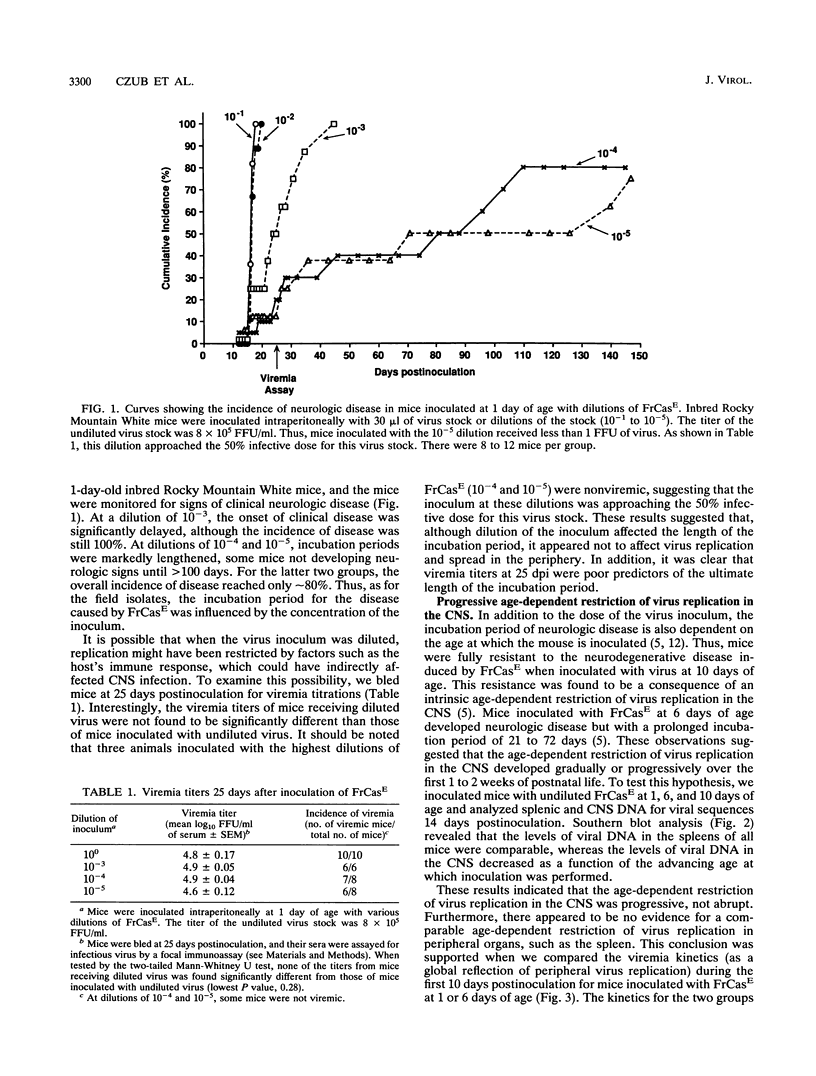
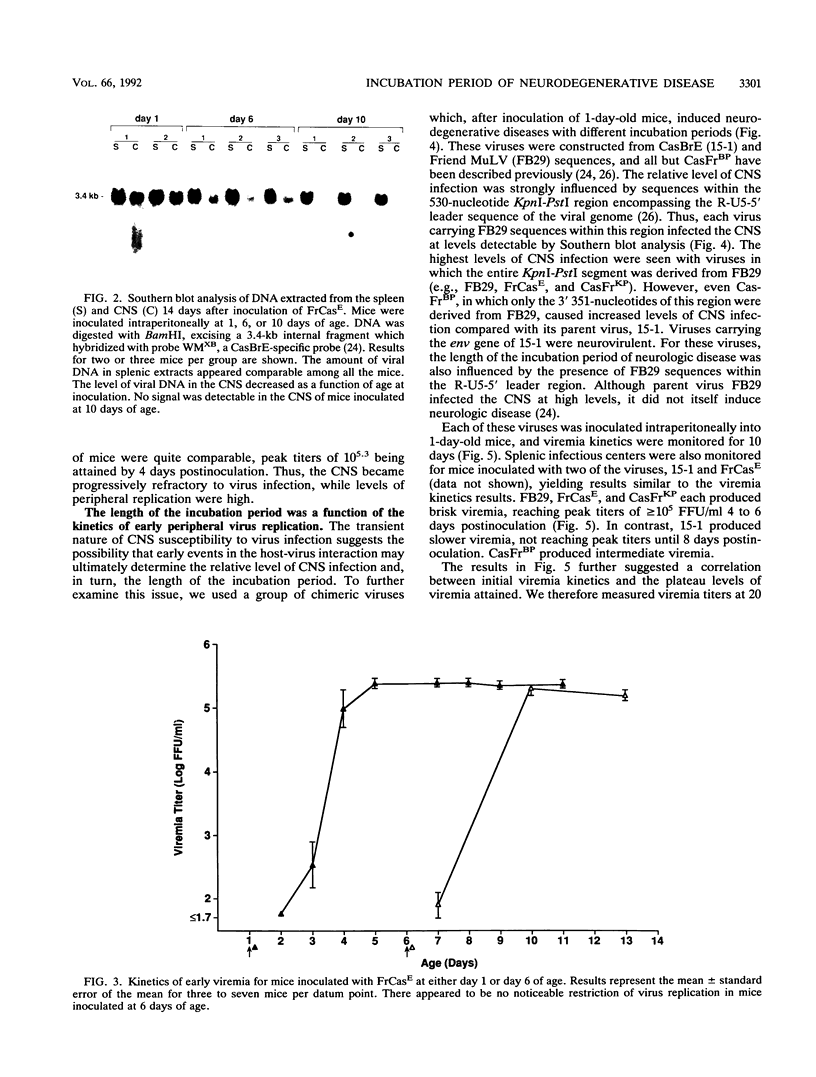
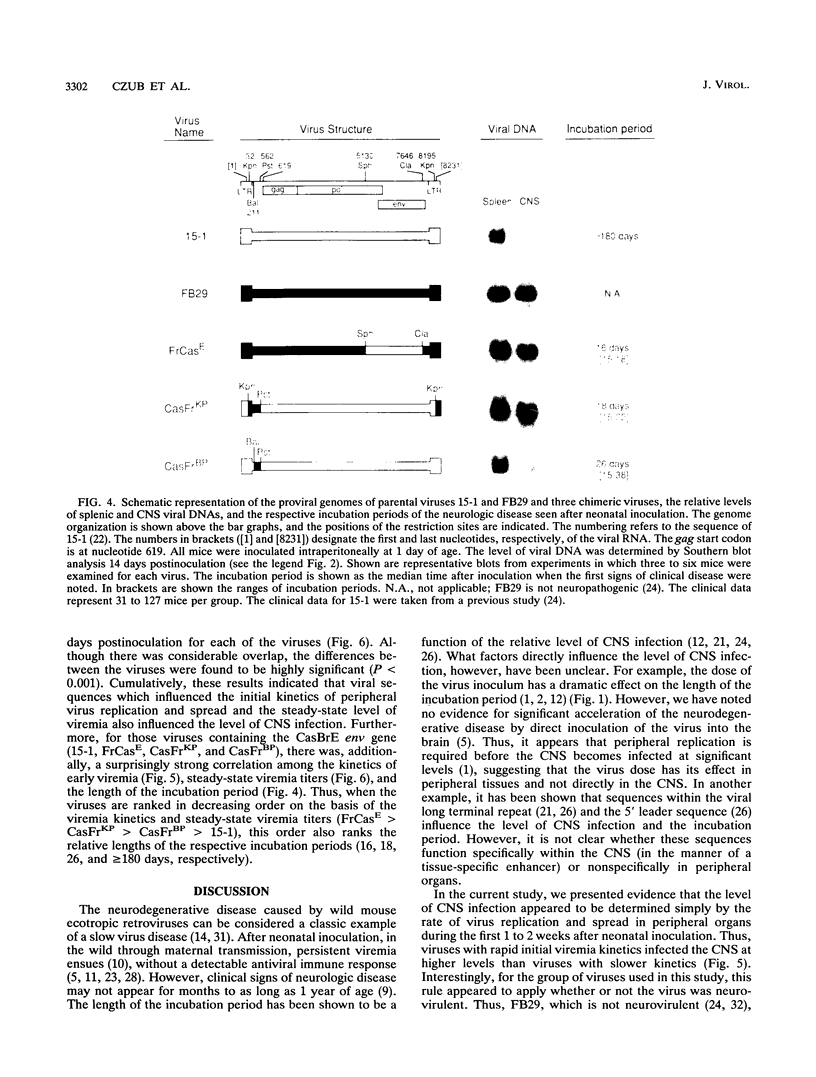
Abstract
A molecular clone of wild mouse ecotropic retrovirus CasBrE (clone 15-1) causes a spongiform neurodegenerative disease with a long incubation period, greater than or equal to 6 months. This virus infects the central nervous system (CNS) at low levels. In contrast, a chimeric virus, FrCasE, containing env and 3' pol sequences of 15-1 in a Friend murine leukemia virus background, infects the CNS at high levels and causes a rapid neurodegenerative disease with an incubation period of only 16 days. With both viruses, the induction of neurologic disease is dependent on inoculation during the perinatal period. Since the length of the incubation period of this disease appears to be a function of the relative level of CNS infection, we have attempted to identify the viral and host factors which determine the relative level of virus infection of the CNS. It was previously shown that the CNS is susceptible to infection only during the perinatal period (M. Czub, S. Czub, F. J. McAtee, and J. L. Portis, J. Virol. 65:2539-2544, 1991). Here we have found that the susceptibility of the CNS wanes progressively or gradually as a function of the age of the host, this age-dependent resistance being complete by 12 to 14 days of age. Utilizing a group of chimeric viruses, we found that the relative level of CNS infection achieved after inoculation of mice at 1 day of age was a function of the kinetics of virus replication and spread in peripheral organs. Viruses which reached peak viremia titers early (5 to 7 days of age) infected the CNS at high levels, and viruses which reached peak titers later infected the CNS at lower levels. Among the group of viruses examined in the current study, the kinetics of peripheral virus replication and spread appeared to be influenced primarily by sequences within the R-U5-5' leader region of the viral genome. These results suggested that the relative level of CNS infection was determined very early in life and appeared to be a function of a dynamic balance between the kinetics of virus replication in the periphery and a progressively developing restriction of virus replication in the CNS.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooks B. R., Swarz J. R., Johnson R. T. Spongiform polioencephalomyelopathy caused by a murine retrovirus. I. Pathogenesis of infection in newborn mice. Lab Invest. 1980 Nov;43(5):480–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks B. R., Swarz J. R., Narayan O., Johnson R. T. Murine neurotropic retrovirus spongiform polioencephalomyelopathy: acceleration of disease by virus inoculum concentration. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):540–544. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.540-544.