Abstract
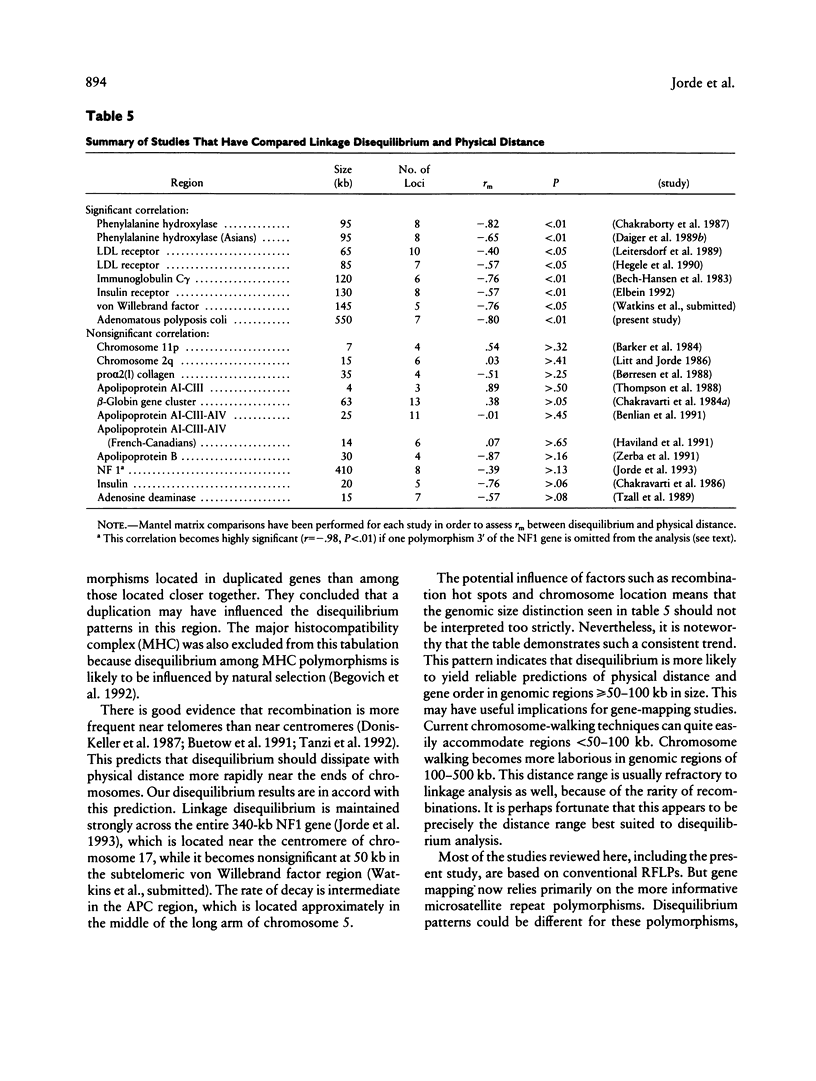
To test the reliability of linkage-disequilibrium analysis for gene mapping, we compared physical distance and linkage disequilibrium among seven polymorphisms in the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) region on chromosome 5. Three of them lie within the APC gene, and two lie within the nearby MCC (mutated in colon cancer) gene. One polymorphism lies between the two genes, and one is likely to be 5' of MCC. Five of these polymorphisms are newly reported. All polymorphisms were typed in the CEPH kindreds, yielding 179-205 unrelated two-locus haplotypes. Linkage disequilibrium between each pair of polymorphisms is highly correlated with physical distance in this 550-kb region (correlation coefficient -.80, P < .006). This result is replicated in both the Utah and non-Utah CEPH kindreds. There is a tendency for greater disequilibrium among pairs of polymorphisms located within the same gene than among other pairs of polymorphisms. Trigenic, quadrigenic, three-locus, and four-locus disequilibrium measures were also estimated, but these measures revealed much less disequilibrium than did the two-locus disequilibrium measures. A review of 19 published disequilibrium studies, including this one, shows that linkage disequilibrium nearly always correlates significantly with physical distance in genomic regions > 50-60 kb but that it does not do so in smaller genomic regions. We show that this agrees with theoretical predictions. This finding helps to resolve controversies regarding the use of disequilibrium for inferring gene order. Disequilibrium mapping is unlikely to predict gene order correctly in regions < 50-60 kb in size but can often be applied successfully in regions of 50-500 kb or so in size. It is convenient that this is the range in which other mapping techniques, including chromosome walking and linkage mapping, become difficult.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker D., Holm T., White R. A locus on chromosome 11p with multiple restriction site polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Nov;36(6):1159–1171. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bech-Hansen N. T., Linsley P. S., Cox D. W. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms associated with immunoglobulin C gamma genes reveal linkage disequilibrium and genomic organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6952–6956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begovich A. B., McClure G. R., Suraj V. C., Helmuth R. C., Fildes N., Bugawan T. L., Erlich H. A., Klitz W. Polymorphism, recombination, and linkage disequilibrium within the HLA class II region. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):249–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Karam J. H., Rutter W. J. Polymorphic DNA region adjacent to the 5' end of the human insulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benlian P., Boileau C., Loux N., Pastier D., Masliah J., Coulon M., Nigou M., Ragab A., Guimard J., Ruidavets J. B. Extended haplotypes and linkage disequilibrium between 11 markers at the APOA1-C3-A4 gene cluster on chromosome 11. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 May;48(5):903–910. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. H. Sample sizes required to detect linkage disequilibrium between two or three loci. Theor Popul Biol. 1975 Oct;8(2):184–201. doi: 10.1016/0040-5809(75)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetow K. H., Shiang R., Yang P., Nakamura Y., Lathrop G. M., White R., Wasmuth J. J., Wood S., Berdahl L. D., Leysens N. J. A detailed multipoint map of human chromosome 4 provides evidence for linkage heterogeneity and position-specific recombination rates. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 May;48(5):911–925. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Børresen A. L., Møller P., Berg K. Linkage disequilibrium analyses and restriction mapping of four RFLPs at the pro alpha 2(I) collagen locus: lack of correlation between linkage disequilibrium and physical distance. Hum Genet. 1988 Mar;78(3):216–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00291664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty R., Lidsky A. S., Daiger S. P., Güttler F., Sullivan S., Dilella A. G., Woo S. L. Polymorphic DNA haplotypes at the human phenylalanine hydroxylase locus and their relationship with phenylketonuria. Hum Genet. 1987 May;76(1):40–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00283048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A., Buetow K. H., Antonarakis S. E., Waber P. G., Boehm C. D., Kazazian H. H. Nonuniform recombination within the human beta-globin gene cluster. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Nov;36(6):1239–1258. