Abstract
Apoptosis of fibroblasts/myofibroblasts is a critical event in the resolution of tissue repair responses; however, mechanisms for the regulation of (myo)fibroblast apoptosis/survival remain unclear. In this study, we demonstrate counter-regulatory interactions between the plasminogen activation system and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) in the control of fibroblast apoptosis. Plasmin treatment induced fibroblast apoptosis in a time- and dose-dependent manner in association with proteolytic degradation of extracellular matrix proteins, as detected by the release of soluble fibronectin peptides. Plasminogen, which was activated to plasmin by fibroblasts, also induced fibronectin proteolysis and fibroblast apoptosis, both of which were blocked by α2-antiplasmin but not by inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase activity. TGF-β1 protected fibroblasts from apoptosis induced by plasminogen but not from apoptosis induced by exogenous plasmin. The protection from plasminogen-induced apoptosis conferred by TGF-β1 is associated with the up-regulation of plasminogen activator-1 (PAI-1) expression and inhibition of plasminogen activation. Moreover, lung fibroblasts from mice genetically deficient in PAI-1 lose the protective effect of TGF-β1 against plasminogen-induced apoptosis. These findings support a novel role for the plasminogen activation system in the regulation of fibroblast apoptosis and a potential role of TGF-β1/PAI-1 in promoting (myo)fibroblast survival in chronic fibrotic disorders.
Keywords: myofibroblast, fibrosis, transforming growth factor-β, anoikis, plasminogen activator inhibitor 1
CLINICAL RELEVANCE
Both plasminogen activation and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 have been strongly implicated in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. This study demonstrates a novel mechanism by which TGF-β1 inhibition of plasminogen activation regulates fibroblast apoptosis.
Fibroblasts, versatile connective tissue cells and key effectors in wound-repair responses, are recruited to sites of tissue injury where extracellular matrix (ECM) components and soluble factors, such as transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), promote myofibroblast differentiation. Myofibroblasts secrete, organize, remodel, and contract the ECM, facilitating wound closure and reepithelialization (1). With the resolution of normal wound repair, fibroblast/myofibroblast numbers decrease substantially due to apoptosis (2). The physiologic stimuli that trigger fibroblast/myofibroblast apoptosis, however, have not been determined (3). Failure of myofibroblast apoptosis is associated with pathologic wound repair characterized by tissue fibrosis (2, 4–6).
TGF-β1 is a potent pro-fibrotic cytokine that promotes myofibroblast differentiation, migration, ECM synthesis, and resistance to apoptosis (1, 7–11). Studies from our laboratory have shown that TGF-β1–induced myofibroblast differentiation requires the integration of cell-matrix adhesion signals through activation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) (8). Moreover, the coordinate activation of FAK and phosphatidylinositol-3′-OH kinase/AKT (PI3K/AKT) through SMAD3 and p38 MAPK-dependent pathways respectively confers fibroblast resistance to anoikis, a type of apoptosis induced by the loss of adhesion or adhesion-dependent signaling (9, 10, 12, 13). These findings suggest that TGF-β1 regulation of ECM–fibroblast interactions may modulate the fates of fibroblasts/myofibroblasts in the context of physiologic and pathologic wound repair responses.
Plasmin, a serine protease with potent fibrinolytic activity, is generated through the proteolytic cleavage of its zymogen, plasminogen, by plasminogen activators (urokinase and tissue, uPA and tPA) (14). In addition to fibrin, plasmin is capable of cleaving extracellular matrix components such as fibronectin and activating growth factors and other matrix proteases (15–19). Inhibition of plasminogen activation by plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) has been causally implicated in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis and other disease processes characterized by tissue fibrosis (20–22). The mechanisms by which PAI-1 promotes tissue fibrosis, while plasminogen activation protects against fibrogenesis, have not been fully defined (23, 24).
Among its potential pro-fibrotic mechanisms, TGF-β1 induces fibroblast elaboration of PAI-1 and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases (TIMPS). Given the susceptibility of fibroblasts to anoikis and the protection afforded by TGF-β1, we hypothesized that plasmin-mediated pericellular fibronectin proteolysis would induce fibroblast anoikis. In addition, we postulated that TGF-β1 up-regulation of PAI-1 would limit fibroblast anoikis by inhibition of plasminogen activation. This study was undertaken to investigate how TGF-β1 modulation of plasminogen activation would regulate fibroblast apoptosis. We report that plasminogen activation provides a potent stimulus for fibroblast apoptosis, and that TGF-β1 inhibits apoptosis induced by plasminogen activation. This demonstrates a novel mechanism by which TGF-β1 up-regulation of PAI-1 may modulate wound repair responses and promote tissue fibrosis. Portions of this work have been previously published in abstract form (25).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cells and Cell Culture
Normal primary human embryonic lung fibroblasts (IMR-90 [26]; Institute for Medical Research, Camden, NJ) were cultured as previously described (9) and studies performed at passages 5 to 9. Cells were plated on cell culture dishes or on 96-well plates with Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) containing 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS) in 5% CO2–95% air and then growth-arrested for 24 hours in DMEM containing 0.01% FBS before treatment in serum-free DMEM without phenol red. Primary murine fibroblasts were grown from lung explants of wild-type (WT) and PAI-1 knockout (PAI-1−/−) mice (C57BL/6 background) and cultured as previously described (19, 27). Experiments with these primary lung fibroblasts were performed between passages 2 and 4.
Reagents
TGF-β1 derived from porcine platelets was obtained from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN) and acid-activated before use. Antibodies to cleaved caspase-3 were from R&D Systems. Plasmin, ɛ-aminocaproic acid and mouse monoclonal antibody to fibronectin (IST-4) were from Sigma (St. Louis, MO). Mouse monoclonal antibody to single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) was from Chemicon International (Temecula, CA). Antibody to GAPDH was from Abcam (Cambridge, MA). Secondary HRP-conjugated anti-mouse and anti-rabbit antibodies were obtained from Pierce (Rockford, IL). α2-antiplasmin and plasminogen were obtained from American Diagnostica (Stamford, CT). BB2516 (Marimastat) was from Calbiochem (San Diego, CA). A genetically engineered variant of PAI-1, 14–1, which retains all of the antiproteolytic and vitronectin binding properties of native PAI-1 but is resistant to spontaneous conversion to the latent form, was obtained from Molecular Innovations, Inc. (Detroit, MI) (28). SB431542 was from Tocris Bioscience (Ellisville, MO).
Western Immunoblotting
Cell culture supernatants were centrifuged for 3 minutes at 10,000 rpm to pellet floating cells. The soluble fraction was separated and frozen at −20°C. Adherent cells on cell culture dishes were washed with PBS and lysed with RIPA buffer. This cell lysate was combined with the insoluble fraction of the supernatant and mixed vigorously. Protein concentrations of both the supernatant and cellular fractions were determined. Equal amounts of protein were then used for SDS-PAGE immunoelectrophoresis and Western immunoblotting under reducing conditions as previously described (9).