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K., Cloyd M., Britt W., Portis J., Collins J., Nishio J. Characterization of mouse monoclonal antibodies specific for Friend murine leukemia virus-induced erythroleukemia cells: friend-specific and FMR-specific antigens. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):131–144. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90619-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czub M., Czub S., McAtee F. J., Portis J. L. Age-dependent resistance to murine retrovirus-induced spongiform neurodegeneration results from central nervous system-specific restriction of virus replication. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2539–2544. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2539-2544.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Barrette M., Jolicoeur P. Physical mapping of the paralysis-inducing determinant of a wild mouse ecotropic neurotropic retrovirus. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):356–363. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.356-363.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B., Chiri A., Dougherty M. F., Casagrande J., Estes J. D. Congenital transmission of murine leukemia virus from wild mice prone to the development of lymphoma and paralysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Jan;62(1):63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B., Henderson B. E., Officer J. E., Rongey R. W., Parker J. C., Oliver C., Estes J. D., Huebner R. J. A spontaneous lower motor neuron disease apparently caused by indigenous type-C RNA virus in wild mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Oct;51(4):1243–1254. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.4.1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B., Klement V., Rongey R. R., McConahey P., Estes J. D., Huebner R. J. Type C virus expression in lymphoma-paralysis-prone wild mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Sep;57(3):585–590. doi: 10.1093/jnci/57.3.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. M., Robbins D. S., Morse H. C., 3rd Role of immunity in age-related resistance to paralysis after murine leukemia virus infection. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):734–738. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.734-738.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. M., Ruscetti S. K., Morse H. C., 3rd Pathogenesis of paralysis and lymphoma associated with a wild mouse retrovirus infection. Part 1. Age- and dose-related effects in susceptible laboratory mice. J Neuroimmunol. 1981 Sep;1(3):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(81)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P., Nicolaiew N., DesGroseillers L., Rassart E. Molecular cloning of infectious viral DNA from ecotropic neurotropic wild mouse retrovirus. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1159–1163. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1159-1163.