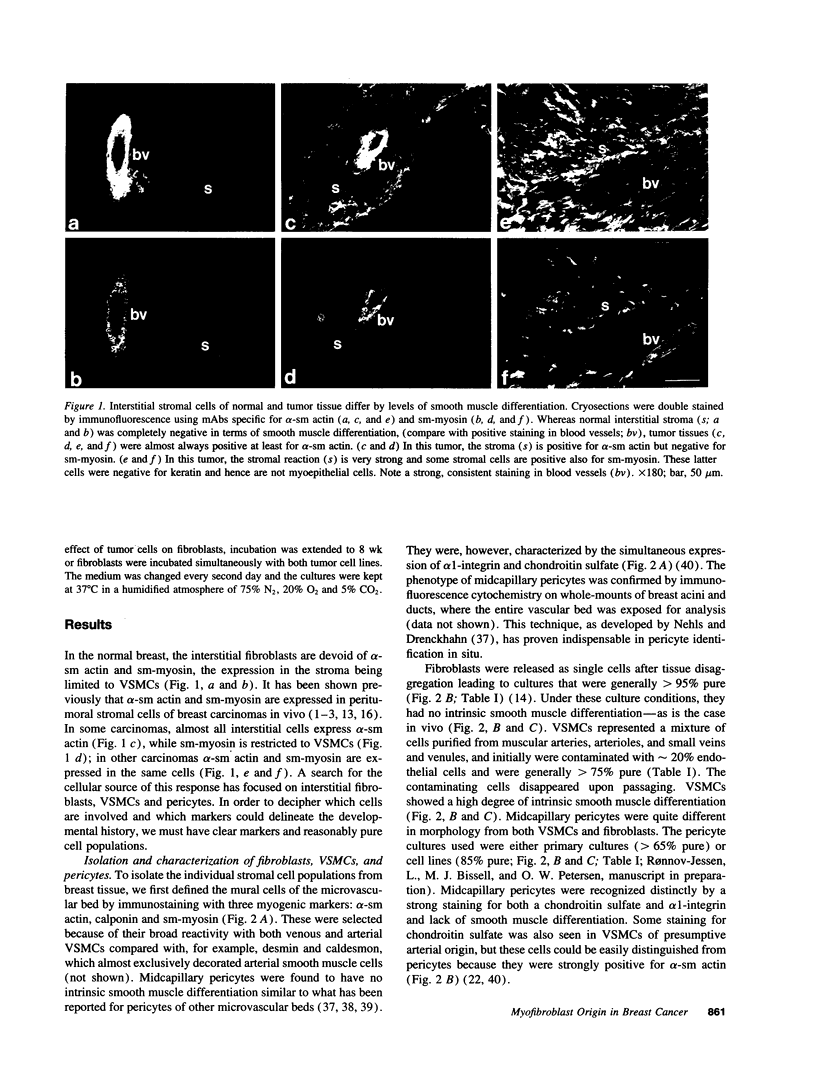
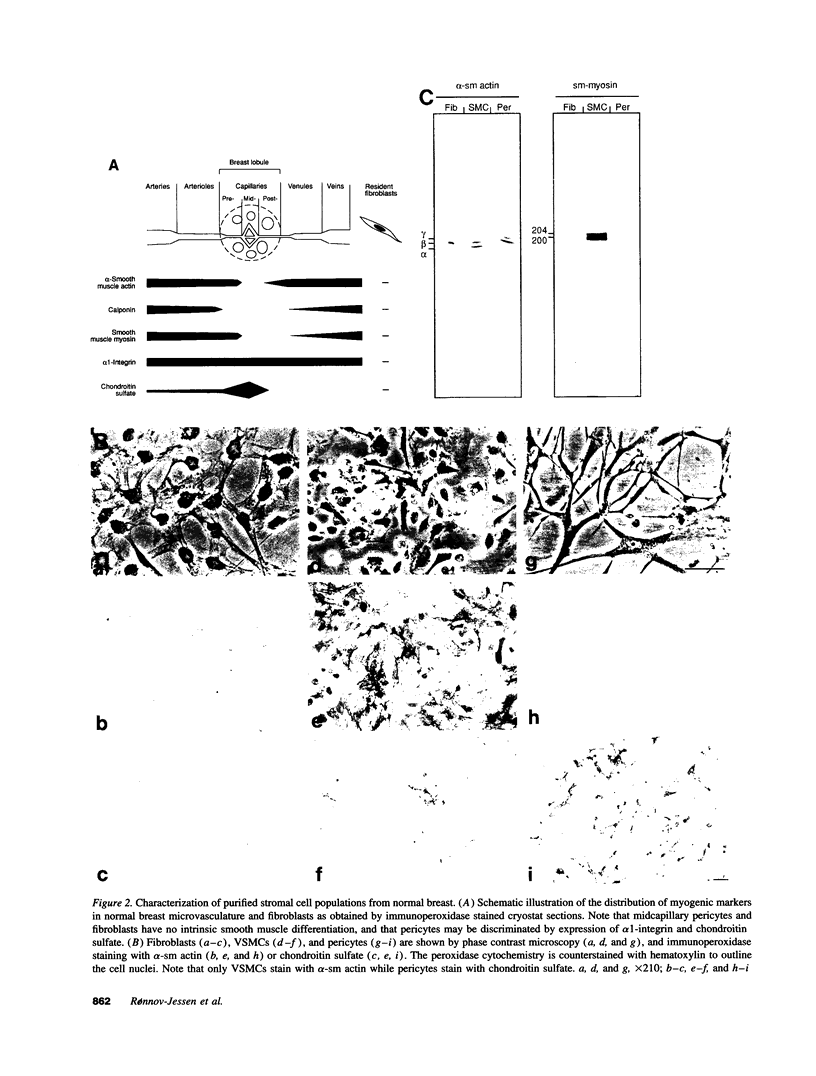
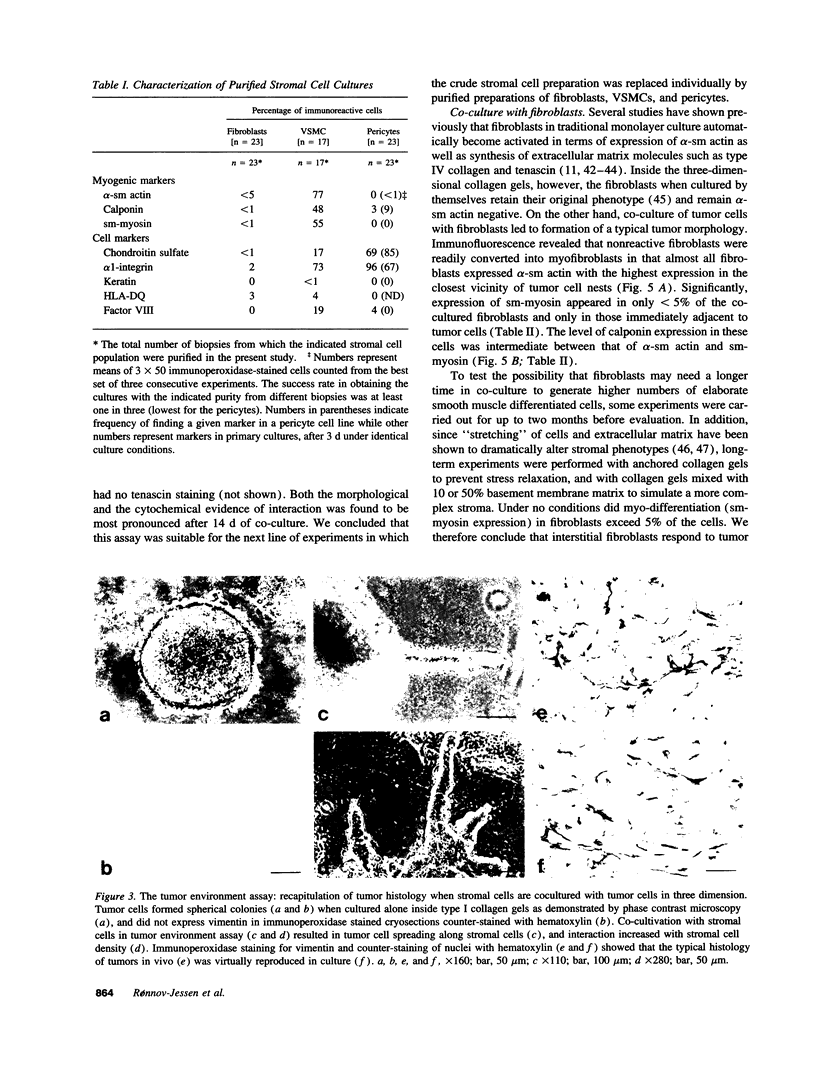
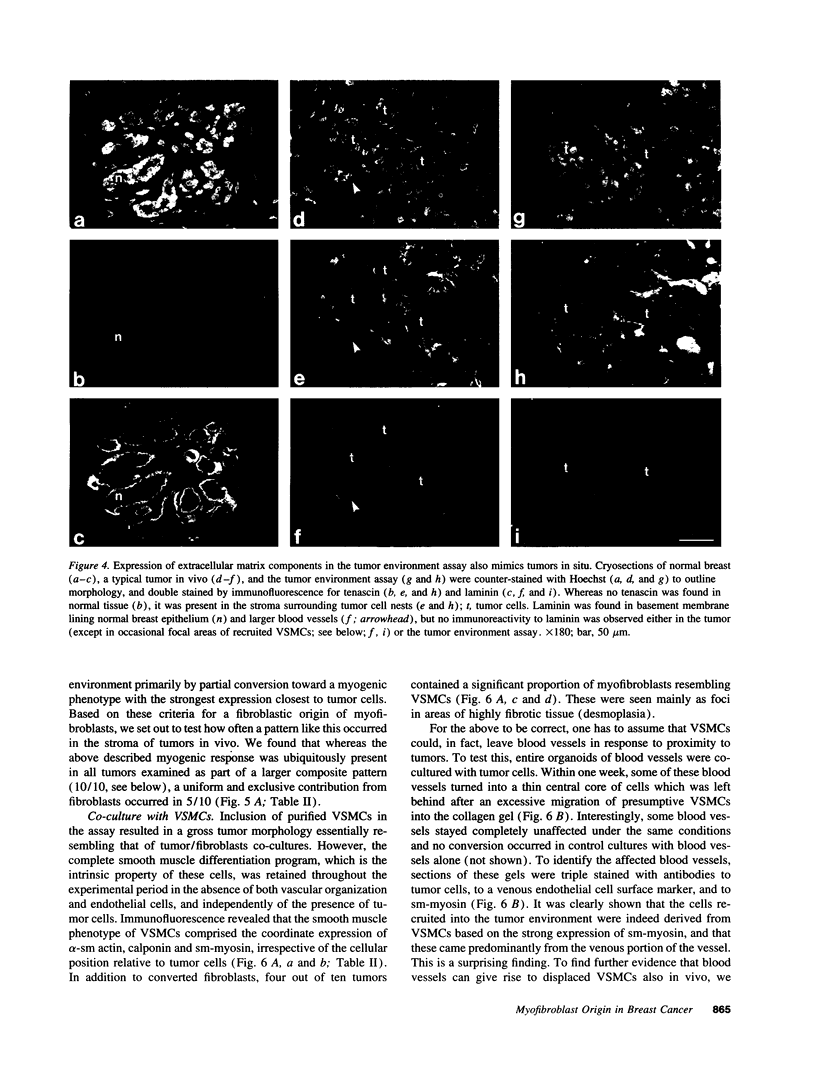
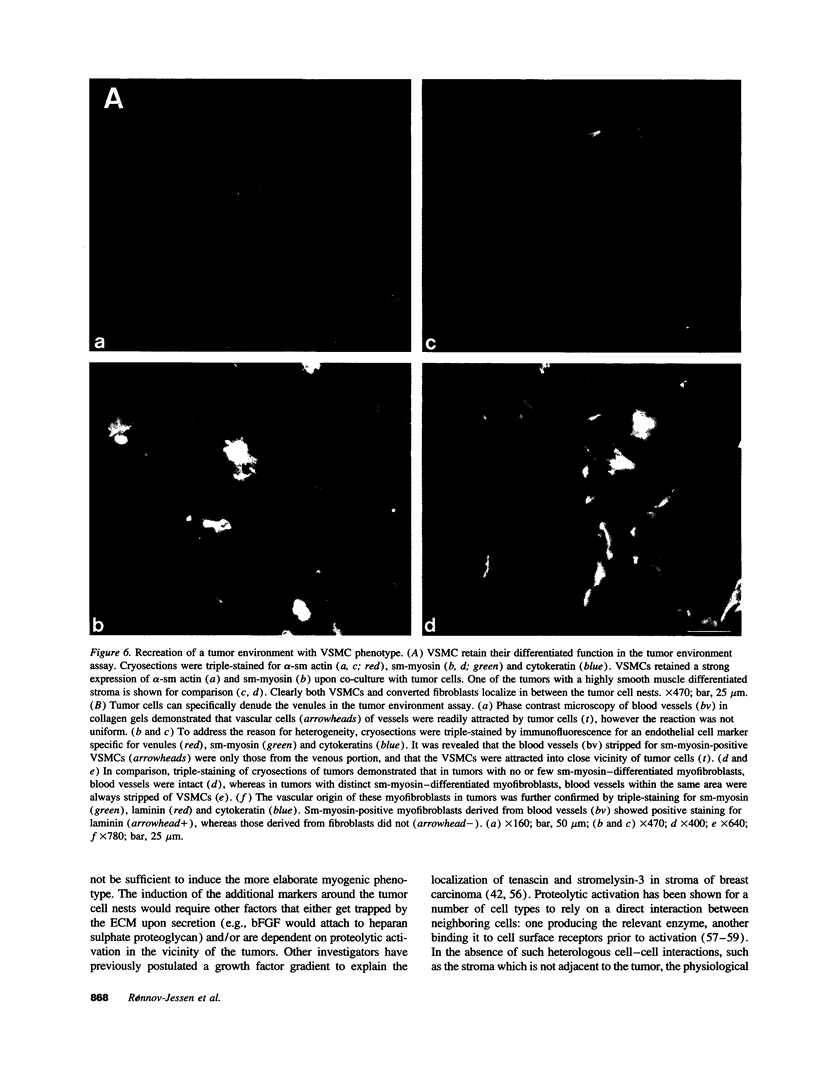
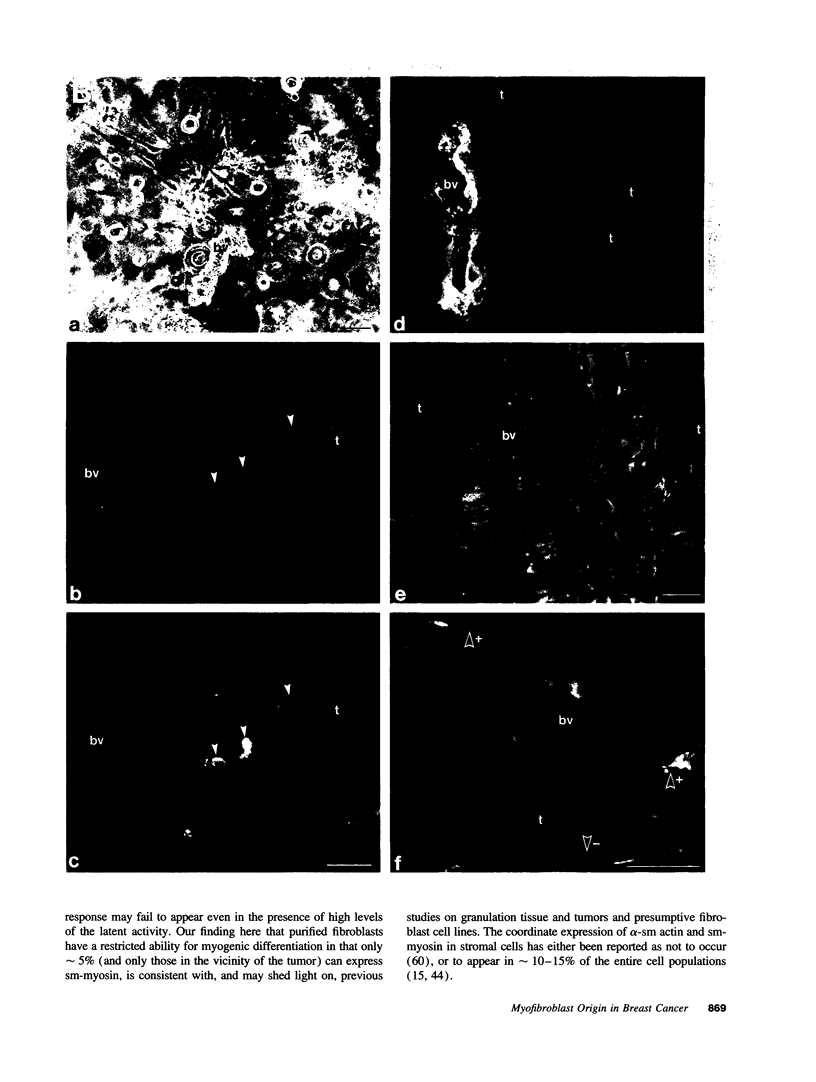
Abstract
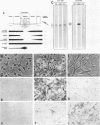
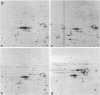
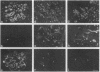
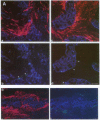
The origin of myofibroblasts in stromal reaction has been a subject of controversy. To address this question definitively, we developed techniques for purification and characterization of major stromal cell types. We defined a panel of markers that could, in combination, unequivocally distinguish these cell types by immunocytochemistry, iso-electric focusing, immunoblotting, and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. We then devised an assay to recapitulate in culture, within two weeks of incubation, critical aspects of the microenvironment in vivo including the typical tissue histology and stromal reaction. When confronted with tumor cells in this assay, fibroblasts readily converted into a graded pattern of myogenic differentiation, strongest in the immediate vicinity of tumor cells. Vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC), in contrast, did not change appreciably and remained coordinately smooth muscle differentiated. Midcapillary pericytes showed only a slight propensity for myogenic differentiation. Analysis of ten primary tumors implicated converted fibroblasts (10/10), vascular smooth muscle cells (4/10), and pericytes (1/10) in the stromal reaction. Tumor cells were shown to specifically denude the venules both in culture and in vivo, explaining the VSMC phenotype in the stroma. The establishment of this assay and clarification of the origin of these cells pave the way for further analysis of the mechanisms of conversion, and of the consequence of such heterogeneity for diagnosis and treatment.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arteaga C. L., Coffey R. J., Jr, Dugger T. C., McCutchen C. M., Moses H. L., Lyons R. M. Growth stimulation of human breast cancer cells with anti-transforming growth factor beta antibodies: evidence for negative autocrine regulation by transforming growth factor beta. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Aug;1(8):367–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arteaga C. L., Hurd S. D., Winnier A. R., Johnson M. D., Fendly B. M., Forbes J. T. Anti-transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta antibodies inhibit breast cancer cell tumorigenicity and increase mouse spleen natural killer cell activity. Implications for a possible role of tumor cell/host TGF-beta interactions in human breast cancer progression. J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;92(6):2569–2576. doi: 