Plasmin Activity Assay
Plasmin activity in cell culture supernatants was determined using the SPECTROZYME PL chromogenic substrate obtained from American Diagnostica according to manufacturer's instructions. Cells were treated in phenol red–free media, and 50 μl of the cell culture supernatant was transferred to a single well of 96-well plate containing 50 μl of SPECTROZYME PL chromogenic substrate and 50 μl of buffer solution. Absorbance was measured at 405 nm using a VERSAmax microplate reader from Molecular Devices (Sunnyvale, CA). In all cases, two replicates of each sample were measured.
ssDNA Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Apoptosis
This assay is based on the susceptibility of double-stranded DNA in apoptotic cells to form single strands when exposed to formamide (23) and was performed as previously described (9).
Affymetrix Microarray
IMR-90 fibroblasts were grown to 80% confluence, serum starved for 48 hours, and treated with TGF-β1 (2.0 ng/ml), or were not treated, for 18 hours. RNA was isolated and Affymetrix microarray analysis was performed. Values represent mean ± SEM (n = 3).
Statistical and Densitometric Analyses
Statistical analysis was performed using Student's t test when comparing two groups and one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction when comparing three or more experimental conditions. This analysis was done using GraphPad Prism version 3.0 for Windows (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA).
RESULTS
Exogenous Plasmin Induces Fibroblast Apoptosis in Association with Fibronectin Proteolysis
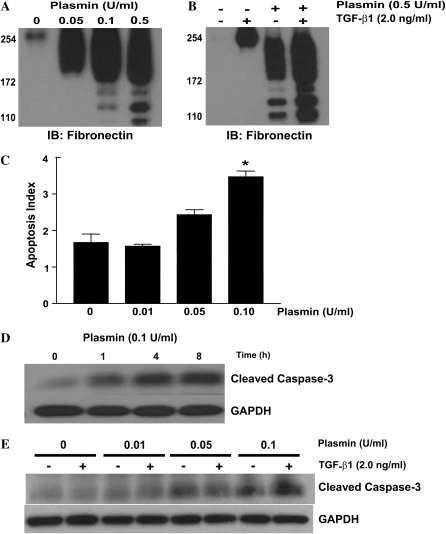
Our previous studies suggest that the interactions of fibroblasts with ECM components regulate their differentiation and susceptibility to apoptosis (8, 10). To investigate the potential induction of fibroblast apoptosis by plasmin-mediated matrix proteolysis, IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated with or without exogenous plasmin in the presence or absence of TGF-β1. Cell culture supernatants collected from plasmin-treated fibroblasts demonstrated dose-dependent fibronectin proteolysis (Figure 1A). TGF-β1 treatment increased the total amount of fibronectin in the cell culture supernatants but failed to inhibit plasmin-mediated fibronectin proteolysis (Figure 1B). In addition, plasmin treatment induced fibroblast apoptosis in a dose- and time-dependent manner (Figures 1C, 1D, and 1E). As with fibronectin proteolysis, exogenous TGF-β1 failed to inhibit plasmin-induced fibroblast apoptosis (Figure 1E).
Figure 1.
Plasmin induces fibroblast apoptosis in association with fibronectin proteolysis. (A) IMR-90 fibroblasts were cultured to 60% confluence and growth arrested for 24 hours before treatment with plasmin (doses indicated) for 16 hours. Equal amounts of protein from the cell culture supernatant were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western immunoblotting for fibronectin. (B) Similarly cultured IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated with plasmin (0.5 U/ml) ± TGF-β1 (2.0 ng/ml) and cell culture supernatants were assessed for fibronectin. (C) IMR-90 fibroblasts were cultured to 60% confluence in a 96-well plate, growth arrested in serum-free media for 24 hours, and treated with plasmin for 16 hours. Apoptosis was assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for ssDNA. *P < 0.001 compared with control (n = 4). (D) IMR-90 fibroblasts cultured as above were treated with plasmin (0.1 U/ml) for the times noted and whole cell lysates were assessed for cleaved caspase-3 by SDS-PAGE and Western immunoblotting. Membranes were stripped and probed for GAPDH. (E) IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated with plasmin ± TGF-β1 (2.0 ng/ml) for 16 hours, and lysates were assessed for cleaved caspase-3 by SDS-PAGE and Western immunoblotting. Membranes were stripped and probed for GAPDH. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments.
Plasminogen Activation by Fibroblasts Is Associated with Fibronectin Proteolysis and Induction of Anoikis
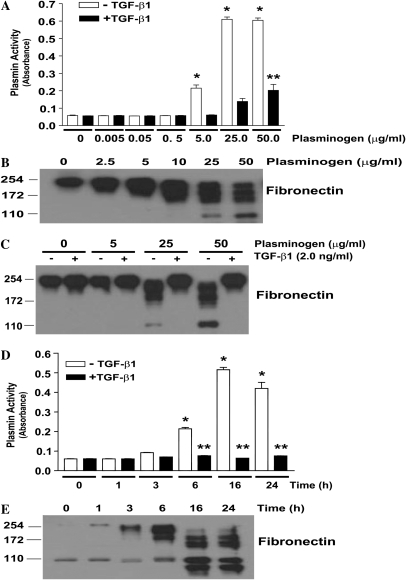
We next sought to determine if endogenous mechanisms of plasminogen activation in IMR-90 fibroblasts would recapitulate the effects of exogenous plasmin on fibronectin degradation and fibroblast anoikis. Fibroblasts were treated with increasing plasminogen concentrations for various periods of time, and cell culture supernatants were assessed for plasmin activity. The addition of plasminogen with concentrations ranging from 5.0 to 50 μg/ml led to detectable plasmin activity at 6 hours, with maximal activity between 16 and 24 hours (Figures 2A and 2D, open bars). The appearance of fibronectin degradation products in the cell culture supernatant closely correlated with plasminogen activation (Figures 2B, 2C, and 2E). At all doses and time points indicated, TGF-β1 co-treatment significantly attenuated plasminogen activation (Figures 2A and 2D, solid bars) and fibronectin proteolysis (Figure 2C).
Figure 2.
TGF-β1 inhibits plasminogen activation and fibronectin proteolysis in normal human lung fibroblasts. (A) IMR-90 fibroblasts were cultured and growth arrested for 24 hours in serum-free media without phenol red before treatment with exogenous plasminogen without (open bars) or with (solid bars) TGF-β1 (2.0 ng/ml) for 16 hours. The cell culture supernatants were assessed for plasmin activity as described in Materials and Methods. *P < 0.001 versus untreated control. **P < 0.001 compared with the equivalent plasminogen dose without TGF-β1. n = 4 per condition. (B) IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated with plasminogen at the indicated doses for 16 hours and cell culture supernatants were assessed for fibronectin by SDS-PAGE and Western immunoblotting. (C) IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated with plasminogen ± TGF-β1 (2.0 ng/ml) for 16 hours, and cell culture supernatants were assessed for fibronectin by SDS-PAGE and Western immunoblotting. (D) IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated with plasminogen (50 μg/ml) for the time periods indicated in the absence (open bars) or presence (solid bars) of TGF-β1 (2.0 ng/ml) and cell culture supernatants were assessed for plasmin activity. *P < 0.001 compared with untreated control. **P < 0.001 compared with equivalent time-point without TGF-β1. n = 4 per condition. (E) Similarly cultured IMR-90 cells were treated with plasminogen (50 μg/ml) for the indicated times and cell culture supernatants were assessed for fibronectin by SDS-PAGE and Western immunoblotting. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments.
