Abstract
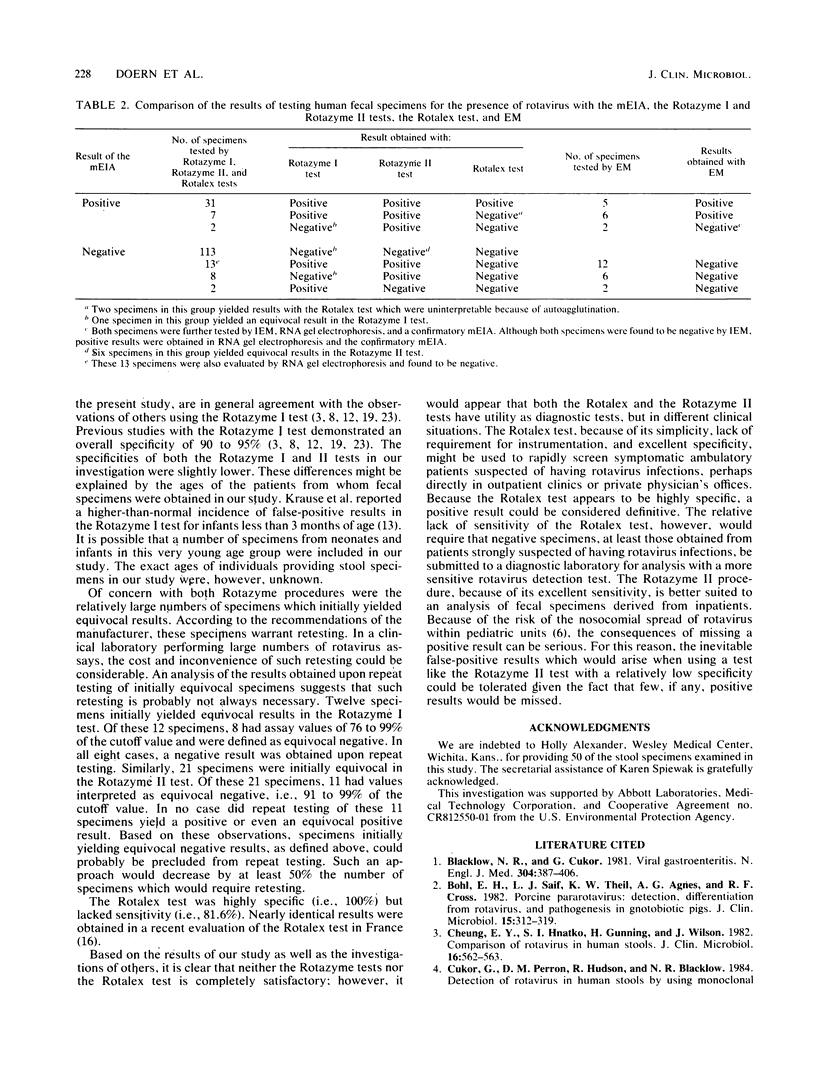
A total of 176 human fecal specimens were examined for the presence of rotavirus by four different assays: a monoclonal antibody enzyme immunoassay; the original polyclonal antibody enzyme immunoassay marketed by Abbott Laboratories, North Chicago, Ill. (Rotazyme I); a modification of this assay which is now commercially available (Rotazyme II); and a latex agglutination test (Rotalex) recently introduced by Medical Technology Corp., Somerset, N.J. In addition, selected specimens were examined for the presence of rotavirus by electron microscopy, immune electron microscopy, and RNA gel electrophoresis. A total of 40 specimens were positive in the monoclonal antibody enzyme immunoassay, and 136 were negative. Using the results obtained with this procedure as the reference standard, we found the sensitivities of the Rotazyme I, Rotazyme II, and Rotalex tests to be 97.4, 100, and 81.6%, respectively. The specificities of these three procedures were 88.8, 83.9, and 100%, respectively.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blacklow N. R., Cukor G. Viral gastroenteritis. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 12;304(7):397–406. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102123040705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Saif L. J., Theil K. W., Agnes A. G., Cross R. F. Porcine pararotavirus: detection, differentiation from rotavirus, and pathogenesis in gnotobiotic pigs. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):312–319. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.312-319.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung E. Y., Hnatko S. I., Gunning H., Wilson J. Comparison of Rotazyme and direct electron microscopy for detection of rotavirus in human stools. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):562–563. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.562-563.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukor G., Perron D. M., Hudson R., Blacklow N. R. Detection of rotavirus in human stools by using monoclonal antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;19(6):888–892. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.6.888-892.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Blacklow N. R., Cukor G. G., Vibulbandhitkit S., Changchawalit S., Boonthai P. Rotavirus as a cause of severe gastroenteritis in adults. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):663–667. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.663-667.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H. Rotavirus in the home and hospital nursery. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Aug 27;287(6392):568–569. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6392.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. W., Ahluwalia G. S., Barker F. G., Horsman G., Hazelton P. R. Comparison of direct and indirect enzyme immunoassays with direct ultracentrifugation before electron microscopy for detection of rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jul;16(1):53–59. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.1.53-59.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa A., Matsuno S., Inouye S., Kono R., Tsurukubo Y., Mukoyama A., Saito Y. Isolation of human rotaviruses in primary cultures of monkey kidney cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):387–390. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.387-390.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann J. E., Blacklow N. R., Perron D. M., Cukor G., Krause P. J., Hyams J. S., Barrett H. J., Ogra P. L. Enzyme immunoassay with monoclonal antibodies for the detection of rotavirus in stool specimens. J Infect Dis. 1985 Oct;152(4):830–832. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.4.830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Purcell R. H., Sereno M. M., Wyatt R. G., Kim H. W., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. A microtiter solid phase radioimmunoassay for detection of the human reovirus-like agent in stools. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1275–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keswick B. H., Hejkal T. W., DuPont H. L., Pickering L. K. Evaluation of a commercial enzyme immunoassay kit for rotavirus detection. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1983 Jun;1(2):111–115. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(83)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause P. J., Hyams J. S., Middleton P. J., Herson V. C., Flores J. Unreliability of Rotazyme ELISA test in neonates. J Pediatr. 1983 Aug;103(2):259–262. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80361-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Nagayoshi S. Quantitative estimation of infantile gastroenteritis virus antigens in stools by immune adherence hemagglutination test. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Mar;7(3):310–311. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.3.310-311.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton P. J., Petric M., Hewitt C. M., Szymanski M. T., Tam J. S. Counter-immunoelectro-osmophoresis for the detection of infantile gastroenteritis virus (orbi-group) antigen and antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Mar;29(3):191–197. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.3.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morinet F., Ferchal F., Colimon R., Pérol Y. Comparison of six methods for detecting human rotavirus in stools. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Apr;3(2):136–140. doi: 10.1007/BF02014331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riepenhoff-Talty M., Barrett H. J., Spada B. A., Ogra P. L. Negative staining and immune electron microscopy as techniques for rapid diagnosis of viral agents. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983;420:391–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb22228.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riepenhoff-Talty M., Saif L. J., Barrett H. J., Suzuki H., Ogra P. L. Potential spectrum of etiological agents of viral enteritis in hospitalized infants. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;17(2):352–356. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.2.352-356.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. S., Miller M. F. Comparison of an enzyme immunoassay with electron microscopic procedures for detecting rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):938–944. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.938-944.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., McCloskey C. M., Saif L. J., Redman D. R., Bohl E. H., Hancock D. D., Kohler E. M., Moorhead P. D. Rapid, simple method of preparing rotaviral double-stranded ribonucleic acid for analysis by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):273–280. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.273-280.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Kim H. W., Clem T., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of human reovirus-like agent of infantile gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1977 Aug 6;2(8032):263–267. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90951-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Leister F. J. Evaluation of enzyme immunoassays for the detection of human rotavirus. J Infect Dis. 1981 Oct;144(4):379–379. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.4.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


