Abstract
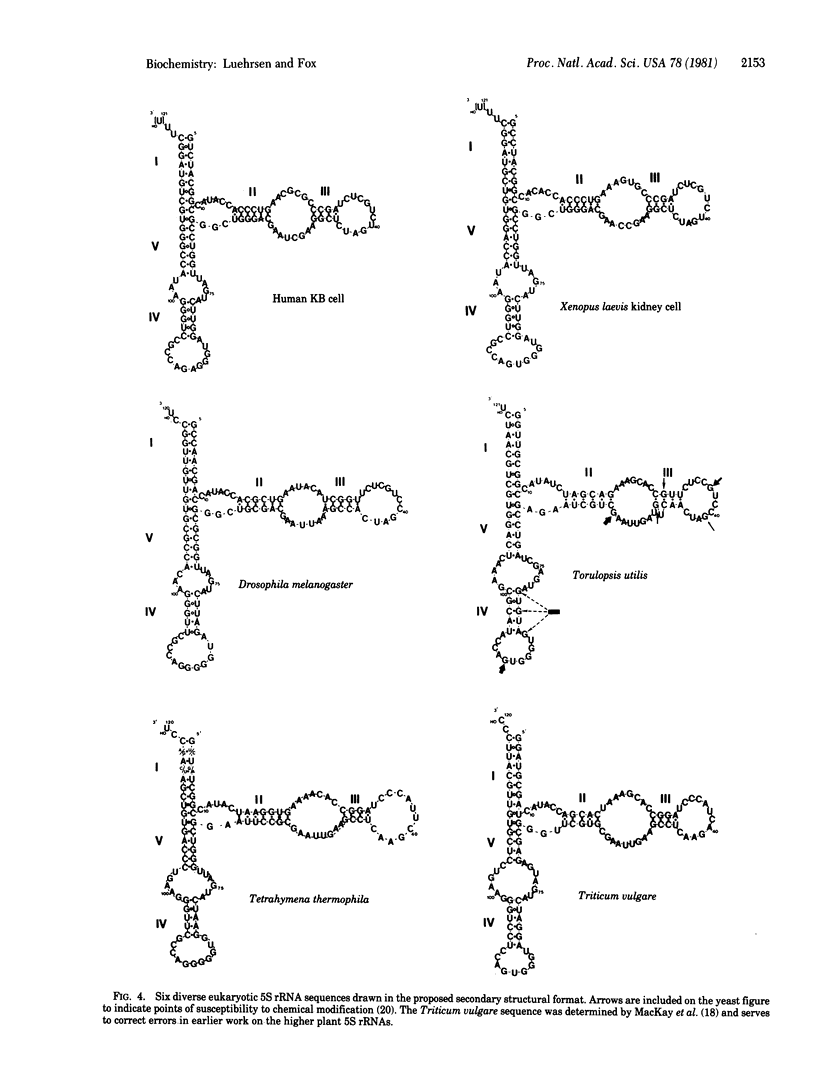
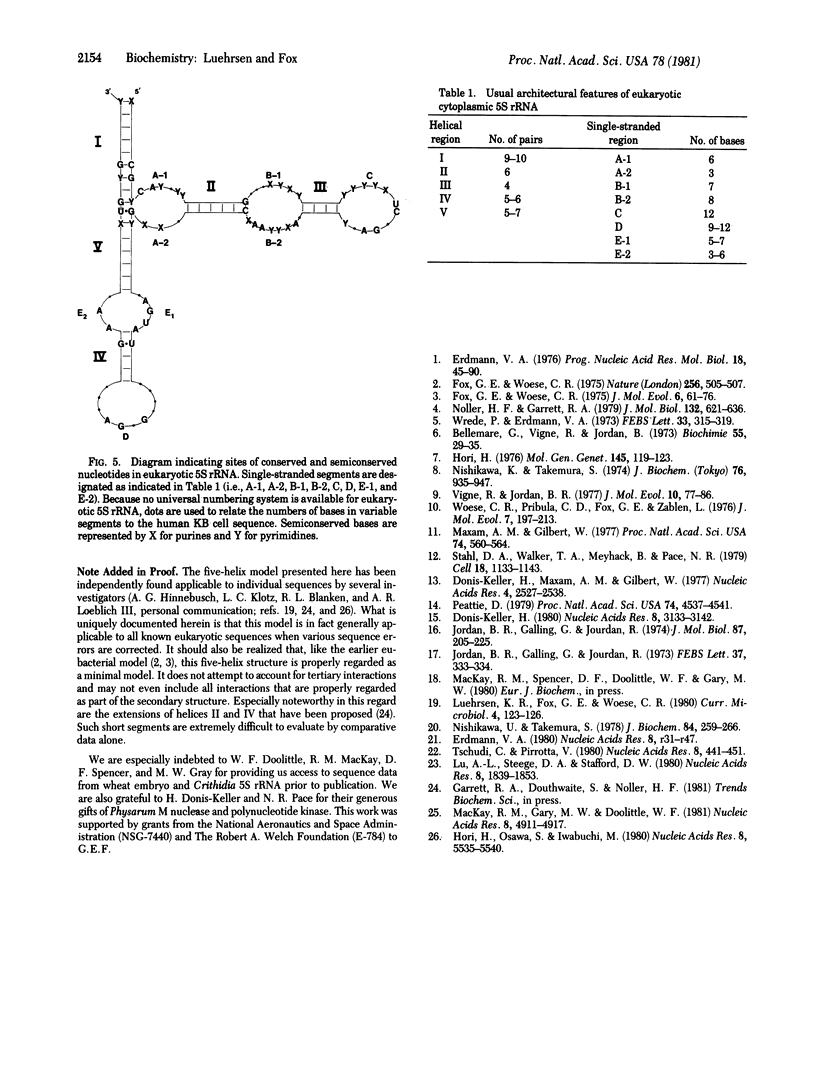
A five-helix secondary structural model is proposed for eukaryotic cytoplasmic 5S rRNA. All available sequence data are consistent with this model including those from Chlorella 5S rRNA whose sequence is revised by data included here. Various architectural features of eukaryotic 5S rRNA are summarized in terms of this secondary structural model. It is observed that previous failures to identify universal models for 5S rRNA secondary structure stem from significant differences in architecture between eukaryotic cytoplasmic and eubacterial 5S rRNAs. The usual four-helix model for eubacterial 5S rRNA secondary structure nevertheless does share several structural features with the five-helix model presented here for cytoplasmic 5S rRNA. It is thus likely that these two classes of 5S rRNA are the result of evolutionary divergence rather than convergence.
Full text
PDF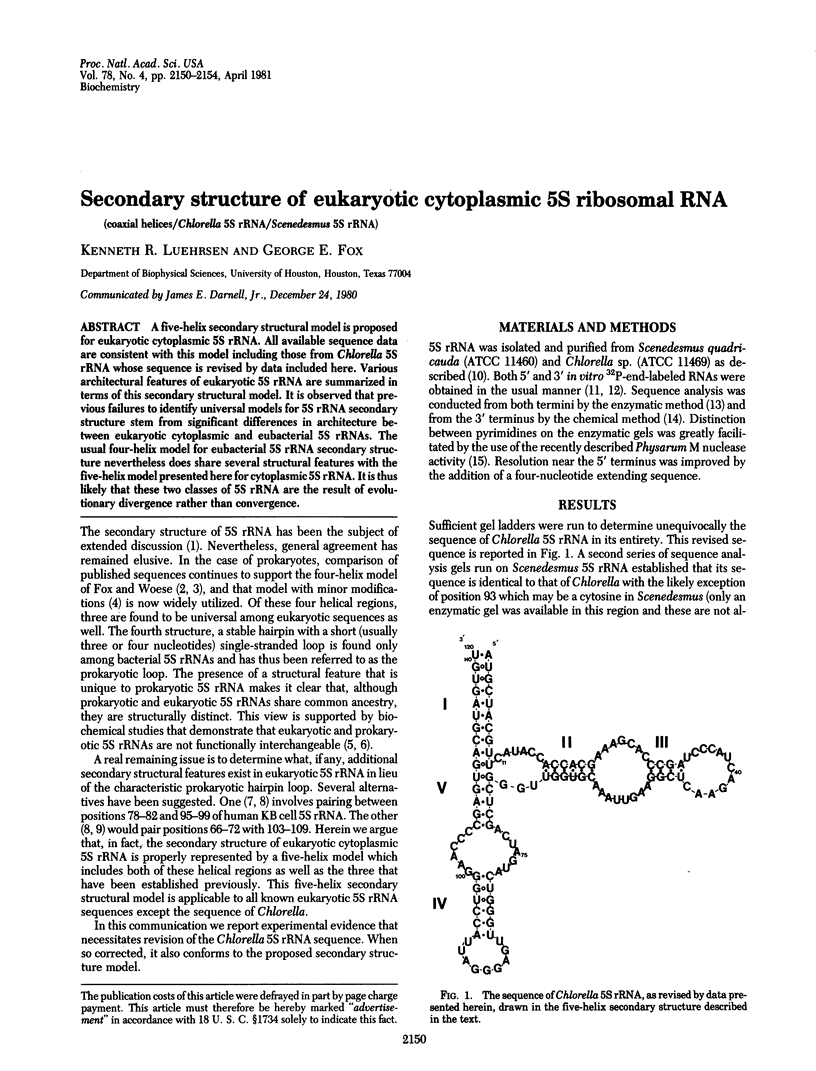


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellemare G., Vigne R., Jordan B. R. Interaction between Escherichia coli ribosomal proteins and 5S RNA molecules: recognition of prokaryotic 5S RNAs and rejection of eukaryotic 5S RNAs. Biochimie. 1973;55(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(73)80233-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Mapping adenines, guanines, and pyrimidines in RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2527–2538. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H. Phy M: an RNase activity specific for U and A residues useful in RNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 25;8(14):3133–3142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.14.3133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A. Collection of published 5S and 5.8S rRNA sequences and their precursors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):r31–r47. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.197-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A. Structure and function of 5S and 5.8 S RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;18:45–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Woese C. R. 5S RNA secondary structure. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):505–507. doi: 10.1038/256505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Woese C. R. The architecture of 5S rRNA and its relation to function. J Mol Evol. 1975 Oct 3;6(1):61–76. doi: 10.1007/BF01732674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori H. Molecular evolution of 5S RNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 May 7;145(2):119–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00269583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan B. R., Galling G., Jourdan R. Sequence and conformation of 5 S RNA from Chlorella cytoplasmic ribosomes: comparison with other 5 S RNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 5;87(2):205–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90144-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan B. R., Galling G. Nucleotide sequence of Chlorella cytoplasmic 5S RNA. FEBS Lett. 1973 Dec 1;37(2):333–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80490-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. L., Steege D. A., Stafford D. W. Nucleotide sequence of a 5S ribosomal RNA gene in the sea urchin Lytechinus variegatus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 25;8(8):1839–1853. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.8.1839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay R. M., Gray M. W., Doolittle W. F. Nucleotide sequence of Crithidia fasciculata cytosol 5S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 11;8(21):4911–4917. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.21.4911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Takemura S. Structure and function of 5S ribosomal ribonucleic acid from Torulopsis utilis. II. Partial digestion with ribonucleases and derivation of the complete sequence. J Biochem. 