Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe R., Sakashita E., Yamamoto K., Sakamoto H. Two different RNA binding activities for the AU-rich element and the poly(A) sequence of the mouse neuronal protein mHuC. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996 Dec 15;24(24):4895–4901. doi: 10.1093/nar/24.24.4895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abe R., Yamamoto K., Sakamoto H. Target specificity of neuronal RNA-binding protein, Mel-N1: direct binding to the 3' untranslated region of its own mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996 Jun 1;24(11):2011–2016. doi: 10.1093/nar/24.11.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. E., Cunningham J. M., Posner J. B. Autoimmune pathogenesis of paraneoplastic neurological syndromes. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1987;3(3):245–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barami K., Iversen K., Furneaux H., Goldman S. A. Hu protein as an early marker of neuronal phenotypic differentiation by subependymal zone cells of the adult songbird forebrain. J Neurobiol. 1995 Sep;28(1):82–101. doi: 10.1002/neu.480280108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd C. G., Dreyfuss G. Conserved structures and diversity of functions of RNA-binding proteins. Science. 1994 Jul 29;265(5172):615–621. doi: 10.1126/science.8036511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos A. R., Grossman D., White K. Mutant alleles at the locus elav in Drosophila melanogaster lead to nervous system defects. A developmental-genetic analysis. J Neurogenet. 1985 Jun;2(3):197–218. doi: 10.3109/01677068509100150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chagnovich D., Fayos B. E., Cohn S. L. Differential activity of ELAV-like RNA-binding proteins in human neuroblastoma. J Biol Chem. 1996 Dec 27;271(52):33587–33591. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.52.33587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers J. C., Kenan D., Martin B. J., Keene J. D. Genomic structure and amino acid sequence domains of the human La autoantigen. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18043–18051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. Y., Shyu A. B. AU-rich elements: characterization and importance in mRNA degradation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Nov;20(11):465–470. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)89102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S., Eckrich M., Perrone-Bizzozero N., Kohn D. T., Furneaux H. The Elav-like proteins bind to a conserved regulatory element in the 3'-untranslated region of GAP-43 mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1997 Mar 7;272(10):6593–6598. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.10.6593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S., Jiang L., Cheng S., Furneaux H. Purification and properties of HuD, a neuronal RNA-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1996 May 10;271(19):11518–11524. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.19.11518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
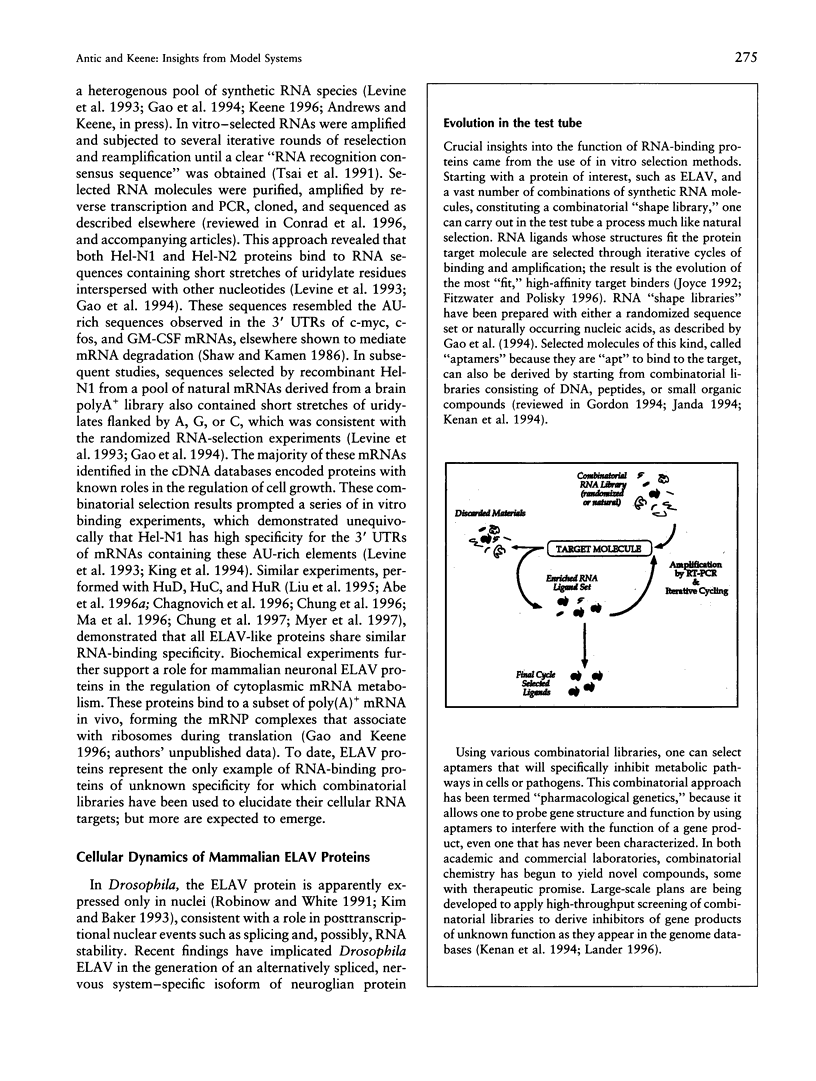
- Conrad R. C., Giver L., Tian Y., Ellington A. D. In vitro selection of nucleic acid aptamers that bind proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1996;267:336–367. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(96)67022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalmau J., Furneaux H. M., Gralla R. J., Kris M. G., Posner J. B. Detection of the anti-Hu antibody in the serum of patients with small cell lung cancer--a quantitative western blot analysis. Ann Neurol. 