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A., Elbein S. C., Permutt M. A. Evidence for increased recombination near the human insulin gene: implication for disease association studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1045–1049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A., Phillips J. A., 3rd, Mellits K. H., Buetow K. H., Seeburg P. H. Patterns of polymorphism and linkage disequilibrium suggest independent origins of the human growth hormone gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6085–6089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daiger S. P., Chakraborty R., Reed L., Fekete G., Schuler D., Berenssi G., Nasz I., Brdicka R., Kamarýt J., Pijácková A. Polymorphic DNA haplotypes at the phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) locus in European families with phenylketonuria (PKU). Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Aug;45(2):310–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daiger S. P., Reed L., Huang S. S., Zeng Y. T., Wang T., Lo W. H., Okano Y., Hase Y., Fukuda Y., Oura T. Polymorphic DNA haplotypes at the phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) locus in Asian families with phenylketonuria (PKU). Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Aug;45(2):319–324. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Green P., Helms C., Cartinhour S., Weiffenbach B., Stephens K., Keith T. P., Bowden D. W., Smith D. R., Lander E. S. A genetic linkage map of the human genome. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):319–337. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein S. C. Linkage disequilibrium among RFLPs at the insulin-receptor locus despite intervening Alu repeat sequences. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Nov;51(5):1103–1110. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estivill X., Farrall M., Scambler P. J., Bell G. M., Hawley K. M., Lench N. J., Bates G. P., Kruyer H. C., Frederick P. A., Stanier P. A candidate for the cystic fibrosis locus isolated by selection for methylation-free islands. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):840–845. doi: 10.1038/326840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhard D. S., Kidd K. K., Kidd J. R., Egeland J. A., Housman D. E. Identification of a recent recombination event within the human beta-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7875–7879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding G. B. The sampling distribution of linkage disequilibrium. Genetics. 1984 Sep;108(1):257–274. doi: 10.1093/genetics/108.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm T., Müller B., Dreier M., Kind E., Bettecken T., Meng G., Müller C. R. Hot spot of recombination within DXS164 in the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Sep;45(3):368–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groden J., Thliveris A., Samowitz W., Carlson M., Gelbert L., Albertsen H., Joslyn G., Stevens J., Spirio L., Robertson M. Identification and characterization of the familial adenomatous polyposis coli gene. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):589–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanauer A., Chery M., Fujita R., Driesel A. J., Gilgenkrantz S., Mandel J. L. The Friedreich ataxia gene is assigned to chromosome 9q13-q21 by mapping of tightly linked markers and shows linkage disequilibrium with D9S15. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jan;46(1):133–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley H. G., Brook J. D., Floyd J., Rundle S. A., Crow S., Walsh K. V., Thibault M. C., Harper P. S., Shaw D. J. Detection of linkage disequilibrium between the myotonic dystrophy locus and a new polymorphic DNA marker. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jul;49(1):68–75. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haviland M. B., Kessling A. M., Davignon J., Sing C. F. Estimation of Hardy-Weinberg and pairwise disequilibrium in the apolipoprotein AI-CIII-AIV gene cluster. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Aug;49(2):350–365. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearne C. M., Ghosh S., Todd J. A. Microsatellites for linkage analysis of genetic traits. Trends Genet. 1992 Aug;8(8):288–294. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90256-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick P. W. Gametic disequilibrium measures: proceed with caution. Genetics. 1987 Oct;117(2):331–341. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegele R. A., Plaetke R., Lalouel J. M. Linkage disequilibrium between DNA markers at the low-density lipoprotein receptor gene. Genet Epidemiol. 1990;7(1):69–81. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370070114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. G., Weir B. S. Variances and covariances of squared linkage disequilibria in finite populations. Theor Popul Biol. 1988 Feb;33(1):54–78. doi: 10.1016/0040-5809(88)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson R. R. The sampling distribution of linkage disequilibrium under an infinite allele model without selection. Genetics. 1985 Mar;109(3):611–631. doi: 10.1093/genetics/109.3.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hästbacka J., de la Chapelle A., Kaitila I., Sistonen P., Weaver A., Lander E. Linkage disequilibrium mapping in isolated founder populations: diastrophic dysplasia in Finland. Nat Genet. 