Abstract
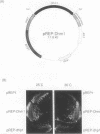
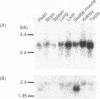
The dhp1+ gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe is a homolog of Saccharomyces cerevisiae HKE1/RAT1/TAP1 gene that is involved in RNA metabolism such as RNA trafficking and RNA synthesis. dhp1+ is also related to S. cerevisiae DST2 (SEP1) that encodes a DNA strand exchange protein required for sporulation and homologous recombination in S.cerevisiae. We isolated several clones of Dhm1, a mouse homolog of dhp1+, from mouse spermatocyte cDNA library and determined its nucleotide sequence. The Dhm1 gene consists of an open reading frame predicting a protein with 947 amino acids and molecular weight of 107,955. Northern blot analysis revealed that Dhm1 is transcribed at high level in testis, liver and kidney. The predicted product of Dhm1 (Dhm1p) has a significant homology with Dhp1p, Hke1p/Rat1p/Tap1p and Dst2p. In particular, Dhm1p, Dhp1p and Hke1p/Rat1p/Tap1p share strong similarity at the two regions of their N- and C-terminal parts. The Dhm1 gene on a multicopy plasmid rescued the temperature-sensitivity of dhp1ts and lethality of dhp1 null mutation, suggesting that Dhm1 is a mouse homolog of S.pombe dhp1+ and functions similarly in mouse as dhp1+.
Full text
PDF


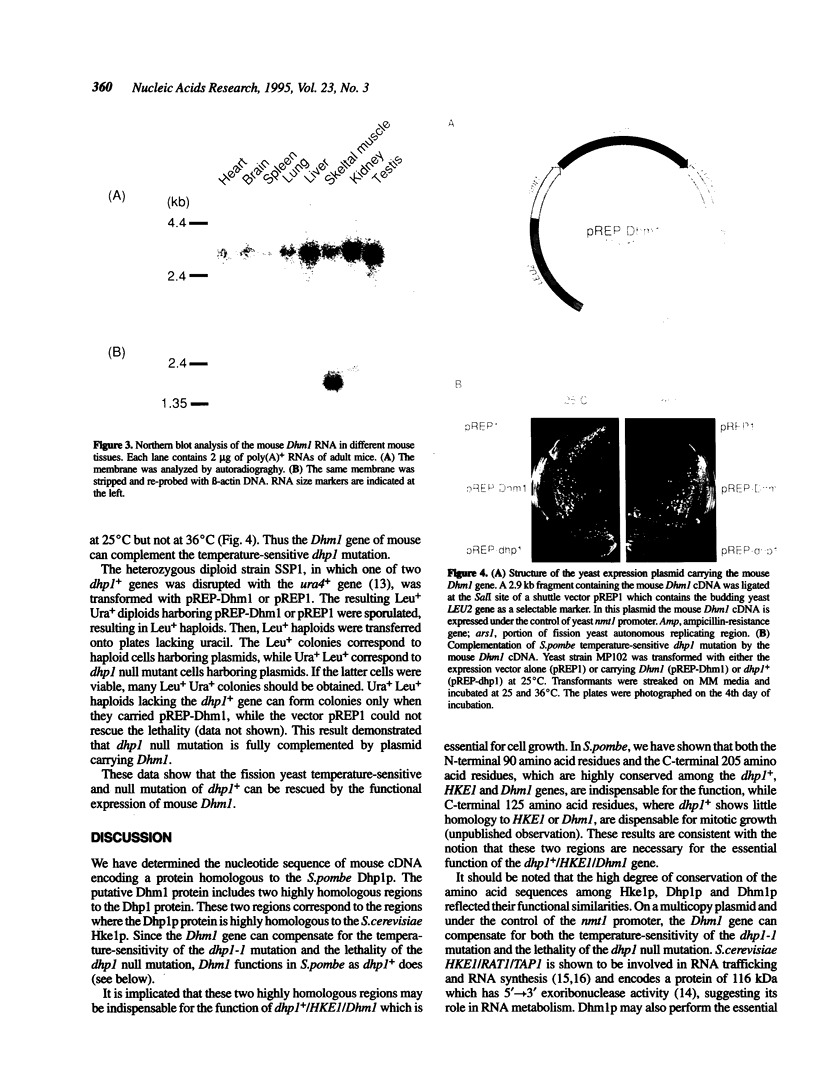

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldrich T. L., Di Segni G., McConaughy B. L., Keen N. J., Whelen S., Hall B. D. Structure of the yeast TAP1 protein: dependence of transcription activation on the DNA context of the target gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3434–3444. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amberg D. C., Goldstein A. L., Cole C. N. Isolation and characterization of RAT1: an essential gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae required for the efficient nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of mRNA. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1173–1189. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Segni G., McConaughy B. L., Shapiro R. A., Aldrich T. L., Hall B. D. TAP1, a yeast gene that activates the expression of a tRNA gene with a defective internal promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3424–3433. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykstra C. C., Hamatake R. K., Sugino A. DNA strand transfer protein beta from yeast mitotic cells differs from strand transfer protein alpha from meiotic cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10968–10973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dykstra C. C., Kitada K., Clark A. B., Hamatake R. K., Sugino A. Cloning and characterization of DST2, the gene for DNA strand transfer protein beta from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2583–2592. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eperon I. C., Janssen J. W., Hoeijmakers J. H., Borst P. The major transcripts of the kinetoplast DNA of Trypanosoma brucei are very small ribosomal RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):105–125. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. W., Kolodner R. D. Strand exchange protein 1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. A novel multifunctional protein that contains DNA strand exchange and exonuclease activities. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):14046–14054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenna M., Stevens A., McCammon M., Douglas M. G. An essential yeast gene with homology to the exonuclease-encoding XRN1/KEM1 gene also encodes a protein with exoribonuclease activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):341–350. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Ljungdahl P. O., Fink G. R. kem mutations affect nuclear fusion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1990 Dec;126(4):799–812. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.4.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipling D., Tambini C., Kearsey S. E. rar mutations which increase artificial chromosome stability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae identify transcription and recombination proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1385–1391. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R., Evans D. H., Morrison P. T. Purification and characterization of an activity from Saccharomyces cerevisiae that catalyzes homologous pairing and strand exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5560–5564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larimer F. W., Stevens A. Disruption of the gene XRN1, coding for a 5'----3' exoribonuclease, restricts yeast cell growth. Gene. 1990 Oct 30;95(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90417-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z., Gilbert W. The yeast KEM1 gene encodes a nuclease specific for G4 tetraplex DNA: implication of in vivo functions for this novel DNA structure. Cell. 1994 Jul 1;77(7):1083–1092. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90447-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maundrell K. nmt1 of fission yeast. A highly transcribed gene completely repressed by thiamine. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10857–10864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M. S., Radding C. M. A general model for genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):358–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. P., Erdile L., Kelly T., Fishel R. The human homologous pairing protein HPP-1 is specifically stimulated by the cognate single-stranded binding protein hRP-A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9067–9071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. P., Fishel R. Purification and characterization of a protein from human cells which promotes homologous pairing of DNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11108–11117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M., Elledge S., Sweetser D., Young R. A., Davis R. W. Lambda gt 11: gene isolation with antibody probes and other applications. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:107–128. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugano S., Shobuike T., Takeda T., Sugino A., Ikeda H. Molecular analysis of the dhp1+ gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe: an essential gene that has homology to the DST2 and RAT1 genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1994 Apr;243(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00283869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tishkoff D. X., Johnson A. W., Kolodner R. D. Molecular and genetic analysis of the gene encoding the Saccharomyces cerevisiae strand exchange protein Sep1. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2593–2608. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]