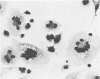
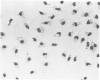
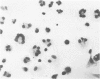
Abstract
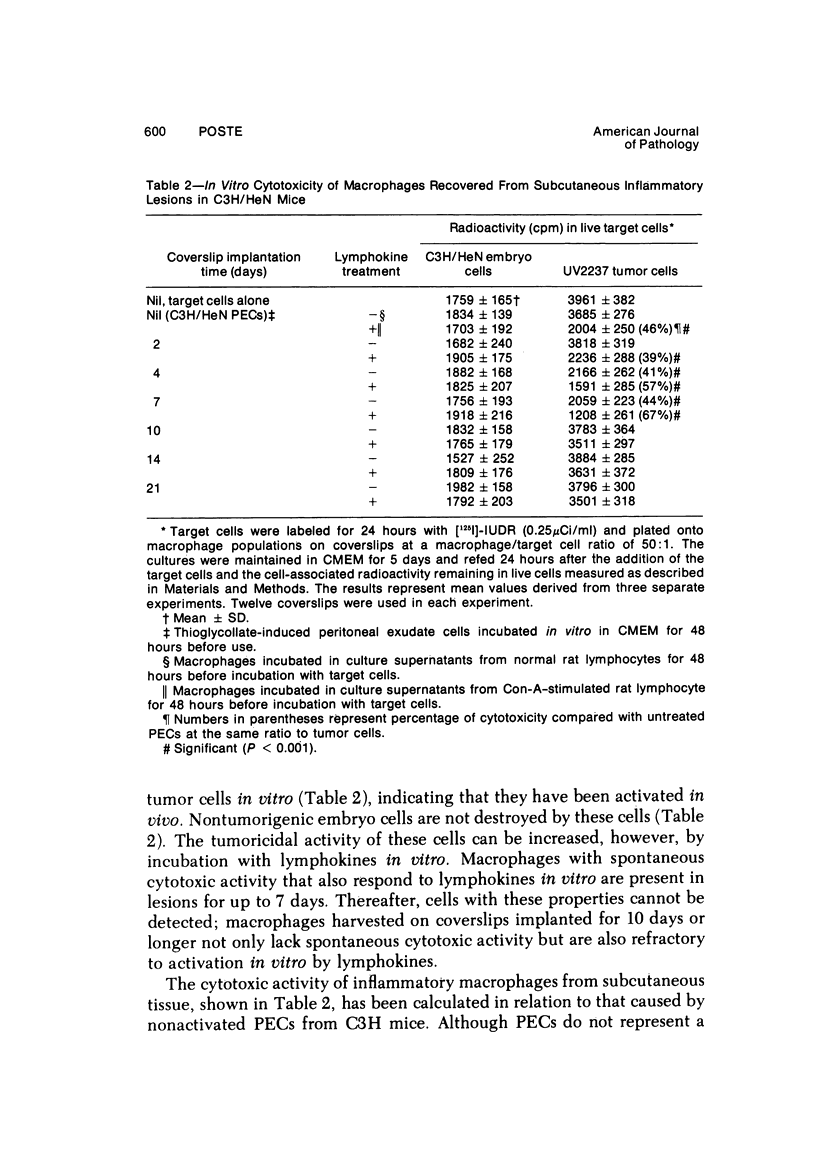
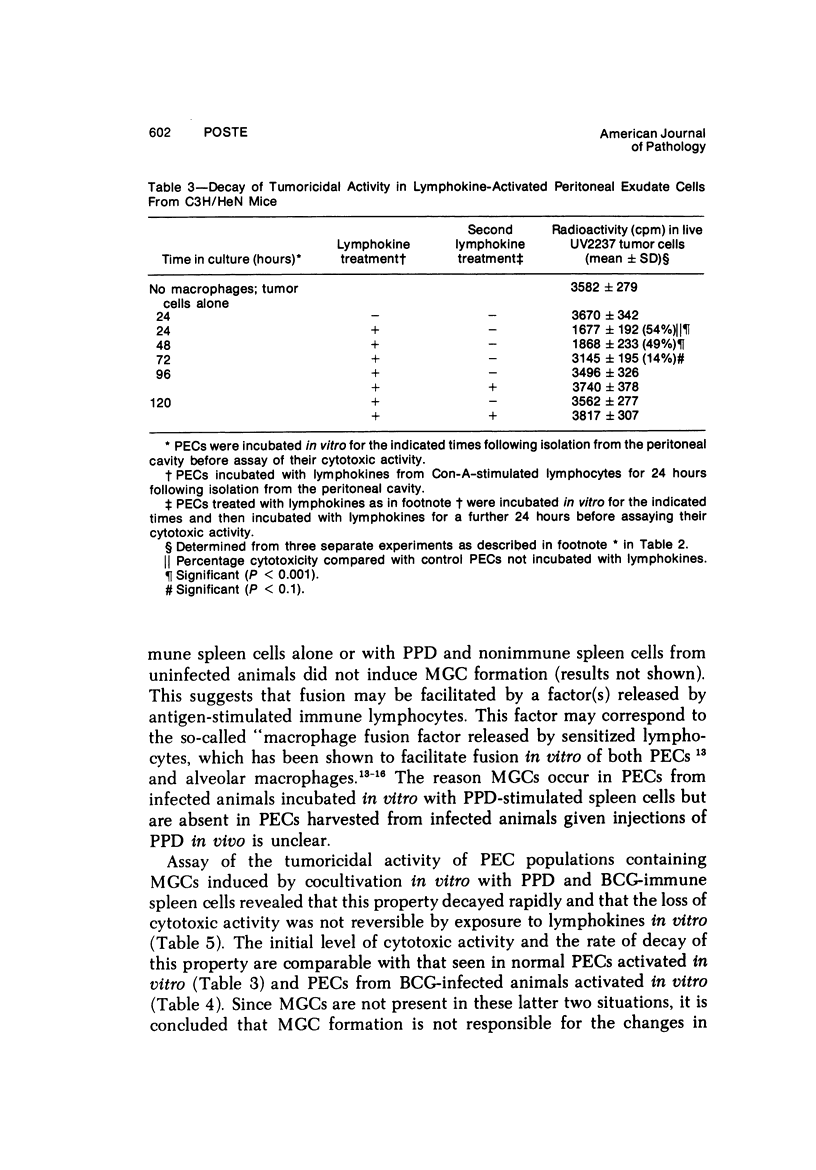
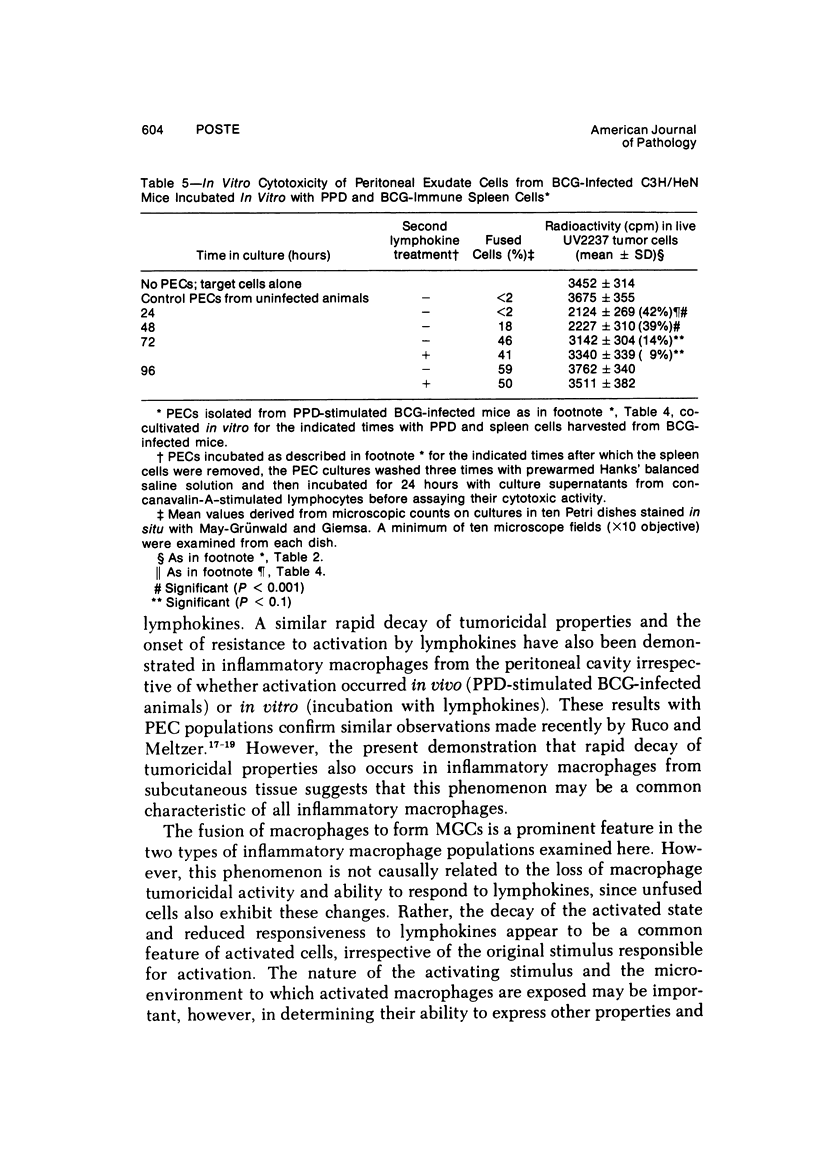
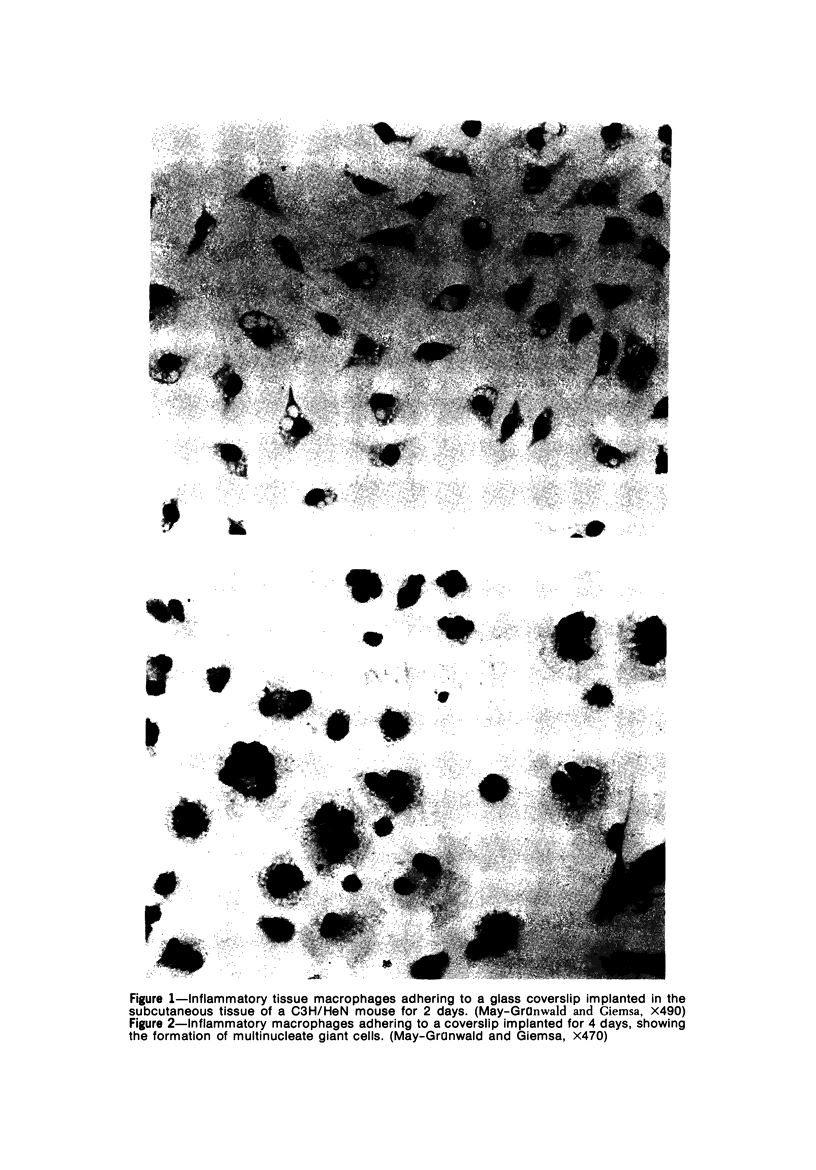
Peritoneal exudate cells from C3H/HeN mice infected with bacille Calmette Guérin (BCG) and subcutaneous inflammatory macrophages from uninfected mice exhibit spontaneous cytotoxicity for tumor cells in vitro, but their tumoricidal activity can be increased by incubation in vitro with lymphokines released by mitogen- or antigen-stimulated lymphocytes. Inflammatory macrophages from these sites are only susceptible to activation in vitro by lymphokines for a short period (less than 4 days) following their initial emigration from the circulation to the site of inflammation. The expression of tumoricidal activity by activated macrophages is similarly short-lived (less than 4 days). Once the tumoricidal state is lost it cannot be restored by further incubation with lymphokines in vitro. Fusion of macrophages to form multinucleate giant cells (MGCs) accompanies the loss of tumoricidal activity and the onset of resistance to activation by lymphokines, but the fusion process is not responsible for these changes, since unfused macrophages are similarly affected. Activation and acquisition of tumoricidal properties is confined to young macrophages recruited from the circulation during acute inflammation. Older