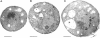Abstract
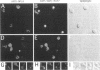
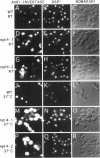
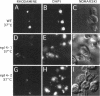
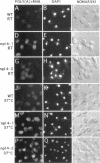
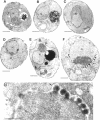
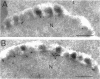
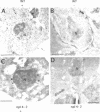
To identify components involved in nuclear protein import, we used a genetic selection to isolate mutants that mislocalized a nuclear-targeted protein. We identified temperature-sensitive mutants that accumulated several different nuclear proteins in the cytoplasm when shifted to the semipermissive temperature of 30 degrees C; these were termed npl (nuclear protein localization) mutants. We now present the properties of yeast strains bearing mutations in the NPL4 gene and report the cloning of the NPL4 gene and the characterization of the Np14 protein. The npl4-1 mutant was isolated by the previously described selection scheme. The second allele, npl4-2, was identified from an independently derived collection of temperature-sensitive mutants. The npl4-1 and npl4-2 strains accumulate nuclear-targeted proteins in the cytoplasm at the nonpermissive temperature consistent with a defect in nuclear protein import. Using an in vitro nuclear import assay, we show that nuclei prepared from temperature-shifted npl4 mutant cells are unable to import nuclear-targeted proteins, even in the presence of cytosol prepared from wild-type cells. In addition, npl4-2 cells accumulate poly(A)+ RNA in the nucleus at the nonpermissive temperature, consistent with a failure to export mRNA from the nucleus. The npl4-1 and npl4-2 cells also exhibit distinct, temperature-sensitive structural defects: npl4-1 cells project extra nuclear envelope into the cytoplasm, whereas npl4-2 cells from nuclear envelope herniations that appear to be filled with poly(A)+ RNA. The NPL4 gene encodes an essential M(r) 64,000 protein that is located at the nuclear periphery and localizes in a pattern similar to nuclear pore complex proteins. Taken together, these results indicate that this gene encodes a novel nuclear pore complex or nuclear pore complex-associated component required for nuclear membrane integrity and nuclear transport.
Full text
PDF




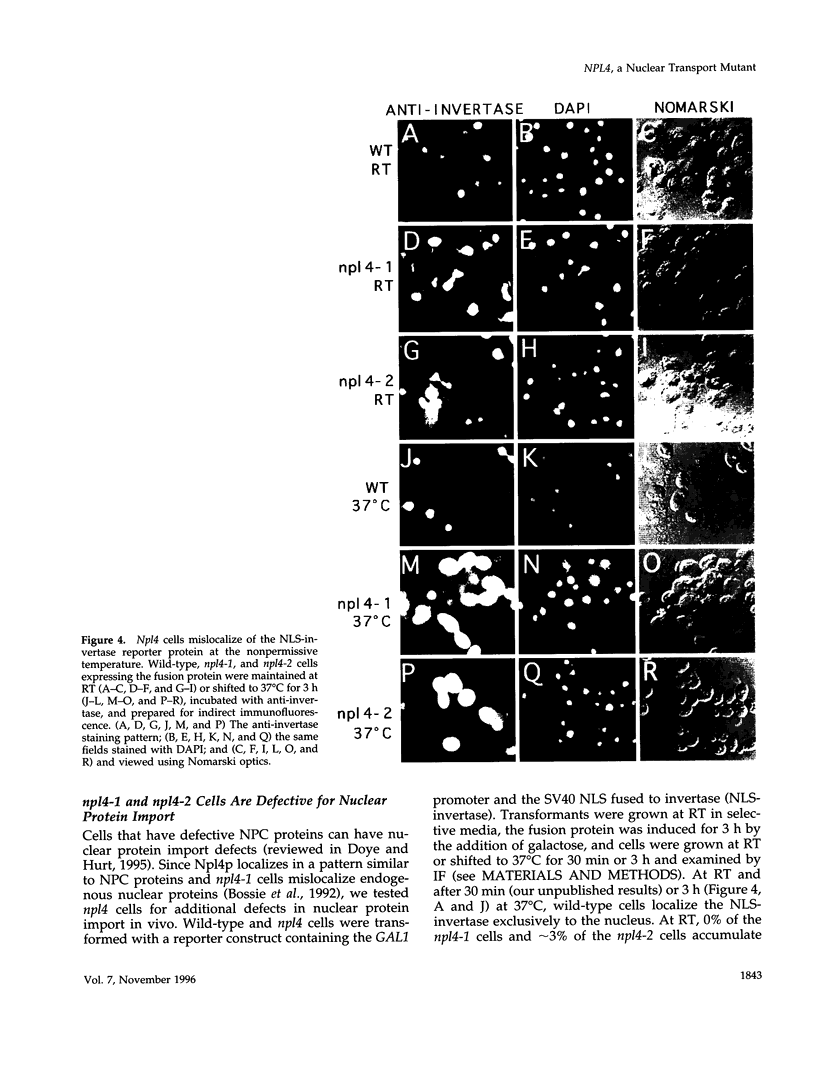

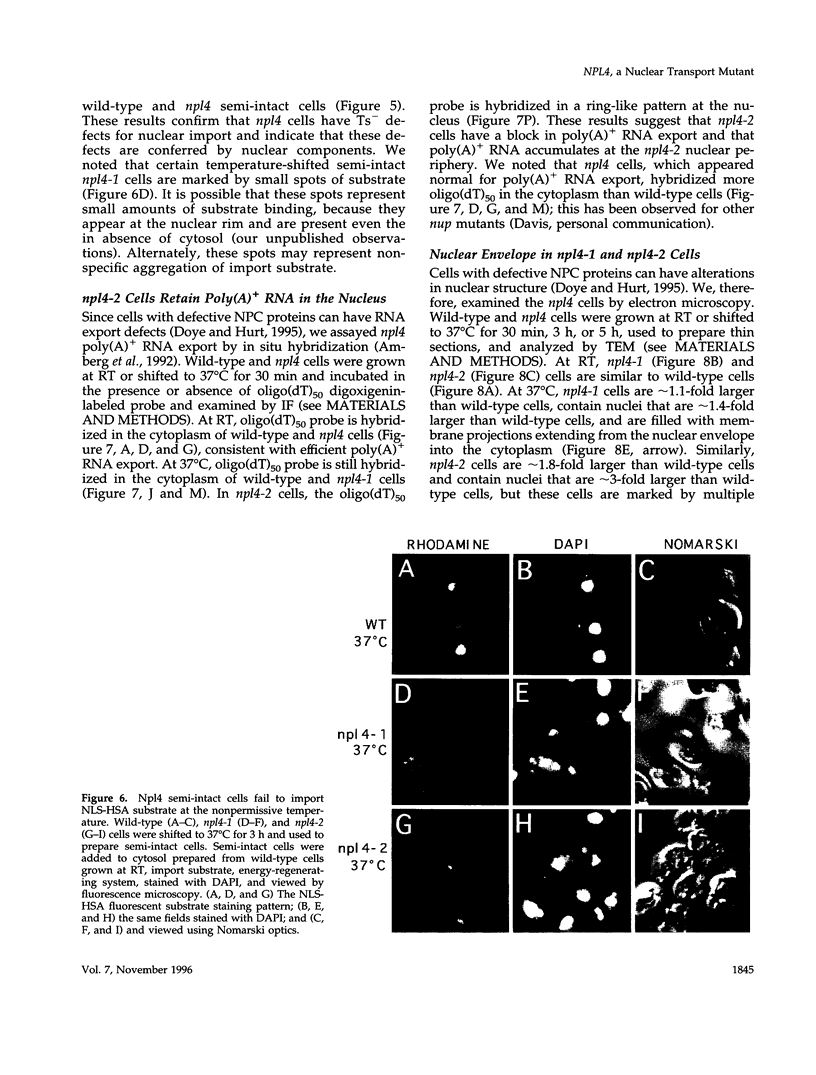
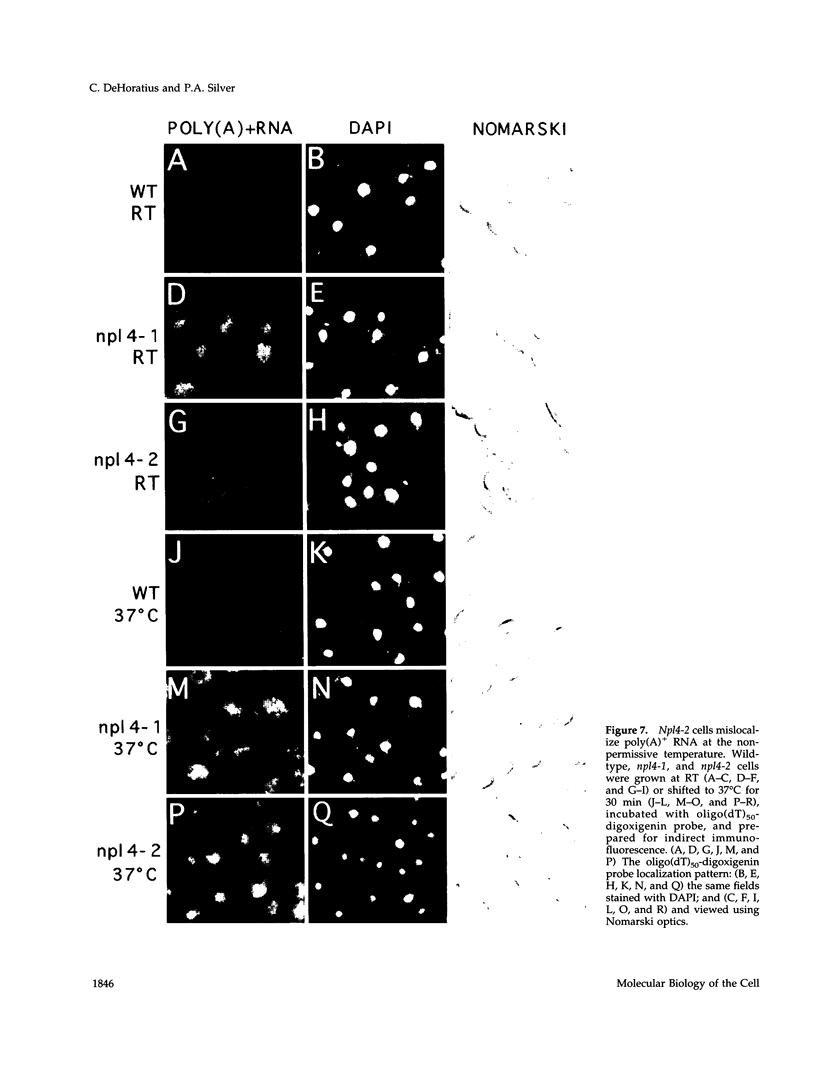
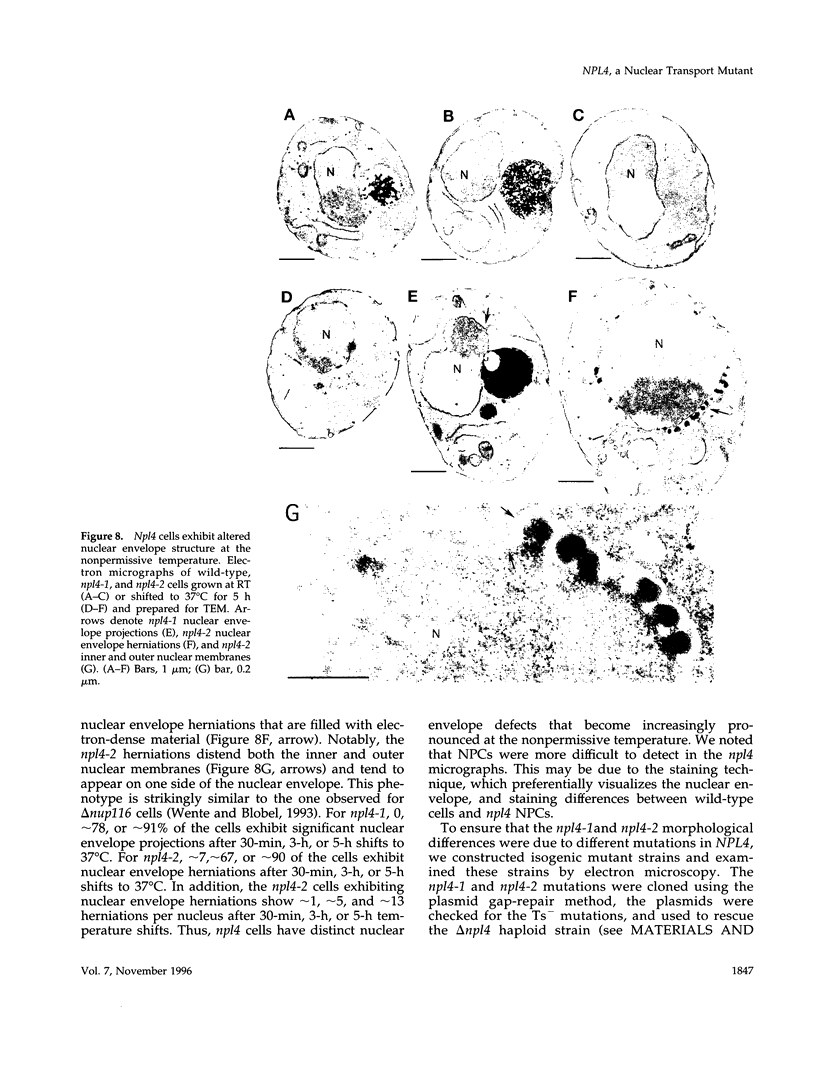





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi M., Clark M. W., Vijayraghavan U., Abelson J. A yeast mutant, PRP20, altered in mRNA metabolism and maintenance of the nuclear structure, is defective in a gene homologous to the human gene RCC1 which is involved in the control of chromosome condensation. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Oct;224(1):72–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00259453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitchison J. D., Blobel G., Rout M. P. Nup120p: a yeast nucleoporin required for NPC distribution and mRNA transport. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(6 Pt 2):1659–1675. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitchison J. D., Rout M. P., Marelli M., Blobel G., Wozniak R. W. Two novel related yeast nucleoporins Nup170p and Nup157p: complementation with the vertebrate homologue Nup155p and functional interactions with the yeast nuclear pore-membrane protein Pom152p. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(5):1133–1148. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.5.