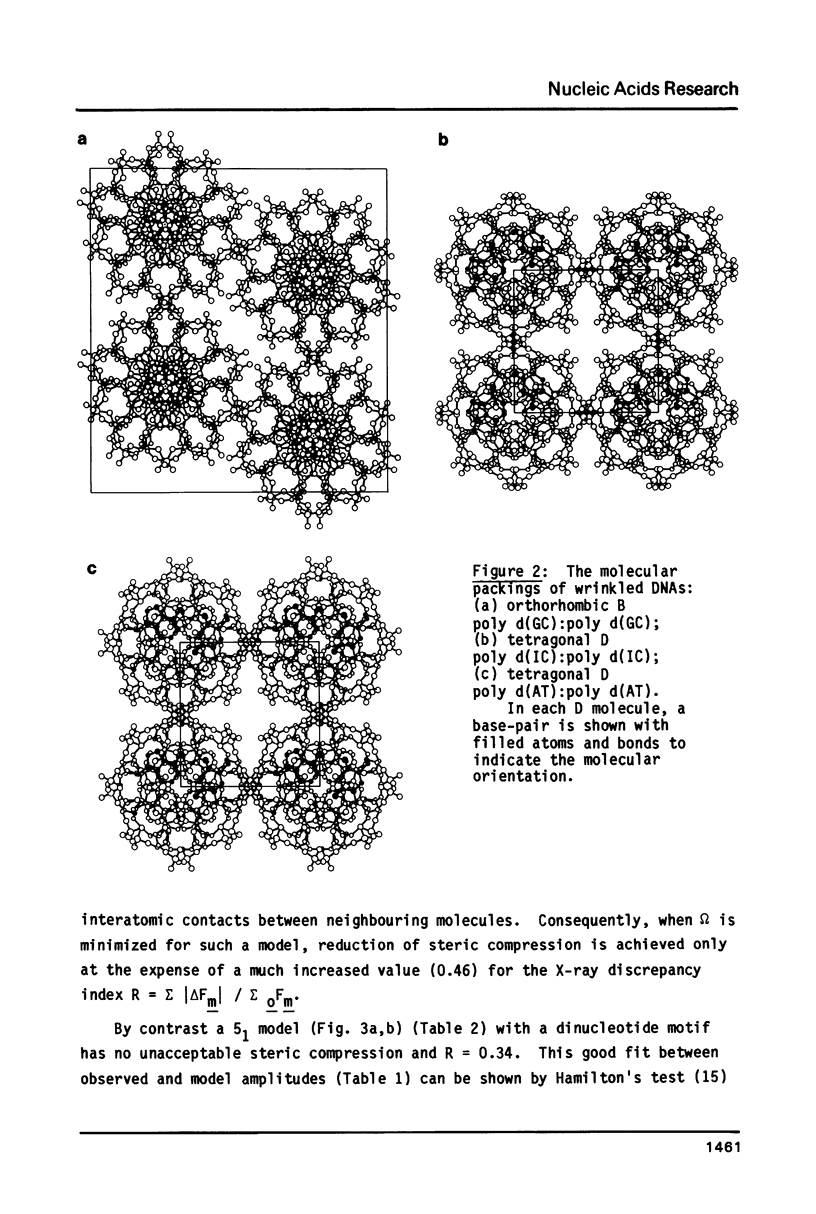
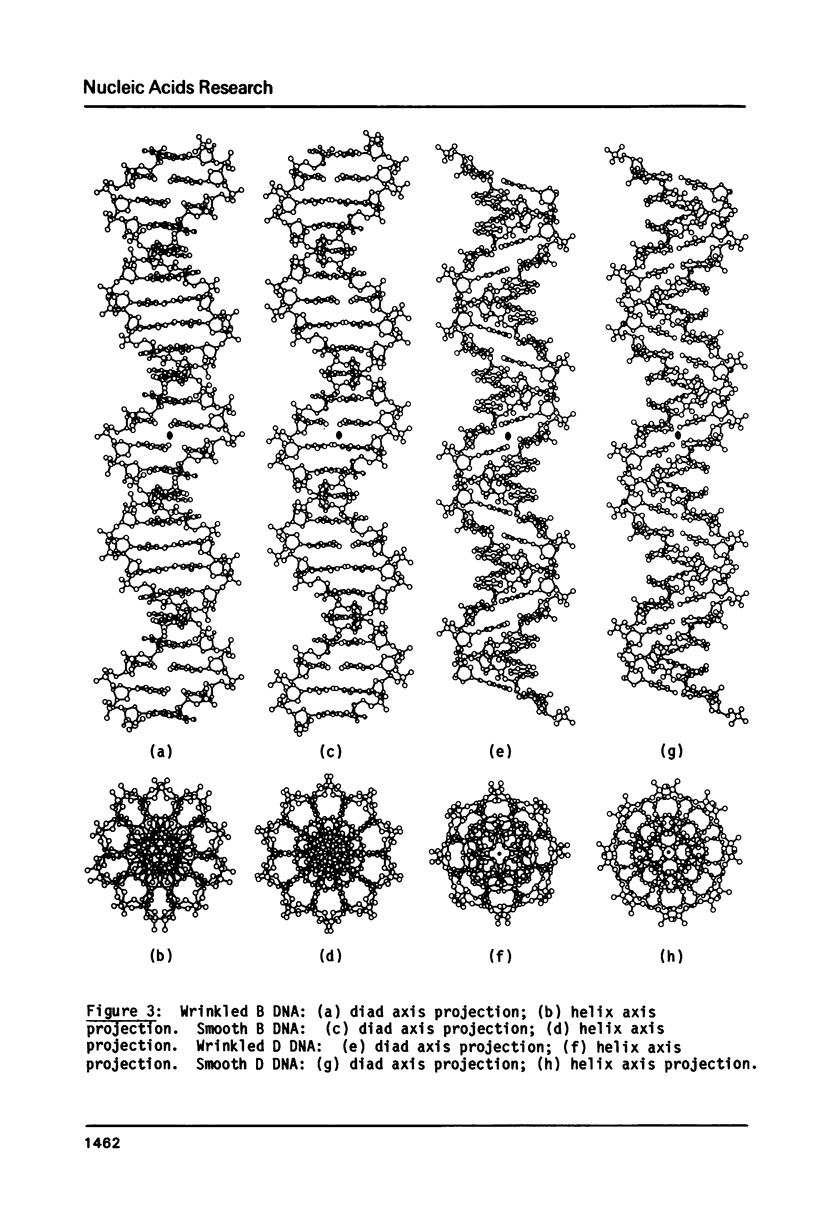
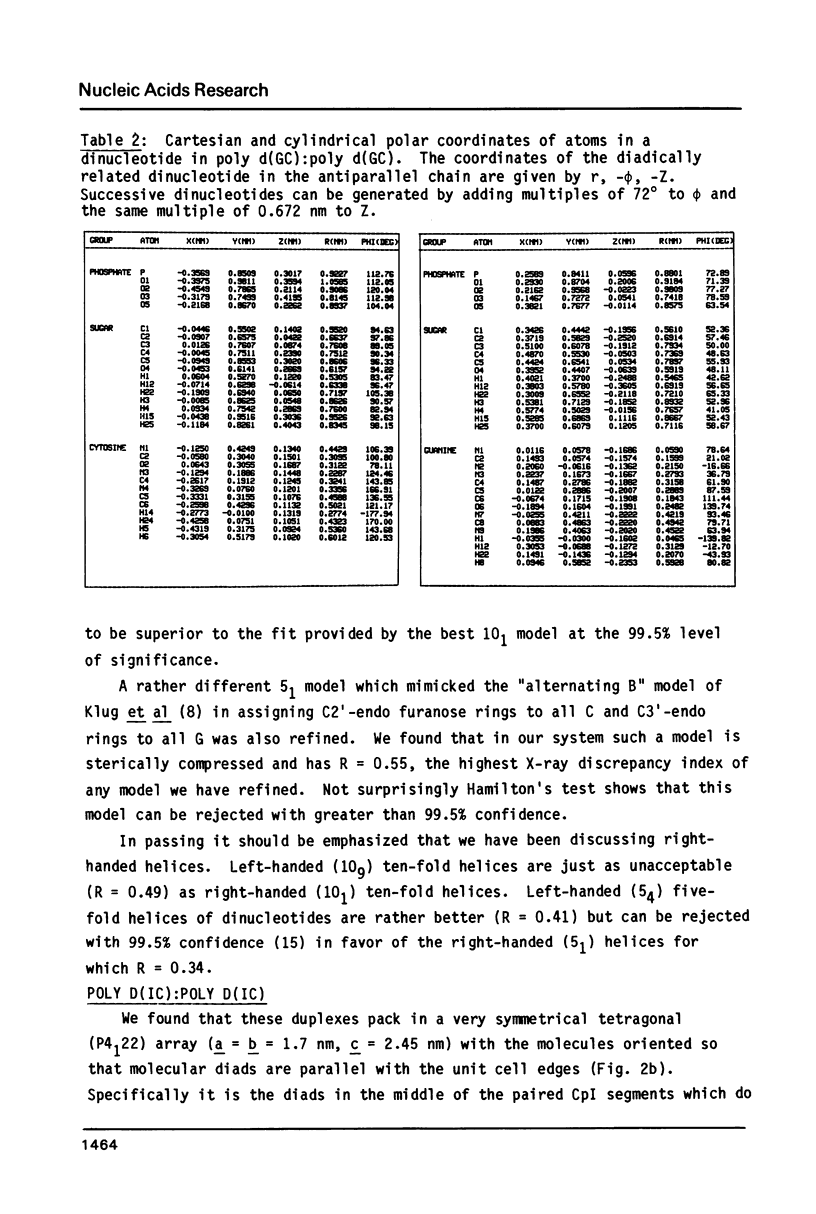
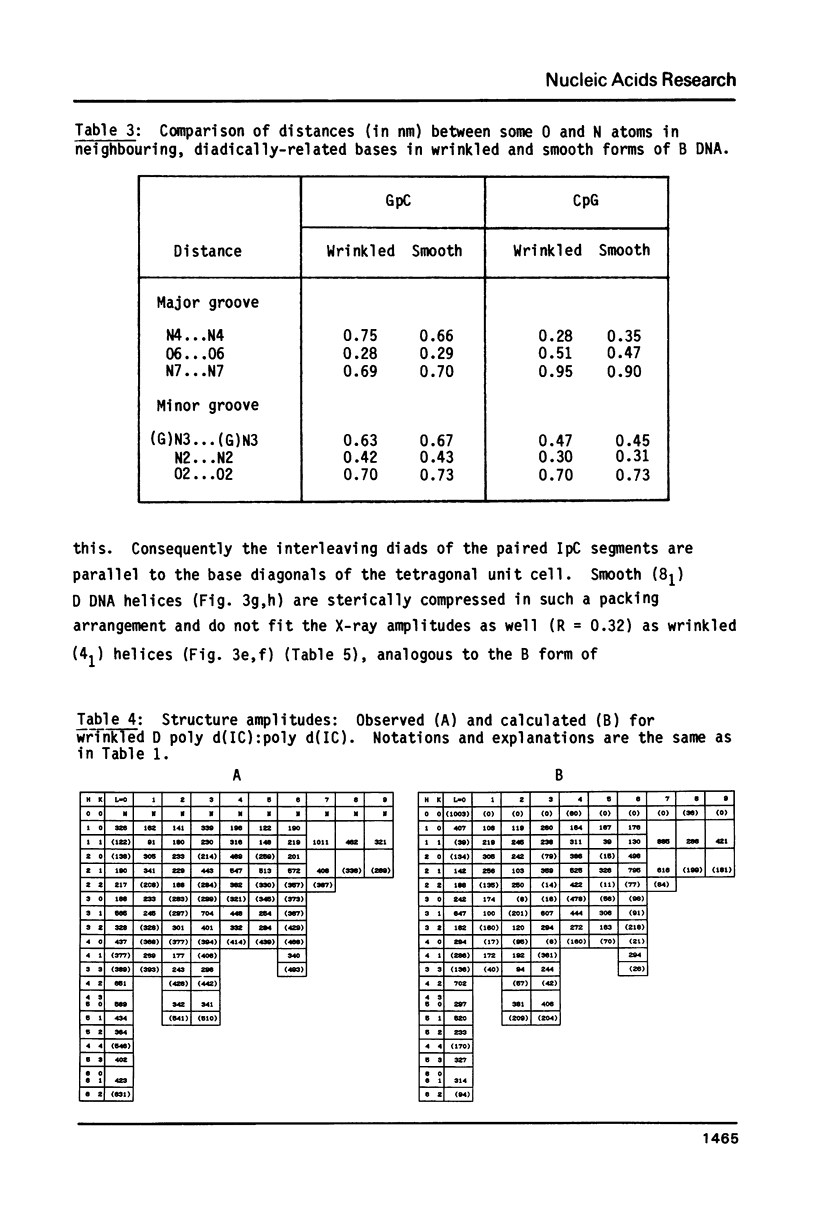
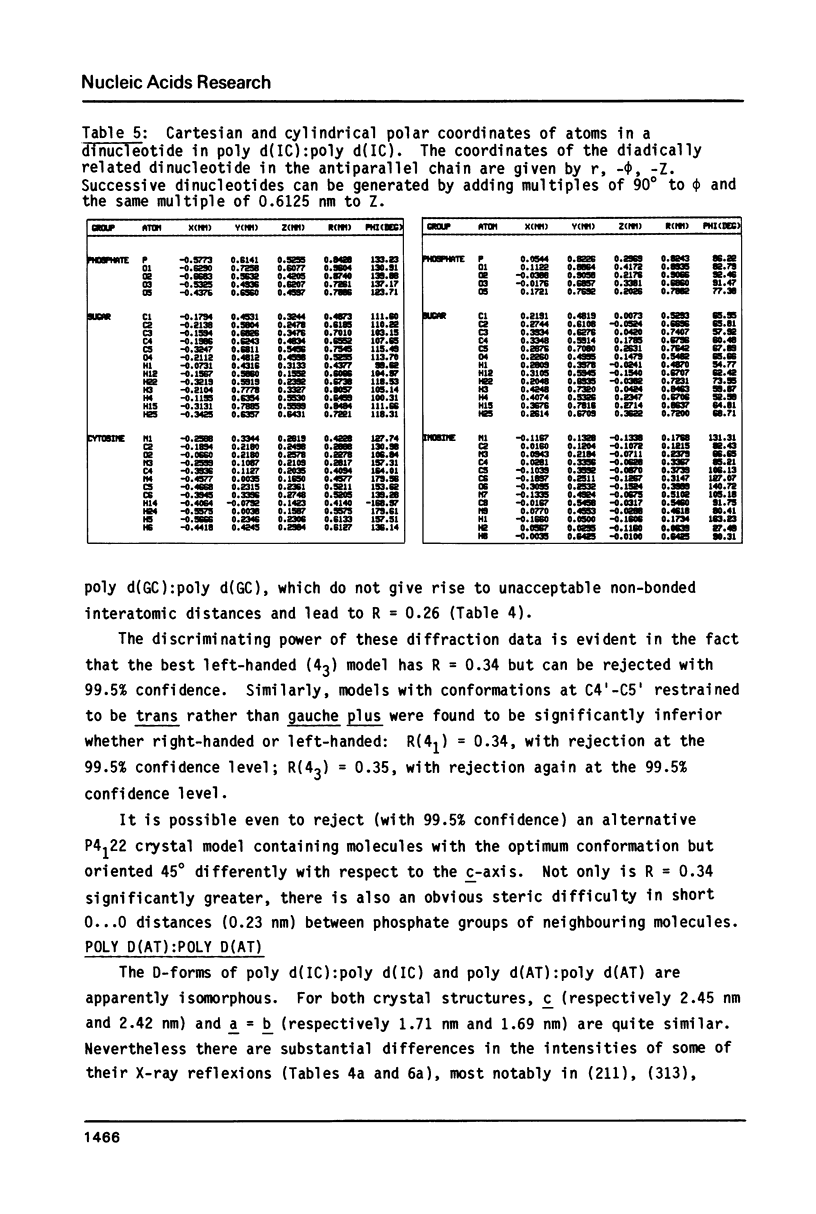
