Abstract
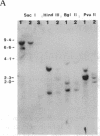
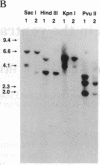
The biologic, serologic, and molecular properties of isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) from the central nervous system (CNS) were determined and compared to those of isolates from peripheral blood and lymph nodes. Among these were pairs of CNS and blood isolates obtained from six infected individuals. The data show that HIV-1 isolates from the CNS can be distinguished from peripheral blood isolates by their (i) relative inability to infect established T-cell lines, (ii) reduced cytopathogenicity, (iii) inability to modulate CD4 antigen expression on infected cells, (iv) efficient replication in peripheral blood macrophages, and (v) insensitivity to serum neutralization. Paired CNS and peripheral blood isolates from the same individual also display some differences in cellular tropism. The blood isolates replicate better in T-cell lines and glioma cell lines, whereas the paired CNS isolates replicate more efficiently in primary macrophages. These results suggest that viruses isolated from the CNS of infected individuals may represent a specific HIV-1 subgroup.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argov Z., Soffer D., Eisenberg S., Zimmerman Y. Chronic demyelinating peripheral neuropathy in cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jul;20(1):89–91. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Homsy J., Evans L. A., Levy J. A. Identification of human immunodeficiency virus subtypes with distinct patterns of sensitivity to serum neutralization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2815–2819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Rutka J. T., Rosenblum M. L., McHugh T., Stites D. P., Levy J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus can productively infect cultured human glial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3526–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Seto D., Tateno M., Levy J. A. Biologic features of HIV-1 that correlate with virulence in the host. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):80–82. doi: 10.1126/science.2832945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodi F., Fuerstenberg S., Gidlund M., Asjö B., Fenyö E. M. Infection of brain-derived cells with the human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1244–1247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1244-1247.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalakas M., Wichman A., Sever J. AIDS and the nervous system. JAMA. 1989 Apr 28;261(16):2396–2399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst S., Sakai K., Bresser J., Stevenson M., Evinger-Hodges M. J., Volsky D. J. Persistent productive infection of human glial cells by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and by infectious molecular clones of HIV. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3774–3782. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3774-3782.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilbott D. J., Peress N., Burger H., LaNeve D., Orenstein J., Gendelman H. E., Seidman R., Weiser B. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in spinal cords of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients with myelopathy: expression and replication in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3337–3341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. A., McHugh T. M., Stites D. P., Levy J. A. Differential ability of human immunodeficiency virus isolates to productively infect human cells. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3415–3418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. A., Moreau J., Odehouri K., Legg H., Barboza A., Cheng-Mayer C., Levy J. A. Characterization of a noncytopathic HIV-2 strain with unusual effects on CD4 expression. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1522–1525. doi: 10.1126/science.2836951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner S., Markovits P., Markovitz D. M., Kaplan M. H., Gallo R. C., Popovic M. The role of mononuclear phagocytes in HTLV-III/LAV infection. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):215–219. doi: 10.1126/science.3014648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyorkey F., Melnick J. L., Gyorkey P. Human immunodeficiency virus in brain biopsies of patients with AIDS and progressive encephalopathy. J Infect Dis. 1987 May;155(5):870–876. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.5.870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Rota T. R., Schooley R. T., Kaplan J. C., Allan J. D., Groopman J. E., Resnick L., Felsenstein D., Andrews C. A., Hirsch M. S. Isolation of HTLV-III from cerebrospinal fluid and neural tissues of patients with neurologic syndromes related to the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 12;313(24):1493–1497. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512123132401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander H., Levy J. A. Neurologic abnormalities and recovery of human immunodeficiency virus from cerebrospinal fluid. Ann Intern Med. 1987 May;106(5):692–695. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-5-692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminsky L. S., McHugh T., Stites D., Volberding P., Henle G., Henle W., Levy J. A. High prevalence of antibodies to acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)-associated retrovirus (ARV) in AIDS and related conditions but not in other disease states. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5535–5539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Dal Canto M. C., Pezeshkpour G. H., Yungbluth M., Janotta F., Aksamit A., Martin M. A., Fauci A. S. Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1089–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.3016903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyanagi Y., Miles S., Mitsuyasu R. T., Merrill J. E., Vinters H. V., Chen I. S. Dual infection of the central nervous system by AIDS viruses with distinct cellular tropisms. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):819–822. doi: 10.1126/science.3646751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Shimabukuro J., Hollander H., Mills J., Kaminsky L. Isolation of AIDS-associated retroviruses from cerebrospinal fluid and brain of patients with neurological symptoms. Lancet. 1985 Sep 14;2(8455):586–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luciw P. A., Oppermann H., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Integration and expression of several molecular forms of Rous sarcoma virus DNA used for transfection of mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1260–1269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels J., Sharer L. R., Epstein L. G. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection of the nervous system: a review. Immunodefic Rev. 1988;1(1):71–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan L. Z., Cheng-Mayer C., Levy J. A. Patterns of antibody response in individuals infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):626–632. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Brew B., Sidtis J., Rosenblum M., Scheck A. C., Cleary P. The brain in AIDS: central nervous system HIV-1 infection and AIDS dementia complex. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):586–592. doi: 10.1126/science.3277272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumarola-Sune T., Navia B. A., Cordon-Cardo C., Cho E. S., Price R. W. HIV antigen in the brains of patients with the AIDS dementia complex. Ann Neurol. 1987 May;21(5):490–496. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. M., Harper M. E., Hahn B. H., Epstein L. G., Gajdusek D. C., Price R. W., Navia B. A., Petito C. K., O'Hara C. J., Groopman J. E. HTLV-III infection in brains of children and adults with AIDS encephalopathy. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.2981429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateno M., Levy J. A. MT-4 plaque formation can distinguish cytopathic subtypes of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):299–301. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Schrier R. D., Nelson J. A., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Cellular localization of human immunodeficiency virus infection within the brains of acquired immune deficiency syndrome patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7089–7093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]