1974 Nov;76(5):935–947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Takemura S. Structure and function of 5S ribosomal ribonucleic acid from Torulopsis utilis. IV. Detection of exposed guanine residues by chemical modification with kethoxal. J Biochem. 1978 Aug;84(2):259–266. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Garrett R. A. Structure of 5 S ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli: identification of kethoxal-reactive sites in the A and B conformations. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 25;132(4):621–636. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90378-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl D. A., Walker T. A., Meyhack B., Pace N. R. Precursor-specific nucleotide sequences can govern RNA folding. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1133–1143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90226-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschudi C., Pirrotta V. Sequence and heterogeneity in the 5S RNA gene cluster of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Feb 11;8(3):441–451. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.3.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigne R., Jordan B. R. Partial enzyme digestion studies on Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas, Chlorella, Drosophila, HeLa and yeast 5S RNAs support a general class of 5S RNA models. J Mol Evol. 1977 Sep 20;10(1):77–86. doi: 10.1007/BF01796136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C., Sogin M., Stahl D., Lewis B. J., Bonen L. A comparison of the 16S ribosomal RNAs from mesophilic and thermophilic bacilli: some modifications in the Sanger method for RNA sequencing. J Mol Evol. 1976 Apr 9;7(3):197–213. doi: 10.1007/BF01731489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrede P., Erdmann V. A. Activities of B. stearothermophilus 50 S ribosomes reconstituted with prokaryotic and eukaryotic 5 S RNA. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jul 15;33(3):315–319. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]