Abstract
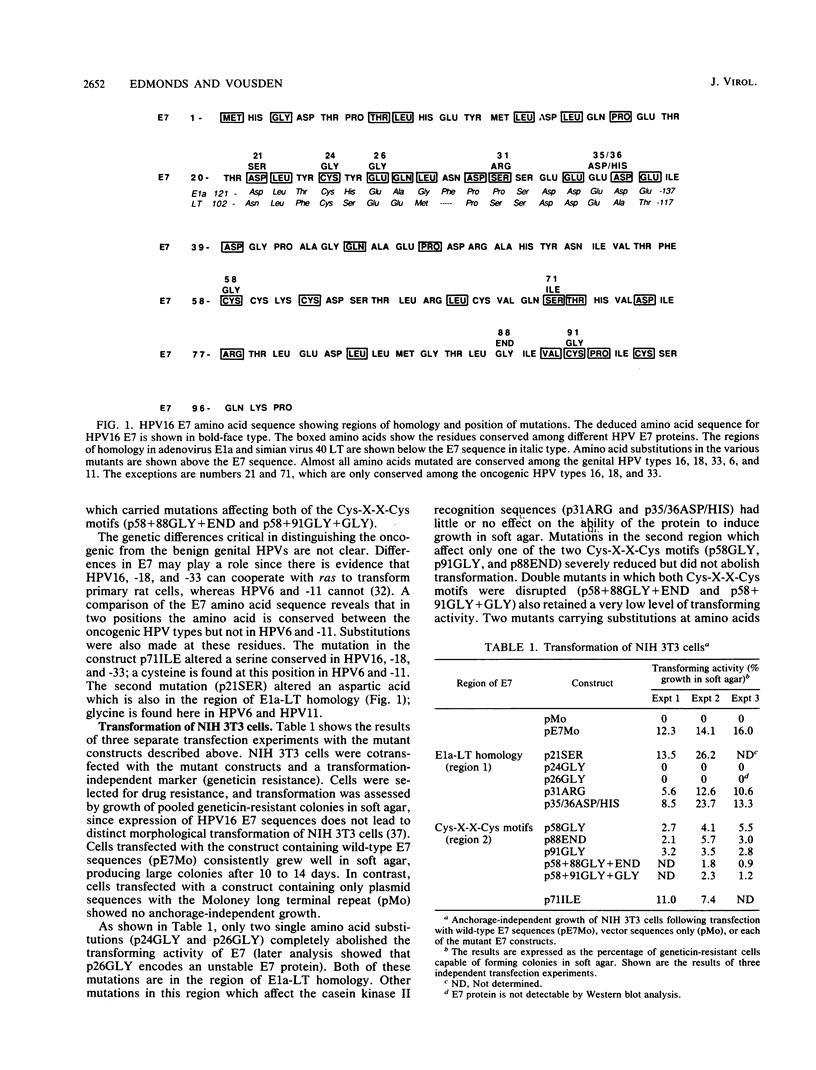
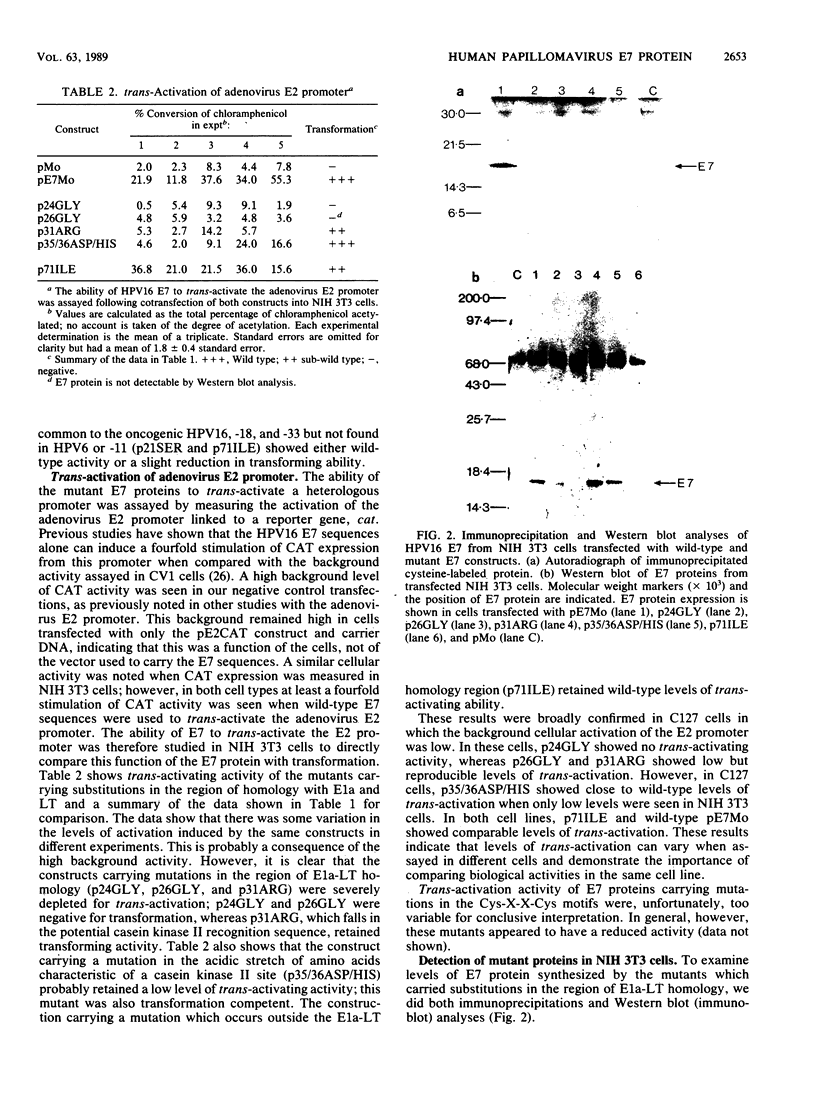
The E7 open reading frame of human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV16) has been shown to be selectively retained in cervical tumors and to encode both transforming and trans-activating functions in murine cells, supporting the notion that expression of E7 contributes towards the progression of premalignant cervical lesions. A comparison among E7 sequences of different HPV types reveals some homology at the amino acid level. Of particular interest are two regions, one which contains significant homology to a region of adenovirus E1a and simian virus 40 large T (LT), and a second region which contains two conserved Cys-X-X-Cys motifs. To determine the importance of these domains to the function of the E7 protein, a series of mutants carrying substitutions at amino acids in the region of E1a-LT homology and at the Cys-X-X-Cys motifs were constructed. The mutated E7 sequences were placed under the control of a strong heterologous promoter (Moloney long terminal repeat), and the activity of the mutants was assayed in NIH 3T3 cells, a cell line in which both the transforming function and the trans-activating function of E7 could be determined. A single amino acid substitution analogous to a mutation in E1a which destroys the transforming ability of this protein abolished both transformation and trans-activation by E7. Mutations at the Cys-X-X-Cys motifs demonstrated that this region contributes to the transforming potential of E7, although proteins in which both motifs were interrupted retained a low level of transforming activity. Mutations in the region of E1a-LT homology which occur within a recognition sequence for casein kinase II did not markedly affect transforming activity of E7 but severely reduced trans-activating ability. This indicates that efficient trans-activation is not required for transformation by HPV16 E7 in these cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Androphy E. J., Hubbert N. L., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R. Identification of the HPV-16 E6 protein from transformed mouse cells and human cervical carcinoma cell lines. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):989–992. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04849.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Phelps W. C., Lindgren V., Braun M. J., Gonda M. A., Howley P. M. Structural and transcriptional analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 sequences in cervical carcinoma cell lines. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):962–971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.962-971.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa M. S., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. Papillomavirus polypeptides E6 and E7 are zinc-binding proteins. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1404–1407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1404-1407.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaudenon S., Kremsdorf D., Croissant O., Jablonska S., Wain-Hobson S., Orth G. A novel type of human papillomavirus associated with genital neoplasias. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):246–249. doi: 10.1038/321246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., Kleinheinz A., Scheurlen W., zur Hausen H. A new type of papillomavirus DNA, its presence in genital cancer biopsies and in cell lines derived from cervical cancer. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01944.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Morgenstern J. P., Crawford L., Banks L. Continued expression of HPV-16 E7 protein is required for maintenance of the transformed phenotype of cells co-transformed by HPV-16 plus EJ-ras. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):513–519. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03405.