macrophages and MGCs in chronic inflammatory lesions in which recruitment of new macrophages has ceased are nontumoricidal and are refractory to activation by lymphokines in vitro. These findings are discussed in relation to the efficiency of macrophage-mediated destruction of tumors in vivo and the amplification of macrophage antitumor activity by immunotherapeutic agents.
Full text
PDF









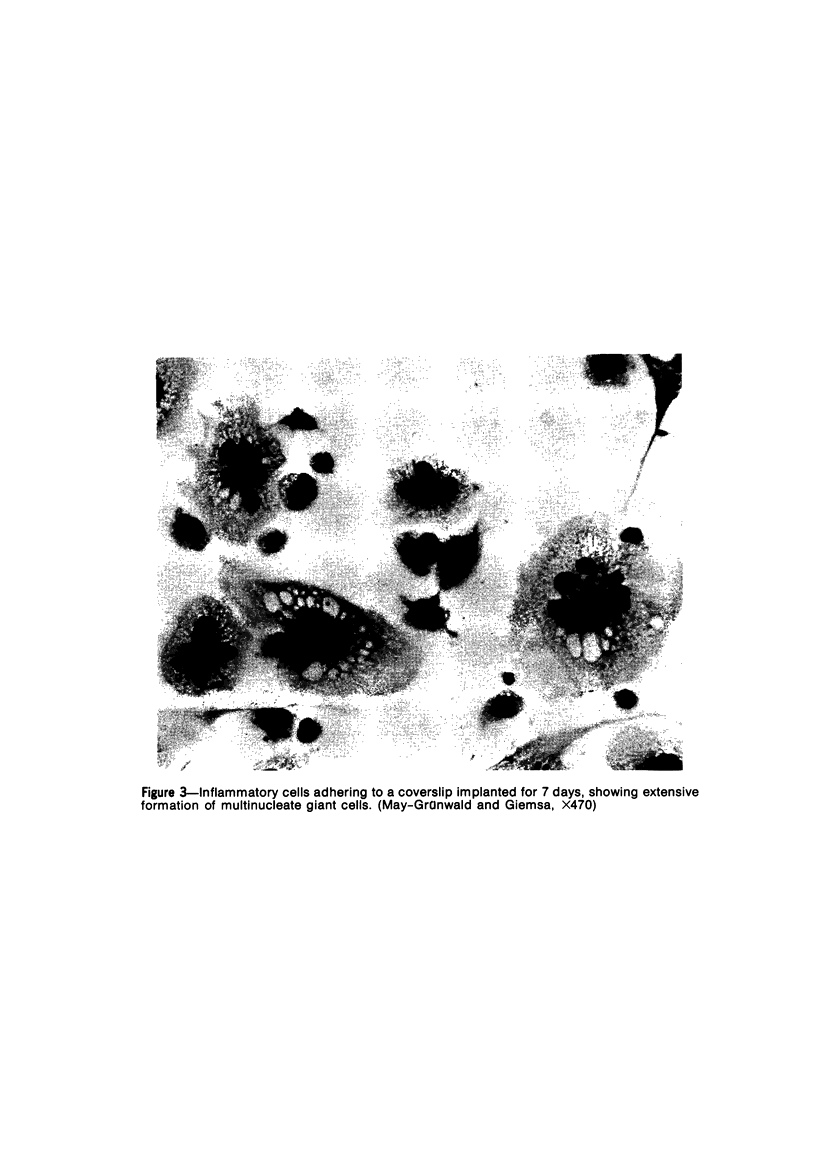
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein I. D., Zbar B., Rapp H. J. Impaired inflammatory response in tumor-bearing guinea pigs. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Dec;49(6):1641–1647. doi: 10.1093/jnci/49.6.1641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman H. A., Jr, Hibbs J. B., Jr Modulation of macrophage tumoricidal capability by components of normal serum: a central role for lipid. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):282–285. doi: 10.1126/science.195338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn Z. A. Activation of mononuclear phagocytes: fact, fancy, and future. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):813–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doe W. F., Henson P. M. Macrophage stimulation by bacterial lipopolysaccharides. I. Cytolytic effect on tumor target cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Aug 1;148(2):544–556. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.2.