Abstract
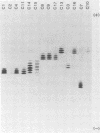
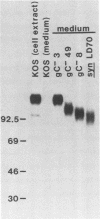
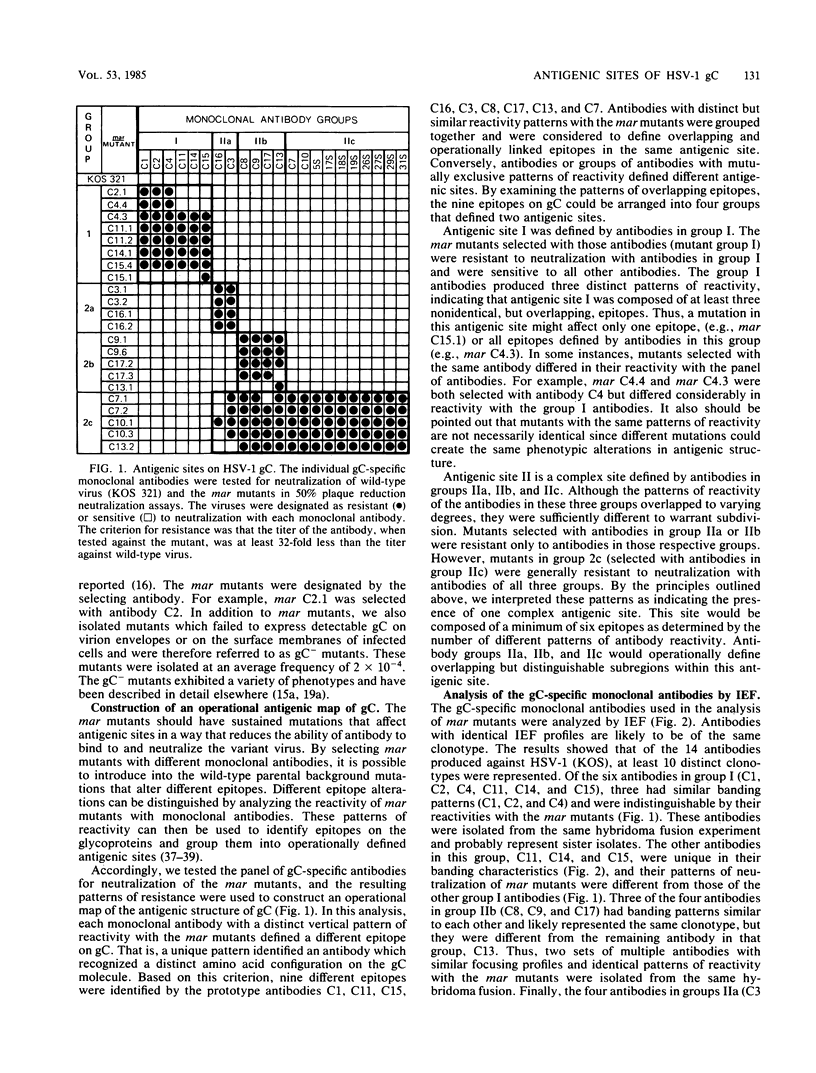
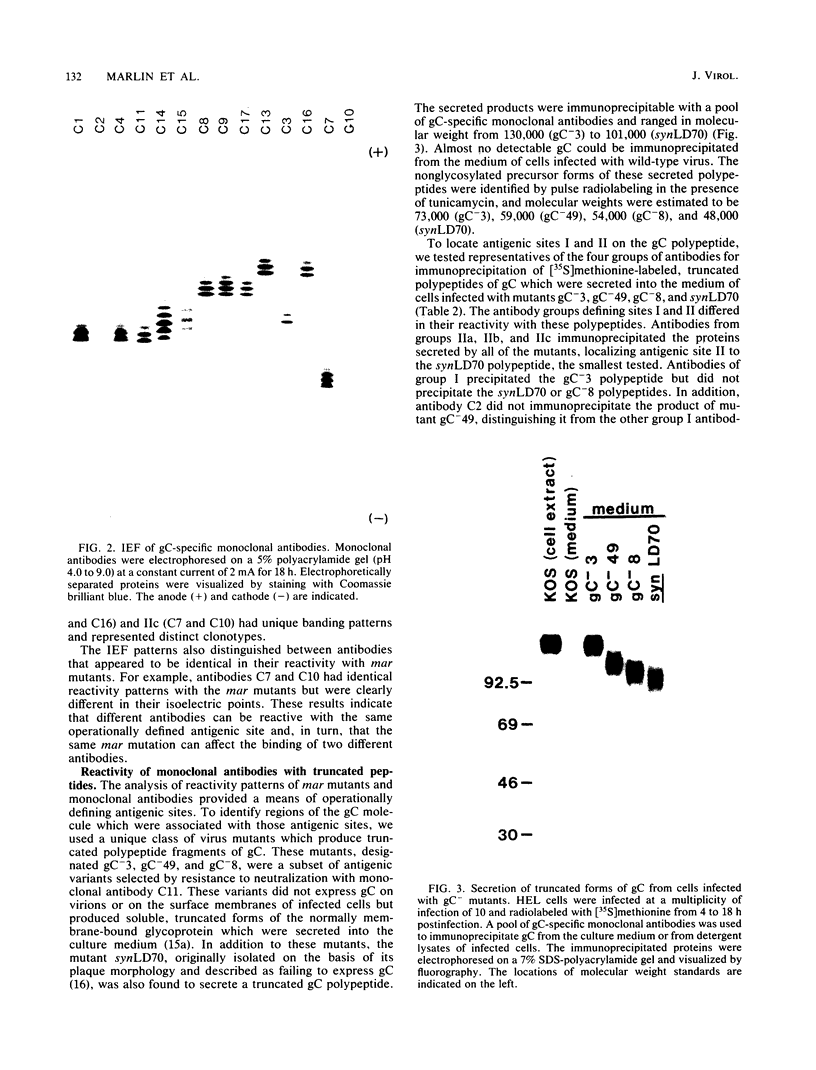
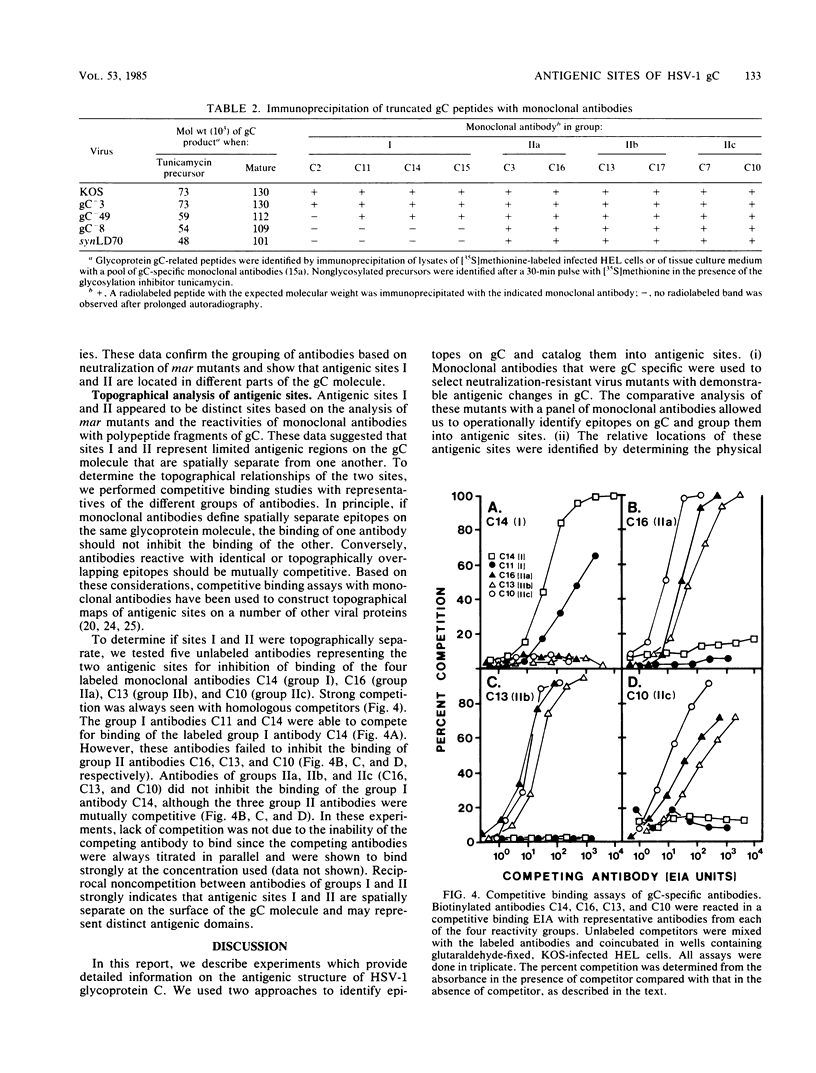
Epitopes of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) strain KOS glycoprotein gC were identified by using a panel of gC-specific, virus-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies and a series of antigenic variants selected for resistance to neutralization with individual members of the antibody panel. Variants that were resistant to neutralization and expressed an antigenically altered form of gC were designated monoclonal antibody-resistant (mar) mutants. mar mutants were isolated at frequencies of 10(-3) to 10(-5), depending on the antibody used for selection. The epitopes on gC were operationally grouped into antigenic sites by evaluating the patterns of neutralization observed when a panel of 22 antibodies was tested against 22 mar mutants. A minimum of nine epitopes was identified by this process. Three epitopes were assigned to one antigenic site (I), and six were clustered in a second complex site (II) composed of three distinct subsites, IIa, IIb, and IIc. The two antigenic sites were shown to reside in physically distinct domains of the glycoprotein, by radioimmunoprecipitation of truncated forms of gC. These polypeptides lacked portions of the carboxy terminus and ranged in size from approximately one-half that of the wild-type molecule to nearly full size. Antibodies recognizing epitopes in site II immunoprecipitated the entire series of truncated polypeptides and thereby demonstrated that site II resided in the N-terminal half of gC. Antibodies reactive with site I, however, did not immunoprecipitate fragments smaller than at least two-thirds the size of the wild-type polypeptide, suggesting that site I was located in the C-terminal portion. Sites I and II were also shown to be spatially separate on the gC polypeptide by competition enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with monoclonal antibodies representative of different site I and site II epitopes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atassi M. Z., Smith J. A. A proposal for the nomenclature of antigenic sites in peptides and proteins. Immunochemistry. 1978 Aug;15(8):609–610. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balachandran N., Bacchetti S., Rawls W. E. Protection against lethal challenge of BALB/c mice by passive transfer of monoclonal antibodies to five glycoproteins of herpes simplex virus type 2. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1132–1137. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1132-1137.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. V. Identification of an Fc-binding glycoprotein. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):779–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.779-789.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop G. A., Glorioso J. C., Schwartz S. A. Relationship between expression of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins and susceptibility of target cells to human natural killer activity. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1544–1561. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter V. C., Schaffer P. A., Tevethia S. S. The involvement of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins in cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1655–1660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. L. Protective immunization of mice with specific HSV-1 glycoproteins. Immunology. 1983 Jun;49(2):343–352. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dix R. D., Pereira L., Baringer J. R. Use of monoclonal antibody directed against herpes simplex virus glycoproteins to protect mice against acute virus-induced neurological disease. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):192–199. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.192-199.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle R., Courtney R. J. Preparation and characterization of specific antisera to individual glycoprotein antigens comprising the major glycoprotein region of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):902–917. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.902-917.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Eisenberg R., Cohen G., Wagner E. K. Detailed analysis of the portion of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome encoding glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):634–647. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.634-647.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glorioso J. C., Levine M., Holland T. C., Szczesiul M. S. Mutant analysis of herpes simplex virus-induced cell surface antigens: resistance to complement-mediated immune cytolysis. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):672–681. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.672-681.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glorioso J. C., Smith J. W. Immune interactions with cells infected with herpes simplex virus: antibodies to radioiodinated surface antigens. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):114–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glorioso J., Schröder C. H., Kumel G., Szczesiul M., Levine M. Immunogenicity of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins gC and gB and their role in protective immunity. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):805–812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.805-812.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glorioso J., Szczesiul M. S., Marlin S. D., Levine M. Inhibition of glycosylation of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins: identification of antigenic and immunogenic partially glycosylated glycopeptides on the cell surface membrane. Virology. 1983 Apr 15;126(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90458-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guesdon J. L., Ternynck T., Avrameas S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Aug;27(8):1131–1139. doi: 10.1177/27.8.90074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine J. W., Honess R. W., Cassai E., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XII. The virion polypeptides of type 1 strains. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):640–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.640-651.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland T. C., Homa F. L., Marlin S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. Herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein C-negative mutants exhibit multiple phenotypes, including secretion of truncated glycoproteins. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):566–574. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.566-574.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland T. C., Marlin S. D., Levine M., Glorioso J. Antigenic variants of herpes simplex virus selected with glycoprotein-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):672–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.672-682.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JERNE N. K. Immunological speculations. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1960;14:341–358. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.14.100160.