10.1172/JCI116871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsky S. H., Gopalakrishna R. Increased invasion and spontaneous metastasis of BL6 melanoma with inhibition of the desmoplastic response in C57 BL/6 mice. Cancer Res. 1987 Mar 15;47(6):1663–1667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsky S. H., Rao C. N., Grotendorst G. R., Liotta L. A. Increased content of Type V Collagen in desmoplasia of human breast carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1982 Sep;108(3):276–283. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basset P., Bellocq J. P., Wolf C., Stoll I., Hutin P., Limacher J. M., Podhajcer O. L., Chenard M. P., Rio M. C., Chambon P. A novel metalloproteinase gene specifically expressed in stromal cells of breast carcinomas. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):699–704. doi: 10.1038/348699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzonana G., Skalli O., Gabbiani G. Correlation between the distribution of smooth muscle or non muscle myosins and alpha-smooth muscle actin in normal and pathological soft tissues. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1988;11(4):260–274. doi: 10.1002/cm.970110405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz E., Fallier-Becker P., Wolburg-Buchholz K., Fotev Z. Proliferation of smooth muscle cells in the inner and outer layers of the tunica media of arteries: an in vitro study. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Jun;147(3):385–395. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041470302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissell M. J. The differentiated state of normal and malignant cells or how to define a "normal" cell in culture. Int Rev Cytol. 1981;70:27–100. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61130-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasi F. Urokinase and urokinase receptor: a paracrine/autocrine system regulating cell migration and invasiveness. Bioessays. 1993 Feb;15(2):105–111. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau H. M., Baltimore D. Differentiation requires continuous regulation. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):781–783. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briand P., Lykkesfeldt A. E. Long-term cultivation of a human breast cancer cell line, MCF-7, in a chemically defined medium. Effect of estradiol. Anticancer Res. 1986 Jan-Feb;6(1):85–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouty-Boyé D., Raux H., Azzarone B., Tamboise A., Tamboise E., Béranger S., Magnien V., Pihan I., Zardi L., Israël L. Fetal myofibroblast-like cells isolated from post-radiation fibrosis in human breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1991 Mar 12;47(5):697–702. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910470512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buoro S., Ferrarese P., Chiavegato A., Roelofs M., Scatena M., Pauletto P., Passerini-Glazel G., Pagano F., Sartore S. Myofibroblast-derived smooth muscle cells during remodelling of rabbit urinary bladder wall induced by partial outflow obstruction. Lab Invest. 1993 Nov;69(5):589–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Gesser B., Rasmussen H. H., Madsen P., Leffers H., Dejgaard K., Honore B., Olsen E., Ratz G., Lauridsen J. B. Comprehensive two-dimensional gel protein databases offer a global approach to the analysis of human cells: the transformed amnion cells (AMA) master database and its link to genome DNA sequence data. Electrophoresis. 1990 Dec;11(12):989–1071. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150111202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Madsen P., Rasmussen H. H., Leffers H., Honoré B., Gesser B., Dejgaard K., Olsen E., Magnusson N., Kiil J. A comprehensive two-dimensional gel protein database of noncultured unfractionated normal human epidermal keratinocytes: towards an integrated approach to the study of cell proliferation, differentiation and skin diseases. Electrophoresis. 1991 Nov;12(11):802–872. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150121105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamley-Campbell J., Campbell G. R., Ross R. The smooth muscle cell in culture. Physiol Rev. 1979 Jan;59(1):1–61. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1979.59.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiavegato A., Scatena M., Roelofs M., Ferrarese P., Pauletto P., Passerini-Glazel G., Pagano F., Sartore S. Cytoskeletal and cytocontractile protein composition of smooth muscle cells in developing and obstructed rabbit bladder. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Aug;207(2):310–320. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Kalla P., Pearson C. A. Participation of tenascin and transforming growth factor-beta in reciprocal epithelial-mesenchymal interactions of MCF7 cells and fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1989 Aug 1;49(15):4322–4325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cintorino M., Bellizzi de Marco E., Leoncini P., Tripodi S. A., Xu L. J., Sappino A. P., Schmitt-Gräff A., Gabbiani G. Expression of alpha-smooth-muscle actin in stromal cells of the uterine cervix during epithelial neoplastic changes. Int J Cancer. 1991 Apr 1;47(6):843–846. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910470609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernobilsky B., Shezen E., Lifschitz-Mercer B., Fogel M., Luzon A., Jacob N., Skalli O., Gabbiani G. Alpha smooth muscle actin (alpha-SM actin) in normal human ovaries, in ovarian stromal hyperplasia and in ovarian neoplasms. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1989;57(1):55–61. doi: 10.1007/BF02899065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmoulière A., Geinoz A., Gabbiani F., Gabbiani G. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 induces alpha-smooth muscle actin expression in granulation tissue myofibroblasts and in quiescent and growing cultured fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(1):103–111. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmoulière A., Rubbia-Brandt L., Abdiu A., Walz T., Macieira-Coelho A., Gabbiani G. Alpha-smooth muscle actin is expressed in a subpopulation of cultured and cloned fibroblasts and is modulated by gamma-interferon. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Jul;201(1):64–73. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90348-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimanche-Boitrel M. T., Vakaet L., Jr, Pujuguet P., Chauffert B., Martin M. S., Hammann A., Van Roy F., Mareel M., Martin F. In vivo and in vitro invasiveness of a rat colon-cancer cell line maintaining E-cadherin expression: an enhancing role of tumor-associated myofibroblasts. Int J Cancer. 1994 Feb 15;56(4):512–521. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910560410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doane K. J., Birk D. E. Fibroblasts retain their tissue phenotype when grown in three-dimensional collagen gels. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Aug;195(2):432–442. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90394-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duband J. L., Belkin A. M., Syfrig J., Thiery J. P., Koteliansky V. E. Expression of alpha 1 integrin, a laminin-collagen receptor, during myogenesis and neurogenesis in the avian embryo. Development. 1992 Nov;116(3):585–600. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.3.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy R. J., Petro J. A., Tomasek J. J. Evidence for the nonmuscle nature of the "myofibroblast" of granulation tissue and hypertropic scar. An immunofluorescence study. Am J Pathol. 1988 Feb;130(2):252–260. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabra A., Nakajima M., Bucana C. D., Fidler I. J. Modulation of the invasive phenotype of human colon carcinoma cells by organ specific fibroblasts of nude mice. Differentiation. 1992 Dec;52(1):101–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1992.tb00504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. How is blood vessel growth regulated in normal and neoplastic tissue? G.H.A. Clowes memorial Award lecture. Cancer Res. 1986 Feb;46(2):467–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;43:175–203. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60946-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frid M. G., Shekhonin B. V., Koteliansky V. E., Glukhova M. A. Phenotypic changes of human smooth muscle cells during development: late expression of heavy caldesmon and calponin. Dev Biol. 1992 Oct;153(2):185–193. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90104-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell F. Fibroblasts, myofibroblasts, and wound contraction. J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;124(4):401–404. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.4.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horgan K., Jones D. L., Mansel R. E. Mitogenicity of human fibroblasts in vivo for human breast cancer cells. Br J Surg. 1987 Mar;74(3):227–229. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800740326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan R., Cleary E. G. Elastin gene expression in elastotic human breast cancers and epithelial cell lines. Cancer Res. 1990 Apr 1;50(7):2164–2171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazard D., Sastre X., Frid M. G., Glukhova M. A., Thiery J. P., Koteliansky V. E. Expression of smooth muscle-specific proteins in myoepithelium and stromal myofibroblasts of normal and malignant human breast tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):999–1003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. Q., Bissell M. J. Multi-faceted regulation of cell differentiation by extracellular matrix. FASEB J. 1993 Jun;7(9):737–743. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.9.8330681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. M., Keski-Oja J., Moses H. L. Proteolytic activation of latent transforming growth factor-beta from fibroblast-conditioned medium. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1659–1665. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J., Woodcock-Mitchell J., Reynolds S., Low R., Leslie K., Adler K., Gabbiani G., Skalli O. Alpha-smooth muscle actin in parenchymal cells of bleomycin-injured rat lung. Lab Invest. 1989 May;60(5):643–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukaida H., Hirabayashi N., Hirai T., Iwata T., Saeki S., Toge T. Significance of freshly cultured fibroblasts from different tissues in promoting cancer cell growth. Int J Cancer. 1991 May 30;48(3):423–427. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910480320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehls V., Denzer K., Drenckhahn D. Pericyte involvement in capillary sprouting during angiogenesis in situ. Cell Tissue Res. 1992 Dec;270(3):469–474. doi: 10.1007/BF00645048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehls V., Drenckhahn D. Heterogeneity of microvascular pericytes for smooth muscle type alpha-actin. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):147–154. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehls V., Drenckhahn D. The versatility of microvascular pericytes: from mesenchyme to smooth muscle? Histochemistry. 