Abstract
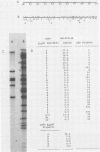
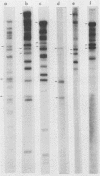
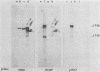
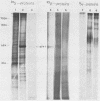
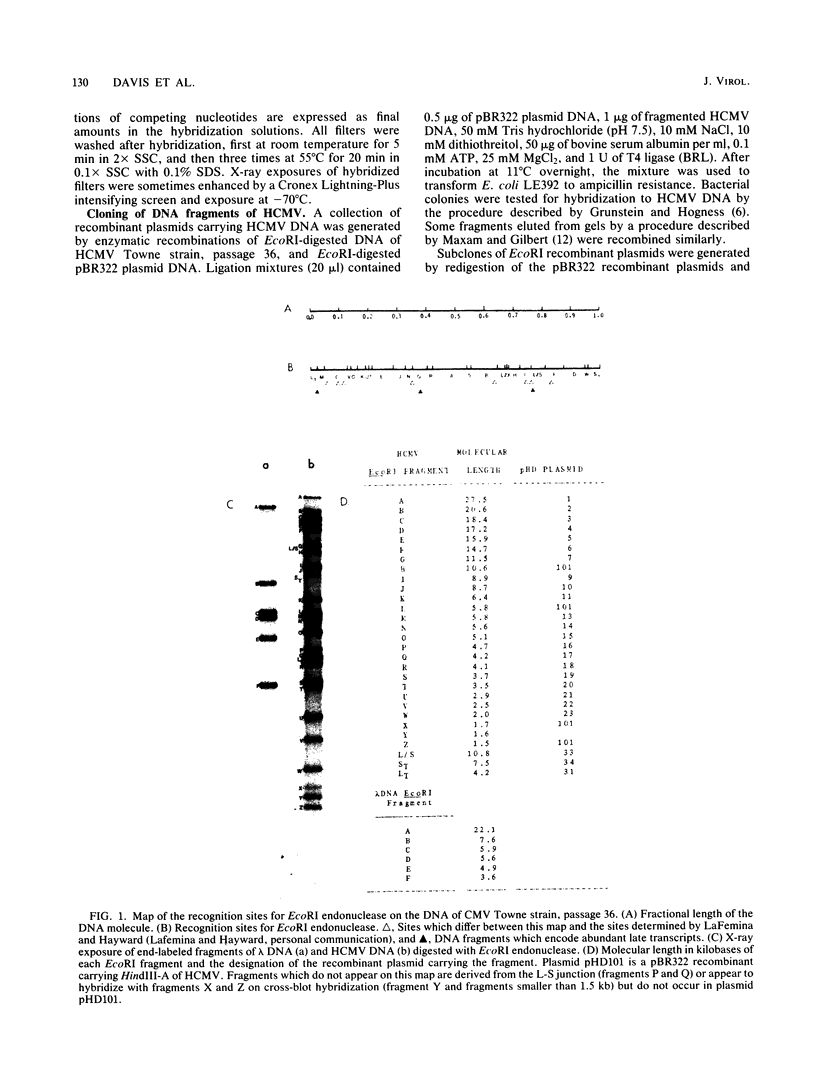
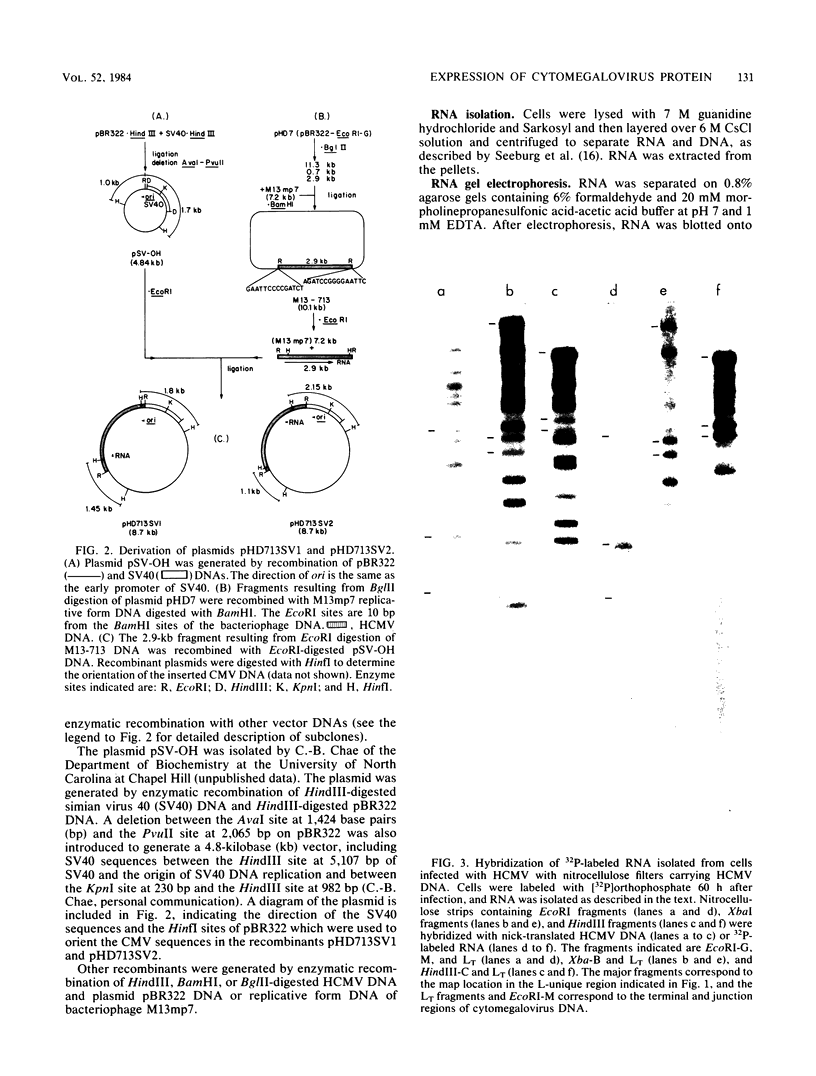
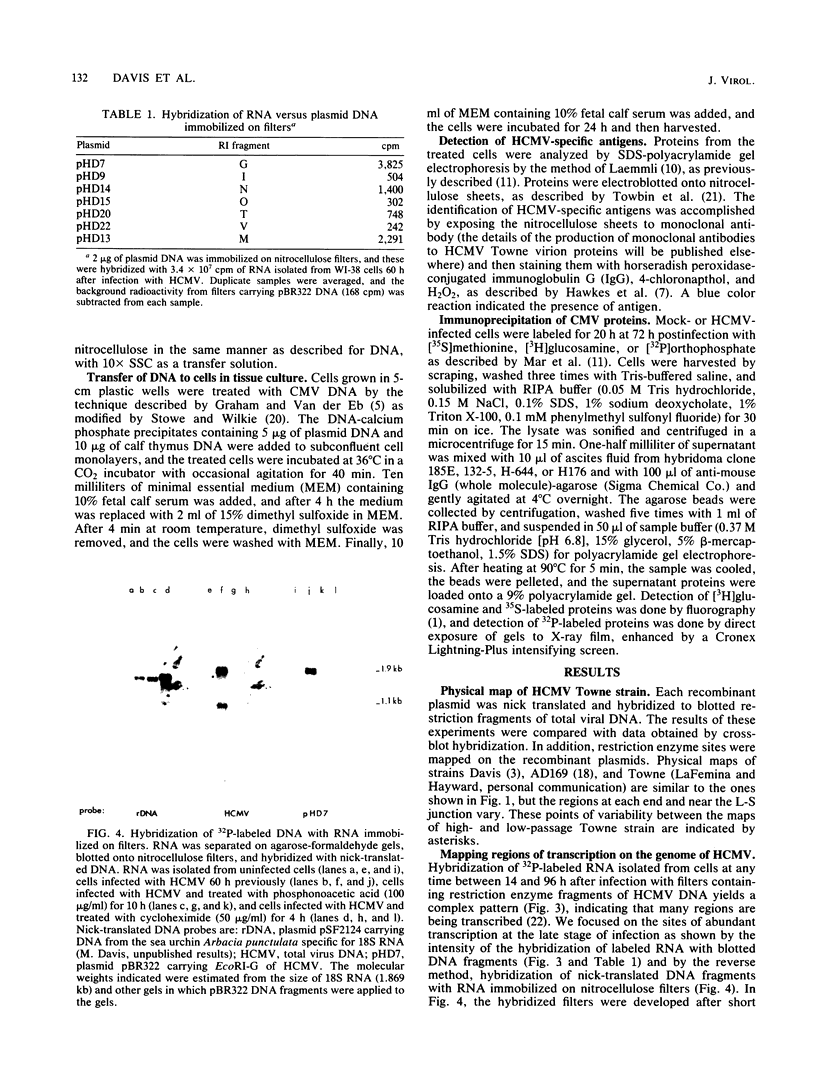
We constructed a DNA fragment map of low-passage Towne strain cytomegalovirus by analyzing cross-blot hybridization and hybridizations of isolated recombinant clones. The abundant late transcripts were located on this map by hybridization of labeled total RNA of virus-infected cells to blotted DNA fragments. The most abundant late transcript, carried by the 11.7-kilobase EcoRI fragment (EcoRI-G), was precisely mapped. The EcoRI fragment was fragmented and subcloned in a plasmid carrying simian virus 40 sequences (pSV-OH, constructed by Chi-Bom Chae, Department of Biochemistry, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill). One resulting recombinant plasmid, pHD713SV2, was transferred to simian virus 40-transformed monkey kidney cells (COS-1) by DNA transfection. Synthesis of a cytomegalovirus-specific 67-kilodalton protein was detected in these cells by reaction of blotted proteins with virus-specific monoclonal antibody. The 67-kilodalton protein is a major phosphorylated protein found in virions; it is not glycosylated. The location of the gene for this 67-kilodalton protein is therefore assigned to the center of the L-unique region of human cytomegalovirus, at 0.37 to 0.39 map units.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark B. R., Zaia J. A., Balce-Directo L., Ting Y. P. Isolation and partial chemical characterization of a 64,000-dalton glycoprotein of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):279–282. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.279-282.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demarchi J. M. Human cytomegalovirus DNA: restriction enzyme cleavage maps and map locations for immediate-early, early, and late RNAs. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. Structural and nonstructural proteins of strain Colburn cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1981 Jun;111(2):516–537. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90354-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Matus A. Monoclonal antibodies identify novel neural antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2410–2414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S., Chen S. T., Pagano J. S. Human cytomegalovirus. I. Purification and characterization of viral DNA. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1473–1481. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1473-1481.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S., Huong S. M., Tegtmeier G. E., Alford C. Cytomegalovirus: genetic variation of viral genomes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;354:332–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb27976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar E. C., Patel P. C., Huang E. S. Effect of 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine on viral-specific polypeptide synthesis in human cytomegalovirus-infected cells. Am J Med. 1982 Jul 20;73(1A):82–85. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough S. H., Spector D. H. Transcription in human fibroblasts permissively infected by human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):31–46. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. A., Fleckenstein B., Galloway D. A., McDougall J. K. Transformation of NIH 3T3 cells with cloned fragments of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):83–91. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.83-91.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett R. F. DNA nucleotide sequence heterogeneity between the Towne and AD169 strains of cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):152–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.152-161.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H., Shine J., Martial J. A., Ullrich A., Baxter J. D., Goodman H. M. Nucleotide sequence of part of the gene for human chorionic somatomammotropin: purification of DNA complementary to predominant mRNA species. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90193-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Hock L., Tamashiro J. C. Cleavage maps for human cytomegalovirus DNA strain AD169 for restriction endonucleases EcoRI, BglII, and HindIII. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):558–582. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.558-582.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Jeor S. C., Hutt R. Cell DNA replication as a function in the synthesis of human cytomegalovirus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Oct;37(1):65–73. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-1-65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Wilkie N. M. An improved technique for obtaining enhanced infectivity with herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):447–458. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Stinski M. F. Temporal patterns of human cytomegalovirus transcription: mapping the viral RNAs synthesized at immediate early, early, and late times after infection. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):462–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.462-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weststrate M. W., Geelen J. L., Wertheim P. M., van der Noordaa J. Comparison of the physical maps of the DNAs of two cytomegalovirus strains. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jan;64(Pt 1):47–55. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]