Abstract
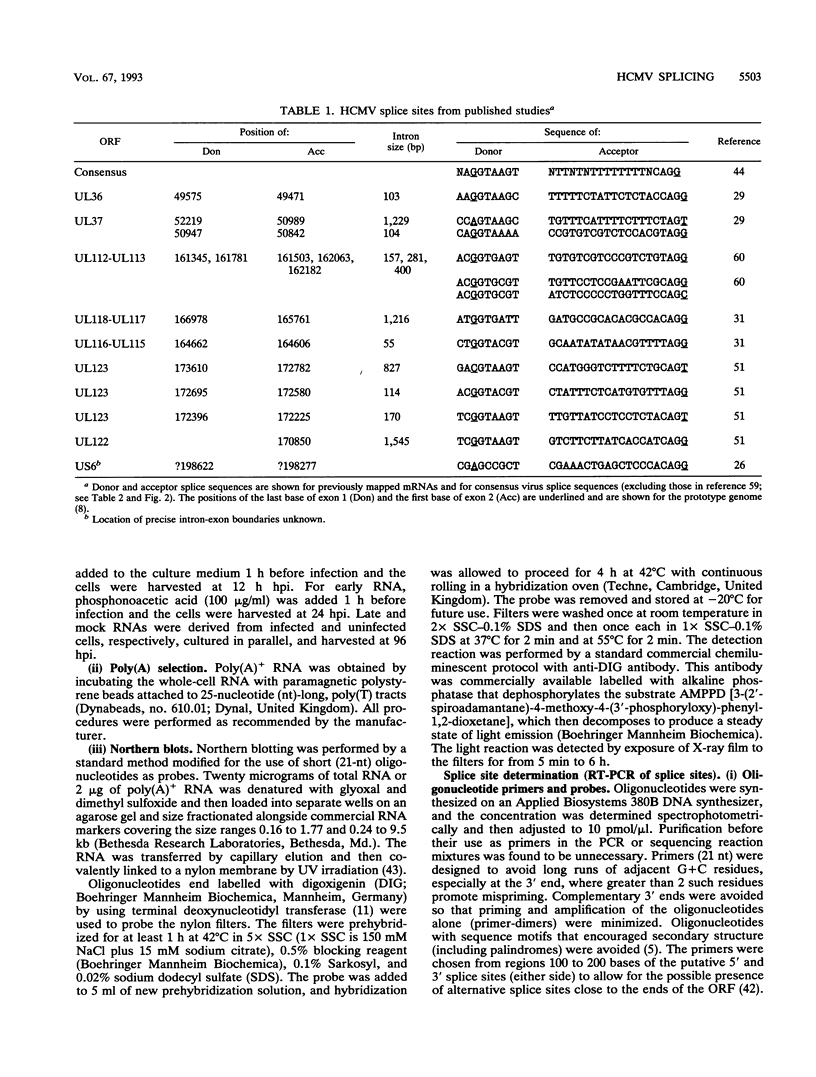
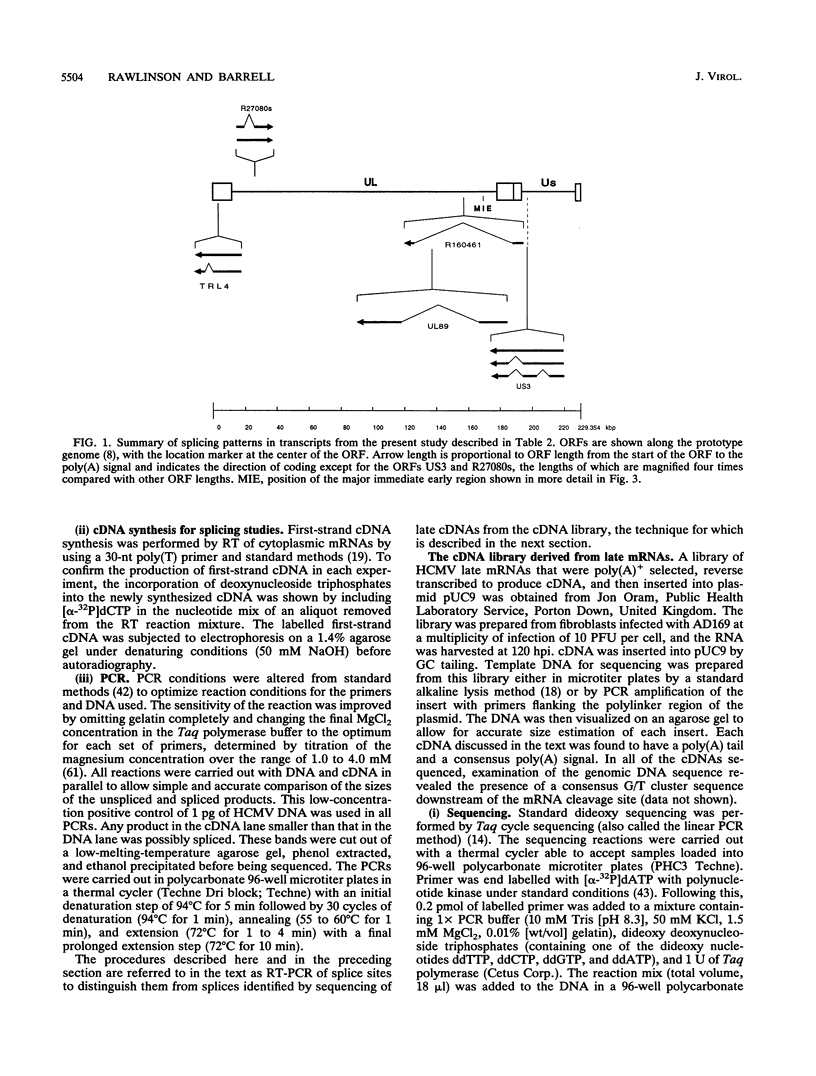
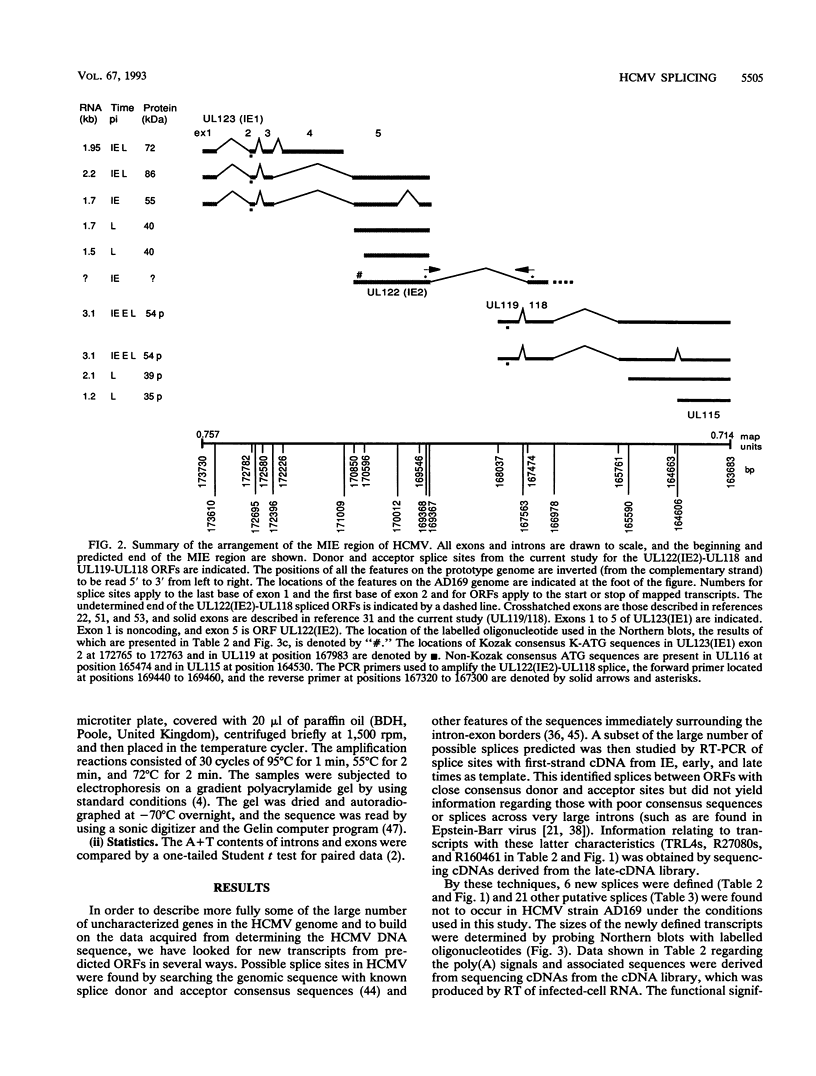
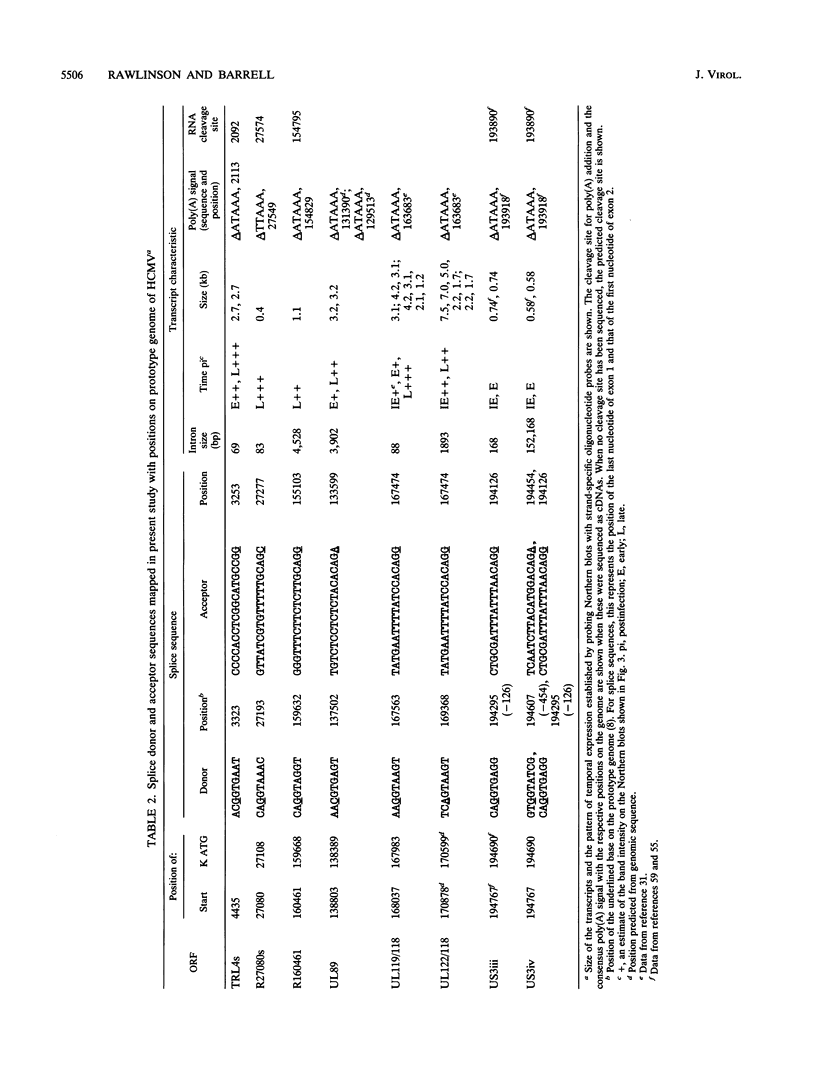
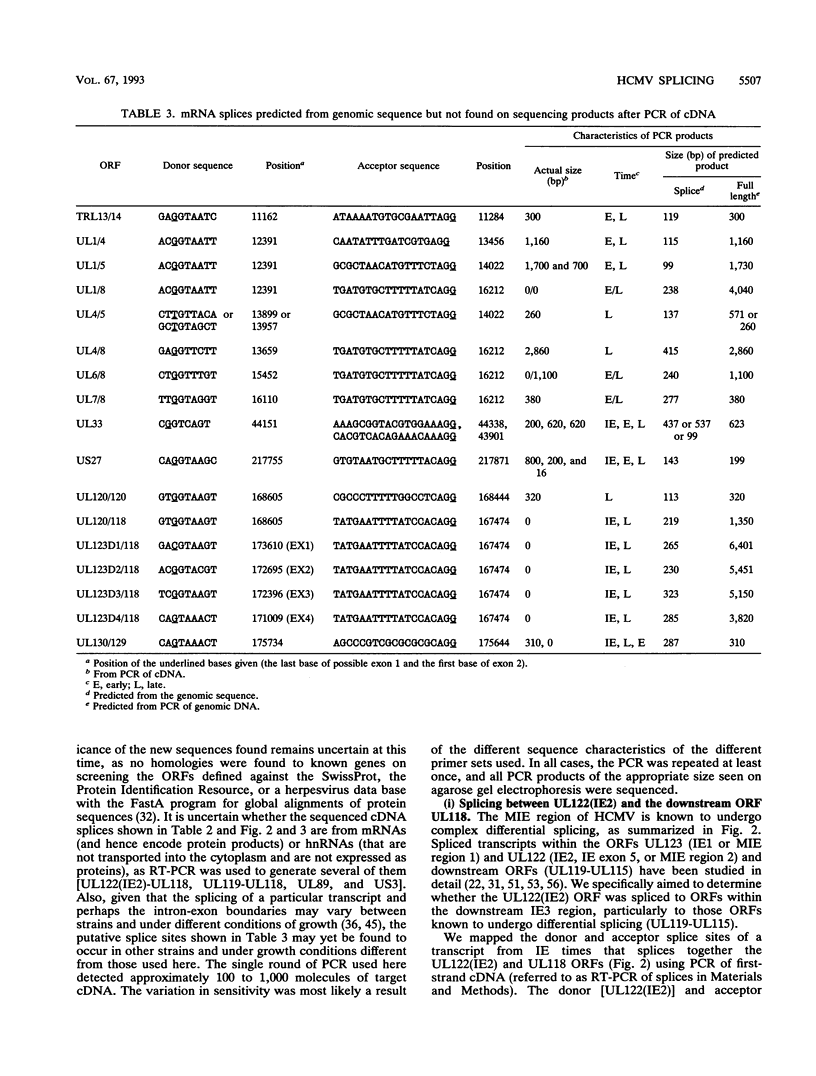
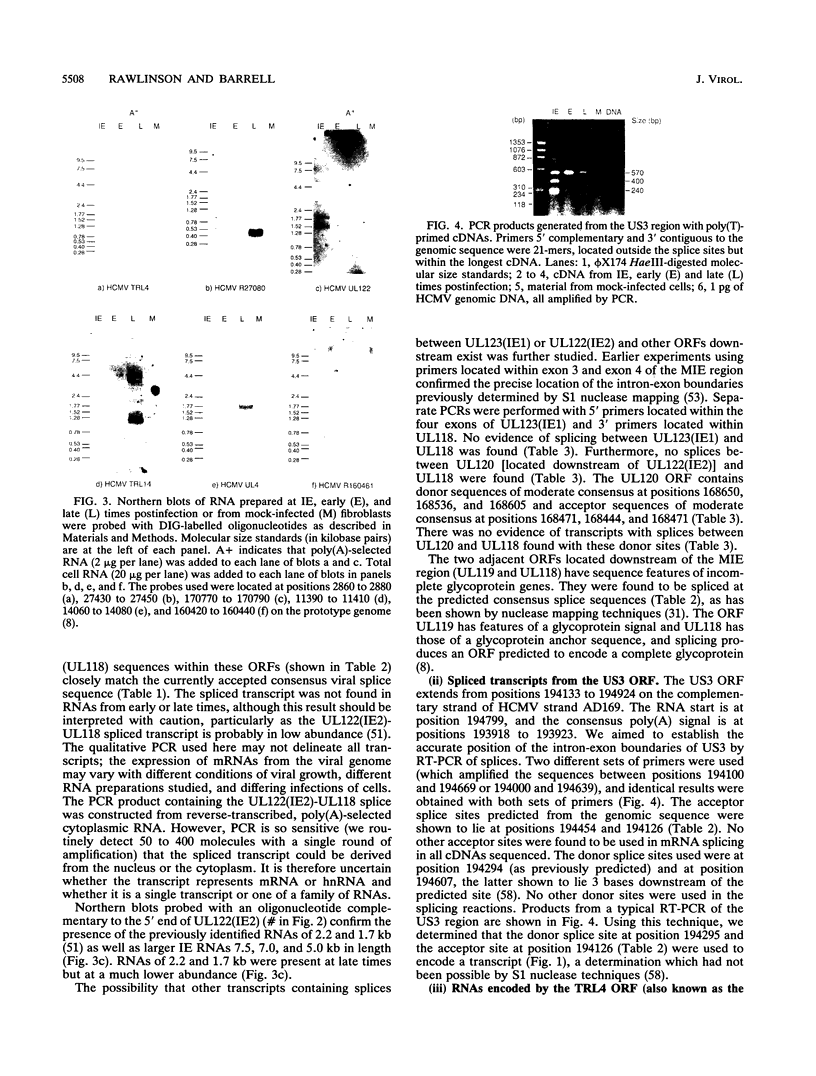
The availability of the human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) genomic sequence has resulted in more extensive knowledge of the overall coding capacity of the virus. Using polymerase chain reaction and rapid sequencing techniques, we have studied the splicing of mRNAs from a number of the predicted open reading frames (ORFs). Splicing was found between the UL122(IE2) ORF present within major immediate-early (MIE) region 2 and the downstream ORF (UL118) predicted to encode an incomplete glycoprotein. This locates the IE2 3' donor site and provides evidence of a link between the MIE region and downstream ORFs. The downstream UL119-UL118-UL115 ORFs also undergo differential splicing, further increasing the known complexity of this region of the genome. A detailed map of the differential splicing within the region encoding the MIE ORF is presented. Also described are several previously unidentified spliced ORFs found in the long repeats and long unique regions, including one encoding a transcript with a large (4-kb) intron. The results show that spliced transcripts are encoded from throughout the genome at immediate-early, early, and late times postinfection.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bankier A. T., Beck S., Bohni R., Brown C. M., Cerny R., Chee M. S., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Kouzarides T., Martignetti J. A., Preddie E. The DNA sequence of the human cytomegalovirus genome. DNA Seq. 1991;2(1):1–12. doi: 10.3109/10425179109008433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankier A. T., Weston K. M., Barrell B. G. Random cloning and sequencing by the M13/dideoxynucleotide chain termination method. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:51–93. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. The polymerase chain reaction. Immunol Today. 1989 Oct;10(10):351–355. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90193-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. P., Vesole D. H., Nelson J., Oldstone M. B., Stinski M. F. Identification and expression of a human cytomegalovirus early glycoprotein. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3330–3337. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3330-3337.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M. S., Bankier A. T., Beck S., Bohni R., Brown C. M., Cerny R., Horsnell T., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Kouzarides T., Martignetti J. A. Analysis of the protein-coding content of the sequence of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:125–169. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M. S., Satchwell S. C., Preddie E., Weston K. M., Barrell B. G. Human cytomegalovirus encodes three G protein-coupled receptor homologues. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):774–777. doi: 10.1038/344774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M., Rudolph S. A., Plachter B., Barrell B., Jahn G. Identification of the major capsid protein gene of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1345–1353. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1345-1353.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Kieffer-Higgins S. Multiplex DNA sequencing. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):185–188. doi: 10.1126/science.3353714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Draper K. G., Kelly T. J., Wagner E. K. An unusual spliced herpes simplex virus type 1 transcript with sequence homology to Epstein-Barr virus DNA. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):317–328. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.317-328.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranage M. P., Kouzarides T., Bankier A. T., Satchwell S., Weston K., Tomlinson P., Barrell B., Hart H., Bell S. E., Minson A. C. Identification of the human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B gene and induction of neutralizing antibodies via its expression in recombinant vaccinia virus. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3057–3063. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csank C., Taylor F. M., Martindale D. W. Nuclear pre-mRNA introns: analysis and comparison of intron sequences from Tetrahymena thermophila and other eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5133–5141. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demarchi J. M. Human cytomegalovirus DNA: restriction enzyme cleavage maps and map locations for immediate-early, early, and late RNAs. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott R. M., Crook N. E., Desselberger U., Hull R., McGeoch D. J. Some highlights of virus research in 1990. J Gen Virol. 1991 Aug;72(Pt 8):1761–1779. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-8-1761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T. J., Sulston J. E. Preparation of large numbers of plasmid DNA samples in microtiter plates by the alkaline lysis method. Gene Anal Tech. 1987 May-Jun;4(3):41–44. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(87)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman K. B., Steinberg R. A. Simplified method for selective amplification and direct sequencing of cDNAs. Biotechniques. 1989 Apr;7(4):326-8, 331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenaway P. J., Wilkinson G. W. Nucleotide sequence of the most abundantly transcribed early gene of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Virus Res. 1987 Feb;7(1):17–31. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Kieff E. A second nuclear protein is encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent infection. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1238–1240. doi: 10.1126/science.2983420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermiston T. W., Malone C. L., Witte P. R., Stinski M. F. Identification and characterization of the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early region 2 gene that stimulates gene expression from an inducible promoter. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3214–3221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3214-3221.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson N. I., Sondermeyer R. T., Tocci M. J. Organization and expression of the major genes from the long inverted repeat of the human cytomegalovirus genome. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):160–171. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90176-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson I. J. A reappraisal of non-consensus mRNA splice sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3795–3798. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn G., Kouzarides T., Mach M., Scholl B. C., Plachter B., Traupe B., Preddie E., Satchwell S. C., Fleckenstein B., Barrell B. G. Map position and nucleotide sequence of the gene for the large structural phosphoprotein of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1358–1367. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1358-1367.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. R., Muzithras V. P. Fine mapping of transcripts expressed from the US6 gene family of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):2024–2036. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.2024-2036.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J. F., Gompels U. A., Minson A. C. Glycoprotein H of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) forms a stable complex with the HCMV UL115 gene product. J Gen Virol. 1992 Oct;73(Pt 10):2693–2698. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-10-2693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Bankier A. T., Satchwell S. C., Preddy E., Barrell B. G. An immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus encodes a potential membrane glycoprotein. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):151–164. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90668-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach F. S., Mocarski E. S. Regulation of cytomegalovirus late-gene expression: differential use of three start sites in the transcriptional activation of ICP36 gene expression. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1783–1791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1783-1791.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leatham M. P., Witte P. R., Stinski M. F. Alternate promoter selection within a human cytomegalovirus immediate-early and early transcription unit (UL119-115) defines true late transcripts containing open reading frames for putative viral glycoproteins. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6144–6153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6144-6153.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mach M., Stamminger T., Jahn G. Human cytomegalovirus: recent aspects from molecular biology. J Gen Virol. 1989 Dec;70(Pt 12):3117–3146. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-12-3117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough S. H., Staprans S. I., Spector D. H. Analysis of the major transcripts encoded by the long repeat of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):711–718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.711-718.