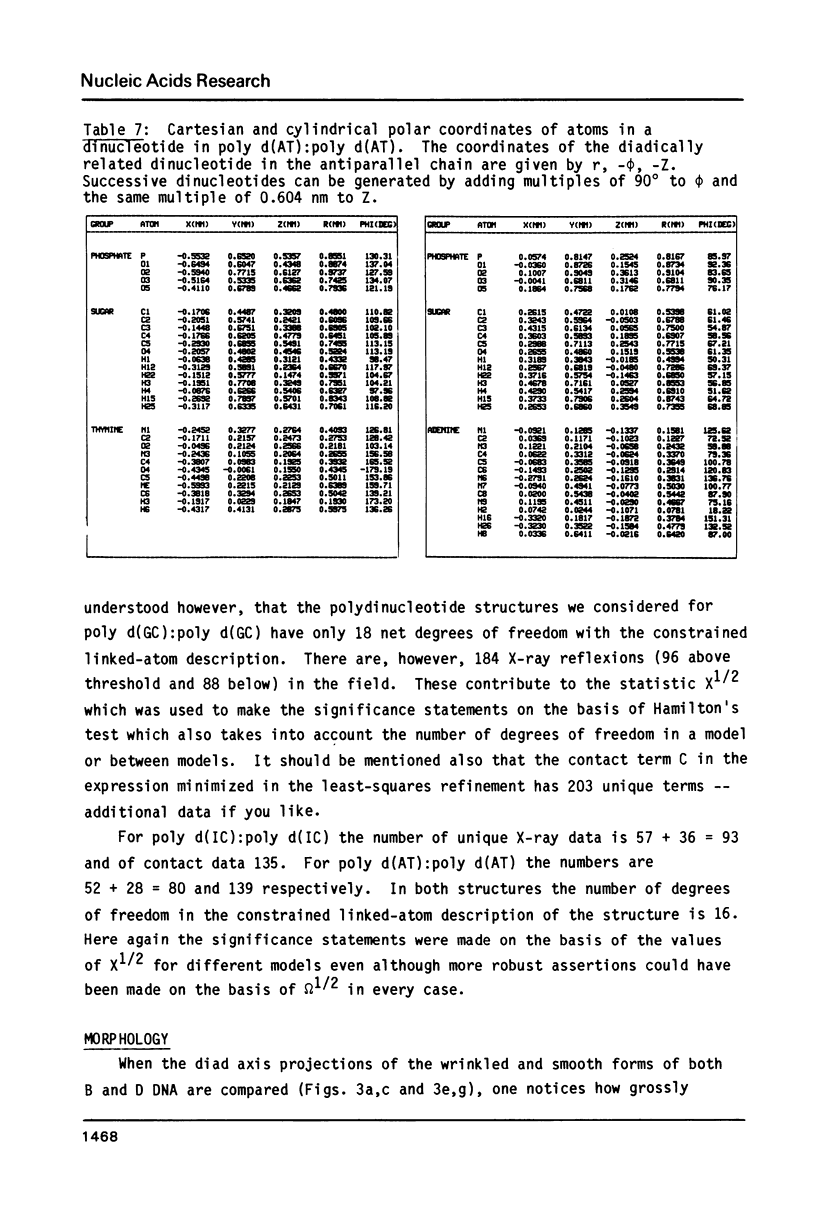
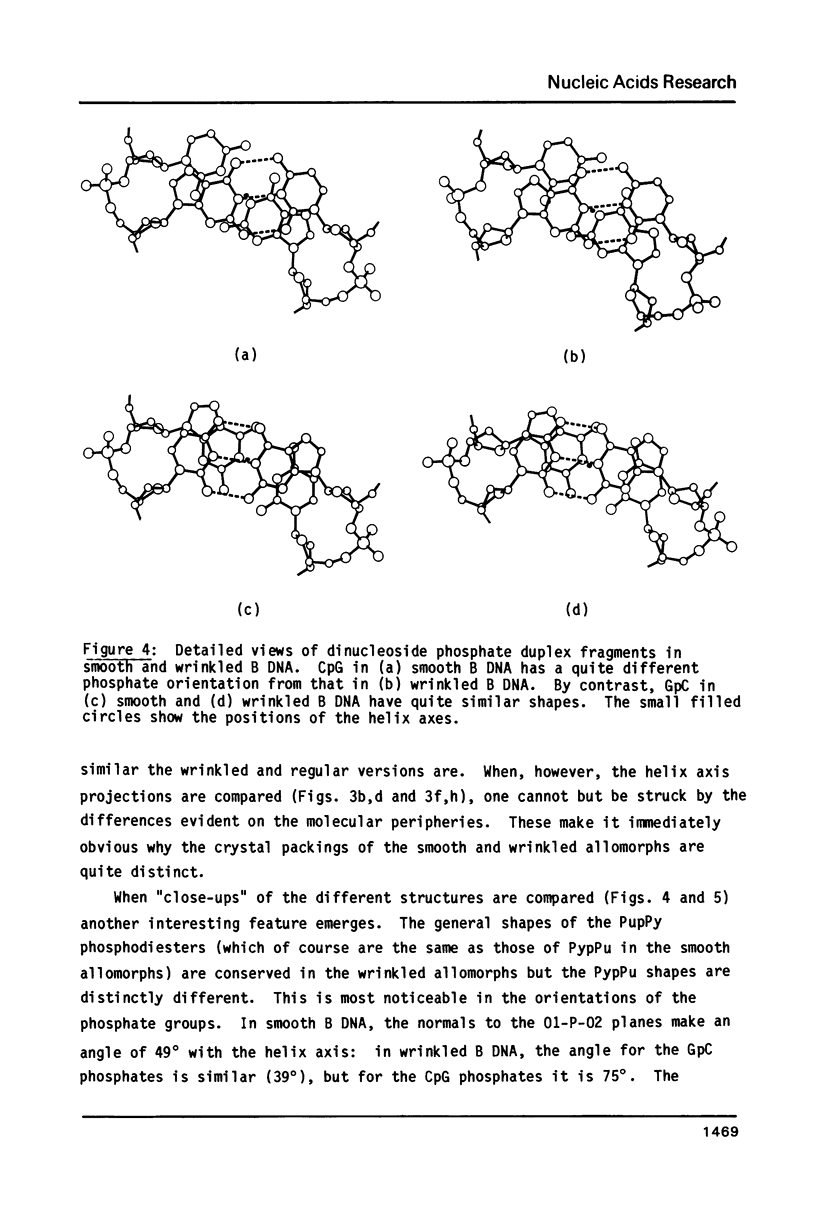
The B form of poly d(GC):poly d(GC) in orthorhombic microcrystallites in oriented fibers has a secondary structure in which a dinucleotide is the repeated motif rather than a mononucleotide as in standard, smooth B DNA. One set of nucleotides (probably GpC) has the same conformations as the smooth form but the alternate (CpG) nucleotides have a different conformation at C3'-O3'. This leads to a distinctive change in the orientation of the phosphate groups. Similar perturbations can be detected in other poly d(PuPy):poly d(PuPy) DNAs such as poly d(IC):poly d(IC) and poly d(AT):poly d(AT) in their D forms which have tetragonal crystal environments. This suggests that such perturbations are intrinsic to all stretches of duplex DNA where purines and pyrimidines alternate and may play a role in the detection and exploitation of such sequences by regulatory proteins.
