Abstract
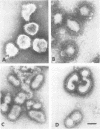
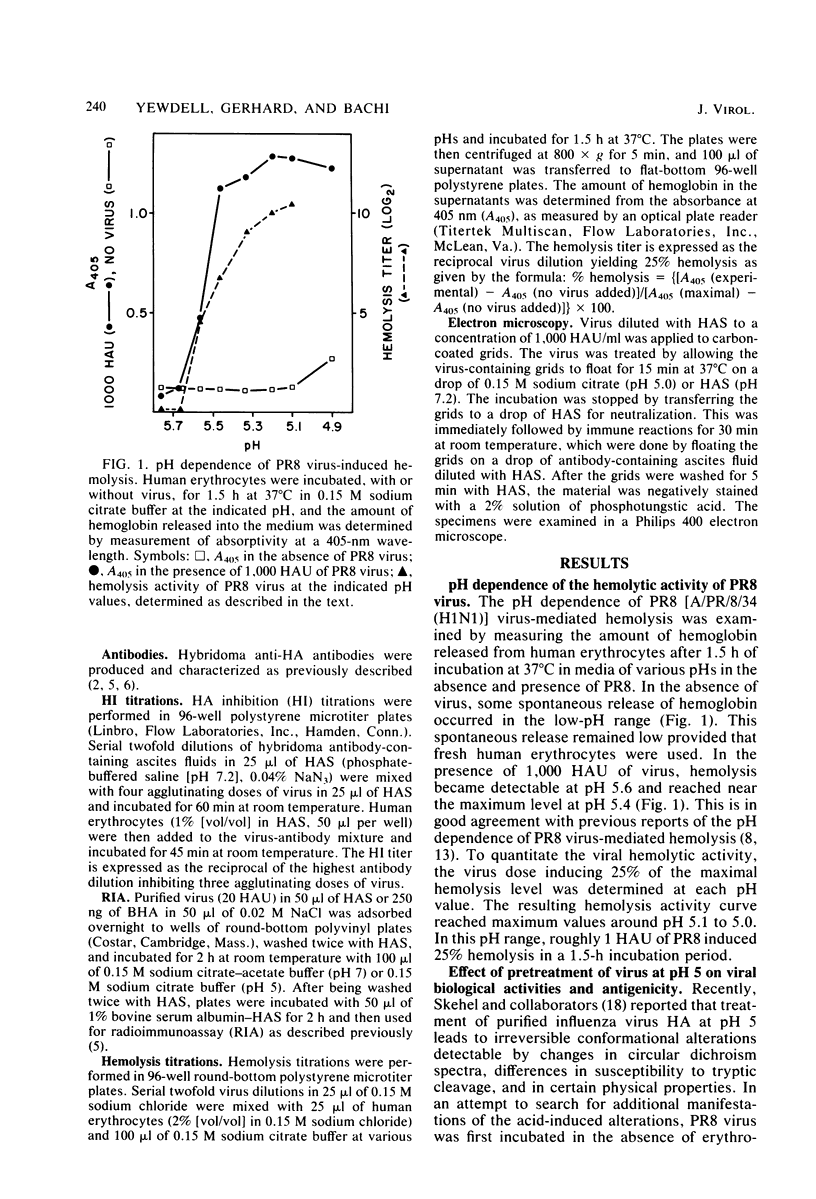
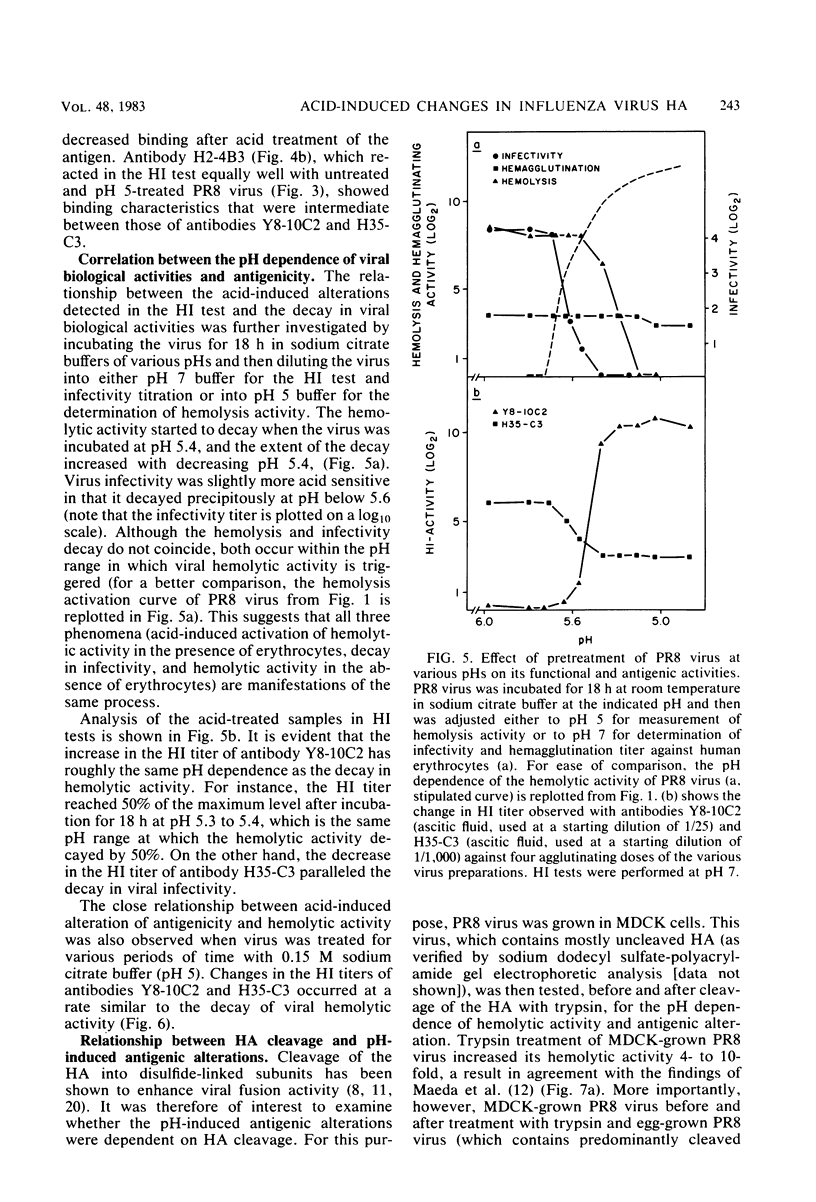
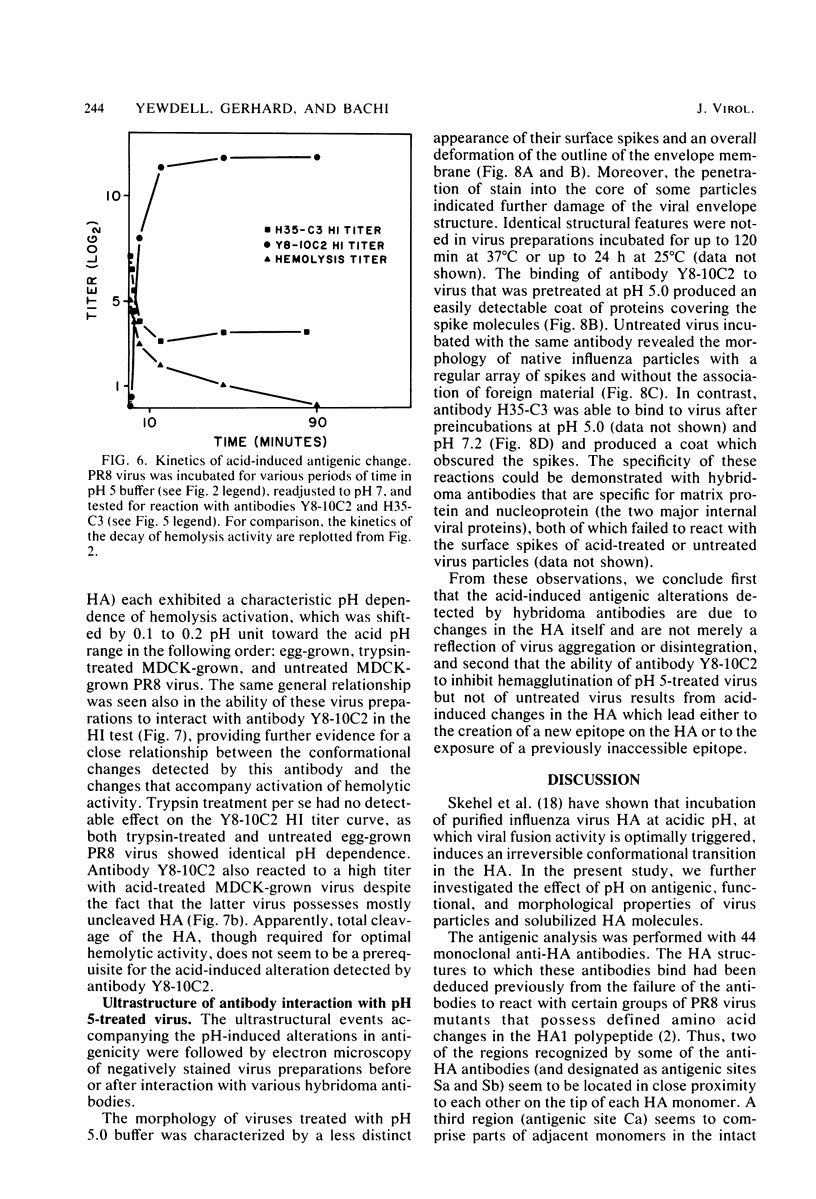
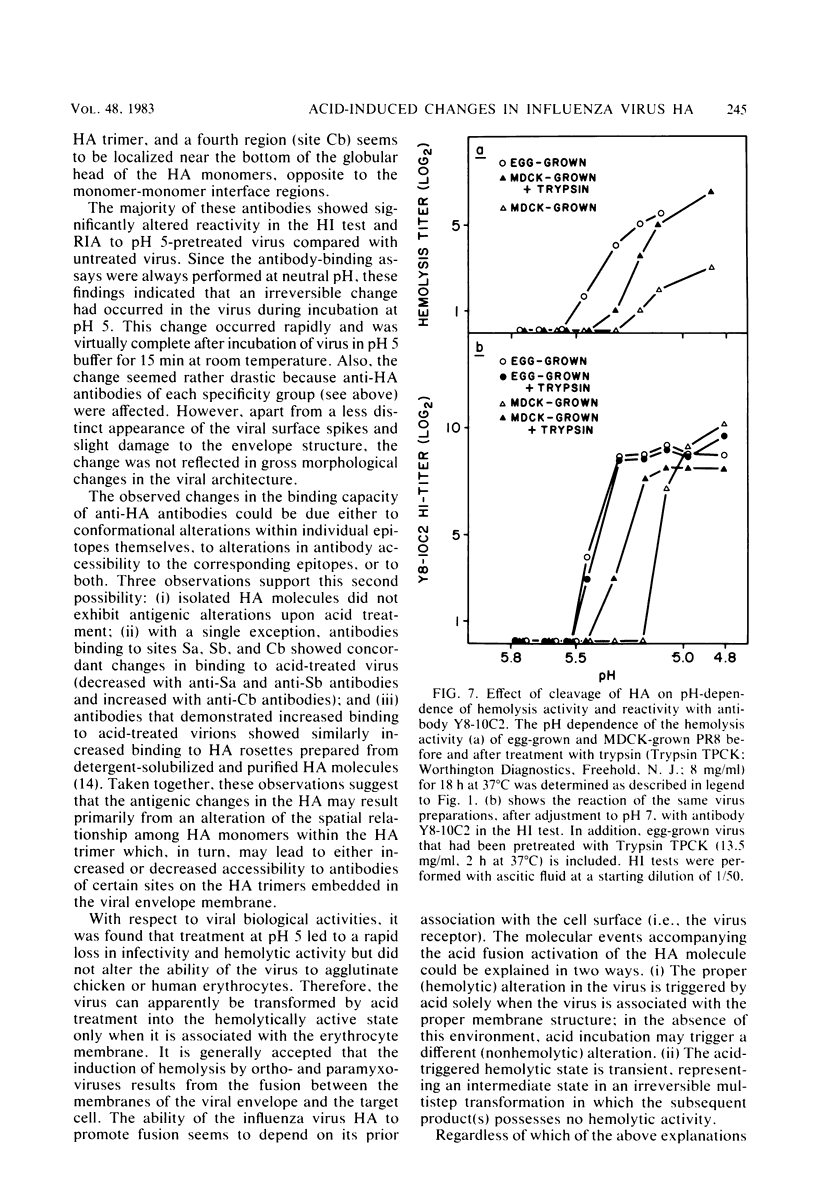
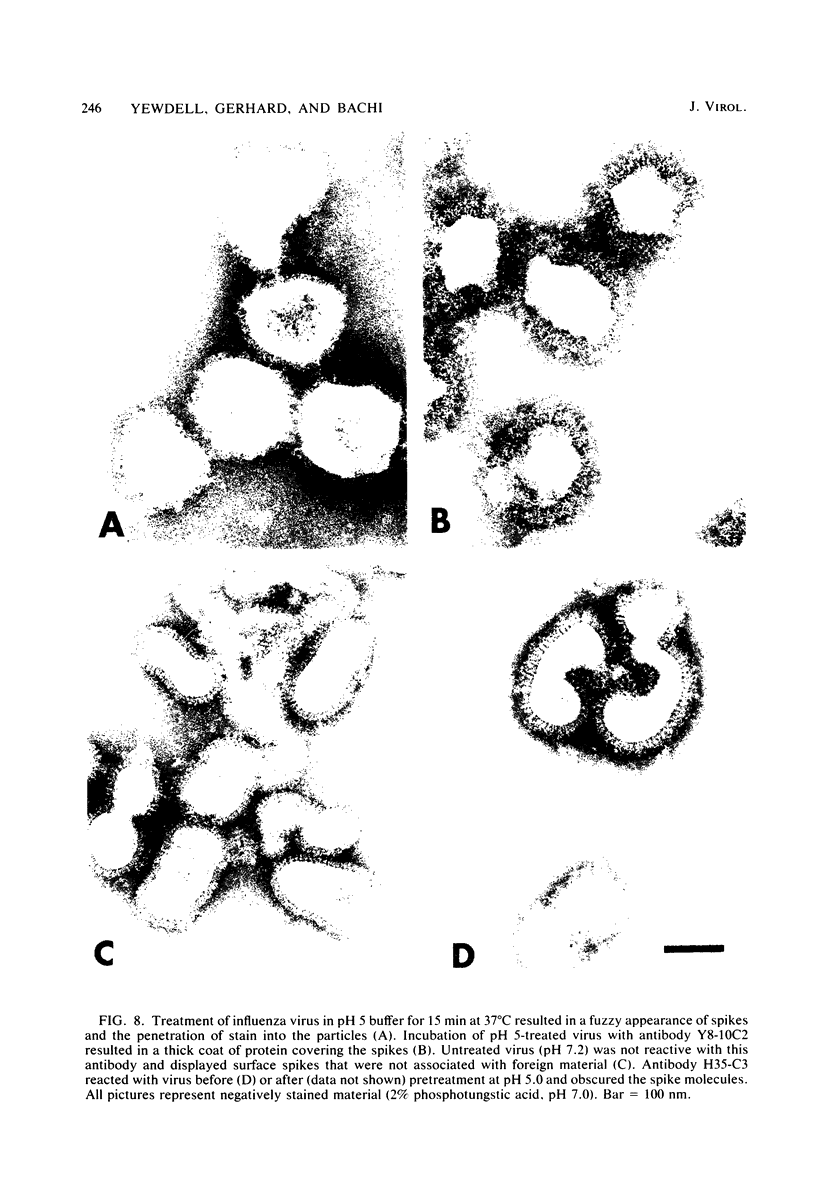
Exposure of influenza virus to an acidic environment, which is known to be required for viral fusion and hemolysis, has recently been shown to induce a conformational change in the hemagglutinin molecule. In the present study, we examined the effects of acid incubation on the antigenicity, biological activity, and morphology of influenza virus A/PR/8/34 (H1N1). Incubation of PR8 virus at pH 5 in the absence of erythrocytes resulted in a rapid and irreversible loss of viral hemolytic activity and infectivity. Apart from a less distinct appearance of the viral surface projections and slight damage to the envelope structure, acid incubation did not result in gross morphological changes in the viral architecture. The acid-induced change could be detected in the form of greatly increased or decreased binding of many monoclonal antibodies directed to each of the four major antigenic regions of the hemagglutinin. Triggering of viral hemolytic activity and antigenic alterations was similarly pH dependent. In addition, the different pH dependencies of egg-grown and trypsin-treated MDCK-grown viruses coincided with an analogous pH dependence