TGF-β1 Inhibits Plasminogen-Induced Fibroblast Apoptosis
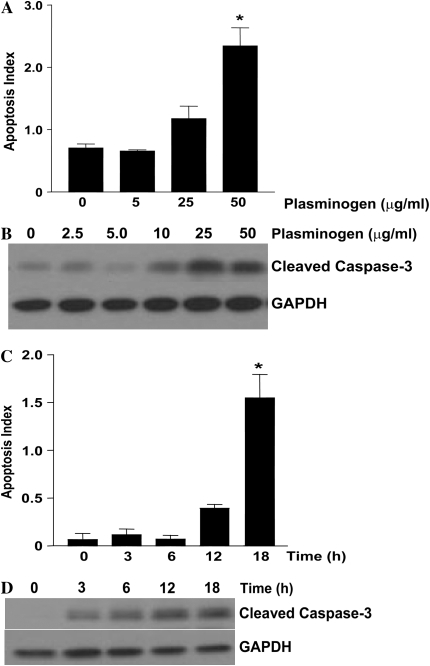
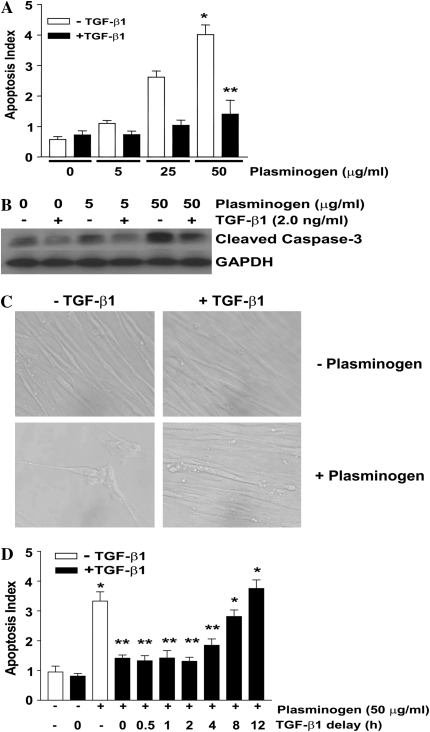
Having shown that plasmin induces fibroblast apoptosis, that fibroblasts activate plasminogen, and that plasminogen activation leads to fibronectin proteolysis, we next investigated the effects of exogenous plasminogen on fibroblast apoptosis. Treatment of IMR-90 fibroblasts with exogenous plasminogen induced apoptosis with a dose response (Figures 3A and 3B) and time course (Figures 3C and 3D) similar to that of plasminogen activation and plasminogen-mediated fibronectin proteolysis. To determine if TGF-β1 would also attenuate plasminogen-induced apoptosis, fibroblasts were exposed to plasminogen with or without TGF-β1 (2 ng/ml) for 18 hours and apoptosis was assessed (Figures 4A, 4B, and 4C). In contrast to its inability to limit plasmin-induced apoptosis, TGF-β1 conferred significant protection from the pro-apoptotic effects of plasminogen (Figures 4A, 4B, and 4C). TGF-β1–mediated protection from plasminogen-induced apoptosis was maintained when its administration was delayed up to 4 hours after plasminogen treatment, but the protection was lost if TGF-β1 was administered 8 or more hours after plasminogen (Figure 4D). These findings suggest that to inhibit apoptosis, the TGF-β1–induced “protective factor(s)” must be present before significant plasminogen activation has occurred.
Figure 3.
Plasminogen-induced fibroblast apoptosis is dose- and time-dependent. IMR-90 fibroblasts were cultured in a 96-well plate or in 35-mm dishes to 60% confluence and growth arrested for 24 hours before treatment with plasminogen. (A) Fibroblasts were treated with plasminogen for 18 hours and apoptosis was assessed via ELISA for ssDNA (n = 4; * P < 0.001 versus control). (B) Fibroblasts were treated with plasminogen (doses indicated) for 18 hours and cell lysates were assessed for cleaved caspase-3 by Western immunoblotting. The blot was then stripped and probed for GAPDH. (C) Fibroblasts in a 96-well plate were treated with plasminogen (50 μg/ml) and apoptosis was assessed by ELISA for ssDNA (n = 4; *P < 0.001 versus time 0). (D) Fibroblasts were treated with plasminogen (50 μg/ml) and whole cell lysates were assessed for cleaved caspase-3 by Western immunoblotting. The blots were stripped and re-probed for GAPDH. All data represent experiments performed at least three times.
Figure 4.
TGF-β1 inhibits plasminogen-induced fibroblast apoptosis. (A and B) IMR-90 fibroblasts were cultured and treated with plasminogen ± TGF-β1 (2.0 ng/ml) for 18 hours. (A) Apoptosis was assessed by ELISA for ssDNA. n = 4; *P < 0.001 versus control, **P < 0.001 versus plasminogen without TGF-β1. (B) Apoptosis was assessed by Western immunoblotting for cleaved caspase-3. The blot was then stripped and probed for GAPDH. (C) IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated with/without plasminogen (50 μg/ml) in the presence/absence of TGF-β1 (2 ng/ml) for 18 hours and visualized by microscopy. Representative photomicrographs are shown at ×20 power. (D) IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated with/without plasminogen (50 μg/ml) in the presence/absence of TGF-β1 given as a co-treatment or delayed for the times noted. Apoptosis was assessed by ELISA for ssDNA 18 hours after the plasminogen treatment. *P < 0.001 versus untreated control, **P < 0.001 versus compared with plasminogen treatment alone.
Next, we compared the effects of TGF-β1 and α2 antiplasmin or ɛ-aminocaproic acid on plasminogen-induced apoptosis (Figure E1 in the online supplement). α2-antiplasmin, a plasmin inhibitor, completely blocked plasminogen-induced fibroblast apoptosis and TGF-β1 conferred nearly equivalent protection (Figure E1-A and E1-B). The lysine analog, ɛ-aminocaproic acid also blocked plasminogen-induced apoptosis (Figure E1-C) (19, 29). These experiments confirm that fibroblast apoptosis induced by plasminogen requires plasminogen activation.