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberlin R. H. General introduction to some slow virus diseases. Front Biol. 1976;44:3–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAtee F. J., Portis J. L. Monoclonal antibodies specific for wild mouse neurotropic retrovirus: detection of comparable levels of virus replication in mouse strains susceptible and resistant to paralytic disease. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):1018–1022. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.1018-1022.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau-Gachelin F., Robert-Lezenes J., Mathieu-Mahul D., Gisselbrecht S., Larsen C. J. Isolation and characterization of a gp 70+ non producer Friend tumor cell clone. Biochimie. 1983 Apr-May;65(4-5):259–266. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(83)80277-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Officer J. E., Tecson N., Estes J. D., Fontanilla E., Rongey R. W., Gardner M. B. Isolation of a neurotropic type C virus. Science. 1973 Sep 7;181(4103):945–947. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4103.945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Jensen F., Elder J., Dixon F. J., Lampert P. W. Pathogenesis of the slow disease of the central nervous system associated with wild mouse virus. III. Role of input virus and MCF recombinants in disease. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):154–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Lampert P. W., Lee S., Dixon F. J. Pathogenesis of the slow disease of the central nervous system associated with WM 1504 E virus. I. Relationship of strain susceptibility and replication to disease. Am J Pathol. 1977 Jul;88(1):193–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paquette Y., Hanna Z., Savard P., Brousseau R., Robitaille Y., Jolicoeur P. Retrovirus-induced murine motor neuron disease: mapping the determinant of spongiform degeneration within the envelope gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3896–3900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paquette Y., Kay D. G., Rassart E., Robitaille Y., Jolicoeur P. Substitution of the U3 long terminal repeat region of the neurotropic Cas-Br-E retrovirus affects its disease-inducing potential. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3742–3752. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3742-3752.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perryman S. M., McAtee F. J., Portis J. L. Complete nucleotide sequence of the neurotropic murine retrovirus CAS-BR-E. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1707–1707. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis J. L., Czub S., Garon C. F., McAtee F. J. Neurodegenerative disease induced by the wild mouse ecotropic retrovirus is markedly accelerated by long terminal repeat and gag-pol sequences from nondefective Friend murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1648–1656. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1648-1656.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis J. L., McAtee F. J., Evans L. H. Infectious entry of murine retroviruses into mouse cells: evidence of a postadsorption step inhibited by acidic pH. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):806–812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.806-812.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis J. L., Perryman S., McAtee F. J. The R-U5-5' leader sequence of neurovirulent wild mouse retrovirus contains an element controlling the incubation period of neurodegenerative disease. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1877–1883. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1877-1883.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis J. L. Wild mouse retrovirus: pathogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;160:11–27. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75267-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prats A. C., De Billy G., Wang P., Darlix J. L. CUG initiation codon used for the synthesis of a cell surface antigen coded by the murine leukemia virus. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 20;205(2):363–372. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90347-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins D. S., Hoffman P. M. Virus-specific cytotoxic lymphocyte response in a neurotropic murine leukemia virus infection. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Jan;31(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90081-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha K., Wong P. K. T, not B, lymphocytes are required for immunodeficiency and paralysis induced by ts1, a mutant of Moloney murine leukemia virus-TB. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)91017-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe A. H., Jaenisch R., Ruprecht R. M. Retroviruses and mouse embryos: a rapid model for neurovirulence and transplacental antiviral therapy. Science. 1987 Jun 26;236(4809):1671–1674. doi: 10.1126/science.3037694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Sola B., Evans L., Nishio J., Hayes S. F., Nathanson K., Garon C. F., Chesebro B. Hemolytic anemia and erythroleukemia, two distinct pathogenic effects of Friend MuLV: mapping of the effects to different regions of the viral genome. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):851–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90800-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. K. Moloney murine leukemia virus temperature-sensitive mutants: a model for retrovirus-induced neurologic disorders. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;160:29–60. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75267-4_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]