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Dolan A., McNab D., Perry L. J., Taylor P., Challberg M. D. Structures of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for replication of virus DNA. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):444–453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.444-453.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengeritsky G., Smith T. F. New analytical tool for analysis of splice site sequence determinants. Comput Appl Biosci. 1989 Apr;5(2):97–100. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/5.2.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pande H., Lee T. D., Churchill M. A., Zaia J. A. Structural analysis of a 64-kDa major structural protein of human cytomegalovirus (Towne): identification of a phosphorylation site and comparison to pp65 of HCMV (AD169). Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):6–14. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90374-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petti L., Kieff E. A sixth Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein (EBNA3B) is expressed in latently infected growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2173–2178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2173-2178.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzorno M. C., Mullen M. A., Chang Y. N., Hayward G. S. The functionally active IE2 immediate-early regulatory protein of human cytomegalovirus is an 80-kilodalton polypeptide that contains two distinct activator domains and a duplicated nuclear localization signal. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3839–3852. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3839-3852.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. R., Milman G., Hayward S. D., Hayward G. S. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA-1) to clustered sites in the plasmid maintenance region. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):859–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senapathy P., Shapiro M. B., Harris N. L. Splice junctions, branch point sites, and exons: sequence statistics, identification, and applications to genome project. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:252–278. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Porro E. B., Patton J. G., Nadal-Ginard B. Scanning from an independently specified branch point defines the 3' splice site of mammalian introns. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):243–247. doi: 10.1038/342243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Klucher K. M., Rabert D. K., Wright D. A. Human cytomegalovirus early gene expression. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:21–45. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A computer program to enter DNA gel reading data into a computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):499–503. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamminger T., Fleckenstein B. Immediate-early transcription regulation of human cytomegalovirus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:3–19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamminger T., Puchtler E., Fleckenstein B. Discordant expression of the immediate-early 1 and 2 gene regions of human cytomegalovirus at early times after infection involves posttranscriptional processing events. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2273–2282. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2273-2282.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staprans S. I., Rabert D. K., Spector D. H. Identification of sequence requirements and trans-acting functions necessary for regulated expression of a human cytomegalovirus early gene. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3463–3473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3463-3473.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Depto A. S., Fortney J., Nelson J. A. Regulated expression of early and late RNAs and proteins from the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene region. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2699–2708. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2699-2708.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Thomsen D. R., Stinski M. F. Structural analysis of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):190–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.190-199.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Witte P. R., Stinski M. F. Multiple spliced and unspliced transcripts from human cytomegalovirus immediate-early region 2 and evidence for a common initiation site within immediate-early region 1. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):665–675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.665-675.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Thomsen D. R., Stenberg R. M., Goldstein L. C. Organization and expression of the immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):1–14. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.1-14.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenney D. J., Colberg-Poley A. M. Human cytomegalovirus UL36-38 and US3 immediate-early genes: temporally regulated expression of nuclear, cytoplasmic, and polysome-associated transcripts during infection. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6724–6734. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6724-6734.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathen M. W., Stinski M. F. Temporal patterns of human cytomegalovirus transcription: mapping the viral RNAs synthesized at immediate early, early, and late times after infection. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):462–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.462-477.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch A. R., McGregor L. M., Gibson W. Cytomegalovirus homologs of cellular G protein-coupled receptor genes are transcribed. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3915–3918. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3915-3918.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston K. An enhancer element in the short unique region of human cytomegalovirus regulates the production of a group of abundant immediate early transcripts. Virology. 1988 Feb;162(2):406–416. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90481-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston K., Barrell B. G. Sequence of the short unique region, short repeats, and part of the long repeats of human cytomegalovirus. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 20;192(2):177–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90359-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. A., Staprans S. I., Spector D. H. Four phosphoproteins with common amino termini are encoded by human cytomegalovirus AD169. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):331–340. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.331-340.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. L., Maher V. M., McCormick J. J. Amplification and direct nucleotide sequencing of cDNA from the lysate of low numbers of diploid human cells. Gene. 1989 Nov 30;83(2):347–354. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]