Abstract
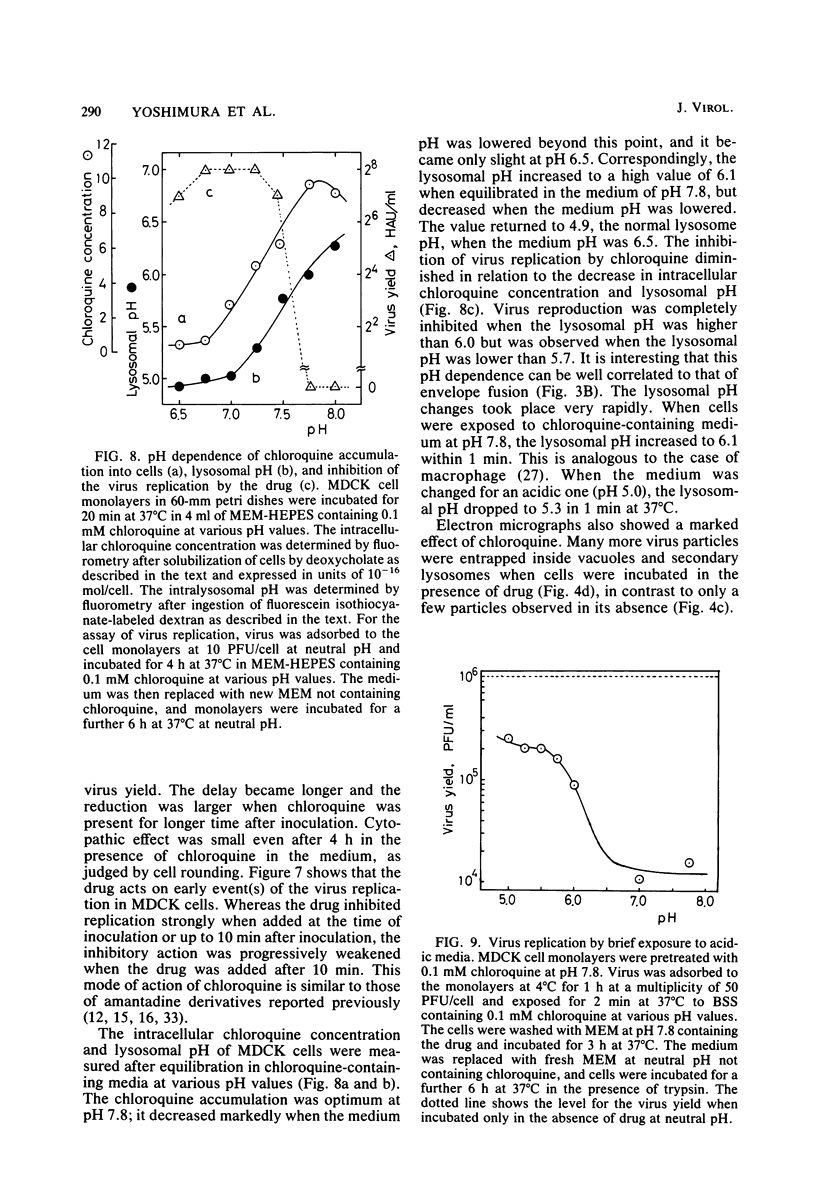
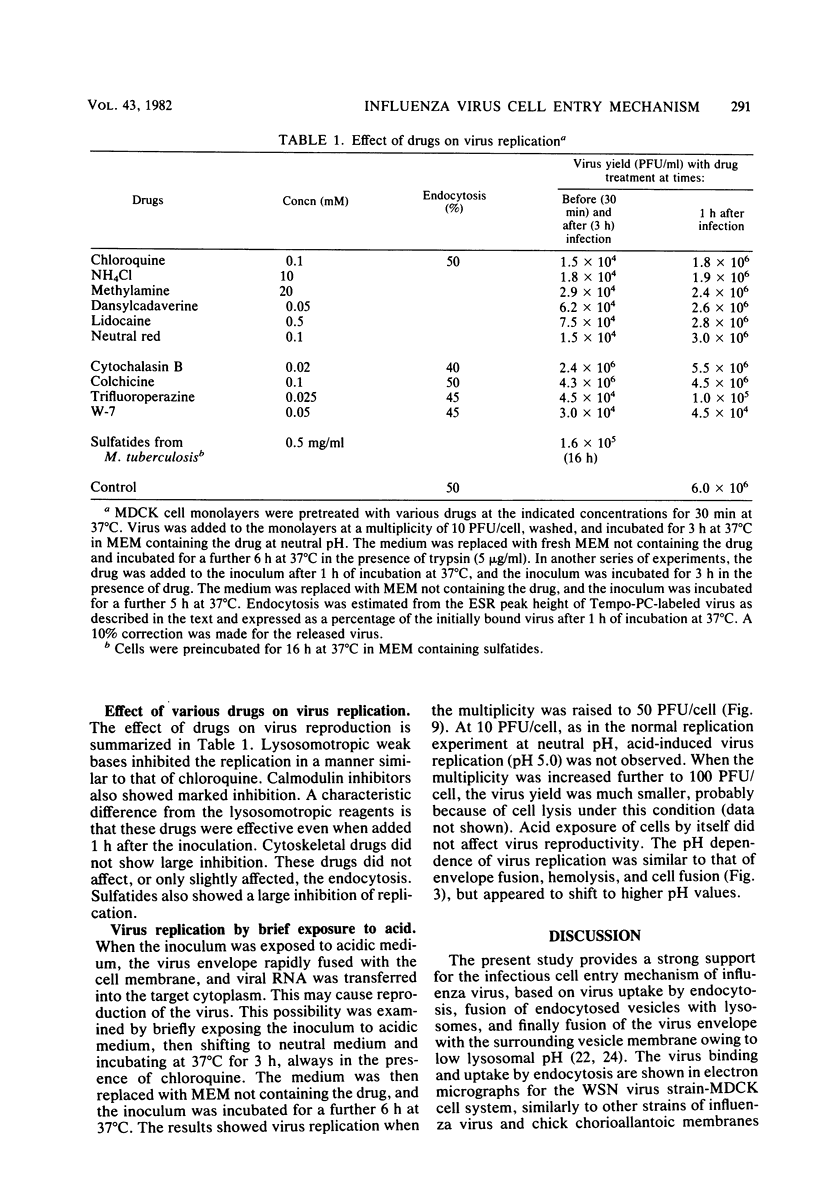
Interaction between influenza virus WSN strain and MDCK cells was studied by using spin-labeled phospholipids and electron microscopy. Envelope fusion was negligibly small at neutral pH but greatly activated in acidic media in a narrow pH range around 5.0. The half-time was less than 1 min at 37°C at pH 5.0. Virus binding was almost independent of the pH. Endocytosis occurred with a half-time of about 7 min at 37°C at neutral pH, and about 50% of the initially bound virus was internalized after 1 h. Electron micrographs showed binding of virus particles in coated pits in the microvillous surface of plasma membrane and endocytosis into coated vesicles. Chloroquine inhibited virus replication. The inhibition occurred when the drug was added not later than 10 min after inoculation. Chloroquine caused an increase in the lysosomal pH 4.9 to 6.1. The drug did not affect virus binding, endocytosis, or envelope fusion at pH 5.0. Electron micrographs showed many virus particles remaining trapped inside vacuoles even after 30 min at 37°C in the presence of drug, in contrast to only a few particles after 10 min in vacuoles and secondary lysosomes in its absence. Virus replication in an artificial condition, i.e., brief exposure of the inoculum to acidic medium followed by incubation in neutral pH in the presence of chloroquine, was also observed. These results are discussed to provide a strong support for the infection mechanism of influenza virus proposed previously: virus uptake by endocytosis, fusion of the endocytosed vesicles with lysosome, and fusion of the virus envelope with the surrounding vesicle membrane in the secondary lysosome because of the low pH. This allows the viral genome to enter the target cell cytoplasm.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BABLANIAN R., EGGERS H. J., TAMM I. STUDIES ON THE MECHANISM OF POLIOVIRUS-INDUCED CELL DAMAGE. I. THE RELATION BETWEEN POLIOVIRUS,-INDUCED METABOLIC AND MORPHOLOGICAL ALTERATIONS IN CULTURED CELLS. Virology. 1965 May;26:100–113. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALES S., CHOPPIN P. W. Attachment and penetration of influenza virus. Virology. 1962 Nov;18:489–493. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALD H. B., ISAACS A. Counts of influenza virus particles. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Jun;10(3):457–464. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-3-457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dourmashkin R. R., Tyrrell D. A. Electron microscopic observations on the entry of influenza virus into susceptible cells. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):129–141. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaush C. R., Smith T. F. Replication and plaque assay of influenza virus in an established line of canine kidney cells. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Apr;16(4):588–594. doi: 10.1128/am.16.4.588-594.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren M. B., D'Arcy Hart P., Young M. R., Armstrong J. A. Prevention of phagosome-lysosome fusion in cultured macrophages by sulfatides of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2510–2514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren M. B. Sulfolipid I of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, strain H37Rv. I. Purification and properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jun 9;210(1):116–126. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90067-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Kartenbeck J., Simons K., Fries E. On the entry of Semliki forest virus into BHK-21 cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):404–420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang R. T., Rott R., Klenk H. D. Influenza viruses cause hemolysis and fusion of cells. Virology. 1981 Apr 15;110(1):243–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang R. T., Wahn K., Klenk H. D., Rott R. Fusion between cell membrane and liposomes containing the glycoproteins of influenza virus. Virology. 1980 Jul 30;104(2):294–302. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90334-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato N., Eggers H. J. Inhibition of uncoating of fowl plague virus by l-adamantanamine hydrochloride. Virology. 1969 Apr;37(4):632–641. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielian M. C., Cohn Z. A. Phagosome-lysosome fusion. Characterization of intracellular membrane fusion in mouse macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):754–765. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Rott R., Orlich M., Blödorn J. Activation of influenza A viruses by trypsin treatment. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):426–439. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90284-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff W. C., Knight V. Effect of rimantadine on influenza virus replication. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Feb;160(2):246–253. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff W. C., Knight V. Inhibition of influenza virus uncoating by rimantadine hydrochloride. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):261–263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.261-263.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., McConnell H. M. Inside-outside transitions of phospholipids in vesicle membranes. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 30;10(7):1111–1120. doi: 10.1021/bi00783a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarowitz S. G., Choppin P. W. Enhancement of the infectivity of influenza A and B viruses by proteolytic cleavage of the hemagglutinin polypeptide. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):440–454. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90285-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenard J., Miller D. K. pH-dependent hemolysis by influenza, Semliki, Forest virus, and Sendai virus. Virology. 1981 Apr 30;110(2):479–482. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Asano A., Okada Y., Ohnishi S. I. Transmembrane phospholipid motions induced by F glycoprotein in hemagglutinating virus of Japan. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):232–241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.232-241.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Asano A., Oki K., Okada Y., Onishi S. A spin-label study on fusion of red blood cells induced by hemagglutinating virus of Japan. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3736–3741. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Kawasaki K., Ohnishi S. Interaction of influenza virus hemagglutinin with target membrane lipids is a key step in virus-induced hemolysis and fusion at pH 5.2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4133–4137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Kuroda K., Toyama S., Ohnishi S. Interaction of hemagglutinating virus of Japan with erythrocytes as studied by release of a spin probe from virus. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 1;20(18):5340–5345. doi: 10.1021/bi00521a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Ohnishi S. Activation of influenza virus by acidic media causes hemolysis and fusion of erythrocytes. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 29;122(2):283–287. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80457-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Reggio H., Helenius A., Simons K. Infectious entry pathway of influenza virus in a canine kidney cell line. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):601–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C., Rose H. M. Structure and development of viruses as observed in the electron microscope. 8. Entry of influenza virus. J Virol. 1968 Sep;2(9):925–936. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.9.925-936.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma S., Poole B. Fluorescence probe measurement of the intralysosomal pH in living cells and the perturbation of pH by various agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3327–3331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Koseki I., Kim J., Maeda Y., Hashimoto T. Modification of cell membranes with viral envelopes during fusion of cells with HVJ (Sendai virus). Exp Cell Res. 1975 Jul;93(2):368–378. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90462-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson S., Oxford J. S., Dourmashkin R. R. Studies on the mechanism of influenza virus entry into cells. J Gen Virol. 1979 Apr;43(1):223–229. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-1-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintart J., Leroy-Houyet M. A., Trouet A., Baudhuin P. Endocytosis and chloroquine accumulation during the cell cycle of hepatoma cells in culture. J Cell Biol. 1979 Sep;82(3):644–653. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.3.644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOPHIANOPOULOS A. J., VANHOLDE K. E. PHYSICAL STUDIES OF MURAMIDASE (LYSOZYME). II. PH-DEPENDENT DIMERIZATION. J Biol Chem. 1964 Aug;239:2516–2524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Hay A. J., Armstrong J. A. On the mechanism of inhibition of influenza virus replication by amantadine hydrochloride. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jan;38(1):97–110. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kartenbeck J., Helenius A. Fusion of Semliki forest virus with the plasma membrane can be induced by low pH. J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;87(1):264–272. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.1.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Matlin K., Helenius A. Cell fusion by Semliki Forest, influenza, and vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):674–679. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the haemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus at 3 A resolution. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):366–373. doi: 10.1038/289366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]