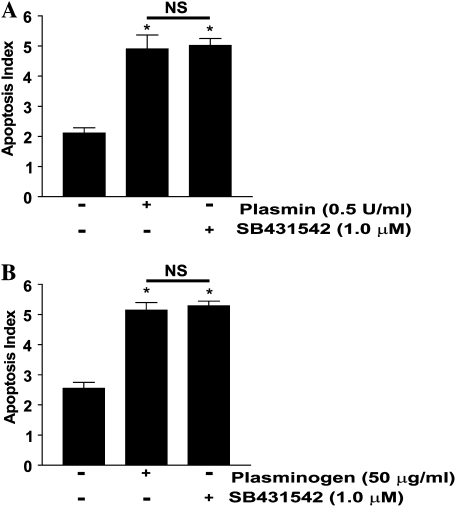
Plasmin has been shown to activate latent TGF-β1 from the ECM (30), providing a potential feedback mechanism to negatively regulate plasminogen-mediated apoptosis. To investigate whether plasmin-mediated TGF-β1 activation may, in the absence of exogenous TGF-β1, limit plasmin-mediated apoptosis, we treated IMR-90 fibroblasts with plasmin or plasminogen in the presence/absence of a pharmacologic inhibitor of the type 1 TGF-β receptor (ALK-5), SB431542. We have previously shown that this inhibitor blocks TGF-β1 SMAD-dependent signaling in IMR-90 fibroblasts (10). Neither plasmin nor plasminogen-mediated apoptosis increased with inhibition of TGF-β1 signaling (Figure 5). This finding suggests that any activation of latent TGF-β1 by plasmin is insufficient to overcome apoptosis induced by pericellular matrix proteolysis.
Figure 5.
Blockade of the type 1 TGF-β receptor does not increase plasminogen- or plasmin-mediated fibroblast apoptosis. (A) IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated with (A) plasmin (0.5 U/ml) or (B) plasminogen (50 μg/ml) in the presence/absence of the ALK-5 inhibitor SB431542 (1.0 μM). Apoptosis was assessed by ELISA for ssDNA after 18 hours. *P < 0.001 versus untreated controls (n = 4 per condition, and the experiment was repeated three times).
Plasminogen-Mediated Fibroblast Apoptosis Is Independent of MMP Activity
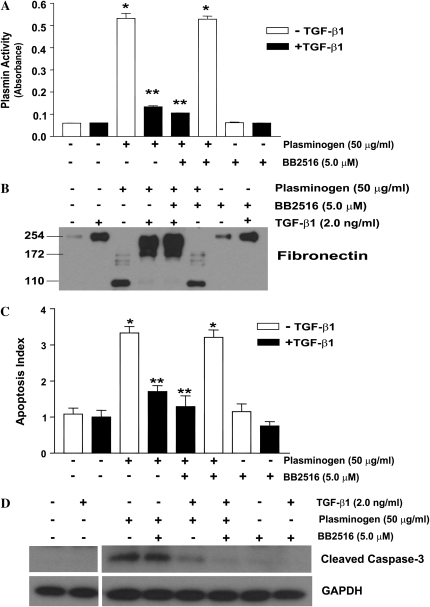
In addition to fibrinolysis and ECM proteolysis, plasmin has been implicated in the activation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), a family of proteinases capable of degrading all components of the ECM. We sought to determine if fibroblast apoptosis induced by plasminogen activation was a direct effect of plasmin-mediated ECM proteolysis or secondary to MMP activation. We first assessed if a broad spectrum MMP inhibitor (marimastat, BB2516), at doses known to inhibit MMPs, would alter plasminogen activation and/or fibronectin proteolysis (31, 32). IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated with plasminogen in the presence/absence of BB2516 (5 μM) and/or TGF-β1 for 18 hours. BB2516 had no significant effect on plasminogen activation, fibronectin proteolysis, or the ability of TGF-β1 to inhibit these cellular and pericellular processes (Figures 6A and 6B). Similarly, BB2516 had no effect on plasminogen-induced fibroblast apoptosis or TGF-β1–mediated protection from apoptosis (Figures 6C and 6D).
Figure 6.
Plasminogen-induced fibroblast apoptosis is not mediated by MMPs. IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated with/without plasminogen (50 μg/ml) ± TGF-β1 (2.0 ng/ml) and/or the broad-spectrum MMP inhibitor BB2516 (5.0 μM) for 18 hours. (A) Cell culture supernatants were assessed for plasmin activity. n = 4; *P < 0.001 versus controls, **P < 0.001 versus plasminogen alone. (B) Cell culture supernatants were assessed for fibronectin by Western immunoblotting. (C) Apoptosis was assessed using ELISA for ssDNA. n = 4; *P < 0.001 versus control, **P < 0.001 versus plasminogen. (D) Apoptosis was also assessed by Western immunoblotting of whole cell lysates for cleaved caspase-3. Blots were stripped and probed for GAPDH. All data represent experiments performed at least three times.
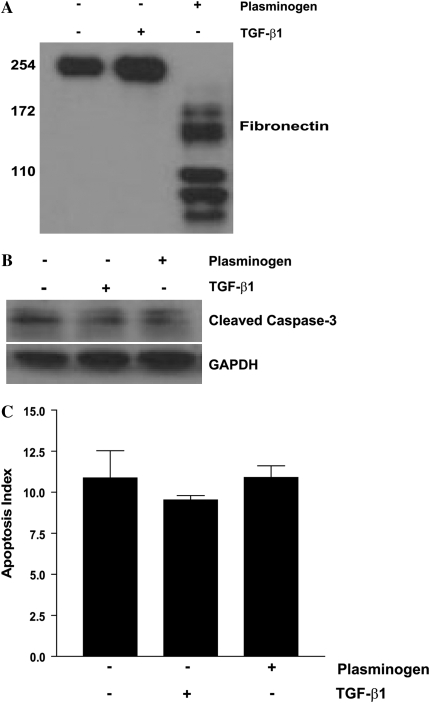
Plasminogen-Induced Fibroblast Apoptosis Is Not Mediated by Fibronectin Degradation Peptides
Soluble fibronectin peptides have been shown to induce fibroblast anoikis through competitive blockade of integrin-dependent adhesion signaling pathways (33). We questioned if plasmin-mediated fibroblast apoptosis might be induced by the generation of soluble fibronectin degradation peptides released into the cellular microenvironment. To test this possibility, conditioned media was collected from fibroblasts treated with/without TGF-β1 or plasminogen. We confirmed that conditioned media from plasminogen-treated fibroblasts, but not the TGF-β1 or control fibroblasts, contained fibronectin proteolytic peptides (Figure 7A). α2-antiplasmin was added to the conditioned media to neutralize residual plasmin activity, and the conditioned media was then transferred to growth-arrested fibroblasts that were pre-treated with suramin (300 μM) to block activation of growth factor receptors (66). Apoptosis was assessed after 18 hours (Figures 7B and 7C). In these experiments, we found no differences in apoptosis of cells treated with conditioned media containing fibronectin peptide fragments compared with fibroblasts treated with conditioned media lacking these cleaved peptides. These studies indicate that, while pericellular fibronectin degradation is associated with fibroblast apoptosis, the soluble fibronectin peptides themselves are incapable of mediating apoptosis in this context.
Figure 7.
Fibronectin proteolytic peptides in conditioned media do not induce fibroblast apoptosis. IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated with/without plasminogen (50 μg/ml) or TGF-β1 (2 ng/ml) for 18 hours. (A) Cell culture supernatants were assessed for fibronectin degradation peptides by Western immunoblotting. (B and C) α2-antiplasmin was added to the culture supernatants to neutralize residual plasmin activity. This conditioned media was then used to treat growth-arrested IMR-90 fibroblasts pre-treated with suramin (300 μM). After 18 hours, apoptosis was assessed by (B) Western immunoblotting for cleaved caspase 3 or by (C) ELISA for ssDNA.
