Abstract
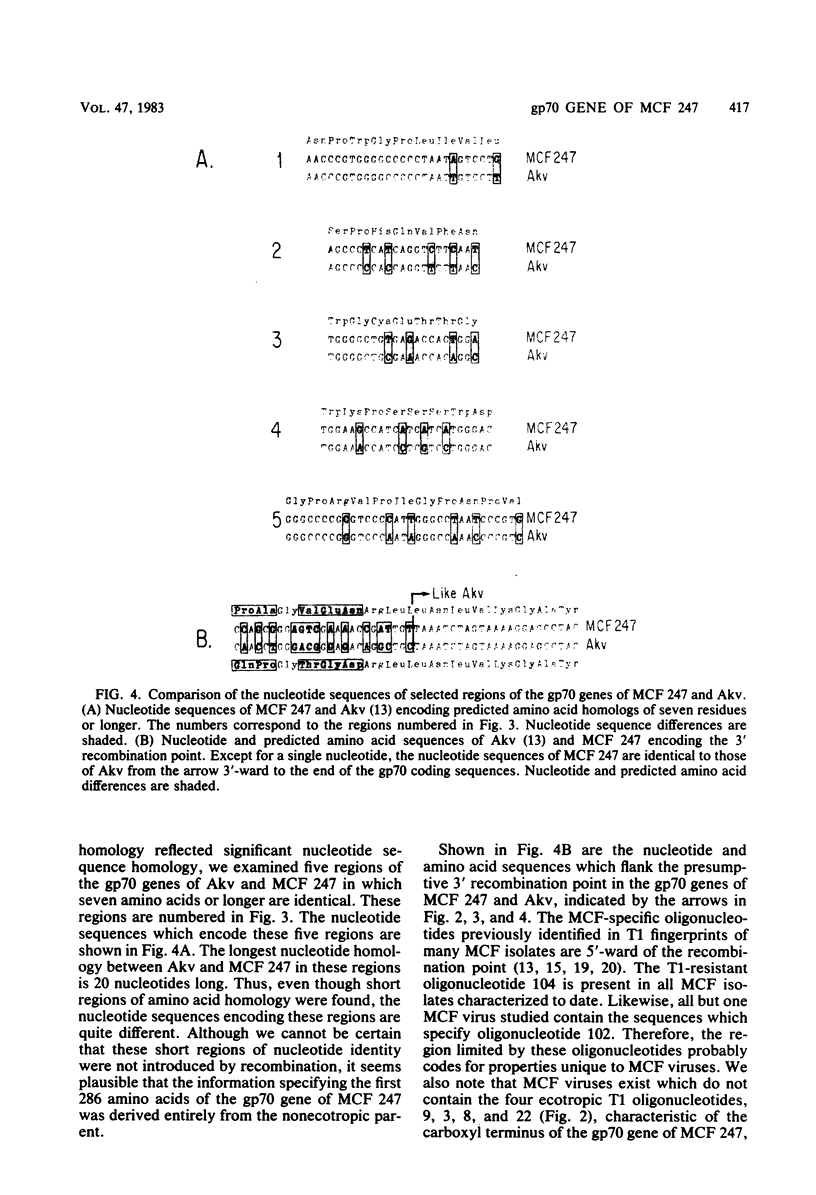
We determined the nucleotide sequence and predicted the amino acid sequence of the gp70 gene of MCF 247, a recombinant murine retrovirus isolated from an AKR mouse. Information specifying the first 286 amino acids of the protein was probably derived from the presumptive nonecotropic parent of MCF 247, whereas the C-terminal 154 amino acids were probably derived from the ecotropic parent Akv. The nonecotropic sequences at the amino terminus of MCF 247 show only 38% homology, at the amino acid level, to those of Akv. In contrast, these sequences are strikingly similar (99% homologous) to those reported for another MCF virus. Moloney MCF, which was isolated from a BALB/c mouse. Moloney MCF also has ecotropic-derived sequences encoding the C-terminal portion of its gp70 protein; however, the recombination event that introduced these sequences occurs 213 nucleotides further towards the C terminus of gp70 than it does in MCF 247.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosselman R. A., van Straaten F., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M., Vogt M. Analysis of the env gene of a molecularly cloned and biologically active Moloney mink cell focus-forming proviral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):19–31. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.19-31.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Gupta S., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Origin of mink cytopathic focus-forming (MCF) viruses:comparison with ecotropic and xenotropic murine leukemia virus genomes. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):465–483. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Lymphomagenicity of recombinant mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):542–552. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A. The spontaneous insertion of proteins into and across membranes: the helical hairpin hypothesis. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischinger P. J., Nomura S., Bolognesi D. P. A novel murine oncornavirus with dual eco- and xenotropic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5150–5155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Shinnick T. M., Witte O., Ponticelli A., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Sequence-specific antibodies show that maturation of Moloney leukemia virus envelope polyprotein involves removal of a COOH-terminal peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6023–6027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Corbin V., Gilbert W. Nucleotide sequence of the 3' half of AKV. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6931–6944. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jou W. M., Verhoeyen M., Devos R., Saman E., Fang R., Huylebroeck D., Fiers W., Threlfall G., Barber C., Carey N. Complete structure of the hemagglutinin gene from the human influenza A/Victoria/3/75 (H3N2) strain as determined from cloned DNA. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):683–696. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80045-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M., Holland C. A., Lung M. L., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R., Hopkins N. H. Nucleotide sequence of the 3' end of MCF 247 murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):291–298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.291-298.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Crowther R., Straceski A., Haseltine W. Nucleotide sequence of the Akv env gene. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):519–529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.519-529.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lung M. L., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. H. Large RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides encoding p15E and the U3 region of the long terminal repeat distinguish two biological classes of mink cell focus-forming type C viruses of inbred mice. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):275–290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.275-290.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lung M. L., Hering C., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. Analysis of the genomes of mink cell focus-inducing murine type-C viruses: a progress report. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1269–1274. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montreuil J. Primary structure of glycoprotein glycans: basis for the molecular biology of glycoproteins. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1980;37:157–223. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinter A., Fleissner E. The presence of disulfide-linked gp70-p15(E) complexes in AKR murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1977 Dec;83(2):417–422. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90187-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommelaere J., Faller D. V., Hopkins N. Characterization and mapping of RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides derived from the genomes of Akv and MCF murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):495–499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommelaere J., Faller D. V., Hopkins N. RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides of Akv-1 and Akv-2 type C viruses of AKR mice. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):690–694. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.690-694.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner M. R., Grinna L. S., Robbins P. W. Differences in glycosylation patterns of closely related murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):67–71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W. Status of the association of mink cell focus-forming viruses with leukemogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1265–1268. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A., Rein A., Henderson L., Oroszlan S. Biological, chemical, and immunological studies of Rauscher ecotropic and mink cell focus-forming viruses from JLS-V9 cells. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):995–1003. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.995-1003.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Speculations on RNA splicing. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):643–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90425-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte O. N., Wirth D. F. Structure of the murine leukemia virus envelope glycoprotein precursor. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):735–743. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.735-743.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]