1993 Jan;99(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00268014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odekon L. E., Blasi F., Rifkin D. B. Requirement for receptor-bound urokinase in plasmin-dependent cellular conversion of latent TGF-beta to TGF-beta. J Cell Physiol. 1994 Mar;158(3):398–407. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041580303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallesen G., Nielsen S., Celis J. E. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody (BG3C8) that reacts with basal cells of stratified epithelia. Histopathology. 1987 Jun;11(6):591–601. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1987.tb02669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. W., Hansen S. H., Laursen I., van Deurs B. Effect of insulin on growth and expression of smooth muscle isoactin in human breast gland myoepithelial cells in a chemically defined culture system. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;50(2):500–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. W., Rønnov-Jessen L., Howlett A. R., Bissell M. J. Interaction with basement membrane serves to rapidly distinguish growth and differentiation pattern of normal and malignant human breast epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9064–9068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. W., van Deurs B. Growth factor control of myoepithelial-cell differentiation in cultures of human mammary gland. Differentiation. 1988 Dec;39(3):197–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1988.tb00094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke C., Kristensen P., Ralfkiaer E., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Eriksen J., Blasi F., Danø K. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator is expressed in stromal cells and its receptor in cancer cells at invasive foci in human colon adenocarcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1991 May;138(5):1059–1067. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockey D. C., Friedman S. L. Cytoskeleton of liver perisinusoidal cells (lipocytes) in normal and pathological conditions. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1992;22(4):227–234. doi: 10.1002/cm.970220402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rønnov-Jessen L., Celis J. E., Van Deurs B., Petersen O. W. A fibroblast-associated antigen: characterization in fibroblasts and immunoreactivity in smooth muscle differentiated stromal cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Apr;40(4):475–486. doi: 10.1177/40.4.1552184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rønnov-Jessen L., Petersen O. W. Induction of alpha-smooth muscle actin by transforming growth factor-beta 1 in quiescent human breast gland fibroblasts. Implications for myofibroblast generation in breast neoplasia. Lab Invest. 