TGF-β1 Protection from Plasminogen-Induced Apoptosis Is Mediated by PAI-1
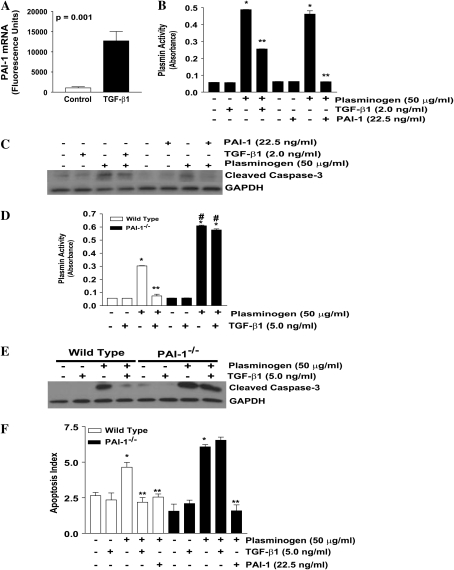
Fibroblast apoptosis induced by plasminogen correlates with plasmin activity. Moreover, we found that plasminogen-mediated apoptosis, but not plasmin-mediated apoptosis, was inhibited by TGF-β1 if the TGF-β1 was given before significant plasminogen activation had occurred. These findings suggested that the apoptosis protection afforded by TGF-β1 may depend on the inhibition of plasminogen activation. Previous studies have shown that the expression of PAI-1, which inhibits plasminogen activation, is upregulated by TGF-β1 in lung fibroblasts (34). In our experimental conditions, PAI-1 expression is potently induced by TGF-β1 in IMR-90 fibroblasts (Figure 8A). To determine if PAI-1 would inhibit plasminogen-mediated apoptosis, IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated with plasminogen ± TGF-β1 or exogenous PAI-1 (Figures 8B and 8C). Analysis of the cell culture supernatants confirmed that both exogenous PAI-1 and TGF-β1 significantly blocked plasminogen activation. In addition, both TGF-β1 and exogenous PAI-1 attenuated plasminogen-induced fibroblast apoptosis (Figure 8C).
Figure 8.
PAI-1 expression is required for TGF-β1 inhibition of plasminogen-induced fibroblast apoptosis. (A) IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated ± TGF-β1 (2.0 ng/ml) for 18 hours. PAI-1 RNA was assessed via Affymetrix microarray gene chip analysis. n = 3; P = 0.001. (B) IMR-90 fibroblasts were treated with plasminogen (50 μg/ml) ± TGF-β1 (2.0 ng/ml) or exogenous PAI-1 (22.5 ng/ml) for 18 hours, and cell culture supernatants were assessed for plasmin activity. n = 2; *P < 0.001 versus control. **P < 0.001 versus plasminogen. (C) Whole cell lysates from IMR-90 fibroblasts were assessed for cleaved caspase-3 by Western immunoblotting, and the blots were stripped and probed for GAPDH. (D) Primary lung fibroblasts isolated from wild-type (open bars) and PAI-1−/− mice (solid bars) were cultured to 60% confluence and treated with plasminogen (50 μg/ml) ± TGF-β1 (5.0 ng/ml) for 18 hours. Cell culture supernatants were assessed for plasmin activity. n = 2; *P < 0.001 versus untreated control, **P < 0.001 versus plasminogen alone; #P < 0.001 versus wild-type + plasminogen. (E) Primary lung fibroblasts from wild-type and PAI-1−/− mice were treated with plasminogen (50 μg/ml) ± TGF-β1 (5.0 ng/ml) for 18 hours and whole cell lysates were assessed for cleaved caspase-3. Membranes were stripped and probed for GAPDH. (F) Primary lung fibroblasts from wild-type (open bars) and PAI-1−/− (solid bars) mice were treated with plasminogen (50 μg/ml) ± TGF-β1 (5.0 ng/ml) or exogenous PAI-1 (22.5 ng/ml) for 18 hours and apoptosis was assessed by ELISA for ssDNA. n = 4; *P < 0.01 versus untreated control; **P < 0.001 versus plasminogen treated. Data represent three independent experiments.
To confirm that PAI-1 is required for TGF-β1 inhibition of plasminogen-induced apoptosis, we used primary lung fibroblasts from wild-type (WT) and PAI-1 null mice (PAI-1−/−). As with IMR-90 fibroblasts and NIH-3T3 fibroblasts, wild-type murine lung fibroblasts activate plasminogen and are susceptible to plasminogen-mediated apoptosis (Figures 8D, open bars; 8E; and 8F, open bars). The effect of TGF-β1 on inhibition of plasminogen activation was found to be greater with 5.0 ng/ml than 2.0 ng/ml. At this dose of TGF-β1, significant inhibition of plasminogen activation and blockade of plasminogen-induced fibroblast apoptosis was observed (Figures 8D, open bars; 8E; and 8F, open bars). Relative to wild-type fibroblasts, PAI-1−/− fibroblasts generated increased plasmin activity after plasminogen administration and, importantly, TGF-β1 failed to inhibit plasminogen activation (Figure 8D, solid bars). Apoptosis in the PAI-1−/− fibroblasts correlated with plasmin activity; PAI- 1−/− fibroblasts displayed increased apoptosis after administration of plasminogen when compared with wild-type fibroblasts, and TGF-β1 failed to confer protection from plasminogen-induced apoptosis (Figures 8E and 8F, solid bars). Finally, the addition of exogenous PAI-1 to PAI-1−/− fibroblasts rescued the knock-out phenotype and restored apoptosis resistance in plasminogen-treated fibroblasts (Figure 8F, solid bars).
DISCUSSION
Reestablishment of normal tissue architecture and function after injury requires the precise spatial and temporal regulation of reparative responses including the recruitment, activation, and elimination of (myo)fibroblasts (35). Fibroblast/myofibroblast apoptosis represents a critical checkpoint in the resolution of wound repair, as myofibroblast resistance to apoptosis is associated with persistent tissue fibrosis (1, 4, 11, 36). Little is known about the physiologic stimulus of fibroblast apoptosis in the context of normal wound healing, but hypotheses have recently focused on the interactions between the cells and their pericellular matrix (3, 36). We, and others, have shown that fibroblasts are susceptible to anoikis, a form of apoptosis induced by loss of adhesion-mediated signals that may represent an important mechanism for mesenchymal cell apoptosis (10, 37). In this study, we sought to define relevant mechanisms regulating fibroblast/myofibroblast anoikis, and our findings provide additional insights into the roles of TGF-β1 and the plasminogen activation system in this process. First, we demonstrate that plasminogen activation by fibroblasts induces pericellular fibronectin proteolysis in association with fibroblast anoikis. We then show that TGF-β1 blocks these plasminogen-mediated effects via up-regulation of PAI-1, suggesting that PAI-1, at least in part, mediates the anti-proteolytic and anti-apoptotic effects of TGF-β1. These data demonstrate a novel mechanism by which TGF-β1 and the plasminogen activation system interact to regulate fibroblast apoptosis.