1990 May;27(5):544–552. doi: 10.1002/ana.410270515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell R. B. Onconeural antigens and the paraneoplastic neurologic disorders: at the intersection of cancer, immunity, and the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 May 14;93(10):4529–4536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.10.4529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao F. B., Carson C. C., Levine T., Keene J. D. Selection of a subset of mRNAs from combinatorial 3' untranslated region libraries using neuronal RNA-binding protein Hel-N1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):11207–11211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.11207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao F. B., Keene J. D. Hel-N1/Hel-N2 proteins are bound to poly(A)+ mRNA in granular RNP structures and are implicated in neuronal differentiation. J Cell Sci. 1996 Mar;109(Pt 3):579–589. doi: 10.1242/jcs.109.3.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
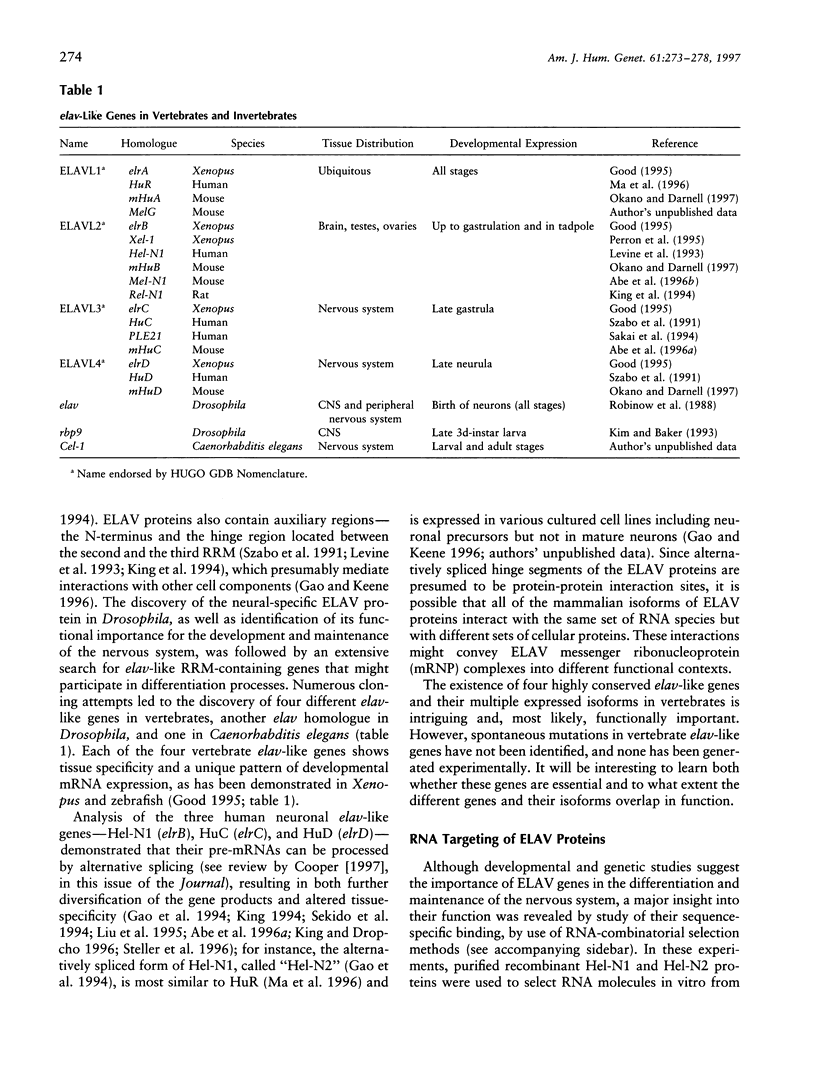
- Good P. J. A conserved family of elav-like genes in vertebrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 9;92(10):4557–4561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.10.4557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon E. M., Barrett R. W., Dower W. J., Fodor S. P., Gallop M. A. Applications of combinatorial technologies to drug discovery. 2. Combinatorial organic synthesis, library screening strategies, and future directions. J Med Chem. 1994 May 13;37(10):1385–1401. doi: 10.1021/jm00036a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves R. A., Pandey N. B., Chodchoy N., Marzluff W. F. Translation is required for regulation of histone mRNA degradation. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):615–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson A., Peltz S. W. Interrelationships of the pathways of mRNA decay and translation in eukaryotic cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1996;65:693–739. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.65.070196.003401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain R. G., Andrews L. G., McGowan K. M., Pekala P. H., Keene J. D. Ectopic expression of Hel-N1, an RNA-binding protein, increases glucose transporter (GLUT1) expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Feb;17(2):954–962. doi: 10.1128/mcb.17.2.954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda K. D. Tagged versus untagged libraries: methods for the generation and screening of combinatorial chemical libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):10779–10785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.10779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce G. F. Directed molecular evolution. Sci Am. 1992 Dec;267(6):90–97. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1292-90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene J. D., Query C. C. Nuclear RNA-binding proteins. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;41:179–202. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keene J. D. Randomization and selection of RNA to identify targets for RRM RNA-binding proteins and antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1996;267:367–383. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(96)67023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenan D. J., Query C. C., Keene J. D. RNA recognition: towards identifying determinants of specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jun;16(6):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90088-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenan D. J., Tsai D. E., Keene J. D. Exploring molecular diversity with combinatorial shape libraries. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Feb;19(2):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. J., Baker B. S. The Drosophila gene rbp9 encodes a protein that is a member of a conserved group of putative RNA binding proteins that are nervous system-specific in both flies and humans. J Neurosci. 1993 Mar;13(3):1045–1056. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-03-01045.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King P. H., Dropcho E. J. Expression of Hel-N1 and Hel-N2 in small-cell lung carcinoma. Ann Neurol. 1996 May;39(5):679–681. doi: 10.1002/ana.410390520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King P. H. Hel-N2: a novel isoform of Hel-N1 which is conserved in rat neural tissue and produced in early embryogenesis. Gene. 1994 Dec 30;151(1-2):261–265. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90668-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King P. H., Levine T. D., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Keene J. D. Mammalian homologs of Drosophila ELAV localized to a neuronal subset can bind in vitro to the 3' UTR of mRNA encoding the Id transcriptional repressor. J Neurosci. 1994 Apr;14(4):1943–1952. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-04-01943.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koushika S. P., Lisbin M. J., White K. ELAV, a Drosophila neuron-specific protein, mediates the generation of an alternatively spliced neural protein isoform. Curr Biol. 1996 Dec 1;6(12):1634–1641. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)70787-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S. The new genomics: global views of biology. Science. 1996 Oct 25;274(5287):536–539. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5287.536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine T. D., Gao F., King P. H., Andrews L. G., Keene J. D. Hel-N1: an autoimmune RNA-binding protein with specificity for 3' uridylate-rich untranslated regions of growth factor mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3494–3504. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Gunderson N., Groudine M. Enhanced transcription of c-myc in bursal lymphoma cells requires continuous protein synthesis. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1126–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.2999973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Dalmau J., Szabo A., Rosenfeld M., Huber J., Furneaux H. Paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis antigens bind to the AU-rich elements of mRNA. Neurology. 1995 Mar;45(3 Pt 1):544–550. doi: 10.1212/wnl.45.3.544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma W. J., Cheng S., Campbell C., Wright A., Furneaux H. Cloning and characterization of HuR, a ubiquitously expressed Elav-like protein. J Biol Chem. 1996 Apr 5;271(14):8144–8151. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.14.8144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayford M., Baranes D., Podsypanina K., Kandel E. R. The 3'-untranslated region of CaMKII alpha is a cis-acting signal for the localization and translation of mRNA in dendrites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Nov 12;93(23):13250–13255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.23.13250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myer V. E., Fan X. C., Steitz J. A. Identification of HuR as a protein implicated in AUUUA-mediated mRNA decay. EMBO J. 1997 Apr 15;16(8):2130–2139. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.8.2130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano H. J., Darnell R. B. A hierarchy of Hu RNA binding proteins in developing and adult neurons. J Neurosci. 1997 May 1;17(9):3024–3037. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-09-03024.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachter J. S., Yen T. J., Cleveland D. W. Autoregulation of tubulin expression is achieved through specific degradation of polysomal tubulin mRNAs. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90155-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perron M., Théodore L., Wegnez M. Isolation and embryonic expression of Xel-1, a nervous system-specific Xenopus gene related to the elav gene family. Mech Dev. 1995 Jun;51(2-3):235–249. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(95)00368-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Bentley R. C., Keene J. D. A common RNA recognition motif identified within a defined U1 RNA binding domain of the 70K U1 snRNP protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinow S., Campos A. R., Yao K. M., White K. The elav gene product of Drosophila, required in neurons, has three RNP consensus motifs. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1570–1572. doi: 10.1126/science.3144044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinow S., White K. The locus elav of Drosophila melanogaster is expressed in neurons at all developmental stages. Dev Biol. 1988 Apr;126(2):294–303. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90139-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai K., Gofuku M., Kitagawa Y., Ogasawara T., Hirose G., Yamazaki M., Koh C. S., Yanagisawa N., Steinman L. A hippocampal protein associated with paraneoplastic neurologic syndrome and small cell lung carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Mar 30;199(3):1200–1208. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiavi S. C., Belasco J. G., Greenberg M. E. Regulation of proto-oncogene mRNA stability. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Dec 16;1114(2-3):95–106. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(92)90009-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiavi S. C., Wellington C. L., Shyu A. B., Chen C. Y., Greenberg M. E., Belasco J. G. Multiple elements in the c-fos protein-coding region facilitate mRNA deadenylation and decay by a mechanism coupled to translation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3441–3448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekido Y., Bader S. A., Carbone D. P., Johnson B. E., Minna J. D. Molecular analysis of the HuD gene encoding a paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis antigen in human lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1994 Sep 15;54(18):4988–4992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Regulation of human histone gene expression during the HeLa cell cycle requires protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2723–2734. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Johnston D. The intracellular localization of messenger RNAs. Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):161–170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90324-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller U., Kohls S., Müller B., Söller R., Müller R., Schlender J., Blohm D. H. The RNA binding protein HuD: rat cDNA and analysis of the alternative spliced mRNA in neuronal differentiating cell lines P19 and PC12. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1996 Jan;35(1-2):285–296. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(95)00231-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo A., Dalmau J., Manley G., Rosenfeld M., Wong E., Henson J., Posner J. B., Furneaux H. M. HuD, a paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis antigen, contains RNA-binding domains and is homologous to Elav and Sex-lethal. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90184-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai D. E., Harper D. S., Keene J. D. U1-snRNP-A protein selects a ten nucleotide consensus sequence from a degenerate RNA pool presented in various structural contexts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):4931–4936. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.4931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vakalopoulou E., Schaack J., Shenk T. A 32-kilodalton protein binds to AU-rich domains in the 3' untranslated regions of rapidly degraded mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3355–3364. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