1993 Jun;68(6):696–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rønnov-Jessen L., Van Deurs B., Nielsen M., Petersen O. W. Identification, paracrine generation, and possible function of human breast carcinoma myofibroblasts in culture. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1992 Apr;28A(4):273–283. doi: 10.1007/BF02634244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rønnov-Jessen L., van Deurs B., Celis J. E., Petersen O. W. Smooth muscle differentiation in cultured human breast gland stromal cells. Lab Invest. 1990 Oct;63(4):532–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Dietrich P. Y., Skalli O., Widgren S., Gabbiani G. Colonic pericryptal fibroblasts. Differentiation pattern in embryogenesis and phenotypic modulation in epithelial proliferative lesions. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1989;415(6):551–557. doi: 10.1007/BF00718649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Skalli O., Jackson B., Schürch W., Gabbiani G. Smooth-muscle differentiation in stromal cells of malignant and non-malignant breast tissues. Int J Cancer. 1988 May 15;41(5):707–712. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlingemann R. O., Dingjan G. M., Emeis J. J., Blok J., Warnaar S. O., Ruiter D. J. Monoclonal antibody PAL-E specific for endothelium. Lab Invest. 1985 Jan;52(1):71–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlingemann R. O., Rietveld F. J., Kwaspen F., van de Kerkhof P. C., de Waal R. M., Ruiter D. J. Differential expression of markers for endothelial cells, pericytes, and basal lamina in the microvasculature of tumors and granulation tissue. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jun;138(6):1335–1347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlingemann R. O., Rietveld F. J., de Waal R. M., Ferrone S., Ruiter D. J. Expression of the high molecular weight melanoma-associated antigen by pericytes during angiogenesis in tumors and in healing wounds. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jun;136(6):1393–1405. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt-Gräff A., Pau H., Spahr R., Piper H. M., Skalli O., Gabbiani G. Appearance of alpha-smooth muscle actin in human eye lens cells of anterior capsular cataract and in cultured bovine lens-forming cells. Differentiation. 1990 Apr;43(2):115–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1990.tb00437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schürch W., Seemayer T. A., Lagacé R. Stromal myofibroblasts in primary invasive and metastatic carcinomas. A combined immunological, light and electron microscopic study. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1981;391(2):125–139. doi: 10.1007/BF00437591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieweke M. H., Thompson N. L., Sporn M. B., Bissell M. J. Mediation of wound-related Rous sarcoma virus tumorigenesis by TGF-beta. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1656–1660. doi: 10.1126/science.2163544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli O., Pelte M. F., Peclet M. C., Gabbiani G., Gugliotta P., Bussolati G., Ravazzola M., Orci L. Alpha-smooth muscle actin, a differentiation marker of smooth muscle cells, is present in microfilamentous bundles of pericytes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 Mar;37(3):315–321. doi: 10.1177/37.3.2918221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli O., Ropraz P., Trzeciak A., Benzonana G., Gillessen D., Gabbiani G. A monoclonal antibody against alpha-smooth muscle actin: a new probe for smooth muscle differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2787–2796. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli O., Schürch W., Seemayer T., Lagacé R., Montandon D., Pittet B., Gabbiani G. Myofibroblasts from diverse pathologic settings are heterogeneous in their content of actin isoforms and intermediate filament proteins. Lab Invest. 1989 Feb;60(2):275–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli C. H., Bailey N., Bissell M. J. Control of mammary epithelial differentiation: basement membrane induces tissue-specific gene expression in the absence of cell-cell interaction and morphological polarity. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(5):1383–1395. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.5.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada T., McNutt M. A., Ross R., Gown A. M. HHF35, a muscle actin-specific monoclonal antibody. II. Reactivity in normal, reactive, and neoplastic human tissues. Am J Pathol. 1987 May;127(2):389–402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vukicevic S., Kleinman H. K., Luyten F. P., Roberts A. B., Roche N. S., Reddi A. H. Identification of multiple active growth factors in basement membrane Matrigel suggests caution in interpretation of cellular activity related to extracellular matrix components. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Sep;202(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90397-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt F. M. Cell culture models of differentiation. FASEB J. 1991 Mar 1;5(3):287–294. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.3.2001788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Tapscott S., Thayer M., Krause M., Benezra R., Blackwell T. K., Turner D., Rupp R., Hollenberg S. The myoD gene family: nodal point during specification of the muscle cell lineage. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):761–766. doi: 10.1126/science.1846704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]