of the antigenic alterations that were observed with these viruses. These observations are compatible with the idea that some of the anti-hemagglutinin antibodies detect conformational changes in the hemagglutinin which are required for the initiation of fusion and hemolysis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brand C. M., Skehel J. J. Crystalline antigen from the influenza virus envelope. Nat New Biol. 1972 Aug 2;238(83):145–147. doi: 10.1038/newbio238145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caton A. J., Brownlee G. G., Yewdell J. W., Gerhard W. The antigenic structure of the influenza virus A/PR/8/34 hemagglutinin (H1 subtype). Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):417–427. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90135-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazekas de St Groth, Webster R. G. Disquisitions of Original Antigenic Sin. I. Evidence in man. J Exp Med. 1966 Sep 1;124(3):331–345. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhard W. The analysis of the monoclonal immune response to influenza virus. II. The antigenicity of the viral hemagglutinin. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):985–995. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhard W., Yewdell J., Frankel M. E., Webster R. Antigenic structure of influenza virus haemagglutinin defined by hybridoma antibodies. Nature. 1981 Apr 23;290(5808):713–717. doi: 10.1038/290713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., White J. M., Waterfield M. D. Purification of the fusion protein of Sendai virus: analysis of the NH2-terminal sequence generated during precursor activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2737–2740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang R. T., Rott R., Klenk H. D. Influenza viruses cause hemolysis and fusion of cells. Virology. 1981 Apr 15;110(1):243–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Rott R., Orlich M., Blödorn J. Activation of influenza A viruses by trypsin treatment. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):426–439. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90284-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarowitz S. G., Choppin P. W. Enhancement of the infectivity of influenza A and B viruses by proteolytic cleavage of the hemagglutinin polypeptide. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):440–454. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90285-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenard J., Miller D. K. pH-dependent hemolysis by influenza, Semliki, Forest virus, and Sendai virus. Virology. 1981 Apr 30;110(2):479–482. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Kawasaki K., Ohnishi S. Interaction of influenza virus hemagglutinin with target membrane lipids is a key step in virus-induced hemolysis and fusion at pH 5.2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4133–4137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Ohnishi S. Activation of influenza virus by acidic media causes hemolysis and fusion of erythrocytes. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 29;122(2):283–287. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80457-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Reggio H., Helenius A., Simons K. Infectious entry pathway of influenza virus in a canine kidney cell line. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):601–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson S., Oxford J. S., Dourmashkin R. R. Studies on the mechanism of influenza virus entry into cells. J Gen Virol. 1979 Apr;43(1):223–229. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-1-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S. B., Kawasaki K., Ohnishi S. Hemolytic activity of influenza virus hemagglutinin glycoproteins activated in mildly acidic environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3153–3157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Bayley P. M., Brown E. B., Martin S. R., Waterfield M. D., White J. M., Wilson I. A., Wiley D. C. Changes in the conformation of influenza virus hemagglutinin at the pH optimum of virus-mediated membrane fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):968–972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Brown L. E., Jackson D. C. Changes in the antigenicity of the hemagglutinin molecule of H3 influenza virus at acidic pH. Virology. 1983 Apr 30;126(2):587–599. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(83)80015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Helenius A., Gething M. J. Haemagglutinin of influenza virus expressed from a cloned gene promotes membrane fusion. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):658–659. doi: 10.1038/300658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Matlin K., Helenius A. Cell fusion by Semliki Forest, influenza, and vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):674–679. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J. Structural identification of the antibody-binding sites of Hong Kong influenza haemagglutinin and their involvement in antigenic variation. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):373–378. doi: 10.1038/289373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura A., Kuroda K., Kawasaki K., Yamashina S., Maeda T., Ohnishi S. Infectious cell entry mechanism of influenza virus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):284–293. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.284-293.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]