Full text
PDF





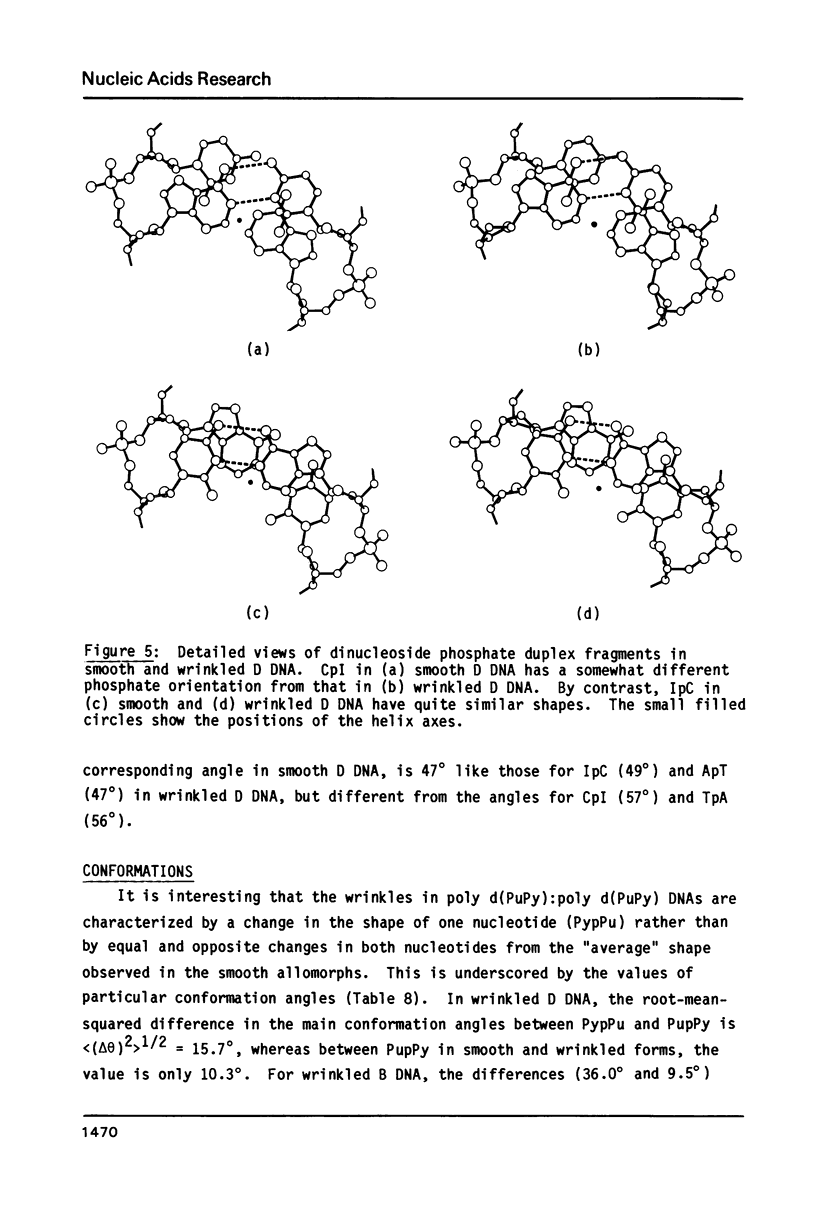
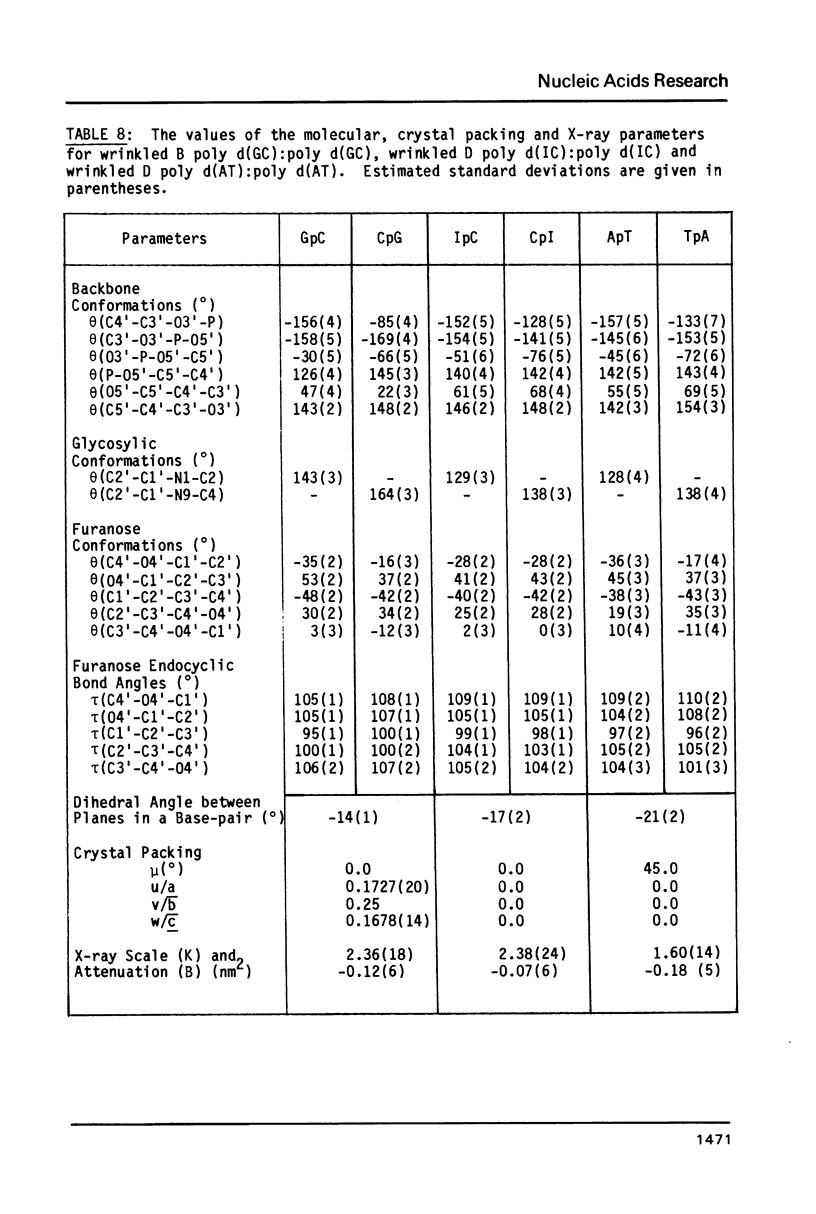



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Birdsall D. L., Leslie A. G., Ratliff R. L. Left-handed DNA helices. Nature. 1980 Feb 21;283(5749):743–745. doi: 10.1038/283743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Hukins D. W., Smith P. J., Watts L. Structural details of double-helix observed for DNAs containing alternating purine and pyrimidine sequences. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90499-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cael J. J., Winter W. T., Arnott S. Calcium chondroitin 4-sulfate: molecular conformation and organization of polysaccharide chains in a proteoglycan. J Mol Biol. 1978 Oct 15;125(1):21–42. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES D. R., BALDWIN R. L. X-ray studies on two synthetic DNA copolymers. J Mol Biol. 1963 Apr;6:251–255. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Drew H. R. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer. II. Influence of base sequence on helix structure. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):761–786. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A., Jack A., Viswamitra M. A., Kennard O., Shakked Z., Steitz T. A. A hypothesis on a specific sequence-dependent conformation of DNA and its relation to the binding of the lac-repressor protein. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 15;131(4):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90196-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavery R., Pullman B., Zakrzewska K. Intrinsic electrostatic properties and base sequence effects in the structure of oligonucleotides. Biophys Chem. 1982 Jul;15(4):343–351. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(82)80017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie A. G., Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Ratliff R. L. Polymorphism of DNA double helices. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 15;143(1):49–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui Y., Langridge R., Shortle B. E., Cantor C. R., Grant R. C., Kodama M., Wells R. D. Physical and enzymatic studies on poly d(I-C)-poly d(I-C), an unusual double-helical DNA. Nature. 1970 Dec 19;228(5277):1166–1169. doi: 10.1038/2281166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Canuel L. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the helix-coil transition of poly (dA-dT) in aqueous solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):674–678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Lin S., Wells R. D. Lac repressor binding to synthetic DNAs of defined nucleotide sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):761–764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler I. E., Elson E. L., Baldwin R. L. Helix formation by dAT oligomers. I. Hairpin and straight-chain helices. J Mol Biol. 1968 Sep 28;36(3):291–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90156-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsing E., Arnott S. Conformations of poly(d(A-T-T))-poly(d(A-A-T)). J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 15;98(1):243–248. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo H., Simpson R. T., Cohen J. S. An alternating conformation characterizes the phosphodiester backbone of poly(dA-dT) in solution. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8125–8128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viswamitra M. A., Kennard O., Jones P. G., Sheldrick G. M., Salisbury S., Favello L., Shakked Z. DNA double helical fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1978 Jun 22;273(5664):687–688. doi: 10.1038/273687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., Kolpak F. J., Crawford J. L., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G., Rich A. Molecular structure of a left-handed double helical DNA fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):680–686. doi: 10.1038/282680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]