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galindo B. Antigen-mediated fusion of specifically sensitized rabbit alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):583–594. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.583-594.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galindo B., Lazdins J., Castillo R. Fusion of normal rabbit alveolar macrophages induced by supernatant fluids from BCG-sensitized lymph node cells after elicitation by antigen. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):212–216. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.212-216.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna M. G., Jr, Snodgrass M. J., Zbar B., Rapp H. J. Histologic and ultrastructural studies of tumor regression in inbred guinea pigs after intralesional injection of Mycobacterium bovis (BCG). Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1973 Dec;39:71–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLOW L. S. SIMPLIFIED MYELOPEROXIDASE STAIN USING BENZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE. Blood. 1965 Aug;26:215–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. M., Morahan P. S., Regelson W. Induction of macrophage-mediated tumor-cell cytotoxicity by pyran copolymer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Jun;52(6):1919–1923. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.6.1919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. L., Lazdins J. K. Biochemical criteria for activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):809–813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kripke M. L. Latency, histology, and antigenicity of tumors induced by ultraviolet light in three inbred mouse strains. Cancer Res. 1977 May;37(5):1395–1400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milas L., Scott M. T. Antitumor activity of Corynebacterium parvum. Adv Cancer Res. 1978;26:257–306. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60090-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normann S. J., Schardt M. A cancer related macrophage dysfunction in inflamed tissues. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Aug;24(2):147–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normann S. J., Sorkin E. Inhibition of macrophage chemotaxis by neoplastic and other rapidly proliferating cells in vitro. Cancer Res. 1977 Mar;37(3):705–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The concept of the activated macrophage. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):806–809. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks D. E., Weiser R. S. The role of phagocytosis and natural lymphokines in the fusion of alveolar macrophages to form Langhans giant cells. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1975 Apr;17(4):219–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Kirsh R., Fogler W. E., Fidler I. J. Activation of tumoricidal properties in mouse macrophages by lymphokines encapsulated in liposomes. Cancer Res. 1979 Mar;39(3):881–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruco L. P., Meltzer M. S. Macrophage activation for tumor cytotoxicity: increased lymphokine responsiveness of peritoneal macrophages during acute inflammation. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):1054–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruco L. P., Meltzer M. S. Macrophage activation for tumor cytotoxicity: induction of tumoricidal macrophages by supernatants of PPD-stimulated Bacillus Calmette-Guérin-immune spleen cell cultures. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):889–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. W., Doe W. F., McIntosh A. T. Functional characterization of a stable, noncytolytic stage of macrophage activation in tumors. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1511–1520. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Pike M. C., Blaylock B. L., Weinstein P. Effects of neoplasms on inflammation: depression of macrophage accumulation after tumor implantation. J Immunol. 1976 Mar;116(3):585–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warfel A. H., Hadden J. W. Macrophage fusion factor elicited from BGG-sensitized lymphocytes. Am J Pathol. 1978 Dec;93(3):753–770. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing E. J., Gardner I. D., Ryning F. W., Remington J. S. Dissociation of effector functions in populations of activated macrophages. Nature. 1977 Aug 18;268(5621):642–644. doi: 10.1038/268642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]