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amberg D. C., Fleischmann M., Stagljar I., Cole C. N., Aebi M. Nuclear PRP20 protein is required for mRNA export. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):233–241. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05649.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amberg D. C., Goldstein A. L., Cole C. N. Isolation and characterization of RAT1: an essential gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae required for the efficient nucleocytoplasmic trafficking of mRNA. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1173–1189. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. T., Wilson S. M., Datar K. V., Swanson M. S. NAB2: a yeast nuclear polyadenylated RNA-binding protein essential for cell viability. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2730–2741. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aris J. P., Blobel G. Yeast nuclear envelope proteins cross react with an antibody against mammalian pore complex proteins. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2059–2067. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff F. R., Krebber H., Kempf T., Hermes I., Ponstingl H. Human RanGTPase-activating protein RanGAP1 is a homologue of yeast Rna1p involved in mRNA processing and transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1749–1753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff F. R., Krebber H., Smirnova E., Dong W., Ponstingl H. Co-activation of RanGTPase and inhibition of GTP dissociation by Ran-GTP binding protein RanBP1. EMBO J. 1995 Feb 15;14(4):705–715. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07049.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff F. R., Ponstingl H. Catalysis of guanine nucleotide exchange on Ran by the mitotic regulator RCC1. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):80–82. doi: 10.1038/354080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogerd A. M., Hoffman J. A., Amberg D. C., Fink G. R., Davis L. I. nup1 mutants exhibit pleiotropic defects in nuclear pore complex function. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(2):319–332. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonneaud N., Minvielle-Sebastia L., Cullin C., Lacroute F. Cellular localization of RNA14p and RNA15p, two yeast proteins involved in mRNA stability. J Cell Sci. 1994 Apr;107(Pt 4):913–921. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.4.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossie M. A., DeHoratius C., Barcelo G., Silver P. A mutant nuclear protein with similarity to RNA binding proteins interferes with nuclear import in yeast. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Aug;3(8):875–893. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.8.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler G., Wolfe K. H. Yeast homologue of mammalian Ran binding protein 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Nov 22;1219(3):711–712. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(94)90233-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett A. H., Koepp D. M., Schlenstedt G., Lee M. S., Hopper A. K., Silver P. A. Rna1p, a Ran/TC4 GTPase activating protein, is required for nuclear import. J Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;130(5):1017–1026. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.5.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbett A. H., Silver P. A. The NTF2 gene encodes an essential, highly conserved protein that functions in nuclear transport in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1996 Aug 2;271(31):18477–18484. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.31.18477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutavas E., Ren M., Oppenheim J. D., D'Eustachio P., Rush M. G. Characterization of proteins that interact with the cell-cycle regulatory protein Ran/TC4. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):585–587. doi: 10.1038/366585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. I. The nuclear pore complex. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:865–896. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.64.070195.004245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Schekman R. A yeast mutant defective at an early stage in import of secretory protein precursors into the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):633–645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Schekman R. SEC62 encodes a putative membrane protein required for protein translocation into the yeast endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2653–2664. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doye V., Hurt E. C. Genetic approaches to nuclear pore structure and function. Trends Genet. 1995 Jun;11(6):235–241. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)89057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doye V., Wepf R., Hurt E. C. A novel nuclear pore protein Nup133p with distinct roles in poly(A)+ RNA transport and nuclear pore distribution. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 15;13(24):6062–6075. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06953.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Vassarotti A., Garrett J., Geller B. L., Takeda M., Douglas M. G. The amino terminus of the yeast F1-ATPase beta-subunit precursor functions as a mitochondrial import signal. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):523–533. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabre E., Boelens W. C., Wimmer C., Mattaj I. W., Hurt E. C. Nup145p is required for nuclear export of mRNA and binds homopolymeric RNA in vitro via a novel conserved motif. Cell. 1994 Jul 29;78(2):275–289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flach J., Bossie M., Vogel J., Corbett A., Jinks T., Willins D. A., Silver P. A. A yeast RNA-binding protein shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;14(12):8399–8407. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.12.8399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz C. C., Green M. R. HIV Rev uses a conserved cellular protein export pathway for the nucleocytoplasmic transport of viral RNAs. Curr Biol. 1996 Jul 1;6(7):848–854. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00608-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz D., St Jean A., Woods R. A., Schiestl R. H. Improved method for high efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1425–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. W., Allen T. D. Structural and functional organization of the nuclear envelope. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;7(3):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A. L., Snay C. A., Heath C. V., Cole C. N. Pleiotropic nuclear defects associated with a conditional allele of the novel nucleoporin Rat9p/Nup85p. Mol Biol Cell. 1996 Jun;7(6):917–934. doi: 10.1091/mbc.7.6.917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorsch L. C., Dockendorff T. C., Cole C. N. A conditional allele of the novel repeat-containing yeast nucleoporin RAT7/NUP159 causes both rapid cessation of mRNA export and reversible clustering of nuclear pore complexes. J Cell Biol. 1995 May;129(4):939–955. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.4.939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandi P., Emig S., Weise C., Hucho F., Pohl T., Hurt E. C. A novel nuclear pore protein Nup82p which specifically binds to a fraction of Nsp1p. J Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;130(6):1263–1273. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.6.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Mattaj I. W. Nucleocytoplasmic transport. Science. 1996 Mar 15;271(5255):1513–1518. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5255.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Vogel F., Mills A. D., Hartmann E., Laskey R. A. Distinct functions for the two importin subunits in nuclear protein import. Nature. 1995 Sep 21;377(6546):246–248. doi: 10.1038/377246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallberg E., Wozniak R. W., Blobel G. An integral membrane protein of the pore membrane domain of the nuclear envelope contains a nucleoporin-like region. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(3):513–521. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.3.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath C. V., Copeland C. S., Amberg D. C., Del Priore V., Snyder M., Cole C. N. Nuclear pore complex clustering and nuclear accumulation of poly(A)+ RNA associated with mutation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAT2/NUP120 gene. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(6 Pt 2):1677–1697. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry M., Borland C. Z., Bossie M., Silver P. A. Potential RNA binding proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae identified as suppressors of temperature-sensitive mutations in NPL3. Genetics. 1996 Jan;142(1):103–115. doi: 10.1093/genetics/142.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Traglia H. M., Dunst R. W. The yeast RNA1 gene product necessary for RNA processing is located in the cytosol and apparently excluded from the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):309–321. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Deerinck T. J., Ellisman M. H., Spector D. L. In vivo analysis of the stability and transport of nuclear poly(A)+ RNA. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(4):877–899. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.4.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz M. E., Blobel G. NUP82 is an essential yeast nucleoporin required for poly(A)+ RNA export. J Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;130(6):1275–1281. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.6.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iovine M. K., Watkins J. L., Wente S. R. The GLFG repetitive region of the nucleoporin Nup116p interacts with Kap95p, an essential yeast nuclear import factor. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(6 Pt 2):1699–1713. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaurralde E., Mattaj I. W. RNA export. Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. S., Prakash L. Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae selectable markers in pUC18 polylinkers. Yeast. 1990 Sep-Oct;6(5):363–366. doi: 10.1002/yea.320060502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Goldfarb D., Spitz L. M., Tartakoff A. M., Ohno M. Regulation of RNA processing and transport by a nuclear guanine nucleotide release protein and members of the Ras superfamily. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2929–2937. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05955.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Zhao Y., Tartakoff A. M. A conditional yeast mutant deficient in mRNA transport from nucleus to cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2312–2316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klyce H. R., McLaughlin C. S. Characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of yeast by a photomicrographic procedure. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Nov;82(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90243-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koepp D. M., Wong D. H., Corbett A. H., Silver P. A. Dynamic localization of the nuclear import receptor and its interactions with transport factors. J Cell Biol. 1996 Jun;133(6):1163–1176. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.6.1163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer D., Wozniak R. W., Blobel G., Radu A. The human CAN protein, a putative oncogene product associated with myeloid leukemogenesis, is a nuclear pore complex protein that faces the cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1519–1523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Henry M., Silver P. A. A protein that shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm is an important mediator of RNA export. Genes Dev. 1996 May 15;10(10):1233–1246. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.10.1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li O., Heath C. V., Amberg D. C., Dockendorff T. C., Copeland C. S., Snyder M., Cole C. N. Mutation or deletion of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAT3/NUP133 gene causes temperature-dependent nuclear accumulation of poly(A)+ RNA and constitutive clustering of nuclear pore complexes. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Apr;6(4):401–417. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.4.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb J. D., Schlenstedt G., Pellman D., Kornitzer D., Silver P. A., Fink G. R. The yeast nuclear import receptor is required for mitosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 15;92(17):7647–7651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.17.7647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald K. Osmium ferricyanide fixation improves microfilament preservation and membrane visualization in a variety of animal cell types. J Ultrastruct Res. 1984 Feb;86(2):107–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(84)80051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior F., Gerace L. Mechanisms of nuclear protein import. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;7(3):310–318. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior F., Guan T., Yokoyama N., Nishimoto T., Gerace L. GTP hydrolysis by Ran occurs at the nuclear pore complex in an early step of protein import. J Cell Biol. 1995 Nov;131(3):571–581. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior F., Paschal B., Evans J., Gerace L. Inhibition of nuclear protein import by nonhydrolyzable analogues of GTP and identification of the small GTPase Ran/TC4 as an essential transport factor. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(6 Pt 2):1649–1659. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. S., Blobel G. Purification of a Ran-interacting protein that is required for protein import into the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):10212–10216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.10212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. S., Blobel G. The GTP-binding protein Ran/TC4 is required for protein import into the nucleus. Nature. 1993 Oct 14;365(6447):661–663. doi: 10.1038/365661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland R. B., Langevin G. L., Singer R. H., Garcea R. L., Hereford L. M. Amino acid sequences that determine the nuclear localization of yeast histone 2B. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4048–4057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroianu J., Blobel G., Radu A. Previously identified protein of uncertain function is karyopherin alpha and together with karyopherin beta docks import substrate at nuclear pore complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 14;92(6):2008–2011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.6.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroianu J., Hijikata M., Blobel G., Radu A. Mammalian karyopherin alpha 1 beta and alpha 2 beta heterodimers: alpha 1 or alpha 2 subunit binds nuclear localization signal and beta subunit interacts with peptide repeat-containing nucleoporins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 3;92(14):6532–6536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.14.6532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehrbass U., Blobel G. Role of the nuclear transport factor p10 in nuclear import. Science. 1996 Apr 5;272(5258):120–122. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5258.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehrbass U., Rout M. P., Maguire S., Blobel G., Wozniak R. W. The yeast nucleoporin Nup188p interacts genetically and physically with the core structures of the nuclear pore complex. J Cell Biol. 1996 Jun;133(6):1153–1162. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.6.1153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M., Silver P. Context affects nuclear protein localization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):384–389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng D. T., Walter P. ER membrane protein complex required for nuclear fusion. J Cell Biol. 1996 Feb;132(4):499–509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.132.4.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W. Yeast recombination: the association between double-strand gap repair and crossing-over. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4417–4421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paschal B. M., Gerace L. Identification of NTF2, a cytosolic factor for nuclear import that interacts with nuclear pore complex protein p62. J Cell Biol. 1995 May;129(4):925–937. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.4.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers M. A., Forbes D. J. Cytosolic factors in nuclear transport: what's importin? Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):931–934. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radu A., Blobel G., Moore M. S. Identification of a protein complex that is required for nuclear protein import and mediates docking of import substrate to distinct nucleoporins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1769–1773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radu A., Moore M. S., Blobel G. The peptide repeat domain of nucleoporin Nup98 functions as a docking site in transport across the nuclear pore complex. Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90331-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rexach M., Blobel G. Protein import into nuclei: association and dissociation reactions involving transport substrate, transport factors, and nucleoporins. Cell. 1995 Dec 1;83(5):683–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90181-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Novick P., Thomas J. H., Botstein D., Fink G. R. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae genomic plasmid bank based on a centromere-containing shuttle vector. Gene. 1987;60(2-3):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblatt J. A., Deshaies R. J., Sanders S. L., Daum G., Schekman R. Multiple genes are required for proper insertion of secretory proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum in yeast. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2641–2652. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rout M. P., Blobel G. Isolation of the yeast nuclear pore complex. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(4):771–783. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.4.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rout M. P., Wente S. R. Pores for thought: nuclear pore complex proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;4(10):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler I., Chiang A., Kurihara T., Rothblatt J., Way J., Silver P. A yeast gene important for protein assembly into the endoplasmic reticulum and the nucleus has homology to DnaJ, an Escherichia coli heat shock protein. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2665–2675. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaaff-Gerstenschläger I., Baur A., Boles E., Zimmermann F. K. Sequence and function analysis of a 4.3 kb fragment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome II including three open reading frames. Yeast. 1993 Aug;9(8):915–921. doi: 10.1002/yea.320090811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlenstedt G., Hurt E., Doye V., Silver P. A. Reconstitution of nuclear protein transport with semi-intact yeast cells. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(4):785–798. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.4.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlenstedt G., Saavedra C., Loeb J. D., Cole C. N., Silver P. A. The GTP-bound form of the yeast Ran/TC4 homologue blocks nuclear protein import and appearance of poly(A)+ RNA in the cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 3;92(1):225–229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siniossoglou S., Wimmer C., Rieger M., Doye V., Tekotte H., Weise C., Emig S., Segref A., Hurt E. C. A novel complex of nucleoporins, which includes Sec13p and a Sec13p homolog, is essential for normal nuclear pores. Cell. 1996 Jan 26;84(2):265–275. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80981-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutz F., Neville M., Rosbash M. Identification of a novel nuclear pore-associated protein as a functional target of the HIV-1 Rev protein in yeast. Cell. 1995 Aug 11;82(3):495–506. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90438-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukegawa J., Blobel G. A nuclear pore complex protein that contains zinc finger motifs, binds DNA, and faces the nucleoplasm. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90047-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet D. J., Gerace L. Taking from the cytoplasm and giving to the pore: soluble transport factors in nuclear protein import. Trends Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;5(12):444–447. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)89108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana T., Imamoto N., Seino H., Nishimoto T., Yoneda Y. Loss of RCC1 leads to suppression of nuclear protein import in living cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):24542–24545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tani T., Derby R. J., Hiraoka Y., Spector D. L. Nucleolar accumulation of poly (A)+ RNA in heat-shocked yeast cells: implication of nucleolar involvement in mRNA transport. Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Nov;6(11):1515–1534. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.11.1515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas B. J., Rothstein R. Elevated recombination rates in transcriptionally active DNA. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):619–630. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90584-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wente S. R., Blobel G. A temperature-sensitive NUP116 null mutant forms a nuclear envelope seal over the yeast nuclear pore complex thereby blocking nucleocytoplasmic traffic. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(2):275–284. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wente S. R., Blobel G. NUP145 encodes a novel yeast glycine-leucine-phenylalanine-glycine (GLFG) nucleoporin required for nuclear envelope structure. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;125(5):955–969. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.5.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wente S. R., Rout M. P., Blobel G. A new family of yeast nuclear pore complex proteins. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):705–723. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. M., Datar K. V., Paddy M. R., Swedlow J. R., Swanson M. S. Characterization of nuclear polyadenylated RNA-binding proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(5):1173–1184. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.5.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Matunis M. J., Kraemer D., Blobel G., Coutavas E. Nup358, a cytoplasmically exposed nucleoporin with peptide repeats, Ran-GTP binding sites, zinc fingers, a cyclophilin A homologous domain, and a leucine-rich region. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 9;270(23):14209–14213. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.23.14209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama N., Hayashi N., Seki T., Panté N., Ohba T., Nishii K., Kuma K., Hayashida T., Miyata T., Aebi U. A giant nucleopore protein that binds Ran/TC4. Nature. 1995 Jul 13;376(6536):184–188. doi: 10.1038/376184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel U., Doye V., Tekotte H., Wepf R., Grandi P., Hurt E. C. Nic96p is required for nuclear pore formation and functionally interacts with a novel nucleoporin, Nup188p. J Cell Biol. 1996 Jun;133(6):1141–1152. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.6.1141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Lindern M., Fornerod M., van Baal S., Jaegle M., de Wit T., Buijs A., Grosveld G. The translocation (6;9), associated with a specific subtype of acute myeloid leukemia, results in the fusion of two genes, dek and can, and the expression of a chimeric, leukemia-specific dek-can mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1687–1697. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]