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culp J. S., Webster L. C., Friedman D. J., Smith C. L., Huang W. J., Wu F. Y., Rosenberg M., Ricciardi R. P. The 289-amino acid E1A protein of adenovirus binds zinc in a region that is important for trans-activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6450–6454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., zur Hausen H. A papillomavirus DNA from a cervical carcinoma and its prevalence in cancer biopsy samples from different geographic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3812–3815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Kleinheinz A., Hotz M., Gissmann L. The physical state of human papillomavirus type 16 DNA in benign and malignant genital tumours. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jul;66(Pt 7):1515–1522. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-7-1515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. G., Girardi F., Pfister H. Human papillomavirus DNA in normal, metaplastic, preneoplastic and neoplastic epithelia of the cervix uteri. Int J Cancer. 1988 Jan 15;41(1):41–45. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Smith A. E. In vitro mutagenesis of a putative DNA binding domain of SV40 large-T. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):109–137. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90334-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda T., Furuno A., Yoshiike K. Human papillomavirus type 16 open reading frame E7 encodes a transforming gene for rat 3Y1 cells. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):610–613. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.610-613.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda T., Watanabe S., Yoshiike K. Immortalization of primary rat cells by human papillomavirus type 16 subgenomic DNA fragments controlled by the SV40 promoter. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):321–325. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90694-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppuswamy M. N., Chinnadurai G. Relationship between the transforming and transcriptional regulatory functions of adenovirus 2 E1a oncogene. Virology. 1987 Jul;159(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90344-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M., Green M. R. An adenovirus E1a protein region required for transformation and transcriptional repression. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90704-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Loewenstein P. M., Green M. R., Green M. Functional domains of adenovirus type 5 E1a proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1091–1100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin O., Meggio F., Marchiori F., Borin G., Pinna L. A. Site specificity of casein kinase-2 (TS) from rat liver cytosol. A study with model peptide substrates. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 15;160(2):239–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09962.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlashewski G., Schneider J., Banks L., Jones N., Murray A., Crawford L. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA cooperates with activated ras in transforming primary cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1741–1746. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mincheva A., Gissmann L., zur Hausen H. Chromosomal integration sites of human papillomavirus DNA in three cervical cancer cell lines mapped by in situ hybridization. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1987;176(5):245–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00190531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E. A region of SV40 large T antigen can substitute for a transforming domain of the adenovirus E1A products. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):168–170. doi: 10.1038/334168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Zerler B., Harrison T. M., Mathews M. B. Identification of separate domains in the adenovirus E1A gene for immortalization activity and the activation of virus early genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3470–3480. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oltersdorf T., Seedorf K., Röwekamp W., Gissmann L. Identification of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein by monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1987 Nov;68(Pt 11):2933–2938. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-11-2933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Yee C. L., Münger K., Howley P. M. The human papillomavirus type 16 E7 gene encodes transactivation and transformation functions similar to those of adenovirus E1A. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):539–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90570-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Gädicke A., Schwarz E. Different human cervical carcinoma cell lines show similar transcription patterns of human papillomavirus type 18 early genes. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2285–2292. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Krämmer G., Dürst M., Suhai S., Röwekamp W. G. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA sequence. Virology. 1985 Aug;145(1):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90214-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. The major human papillomavirus protein in cervical cancers is a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1686–1689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1686-1689.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. Transcription of human papillomavirus type 16 early genes in a cervical cancer and a cancer-derived cell line and identification of the E7 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4680–4684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey A., Pim D., Murray A., Osborn K., Banks L., Crawford L. Comparison of the in vitro transforming activities of human papillomavirus types. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1815–1820. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03013.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian T., Kuppuswamy M., Nasr R. J., Chinnadurai G. An N-terminal region of adenovirus E1a essential for cell transformation and induction of an epithelial cell growth factor. Oncogene. 1988 Feb;2(2):105–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. Adenovirus E1a ras cooperation activity is separate from its positive and negative transcription regulatory functions. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2177–2183. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vousden K. H., Androphy E. J., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R. Mutational analysis of bovine papillomavirus E6 gene. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2340–2342. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2340-2342.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vousden K. H., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A., Lowy D. R. The E7 open reading frame of human papillomavirus type 16 encodes a transforming gene. Oncogene Res. 1988 Sep;3(2):167–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vousden K. H., Jat P. S. Functional similarity between HPV16E7, SV40 large T and adenovirus E1a proteins. Oncogene. 1989 Feb;4(2):153–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Buchkovich K. J., Horowitz J. M., Friend S. H., Raybuck M., Weinberg R. A., Harlow E. Association between an oncogene and an anti-oncogene: the adenovirus E1A proteins bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):124–129. doi: 10.1038/334124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Ruley H. E., Harlow E. Two regions of the adenovirus early region 1A proteins are required for transformation. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):257–265. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.257-265.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Knebel Doeberitz M., Oltersdorf T., Schwarz E., Gissmann L. Correlation of modified human papilloma virus early gene expression with altered growth properties in C4-1 cervical carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Jul 1;48(13):3780–3786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Intracellular surveillance of persisting viral infections. Human genital cancer results from deficient cellular control of papillomavirus gene expression. Lancet. 1986 Aug 30;2(8505):489–491. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90360-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]