This study is the first, to our knowledge, to demonstrate that TGF-β1 regulates fibroblast anoikis induced by plasminogen activation. Plasminogen activation induces dose- and time-dependent fibroblast apoptosis in association with pericellular fibronectin proteolysis. In response to TGF-β1, fibroblasts up-regulate PAI-1 expression, blocking the activation of exogenous plasminogen and decreasing proteolysis of fibronectin (Figure 9). This creates an anti-proteolytic cellular microenvironment that would favor the accumulation and stabilization of extracellular matrix, key features of progressive tissue fibrosis. In addition, our data show that plasminogen activation induces apoptosis of primary human embryonic lung fibroblasts, primary murine lung fibroblasts and NIH-3T3 fibroblasts. Importantly, TGF-β1, a key cytokine implicated in the pathogenesis of fibrotic diseases, inhibits fibroblast apoptosis induced by plasminogen activation. The failure of TGF-β1 to inhibit apoptosis in PAI-1–deficient fibroblasts supports a central role for PAI-1 in the protection against plasminogen-induced apoptosis.
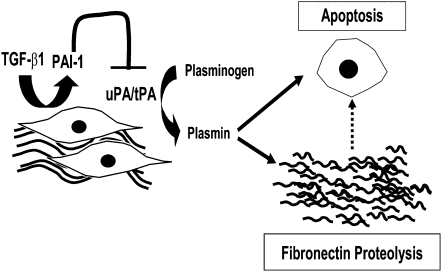
Figure 9.
Proposed mechanism of plasminogen-mediated apoptosis and the effect of TGF-β1. Fibroblasts secrete a fibronectin-rich pericellular matrix and receive adhesion-mediated signals that regulate cell phenotype. Pericellular matrix–generated signals may include biomechanical and tensile forces that promote or sustain pro-survival signals. Fibroblasts express plasminogen activators (uPA and/or tPA), which activate plasminogen in the cellular microenvironment to plasmin, which then mediates fibronectin proteolysis and fibroblast apoptosis. The specific mechanism linking pericellular fibronectin proteolysis to fibroblast apoptosis has not been determined. The pro-fibrotic cytokine, TGF-β1, induces the secretion of PAI-1, which blocks plasminogen activation, fibronectin proteolysis, and fibroblast apoptosis.
In accord with these findings, another recent study reported that plasminogen activation in NIH-3T3 and primary murine lung fibroblasts requires uPA and is inhibited by PAI-1 (19). In addition, plasminogen activation by vascular smooth muscle cells and CHO fibroblasts has been shown to induce ECM proteolysis (38, 39). Our finding that PAI-1 is required for TGF-β1 inhibition of plasminogen-mediated apoptosis is also in agreement with a prior study in vascular smooth muscle cells (40). A related serpin, nexin-1, has been shown to inhibit plasminogen-induced fibroblast apoptosis (39).
The effects of plasminogen activation on extracellular matrix proteolysis and mesenchymal cell fate remain poorly understood and recent investigations, including the current study, suggest that they are diverse and contextual. Studies in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), for example, describe several biological effects of plasminogen activation (38–41). One study in rat aortic VSMCs shows that tPA-mediated plasminogen activation rapidly induces apoptosis (38). Another study shows that human cerebrovascular smooth muscle cells use uPA-mediated plasminogen activation to degrade pathogenic β-amyloid proteins associated with Alzheimer's disease. Sustained plasminogen activation in these cells, however, induces anoikis, a mechanism thought to contribute to loss of blood vessel integrity and cerebral hemorrhage (41). Additional studies have shown that plasmin-mediated release of growth factors from the ECM may stimulate fibroblast proliferation (42) and that increased PAI-1 expression contributes to fibroblast senescence (43). Finally, studies in vascular smooth muscle cells show that plasmin-mediated activation of latent TGF-β1 promotes mesenchymal cell survival (17, 44). In the current study, plasmin-mediated TGF-β1 activation was not directly measured. Inhibition of the ALK-5 receptor, however, did not further increase plasminogen- or plasmin-mediated apoptosis, indicating that TGF-β1 activation by plasmin does not significantly alter fibroblast susceptibility to apoptosis. Collectively, these studies demonstrate the diverse effects of plasminogen activation on mesenchymal cell phenotypes and highlight the complex mechanisms by which specific microenvironments regulate cellular phenotypes.
In the current study, we questioned whether plasmin-mediated proteolysis of fibronectin might induce fibroblast apoptosis through the generation of soluble fibronectin peptides that competitively inhibit integrin-mediated signaling (10, 33, 37). While fibroblast apoptosis closely correlated with plasminogen activation and the appearance of soluble fibronectin fragments in the cell culture supernatant, these soluble fragments were not sufficient to mediate apoptosis when compared with that obtained from untreated or TGF-β1–treated fibroblasts, suggesting that these peptides do not directly mediate fibroblast apoptosis. Plasmin is also known to activate other extracellular matrix proteases, including matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), which have also been implicated in the pathogenesis of fibrotic disease and in the regulation of fibroblast phenotypes (18, 45–47). In our studies, a broad-spectrum MMP inhibitor had no effect on plasminogen-induced apoptosis. Thus, our data indicate that plasminogen-induced fibroblast apoptosis is associated with, but is not dependent on, the generation of soluble products of ECM degradation and that fibroblast apoptosis is independent of MMP activity.
Although the precise mechanism of plasminogen-mediated fibroblast apoptosis remains to be determined, alterations in cell shape and biomechanics may be a plausible explanation. Such disruptions of adhesion-mediated signal transduction have been shown to alter the phenotype of adhesion-dependent cells such as fibroblasts (3, 13, 48). Our studies support a potential role for biomechanical unloading due to ECM proteolysis in the induction of fibroblast apoptosis, and are consistent with studies showing that fibroblasts within collagen matrices undergo apoptosis after release and contraction of an attached matrix (48–51). Similarly, studies have reported that rapid cell shrinkage induces fibroblast apoptosis and that tension activates pro-survival signals such as PI3K/AKT in association with integrin up-regulation (52, 53).
The plasminogen activation system, which is regulated by the balance between plasminogen activators and inhibitors, has been causally linked to fibrosis of the lung and other organ systems (14, 54–60). Mice that overexpress PAI-1 develop severe fibrosis, whereas mice deficient in PAI-1 or overexpressing uPA are highly resistant to pulmonary fibrosis (56, 59). Moreover, the anti-fibrotic effects of plasminogen activation are not attributable to fibrinolysis, as mice deficient in fibrinogen maintain susceptibility to bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis (61). Studies show that bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) from patients with acute and chronic lung disease has alterations in the levels and/or activity of components of the coagulation and fibrinolytic sytems, including fibrin, plasminogen, plasminogen activators, and PAI-1 (58, 62–64). The presence of these components in the BALF during states of lung injury and repair suggests that they diffuse from the vascular compartment and are available to act on cells and the extracellular matrix within the interstitial compartment.
