Abstract
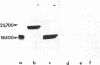
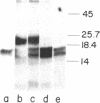
A Mr 25,000 form of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) has been isolated from guinea pig brain along with the typical Mr 18,000 form. Both forms were purified to homogeneity by a combination of heparin-affinity chromatography and ion-exchange chromatography on an FPLC Mono S column. The Mr 25,000 form, like the Mr 18,000 form, was not eluted from the heparin-affinity column with 0.95 M NaCl, but was eluted with 2 M NaCl. The Mr 25,000 guinea pig protein stimulated plasminogen activator production by cultured bovine capillary endothelial cells in a dose-dependent manner at concentrations of 0.1-10 ng/ml, the same range that was effective for guinea pig and human Mr 18,000 bFGFs. The binding of human 125I-labeled bFGF to baby hamster kidney cells is inhibited equally by the Mr 25,000 guinea pig protein and the Mr 18,000 guinea pig and human bFGFs. Polyclonal antibodies raised against human bFGF recognize both the Mr 25,000 and 18,000 guinea pig proteins in an immunoblot analysis. In a radioimmunoassay, both the Mr 25,000 and Mr 18,000 guinea pig proteins compete equally well with iodinated human bFGF for binding to the anti-human bFGF antibodies. When treated with low concentrations of trypsin, the Mr 25,000 guinea pig bFGF was converted to a Mr 18,000 protein. These results show that the two molecules are closely related and suggest that the Mr 25,000 protein shares substantial homology with the Mr 18,000 bFGF.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J. A., Mergia A., Whang J. L., Tumolo A., Friedman J., Hjerrild K. A., Gospodarowicz D., Fiddes J. C. Nucleotide sequence of a bovine clone encoding the angiogenic protein, basic fibroblast growth factor. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):545–548. doi: 10.1126/science.2425435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham J. A., Whang J. L., Tumolo A., Mergia A., Friedman J., Gospodarowicz D., Fiddes J. C. Human basic fibroblast growth factor: nucleotide sequence and genomic organization. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2523–2528. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04530.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird A., Esch F., Gospodarowicz D., Guillemin R. Retina- and eye-derived endothelial cell growth factors: partial molecular characterization and identity with acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 31;24(27):7855–7860. doi: 10.1021/bi00348a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird A., Ling N. Fibroblast growth factors are present in the extracellular matrix produced by endothelial cells in vitro: implications for a role of heparinase-like enzymes in the neovascular response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jan 30;142(2):428–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90292-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Esch F., Baird A., Jones K. L., Gospodarowicz D. Human brain fibroblast growth factor. Isolation and partial chemical characterization. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 3;185(1):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80765-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F., Baird A., Ling N., Ueno N., Hill F., Denoroy L., Klepper R., Gospodarowicz D., Böhlen P., Guillemin R. Primary structure of bovine pituitary basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and comparison with the amino-terminal sequence of bovine brain acidic FGF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6507–6511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Haudenschild C. C., Zetter B. R. Long-term culture of capillary endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5217–5221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimenez-Gallego G., Conn G., Hatcher V. B., Thomas K. A. Human brain-derived acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors: amino terminal sequences and specific mitogenic activities. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Baird A., Cheng J., Lui G. M., Esch F., Bohlen P. Isolation of fibroblast growth factor from bovine adrenal gland: physicochemical and biological characterization. Endocrinology. 1986 Jan;118(1):82–90. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-1-82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Cheng J., Lui G. M., Baird A., Böhlent P. Isolation of brain fibroblast growth factor by heparin-Sepharose affinity chromatography: identity with pituitary fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6963–6967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Cheng J., Lui G. M., Baird A., Esch F., Bohlen P. Corpus luteum angiogenic factor is related to fibroblast growth factor. Endocrinology. 1985 Dec;117(6):2383–2391. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-6-2383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Cheng J., Lui G. M., Fujii D. K., Baird A., Böhlen P. Fibroblast growth factor in the human placenta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):554–562. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90082-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross J. L., Moscatelli D., Jaffe E. A., Rifkin D. B. Plasminogen activator and collagenase production by cultured capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):974–981. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. S., Huang S. S., Kuo M. D. Bovine brain-derived growth factor. Purification and characterization of its interaction with responsive cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11600–11607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Sasse J., Sullivan R., Smith J. A. Human tumor cells synthesize an endothelial cell growth factor that is structurally related to basic fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2448–2452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb R. R., Fett J. W. Purification of two distinct growth factors from bovine neural tissue by heparin affinity chromatography. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6295–6299. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb R. R., Strydom D. J., Fett J. W. Comparison of human and bovine brain derived heparin-binding growth factors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Sep 16;131(2):586–592. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91277-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb R., Sasse J., Sullivan R., Shing Y., D'Amore P., Jacobs J., Klagsbrun M. Purification and characterization of heparin-binding endothelial cell growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1924–1928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D. High and low affinity binding sites for basic fibroblast growth factor on cultured cells: absence of a role for low affinity binding in the stimulation of plasminogen activator production by bovine capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Apr;131(1):123–130. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041310118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D., Presta M., Joseph-Silverstein J., Rifkin D. B. Both normal and tumor cells produce basic fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Nov;129(2):273–276. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041290220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D., Presta M., Rifkin D. B. Purification of a factor from human placenta that stimulates capillary endothelial cell protease production, DNA synthesis, and migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2091–2095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld G., Gospodarowicz D. The identification and partial characterization of the fibroblast growth factor receptor of baby hamster kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13860–13868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presta M., Moscatelli D., Joseph-Silverstein J., Rifkin D. B. Purification from a human hepatoma cell line of a basic fibroblast growth factor-like molecule that stimulates capillary endothelial cell plasminogen activator production, DNA synthesis, and migration. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4060–4066. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweigerer L., Neufeld G., Friedman J., Abraham J. A., Fiddes J. C., Gospodarowicz D. Capillary endothelial cells express basic fibroblast growth factor, a mitogen that promotes their own growth. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):257–259. doi: 10.1038/325257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shing Y., Folkman J., Sullivan R., Butterfield C., Murray J., Klagsbrun M. Heparin affinity: purification of a tumor-derived capillary endothelial cell growth factor. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1296–1299. doi: 10.1126/science.6199844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer A., Brewer M. T., Thompson R. C., Moscatelli D., Presta M., Rifkin D. B. A form of human basic fibroblast growth factor with an extended amino terminus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):543–550. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno N., Baird A., Esch F., Ling N., Guillemin R. Isolation of an amino terminal extended form of basic fibroblast growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 31;138(2):580–588. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80536-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]