Abstract
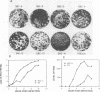
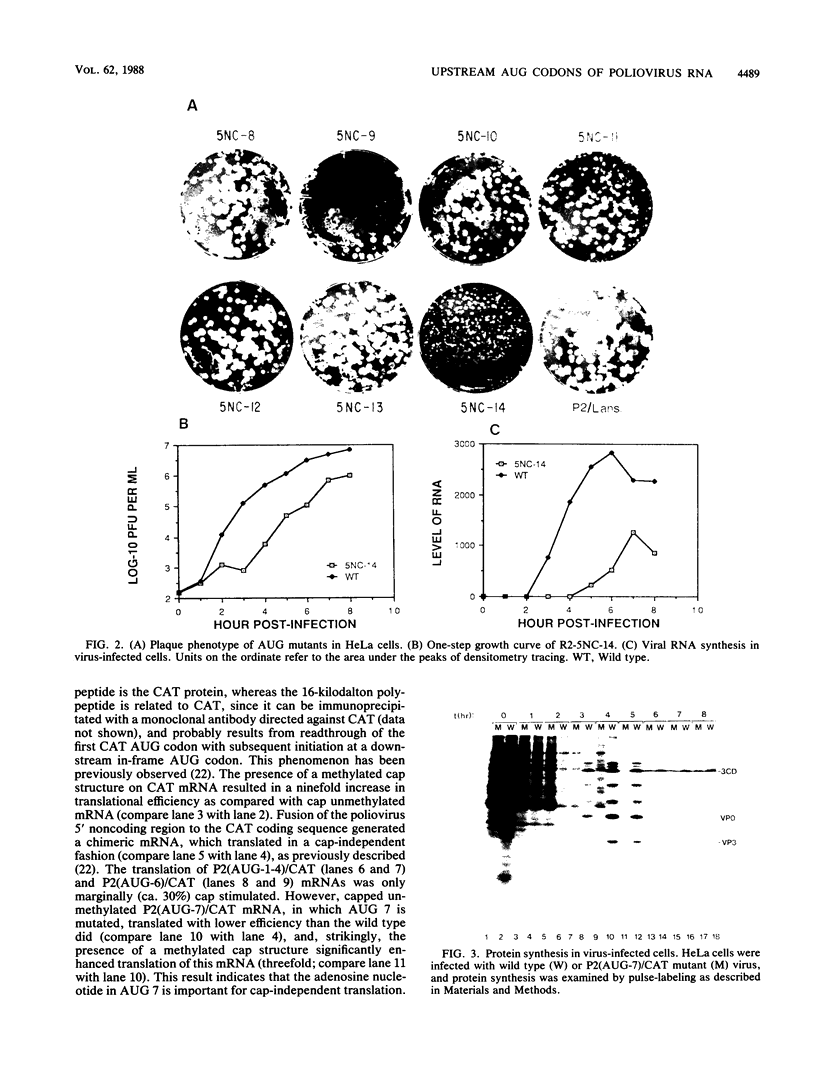
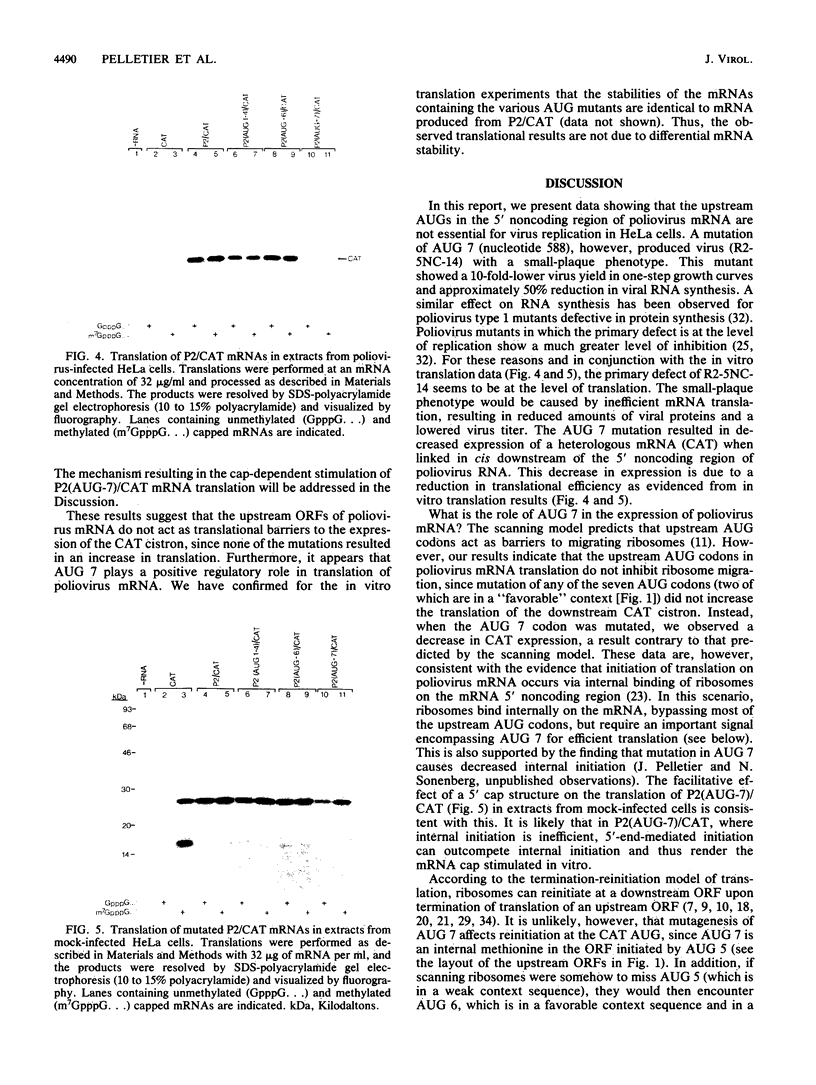
The 5' untranslated region of poliovirus type 2 Lansing RNA consists of 744 nucleotides containing seven AUG codons which are followed by in-frame termination codons, thus forming short open reading frames (ORFs). To determine the biological significance of these small ORFs, all of the upstream AUG codons were mutated to UUG. The point mutations were introduced into an infectious poliovirus cDNA clone, and RNA transcribed in vitro from the altered cDNA was transfected into HeLa cells to recover the virus. Mutation of AUG 7 resulted in a virus (called R2-5NC-14) with a small-plaque phenotype, whereas mutation of the other six AUG codons produced virus with a wild-type plaque morphology. To determine whether the small-plaque phenotype of R2-5NC-14 was due to altered translational efficiency of the viral mRNA, we constructed chimeric mRNAs containing the 5' noncoding region of poliovirus mRNA fused to the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) coding sequence. mRNA containing a mutated AUG 7 codon showed decreased translational efficiency in vitro. The results indicate that the upstream ORFs of poliovirus RNA are not essential for viral replication and do not act as barriers to the translation of poliovirus mRNA. AUG 7 and flanking sequences may play a positive acting role in poliovirus RNA translation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonneau A. M., Sonenberg N. Proteolysis of the p220 component of the cap-binding protein complex is not sufficient for complete inhibition of host cell protein synthesis after poliovirus infection. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):986–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.986-991.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., Banerjee A. K., Shatkin A. J. Methylation-dependent translation of viral messenger RNAs in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1189–1193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., LaFiandra A., Shatkin A. J. 5'-Terminal structure and mRNA stability. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):235–239. doi: 10.1038/266235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett P. B., Petersen R. B., Hensel C. H., Albericio F., Gunderson S. I., Palmenberg A. C., Barany G. Synthesis in vitro of a seven amino acid peptide encoded in the leader RNA of Rous sarcoma virus. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 5;190(1):45–57. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helentjaris T., Ehrenfeld E. Control of protein synthesis in extracts from poliovirus-infected cells. I. mRNA discrimination by crude initiation factors. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):510–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.510-521.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett M. J., Rose J. K., Baltimore D. 5'-terminal structure of poliovirus polyribosomal RNA is pUp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):327–330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Nomura S., Anderson C. W., Khoury G. Identification of the SV40 agnogene product: a DNA binding protein. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):346–349. doi: 10.1038/291346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R. Construction and characterization of poliovirus subgenomic replicons. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1687–1696. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1687-1696.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Murtha P., Davies M. V. Translational efficiency of polycistronic mRNAs and their utilization to express heterologous genes in mammalian cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):187–193. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04737.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalili K., Brady J., Khoury G. Translational regulation of SV40 early mRNA defines a new viral protein. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):639–645. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90242-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuge S., Nomoto A. Construction of viable deletion and insertion mutants of the Sabin strain of type 1 poliovirus: function of the 5' noncoding sequence in viral replication. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1478–1487. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1478-1487.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Monica N., Almond J. W., Racaniello V. R. A mouse model for poliovirus neurovirulence identifies mutations that attenuate the virus for humans. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2917–2920. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2917-2920.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Monica N., Meriam C., Racaniello V. R. Mapping of sequences required for mouse neurovirulence of poliovirus type 2 Lansing. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):515–525. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.515-525.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langridge J., Langridge P., Bergquist P. L. Extraction of nucleic acids from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Apr;103(2):264–271. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Sonenberg N. Inactivation of cap-binding proteins accompanies the shut-off of host protein synthesis by poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3447–3451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. P., Hinnebusch A. G. Multiple upstream AUG codons mediate translational control of GCN4. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Lee Y. F., Wimmer E. The 5' end of poliovirus mRNA is not capped with m7G(5')ppp(5')Np. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):375–380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S., Berg P. Termination-reinitiation occurs in the translation of mammalian cell mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2695–2703. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S., Subramani S., Berg P. Effect of upstream reading frames on translation efficiency in simian virus 40 recombinants. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2704–2711. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Kaplan G., Racaniello V. R., Sonenberg N. Cap-independent translation of poliovirus mRNA is conferred by sequence elements within the 5' noncoding region. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1103–1112. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Internal initiation of translation of eukaryotic mRNA directed by a sequence derived from poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):320–325. doi: 10.1038/334320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Meriam C. Poliovirus temperature-sensitive mutant containing a single nucleotide deletion in the 5'-noncoding region of the viral RNA. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):498–507. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90211-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera V. M., Welsh J. D., Maizel J. V., Jr Comparative sequence analysis of the 5' noncoding region of the enteroviruses and rhinoviruses. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):42–50. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90656-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Trachsel H., Leong K., Baltimore D. Inhibition of translation by poliovirus: inactivation of a specific initiation factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2732–2736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedman S. A., Mertz J. E. Mechanisms of synthesis of virion proteins from the functionally bigenic late mRNAs of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):954–961. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.954-961.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Regulation of translation by poliovirus. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:175–204. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Kohara M., Kataoka Y., Suganuma T., Omata T., Imura N., Nomoto A. Complete nucleotide sequences of all three poliovirus serotype genomes. Implication for genetic relationship, gene function and antigenic determinants. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 25;174(4):561–585. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trono D., Andino R., Baltimore D. An RNA sequence of hundreds of nucleotides at the 5' end of poliovirus RNA is involved in allowing viral protein synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2291–2299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2291-2299.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Petti L., Braun D., Seung S., Kieff E. A bicistronic Epstein-Barr virus mRNA encodes two nuclear proteins in latently infected, growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):945–954. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.945-954.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6487–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf S., Bradley J., Wimmer E., Studier F. W., Dunn J. J. Synthesis of infectious poliovirus RNA by purified T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]