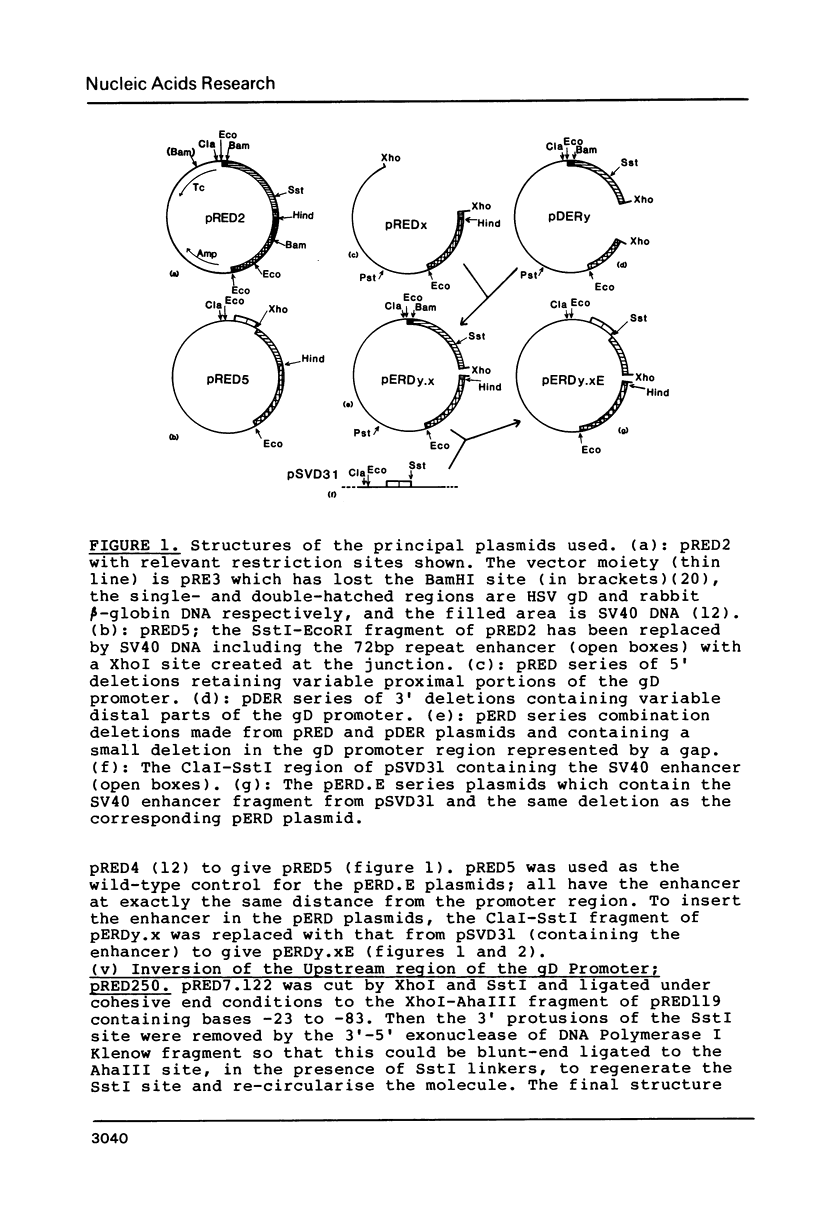
Abstract
This report describes a detailed analysis of the functional DNA sequences within the HSV-1 glycoprotein D gene promoter. The transcriptional activity of deletion and insertion promoter mutants was studied after both trans activation, mediated by viral products, and cis activation by a linked SV40 enhancer. Two G-rich areas (upstream of a TATA signal) were identified as important regions of the promoter. These "upstream" signals were active in both orientations. A functional TATA-box region was detected. A second region, not homologous to the concensus TATA sequence, also appeared to have a role in the positioning of the RNA cap-sites, which included both purine and pyrimidine 5' ends. Deletion of the cap-site region resulted in a moderate reduction in transcription. All the promoter elements were important for both cis and trans activated transcription. No sequence specific for viral (trans) regulation was detected, implying that Early promoters are not distinguished by specific sequences. Since HSV-1 and some other animal viruses can activate transcription from unrelated promoters, this process is probably non-specific and applicable to many, particularly extra-chromosomal, genes. The possible mechanisms of this activation are discussed.
