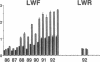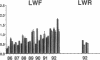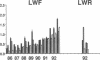Abstract
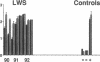
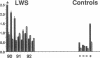
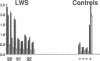
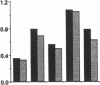
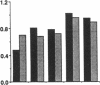
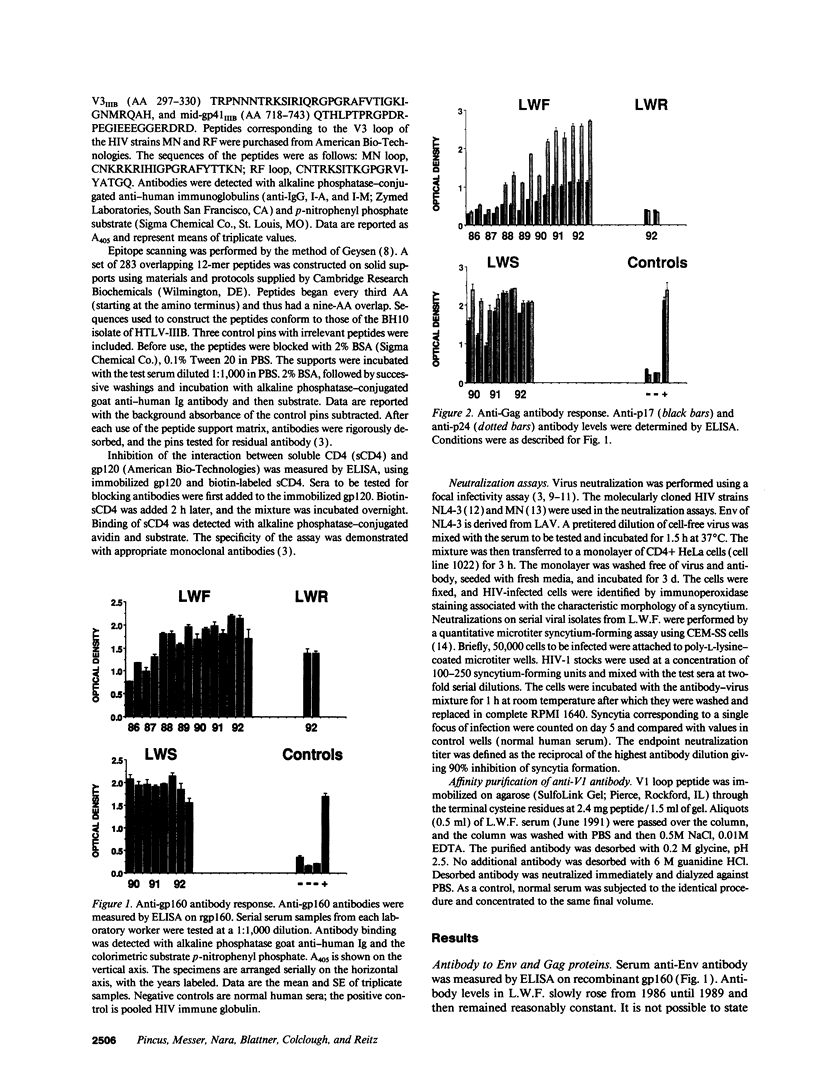
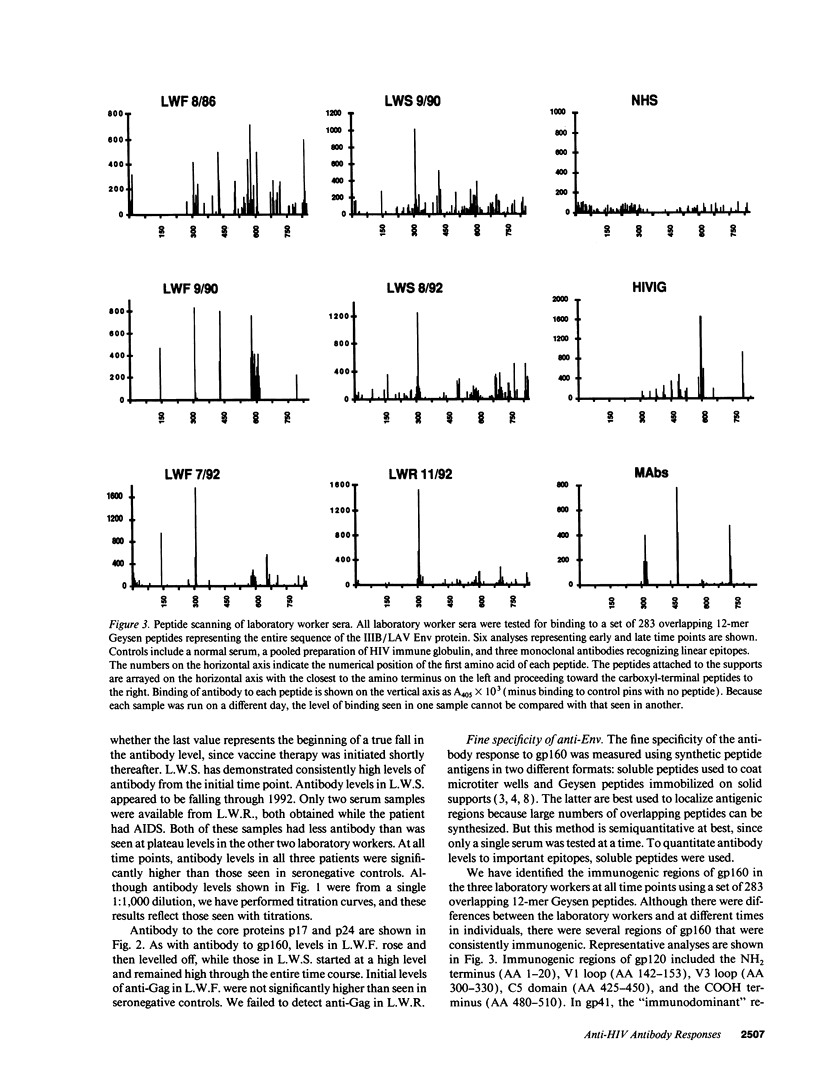
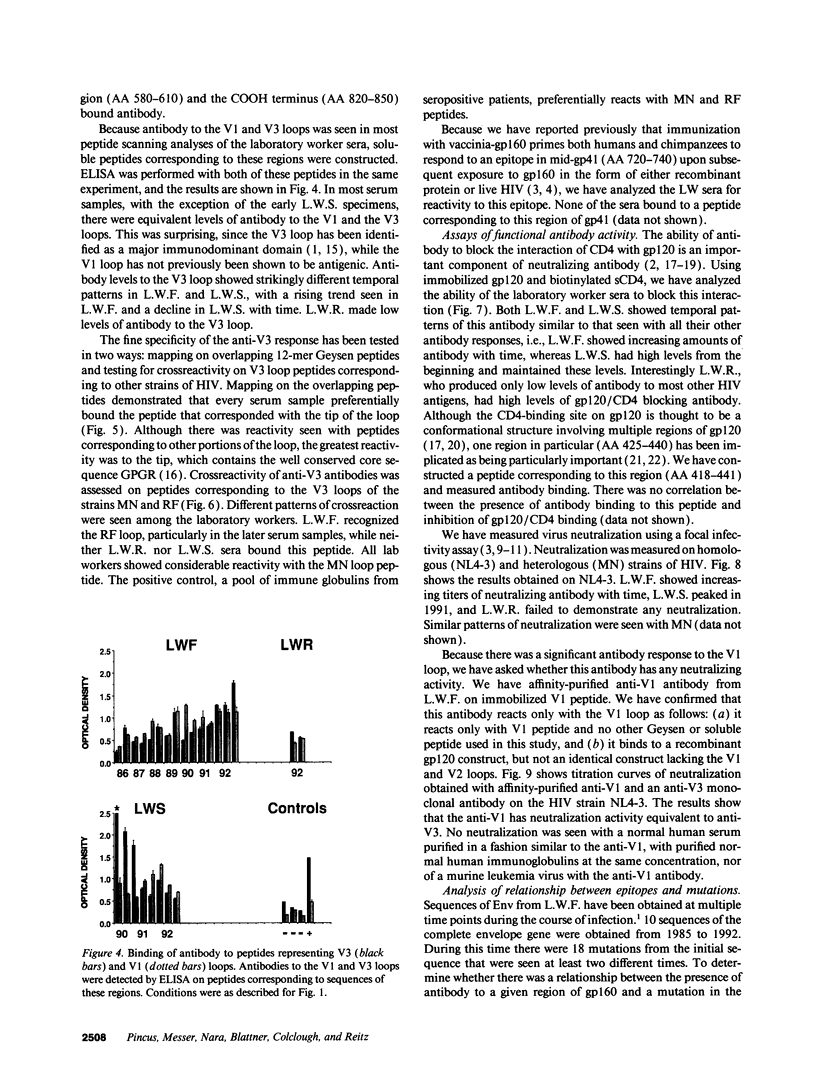
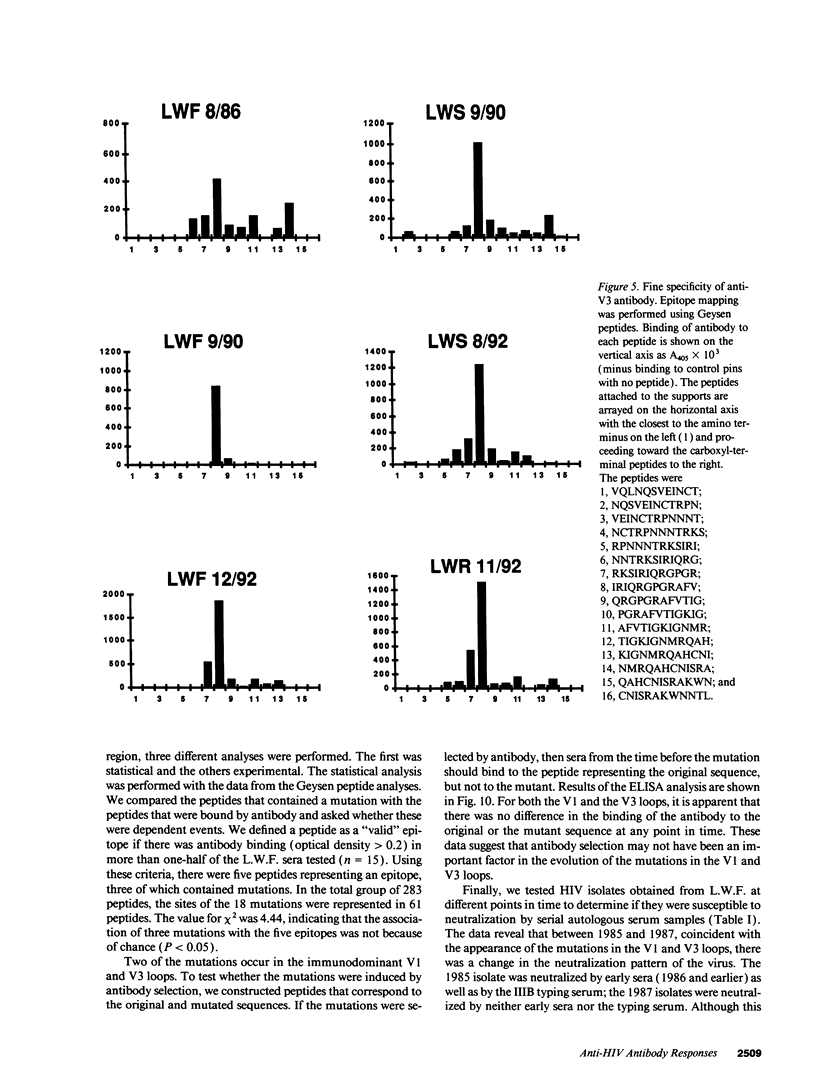
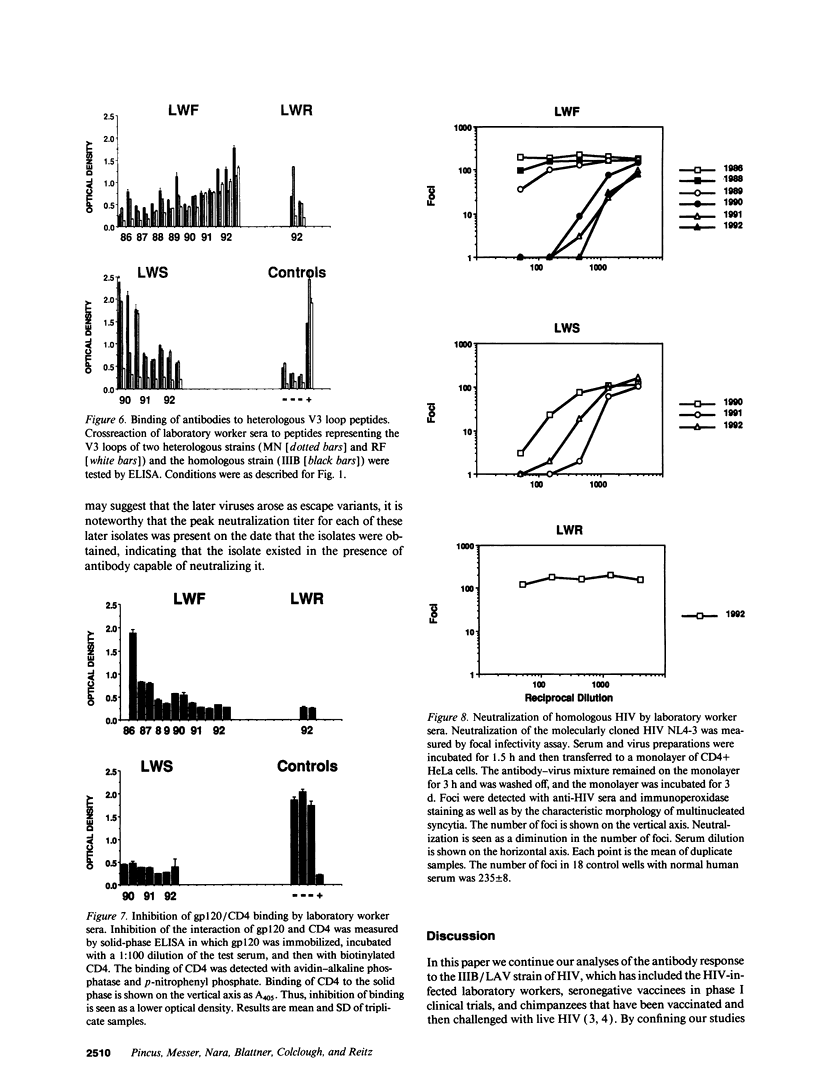
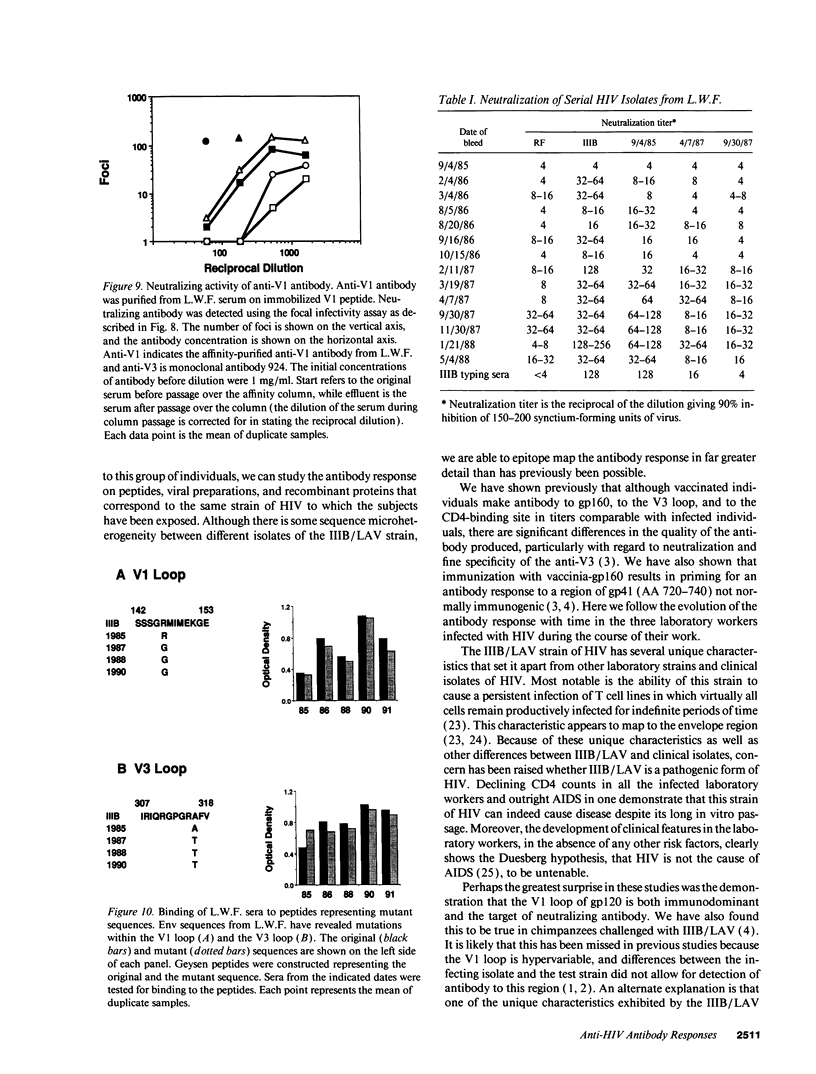
Three laboratory workers have been infected with the IIIB strain of HIV; their antibody response to HIV has been studied in serial serum specimens. Because the infecting virus is known, the fine specificity of the antibody response was studied on the homologous strain of HIV. Anti-p17, anti-p24, anti-gp160, CD4/gp120 blocking and neutralizing antibodies developed in parallel. Epitope mapping of the anti-gp160 response indicated several regions that consistently induced an antibody response. Serum contained antibody which reacted with V3-specific peptides corresponding to the very tip of the loop and crossreactivity was seen with V3 loop peptides from other sequence divergent strains of HIV. Antibody to the V1 loop was produced at levels comparable with that seen for the V3-loop. Anti-V1 neutralized HIV with a titration curve equivalent to an anti-V3 monoclonal antibody. Because the infecting virus is known and serial reisolates have been obtained, we explored the relationship between production of antibody to a given epitope and mutation in the virus. The data suggest that an association exists, but do not clearly indicate that antibody drives the selection for mutant viruses. The findings presented here provide a fine specificity analysis of the evolution of the antibody