1992 Nov;2(3):204–211. doi: 10.1038/ng1192-204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jazwinska E. C., Lee S. C., Webb S. I., Halliday J. W., Powell L. W. Localization of the hemochromatosis gene close to D6S105. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Aug;53(2):347–352. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorde L. B., Watkins W. S., Viskochil D., O'Connell P., Ward K. Linkage disequilibrium in the neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) region: implications for gene mapping. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Nov;53(5):1038–1050. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joslyn G., Carlson M., Thliveris A., Albertsen H., Gelbert L., Samowitz W., Groden J., Stevens J., Spirio L., Robertson M. Identification of deletion mutations and three new genes at the familial polyposis locus. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):601–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Nilbert M. C., Vogelstein B., Bryan T. M., Levy D. B., Smith K. J., Preisinger A. C., Hamilton S. R., Hedge P., Markham A. Identification of a gene located at chromosome 5q21 that is mutated in colorectal cancers. Science. 1991 Mar 15;251(4999):1366–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.1848370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupke K. G., Graeber M. B., Müller U. Dystonia-parkinsonism syndrome (XDP) locus: flanking markers in Xq12-q21.1. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Apr;50(4):808–815. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalouel J. M., Jorde L. B. Idiopathic hemochromatosis: significance and implications of linkage and association to HLA. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;526:34–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb55490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitersdorf E., Chakravarti A., Hobbs H. H. Polymorphic DNA haplotypes at the LDL receptor locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):409–421. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewontin R C. The Interaction of Selection and Linkage. I. General Considerations; Heterotic Models. Genetics. 1964 Jan;49(1):49–67. doi: 10.1093/genetics/49.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M., Jorde L. B. Linkage disequilibria between pairs of loci within a highly polymorphic region of chromosome 2Q. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Aug;39(2):166–178. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucassen A. M., Julier C., Beressi J. P., Boitard C., Froguel P., Lathrop M., Bell J. I. Susceptibility to insulin dependent diabetes mellitus maps to a 4.1 kb segment of DNA spanning the insulin gene and associated VNTR. Nat Genet. 1993 Jul;4(3):305–310. doi: 10.1038/ng0793-305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Lin C., Srinidhi L., Bates G., Altherr M., Whaley W. L., Lehrach H., Wasmuth J., Gusella J. F. Complex patterns of linkage disequilibrium in the Huntington disease region. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Oct;49(4):723–734. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald M. E., Novelletto A., Lin C., Tagle D., Barnes G., Bates G., Taylor S., Allitto B., Altherr M., Myers R. The Huntington's disease candidate region exhibits many different haplotypes. Nat Genet. 1992 May;1(2):99–103. doi: 10.1038/ng0592-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantel N. The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res. 1967 Feb;27(2):209–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLellan T., Jorde L. B., Skolnick M. H. Genetic distances between the Utah Mormons and related populations. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Jul;36(4):836–857. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miserez A. R., Schuster H., Chiodetti N., Keller U. Polymorphic haplotypes and recombination rates at the LDL receptor gene locus in subjects with and without familial hypercholesterolemia who are from different populations. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Apr;52(4):808–826. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E., Simpson S. P. Kinship mapping of multilocus systems. Hum Genet. 1983;64(2):103–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00327102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Roychoudhury A. K. Evolutionary relationships of human populations on a global scale. Mol Biol Evol. 1993 Sep;10(5):927–943. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet C., Hanauer A., Clemens P., Caskey T., Mandel J. L. Two hot spots of recombination in the DMD gene correlate with the deletion prone regions. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Nov;1(8):599–603. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.8.599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozelius L. J., Kramer P. L., de Leon D., Risch N., Bressman S. B., Schuback D. E., Brin M. F., Kwiatkowski D. J., Burke R. E., Gusella J. F. Strong allelic association between the torsion dystonia gene (DYT1) andloci on chromosome 9q34 in Ashkenazi Jews. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Mar;50(3):619–628. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrukhin K., Fischer S. G., Pirastu M., Tanzi R. E., Chernov I., Devoto M., Brzustowicz L. M., Cayanis E., Vitale E., Russo J. J. Mapping, cloning and genetic characterization of the region containing the Wilson disease gene. Nat Genet. 1993 Dec;5(4):338–343. doi: 10.1038/ng1293-338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pound S. E., Carothers A. D., Pignatelli P. M., Macnicol A. M., Watson M. L., Wright A. F. Evidence for linkage disequilibrium between D16S94 and the adult onset polycystic kidney disease (PKD1) gene. J Med Genet. 1992 Apr;29(4):247–248. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.4.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrington R., Melmer G., Dixon M., Curtis D., Mankoo B., Kalsi G., Gurling H. Linkage disequilibrium between two highly polymorphic microsatellites. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Nov;49(5):966–971. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skraastad M. I., Van de Vosse E., Belfroid R., Höld K., Vegter-van der Vlis M., Sandkuijl L. A., Bakker E., van Ommen G. J. Significant linkage disequilibrium between the Huntington disease gene and the loci D4S10 and D4S95 in the Dutch population. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Oct;51(4):730–735. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sved J. A. Linkage disequilibrium and homozygosity of chromosome segments in finite populations. Theor Popul Biol. 1971 Jun;2(2):125–141. doi: 10.1016/0040-5809(71)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Watkins P. C., Stewart G. D., Wexler N. S., Gusella J. F., Haines J. L. A genetic linkage map of human chromosome 21: analysis of recombination as a function of sex and age. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Mar;50(3):551–558. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton A. R., Boerwinkle E., Sing C. F. A cladistic analysis of phenotypic associations with haplotypes inferred from restriction endonuclease mapping. I. Basic theory and an analysis of alcohol dehydrogenase activity in Drosophila. Genetics. 1987 Oct;117(2):343–351. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theilmann J., Kanani S., Shiang R., Robbins C., Quarrell O., Huggins M., Hedrick A., Weber B., Collins C., Wasmuth J. J. Non-random association between alleles detected at D4S95 and D4S98 and the Huntington's disease gene. J Med Genet. 1989 Nov;26(11):676–681. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.11.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. R., Roberts E. A., Rosales T. O., Moroz S. P., Lambert M. A., Wong L. T., Cox D. W. Allelic association and linkage studies in Wilson disease. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Sep;2(9):1401–1405. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.9.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. A., Deeb S., Walker D., Motulsky A. G. The detection of linkage disequilibrium between closely linked markers: RFLPs at the AI-CIII apolipoprotein genes. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;42(1):113–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treco D., Thomas B., Arnheim N. Recombination hot spot in the human beta-globin gene cluster: meiotic recombination of human DNA fragments in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2029–2038. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzall S., Ellenbogen A., Eng F., Hirschhorn R. Identification and characterization of nine RFLPs at the adenosine deaminase (ADA) locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Jun;44(6):864–875. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter M. A., Cox D. W. Nonuniform linkage disequilibrium within a 1,500-kb region of the human immunoglobulin heavy-chain complex. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Nov;49(5):917–931. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir B. S., Hill W. G. Nonuniform recombination within the human beta-globin gene cluster. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 May;38(5):776–781. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Gyapay G., Dib C., Vignal A., Morissette J., Millasseau P., Vaysseix G., Lathrop M. A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):794–801. doi: 10.1038/359794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J. Microsatellite polymorphisms and the genetic linkage map of the human genome. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Jun;3(3):414–417. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90114-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills C. Population size bottleneck. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):398–398. doi: 10.1038/348398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerba K. E., Kessling A. M., Davignon J., Sing C. F. Genetic structure and the search for genotype-phenotype relationships: an example from disequilibrium in the Apo B gene region. Genetics. 1991 Oct;129(2):525–533. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.2.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