Full text
PDF


















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babich A., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr, Weinberger C. Effect of adenovirus on metabolism of specific host mRNAs: transport control and specific translational discrimination. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1212–1221. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Ziff E. B. Promoters and heterogeneous 5' termini of the messenger RNAs of adenovirus serotype 2. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 25;149(2):189–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batterson W., Roizman B. Characterization of the herpes simplex virion-associated factor responsible for the induction of alpha genes. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):371–377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.371-377.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttyan R., Spear P. G. Factors governing expression of the herpes simplex virus gene for thymidine kinase in clonal derivatives of transformed mouse L cells. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):459–472. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.459-472.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., Watson R. J., Wilkie N. M. Temporal regulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription: location of transcripts on the viral genome. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Campbell M. E., Preston C. M. Functional analysis of a herpes simplex virus type 1 promoter: identification of far-upstream regulatory sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2347–2365. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A., Tyndall C., Kamen R. Sequences at the capped 5'-ends of polyoma virus late region mRNAs: an example of extreme terminal heterogeneity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6305–6322. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Jacobs H. T., Britten R. J. Very short repeats and coordinate induction of genes. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):468–470. doi: 10.1038/301468a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Cochran M. D., Dobkin C., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Three regions upstream from the cap site are required for efficient and accurate transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in mouse 3T6 cells. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkaim R., Goding C., Kédinger C. The adenovirus-2 EIIa early gene promoter: sequences required for efficient in vitro and in vivo transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):7105–7117. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.7105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D., Baty D., Chambon P. The repeated GC-rich motifs upstream from the TATA box are important elements of the SV40 early promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2447–2464. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. DNA sequence elements required for regulated expression of the HSV-1 glycoprotein D gene lie within 83 bp of the RNA capsites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6647–6666. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman L. T., Imperiale M. J., Nevins J. R. Activation of early adenovirus transcription by the herpesvirus immediate early gene: evidence for a common cellular control factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4952–4956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Treisman R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation of cloned human beta-globin genes by viral immediate-early gene products. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90216-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Sassone-Corsi P., Corden J., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. Sequences upstream from the T-A-T-A box are required in vivo and in vitro for efficient transcription from the adenovirus serotype 2 major late promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7132–7136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R. Activation of gene expression by adenovirus and herpesvirus regulatory genes acting in trans and by a cis-acting adenovirus enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. C., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. VIII. The transcription program consists of three phases during which both extent of transcription and accumulation of RNA in the cytoplasm are regulated. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):299–314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.299-314.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Dubbs D. R. Regulation of herpesvirus thymidine kinase activity in LM(TK) cells transformed by ultraviolet light-irradiated herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1977 Jan;76(1):331–340. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiden J. M., Buttyan R., Spear P. G. Herpes simplex virus gene expression in transformed cells. I. Regulation of the viral thymidine kinase gene in transformed L cells by products of superinfecting virus. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):413–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.413-424.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Structural features of the herpes simplex virus alpha gene 4, 0, and 27 promoter-regulatory sequences which confer alpha regulation on chimeric thymidine kinase genes. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):939–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.939-949.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J., Varmus H. E. A small region of the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat confers glucocorticoid hormone regulation on a linked heterologous gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5866–5870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L. Functional relationships between transcriptional control signals of the thymidine kinase gene of herpes simplex virus. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau P., Hen R., Wasylyk B., Everett R., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 base repair repeat has a striking effect on gene expression both in SV40 and other chimeric recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6047–6068. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Induction of the synthesis of a 70,000 dalton mammalian heat shock protein by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):913–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Mechanism of activation of early viral transcription by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notarianni E. L., Preston C. M. Activation of cellular stress protein genes by herpes simplex virus temperature-sensitive mutants which overproduce immediate early polypeptides. Virology. 1982 Nov;123(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90299-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Bienz M. A synthetic heat-shock promoter element confers heat-inducibility on the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1473–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01340.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatak M., Subramanian K. N., Roy P., Weissman S. M. Late messenger RNA production by viable simian virus 40 mutants with deletions in the leader region. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 15;153(3):589–618. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90409-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Control of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA synthesis in cells infected with wild-type virus or the temperature-sensitive mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):275–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.275-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley J. R., Swan H., Pater M. M., Pater A., Halpern M. E. Positive control of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene requires upstream DNA sequences. J Virol. 1983 Aug;47(2):301–310. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.2.301-310.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R. I., Wagner E. K. Regulation of synthesis of herpes simplex type 1 virus mRNA during productive infection. Virology. 1974 Aug;60(2):522–533. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90346-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Augereau P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 bp repeat preferentially potentiates transcription starting from proximal natural or substitute promoter elements. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90470-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. A herpes simplex virus type 1 function continuously required for early and late virus RNA synthesis. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):329–330. doi: 10.1038/285329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. Characterization of transcription-deficient temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1978 Dec;91(2):364–379. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90384-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. L., Jones N. C. E1A control of gene expression is mediated by sequences 5' to the transcriptional starts of the early viral genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1222–1234. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipser D., Lipsich L., Kwoh J. Mapping functional domains in the promoter region of the herpes thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6276–6280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Schaffner W. A small segment of polyoma virus DNA enhances the expression of a cloned beta-globin gene over a distance of 1400 base pairs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6251–6264. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]