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor A. K., Nash A. A., Wildy P., Phelan J., McLean C. S., Field H. J. Pathogenesis of herpes simplex virus in congenitally athymic mice: the relative roles of cell-mediated and humoral immunity. J Gen Virol. 1982 Jun;60(Pt 2):225–233. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-60-2-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi G. E., Coligan J. E., Holland T. C., Levine M., Glorioso J. C., Nairn R. Biochemical characterization of peptides from herpes simplex virus glycoprotein gC: loss of CNBr fragments from the carboxy terminus of truncated, secreted gC molecules. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):806–815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.806-815.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafon M., Wiktor T. J., Macfarlan R. I. Antigenic sites on the CVS rabies virus glycoprotein: analysis with monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1983 Apr;64(Pt 4):843–851. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-4-843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawman M. J., Courtney R. J., Eberle R., Schaffer P. A., O'Hara M. K., Rouse B. T. Cell-mediated immunity to herpes simplex virus: specificity of cytotoxic T cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):451–461. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.451-461.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long D., Madara T. J., Ponce de Leon M., Cohen G. H., Montgomery P. C., Eisenberg R. J. Glycoprotein D protects mice against lethal challenge with herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):761–764. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.761-764.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubeck M. D., Gerhard W. Topological mapping antigenic sites on the influenza A/PR/8/34 virus hemagglutinin using monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):64–72. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massey R. J., Schochetman G. Topographical analysis of viral epitopes using monoclonal antibodies: mechanism of virus neutralization. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):20–32. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Bootman J., Evans D. M., Ferguson M., Reeve P., Spitz M., Stanway G., Cann A. J., Hauptmann R. Location and primary structure of a major antigenic site for poliovirus neutralization. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):674–679. doi: 10.1038/301674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrild B., Shore S. L., Nahmias A. J. Herpes simplex virus glycoproteins: participation of individual herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein antigens in immunocytolysis and their correlation with previously identified glycopolypeptides. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):741–748. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.741-748.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Dondero D. V., Gallo D., Devlin V., Woodie J. D. Serological analysis of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 with monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):363–367. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.363-367.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rector J. T., Lausch R. N., Oakes J. E. Use of monoclonal antibodies for analysis of antibody-dependent immunity to ocular herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):168–174. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.168-174.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandri-Goldin R. M., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Method for induction of mutations in physically defined regions of the herpes simplex virus genome. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):41–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.41-49.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Haffey M., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. III. Role of glycoprotein VP7(B2) in virion infectivity. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1149–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1149-1158.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier R. D., Pizer L. I., Moorhead J. W. Type-specific delayed hypersensitivity and protective immunity induced by isolated herpes simplex virus glycoprotein. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1413–1418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Omata Y., Schneweis K. E. Protection of mice from fatal herpes simplex virus type 1 infection by adoptive transfer of cloned virus-specific and H-2-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Gen Virol. 1983 Feb;64(Pt 2):443–447. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-2-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter S. D., Zweig M., Hampar B. Monoclonal antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1 proteins, including the immediate-early protein ICP 4. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):684–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.684-692.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. I. Identification of four glycoprotein precursors and their products in type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):991–1008. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.991-1008.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vestergaard B. F., Norrild B. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis of a herpes simplex virus type 1-specific antigen: immunological and biochemical characterization. J Infect Dis. 1978 Nov;138(5):639–643. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.5.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Laver W. G. Determination of the number of nonoverlapping antigenic areas on Hong Kong (H3N2) influenza virus hemagglutinin with monoclonal antibodies and the selection of variants with potential epidemiological significance. Virology. 1980 Jul 15;104(1):139–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90372-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor T. J., Koprowski H. Antigenic variants of rabies virus. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):99–112. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Gerhard W. Antigenic characterization of viruses by monoclonal antibodies. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:185–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.001153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zezulak K. M., Spear P. G. Characterization of a herpes simplex virus type 2 75,000-molecular-weight glycoprotein antigenically related to herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):553–562. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.553-562.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweig M., Heilman C. J., Jr, Bladen S. V., Showalter S. D., Hampar B. Detection in antisera of antibodies that cross-react with herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein gC. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):482–487. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.482-487.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweig M., Showalter S. D., Bladen S. V., Heilman C. J., Jr, Hampar B. Herpes simplex virus type 2 glycoprotein gF and type 1 glycoprotein gC have related antigenic determinants. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):185–192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.185-192.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]