Our studies primarily used low passage IMR-90 fibroblasts, which are primary human embryonic lung fibroblasts that undergo replicative senescence at higher passage (26). However, plasminogen activation–induced apoptosis and protection by TGF-β1 were recapitulated in NIH-3T3 fibroblasts and in primary murine lung fibroblasts. In the murine cell experiments, higher doses of TGF-β1 were required to inhibit plasminogen activation and fibroblast apoptosis, reflecting possible differences in the sensitivity of these different cell types to TGF-β1 or differences in basal levels of PAI-1. The susceptibility of normal and disease-associated primary adult human lung fibroblasts to plasminogen-induced apoptosis is currently not known. Our in vitro studies demonstrate that plasminogen activation by fibroblasts promotes fibronectin proteolysis, an effect that is consistent with the in vivo anti-fibrotic effects of plasminogen activation (56, 59, 65). Further studies are required to determine the role of plasminogen activation in the regulation of fibroblast apoptosis in vivo. Our finding that TGF-β1 inhibits fibroblast apoptosis by upregulation of PAI-1 demonstrates a novel mechanism by which PAI-1 may mediate pro-fibrotic effects in vivo. Furthermore, this report provides a mechanistic link between TGF-β1 and the plasminogen activation system in regulating fibroblast apoptosis.
Supplementary Material
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health grants K08 HL081059 (J.C.H.), P50 HL074024 (V.J.T.), R01 HL078871 (T.H.S.), P50 HL056402 (R.H.S.), and the American Lung Association Dalsemer Award (J.C.H.).
This article has an online supplement, which is accessible from this issue's table of contents at www.atsjournals.org
Originally Published in Press as DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0174OC on July 26, 2007
Conflict of Interest Statement: None of the authors has a financial relationship with a commercial entity that has an interest in the subject of this manuscript.
References
- 1.Tomasek JJ, Gabbiani G, Hinz B, Chaponnier C, Brown RA. Myofibroblasts and mechano-regulation of connective tissue remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2002;3:349–363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Desmouliere A, Redard M, Darby I, Gabbiani G. Apoptosis mediates the decrease in cellularity during the transition between granulation tissue and scar. Am J Pathol 1995;146:56–66. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hinz B, Phan SH, Thannickal VJ, Galli A, Bochaton-Piallat ML, Gabbiani G. The myofibroblast: one function, multiple origins. Am J Pathol 2007;170:1807–1816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Thannickal VJ, Horowitz JC. Evolving concepts of apoptosis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2006;3:350–356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gabbiani G. The myofibroblast in wound healing and fibrocontractive diseases. J Pathol 2003;200:500–503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Jun JB, Kuechle M, Harlan JM, Elkon KB. Fibroblast and endothelial apoptosis in systemic sclerosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2003;15:756–760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Border WA, Noble NA. Transforming growth factor beta in tissue fibrosis. N Engl J Med 1994;331:1286–1292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Thannickal VJ, Lee DY, White ES, Cui Z, Larios JM, Chacon R, Horowitz JC, Day RM, Thomas PE. Myofibroblast differentiation by transforming growth factor-beta1 is dependent on cell adhesion and integrin signaling via focal adhesion kinase. J Biol Chem 2003;278:12384–12389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Horowitz JC, Lee DY, Waghray M, Keshamouni VG, Thomas PE, Zhang H, Cui Z, Thannickal VJ. Activation of the pro-survival phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/akt pathway by transforming growth factor-beta1 in mesenchymal cells is mediated by p38 mapk-dependent induction of an autocrine growth factor. J Biol Chem 2004;279:1359–1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Horowitz JC, Rogers DS, Sharma V, Vittal R, White ES, Cui Z, Thannickal VJ. Combinatorial activation of fak and akt by transforming growth factor-beta1 confers an anoikis-resistant phenotype to myofibroblasts. Cell Signal 2007;19:761–771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Thannickal VJ, Toews GB, White ES, Lynch JP III, Martinez FJ. Mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. Annu Rev Med 2004;55:395–417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Frisch SM, Vuori K, Ruoslahti E, Chan-Hui PY. Control of adhesion-dependent cell survival by focal adhesion kinase. J Cell Biol 1996;134:793–799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Michel JB. Anoikis in the cardiovascular system: known and unknown extracellular mediators. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2003;23:2146–2154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lijnen HR. Elements of the fibrinolytic system. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2001;936:226–236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bonnefoy A, Legrand C. Proteolysis of subendothelial adhesive glycoproteins (fibronectin, thrombospondin, and von willebrand factor) by plasmin, leukocyte cathepsin g, and elastase. Thromb Res 2000;98:323–332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Houard X, Monnot C, Dive V, Corvol P, Pagano M. Vascular smooth muscle cells efficiently activate a new proteinase cascade involving plasminogen and fibronectin. J Cell Biochem 2003;88:1188–1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lyons RM, Keski-Oja J, Moses HL. Proteolytic activation of latent transforming growth factor-beta from fibroblast-conditioned medium. J Cell Biol 1988;106:1659–1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chakraborti S, Mandal M, Das S, Mandal A, Chakraborti T. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases: An overview. Mol Cell Biochem 2003;253:269–285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Matsuoka H, Sisson TH, Nishiuma T, Simon RH. Plasminogen-mediated activation and release of hepatocyte growth factor from extracellular matrix. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2006;35:705–713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kucharewicz I, Kowal K, Buczko W, Bodzenta-Lukaszyk A. The plasmin system in airway remodeling. Thromb Res 2003;112:1–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chapman HA. Disorders of lung matrix remodeling. J Clin Invest 2004;113:148–157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Singer AJ, Clark RA. Cutaneous wound healing. N Engl J Med 1999;341:738–746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Loskutoff DJ, Quigley JP. Pai-1, fibrosis, and the elusive provisional fibrin matrix. J Clin Invest 2000;106:1441–1443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dellas C, Loskutoff DJ. Historical analysis of pai-1 from its discovery to its potential role in cell motility and disease. Thromb Haemost 2005;93:631–640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Horowitz JC, Rogers DS, Sisson TH, Thannickal VJ. Tgf-beta1 inhibition of plasminogen activation regulates fibroblast apoptosis. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2007;175:A336. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nichols WW, Murphy DG, Cristofalo VJ, Toji LH, Greene AE, Dwight SA. Characterization of a new human diploid cell strain, imr-90. Science 1977;196:60–63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Vittal R, Zhang H, Han MK, Moore BB, Horowitz JC, Thannickal VJ. Effects of the protein kinase inhibitor, imatinib mesylate, on epithelial/mesenchymal phenotypes: implications for treatment of fibrotic diseases. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2007;321:35–44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lazar MH, Christensen PJ, Du M, Yu B, Subbotina NM, Hanson KE, Hansen JM, White ES, Simon RH, Sisson TH. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 impairs alveolar epithelial repair by binding to vitronectin. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2004;31:672–678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ellis V, Whawell SA, Werner F, Deadman JJ. Assembly of urokinase receptor-mediated plasminogen activation complexes involves direct, non-active-site interactions between urokinase and plasminogen. Biochemistry 1999;38:651–659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lyons RM, Gentry LE, Purchio AF, Moses HL. Mechanism of activation of latent recombinant transforming growth factor beta 1 by plasmin. J Cell Biol 1990;110:1361–1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kim J, Yu W, Kovalski K, Ossowski L. Requirement for specific proteases in cancer cell intravasation as revealed by a novel semiquantitative pcr-based assay. Cell 1998;94:353–362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Roy R, Wewer UM, Zurakowski D, Pories SE, Moses MA. Adam 12 cleaves extracellular matrix proteins and correlates with cancer status and stage. J Biol Chem 2004;279:51323–51330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Akiyama SK, Yamada KM. Synthetic peptides competitively inhibit both direct binding to fibroblasts and functional biological assays for the purified cell-binding domain of fibronectin. J Biol Chem 1985;260:10402–10405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Keski-Oja J, Raghow R, Sawdey M, Loskutoff DJ, Postlethwaite AE, Kang AH, Moses HL. Regulation of mrnas for type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor, fibronectin, and type i procollagen by transforming growth factor-beta: divergent responses in lung fibroblasts and carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 1988;263:3111–3115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Desmouliere A, Chaponnier C, Gabbiani G. Tissue repair, contraction, and the myofibroblast. Wound Repair Regen 2005;13:7–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hinz B, Gabbiani G. Cell-matrix and cell-cell contacts of myofibroblasts: role in connective tissue remodeling. Thromb Haemost 2003;90:993–1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hadden HL, Henke CA. Induction of lung fibroblast apoptosis by soluble fibronectin peptides. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;162:1553–1560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Meilhac O, Ho-Tin-Noe B, Houard X, Philippe M, Michel JB, Angles-Cano E. Pericellular plasmin induces smooth muscle cell anoikis. FASEB J 2003;17:1301–1303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Rossignol P, Ho-Tin-Noe B, Vranckx R, Bouton MC, Meilhac O, Lijnen HR, Guillin MC, Michel JB, Angles-Cano E. Protease nexin-1 inhibits plasminogen activation-induced apoptosis of adherent cells. J Biol Chem 2004;279:10346–10356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rossignol P, Angles-Cano E, Lijnen HR. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 impairs plasminogen activation-mediated vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis. Thromb Haemost 2006;96:665–670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Davis J, Wagner MR, Zhang W, Xu F, Van Nostrand WE. Amyloid beta-protein stimulates the expression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (upa) and its receptor (upar) in human cerebrovascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 2003;278:19054–19061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Mandal SK, Rao LV, Tran TT, Pendurthi UR. A novel mechanism of plasmin-induced mitogenesis in fibroblasts. J Thromb Haemost 2005;3:163–169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kortlever RM, Higgins PJ, Bernards R. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 is a critical downstream target of p53 in the induction of replicative senescence. Nat Cell Biol 2006;8:877–884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.George SJ, Johnson JL, Smith MA, Angelini GD, Jackson CL. Transforming growth factor-beta is activated by plasmin and inhibits smooth muscle cell death in human saphenous vein. J Vasc Res 2005;42:247–254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Pardo A, Selman M. Matrix metalloproteases in aberrant fibrotic tissue remodeling. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2006;3:383–388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ramos C, Montano M, Garcia-Alvarez J, Ruiz V, Uhal BD, Selman M, Pardo A. Fibroblasts from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and normal lungs differ in growth rate, apoptosis, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases expression. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2001;24:591–598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Arthur MJ. Fibrogenesis ii. Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in liver fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2000;279:G245–G249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tian B, Lessan K, Kahm J, Kleidon J, Henke C. Beta 1 integrin regulates fibroblast viability during collagen matrix contraction through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/akt/protein kinase b signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 2002;277:24667–24675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Nho RS, Xia H, Diebold D, Kahm J, Kleidon J, White E, Henke CA. Pten regulates fibroblast elimination during collagen matrix contraction. J Biol Chem 2006;281:33291–33301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zhu YK, Umino T, Liu XD, Wang HJ, Romberger DJ, Spurzem JR, Rennard SI. Contraction of fibroblast-containing collagen gels: initial collagen concentration regulates the degree of contraction and cell survival. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 2001;37:10–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Grinnell F, Zhu M, Carlson MA, Abrams JM. Release of mechanical tension triggers apoptosis of human fibroblasts in a model of regressing granulation tissue. Exp Cell Res 1999;248:608–619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Xia H, Nho RS, Kahm J, Kleidon J, Henke CA. Focal adhesion kinase is upstream of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/akt in regulating fibroblast survival in response to contraction of type i collagen matrices via a beta 1 integrin viability signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 2004;279:33024–33034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Katsumi A, Naoe T, Matsushita T, Kaibuchi K, Schwartz MA. Integrin activation and matrix binding mediate cellular responses to mechanical stretch. J Biol Chem 2005;280:16546–16549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Bergheim I, Guo L, Davis MA, Duveau I, Arteel GE. Critical role of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in cholestatic liver injury and fibrosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2006;316:592–600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.de Giorgio-Miller A, Bottoms S, Laurent G, Carmeliet P, Herrick S. Fibrin-induced skin fibrosis in mice deficient in tissue plasminogen activator. Am J Pathol 2005;167:721–732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Eitzman DT, McCoy RD, Zheng X, Fay WP, Shen T, Ginsburg D, Simon RH. Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in transgenic mice that either lack or overexpress the murine plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene. J Clin Invest 1996;97:232–237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Oda T, Jung YO, Kim HS, Cai X, Lopez-Guisa JM, Ikeda Y, Eddy AA. Pai-1 deficiency attenuates the fibrogenic response to ureteral obstruction. Kidney Int 2001;60:587–596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Olman MA, Mackman N, Gladson CL, Moser KM, Loskutoff DJ. Changes in procoagulant and fibrinolytic gene expression during bleomycin-induced lung injury in the mouse. J Clin Invest 1995;96:1621–1630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Sisson TH, Hanson KE, Subbotina N, Patwardhan A, Hattori N, Simon RH. Inducible lung-specific urokinase expression reduces fibrosis and mortality after lung injury in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2002;283:L1023–L1032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Zhang G, Kim H, Cai X, Lopez-Guisa JM, Alpers CE, Liu Y, Carmeliet P, Eddy AA. Urokinase receptor deficiency accelerates renal fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 2003;14:1254–1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Hattori N, Degen JL, Sisson TH, Liu H, Moore BB, Pandrangi RG, Simon RH, Drew AF. Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in fibrinogen-null mice. J Clin Invest 2000;106:1341–1350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Idell S, James KK, Levin EG, Schwartz BS, Manchanda N, Maunder RJ, Martin TR, McLarty J, Fair DS. Local abnormalities in coagulation and fibrinolytic pathways predispose to alveolar fibrin deposition in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Invest 1989;84:695–705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Kotani I, Sato A, Hayakawa H, Urano T, Takada Y, Takada A. Increased procoagulant and antifibrinolytic activities in the lungs with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thromb Res 1995;77:493–504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Nakstad B, Lyberg T, Skjonsberg OH, Boye NP. Local activation of the coagulation and fibrinolysis systems in lung disease. Thromb Res 1990;57:827–838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Sisson TH, Hattori N, Xu Y, Simon RH. Treatment of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by transfer of urokinase-type plasminogen activator genes. Hum Gene Ther 1999;10:2315–2323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Sachsenmaier C, Radler-Pohl A, Zinck R, Nordheim A, Herrlich P, Rahmsdorf HJ. Involvement of growth factor receptors in the mammalian uvc response. Cell 1994;78:963–972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.