response to HIV in greater detail than has previously been performed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi A., Gendelman H. E., Koenig S., Folks T., Willey R., Rabson A., Martin M. A. Production of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated retrovirus in human and nonhuman cells transfected with an infectious molecular clone. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):284–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.284-291.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back N. K., Thiriart C., Delers A., Ramautarsing C., Bruck C., Goudsmit J. Association of antibodies blocking HIV-1 gp 160-sCD4 attachment with virus neutralizing activity in human sera. J Med Virol. 1990 Jul;31(3):200–208. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890310306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broliden P. A., von Gegerfelt A., Clapham P., Rosen J., Fenyö E. M., Wahren B., Broliden K. Identification of human neutralization-inducing regions of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):461–465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K. Development of a sensitive quantitative focal assay for human immunodeficiency virus infectivity. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3779–3788. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3779-3788.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K., Metcalf J., Griffin D. E. Use of a new CD4-positive HeLa cell clone for direct quantitation of infectious human immunodeficiency virus from blood cells of AIDS patients. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;163(1):64–70. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H. AIDS epidemiology: inconsistencies with human immunodeficiency virus and with infectious disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1575–1579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Rodda S. J., Mason T. J., Tribbick G., Schoofs P. G. Strategies for epitope analysis using peptide synthesis. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Sep 24;102(2):259–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90085-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J., Debouck C., Meloen R. H., Smit L., Bakker M., Asher D. M., Wolff A. V., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 neutralization epitope with conserved architecture elicits early type-specific antibodies in experimentally infected chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4478–4482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaherian K., Langlois A. J., LaRosa G. J., Profy A. T., Bolognesi D. P., Herlihy W. C., Putney S. D., Matthews T. J. Broadly neutralizing antibodies elicited by the hypervariable neutralizing determinant of HIV-1. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1590–1593. doi: 10.1126/science.1703322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaherian K., Langlois A. J., McDanal C., Ross K. L., Eckler L. I., Jellis C. L., Profy A. T., Rusche J. R., Bolognesi D. P., Putney S. D. Principal neutralizing domain of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6768–6772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y., Nara P., Chamat S., Caralli V., Ryskamp T., Haigwood N., Newman R., Köhler H. Evidence for non-V3-specific neutralizing antibodies that interfere with gp120/CD4 binding in human immunodeficiency virus 1-infected humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6171–6175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRosa G. J., Davide J. P., Weinhold K., Waterbury J. A., Profy A. T., Lewis J. A., Langlois A. J., Dreesman G. R., Boswell R. N., Shadduck P. Conserved sequence and structural elements in the HIV-1 principal neutralizing determinant. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):932–935. doi: 10.1126/science.2392685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Nakamura G., Smith D. H., Fennie C., Shimasaki C., Patzer E., Berman P., Gregory T., Capon D. J. Delineation of a region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 glycoprotein critical for interaction with the CD4 receptor. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90524-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lori F., Hall L., Lusso P., Popovic M., Markham P., Franchini G., Reitz M. S., Jr Effect of reciprocal complementation of two defective human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) molecular clones on HIV-1 cell tropism and virulence. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5553–5560. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5553-5560.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., Ho D. D. Antibodies to discontinuous or conformationally sensitive epitopes on the gp120 glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 are highly prevalent in sera of infected humans. J Virol. 1993 Feb;67(2):863–875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.2.863-875.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara P. L., Fischinger P. J. Quantitative infectivity assay for HIV-1 and-2. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):469–470. doi: 10.1038/332469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Cole R. L., Hersh E. M., Lake D., Masuho Y., Durda P. J., McClure J. In vitro efficacy of anti-HIV immunotoxins targeted by various antibodies to the envelope protein. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 15;146(12):4315–4324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Messer K. G., Hu S. L. Effect of nonprotective vaccination on antibody response to subsequent human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jan;93(1):140–146. doi: 10.1172/JCI116937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Messer K. G., Schwartz D. H., Lewis G. K., Graham B. S., Blattner W. A., Fisher G. Differences in the antibody response to human immunodeficiency virus-1 envelope glycoprotein (gp160) in infected laboratory workers and vaccinees. J Clin Invest. 1993 May;91(5):1987–1996. doi: 10.1172/JCI116420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Wehrly K. AZT demonstrates anti-HIV-1 activity in persistently infected cell lines: implications for combination chemotherapy and immunotherapy. J Infect Dis. 1990 Dec;162(6):1233–1238. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.6.1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Wehrly K., Chesebro B. Use of a focal infectivity assay for testing susceptibility of HIV to antiviral agents. Biotechniques. 1991 Mar;10(3):336–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. H., Wehrly K., Tschachler E., Hayes S. F., Buller R. S., Reitz M. Variants selected by treatment of human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells with an immunotoxin. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):745–757. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Profy A. T., Salinas P. A., Eckler L. I., Dunlop N. M., Nara P. L., Putney S. D. Epitopes recognized by the neutralizing antibodies of an HIV-1-infected individual. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4641–4647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfield R. R., Birx D. L., Ketter N., Tramont E., Polonis V., Davis C., Brundage J. F., Smith G., Johnson S., Fowler A. A phase I evaluation of the safety and immunogenicity of vaccination with recombinant gp160 in patients with early human immunodeficiency virus infection. Military Medical Consortium for Applied Retroviral Research. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jun 13;324(24):1677–1684. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199106133242401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitz M. S., Jr, Wilson C., Naugle C., Gallo R. C., Robert-Guroff M. Generation of a neutralization-resistant variant of HIV-1 is due to selection for a point mutation in the envelope gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):57–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steimer K. S., Scandella C. J., Skiles P. V., Haigwood N. L. Neutralization of divergent HIV-1 isolates by conformation-dependent human antibodies to Gp120. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):105–108. doi: 10.1126/science.1718036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun N. C., Ho D. D., Sun C. R., Liou R. S., Gordon W., Fung M. S., Li X. L., Ting R. C., Lee T. H., Chang N. T. Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to the putative CD4-binding domain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3579–3585. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3579-3585.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Gegerfelt A., Albert J., Morfeldt-Månson L., Broliden K., Fenyö E. M. Isolate-specific neutralizing antibodies in patients with progressive HIV-1-related disease. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):162–168. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90764-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. H., Goedert J. J., Gartner S., Popovic M., Waters D., Markham P., di Marzo Veronese F., Gail M. H., Barkley W. E., Gibbons J. Risk of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection among laboratory workers. Science. 1988 Jan 1;239(4835):68–71. doi: 10.1126/science.3336776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]