Abstract
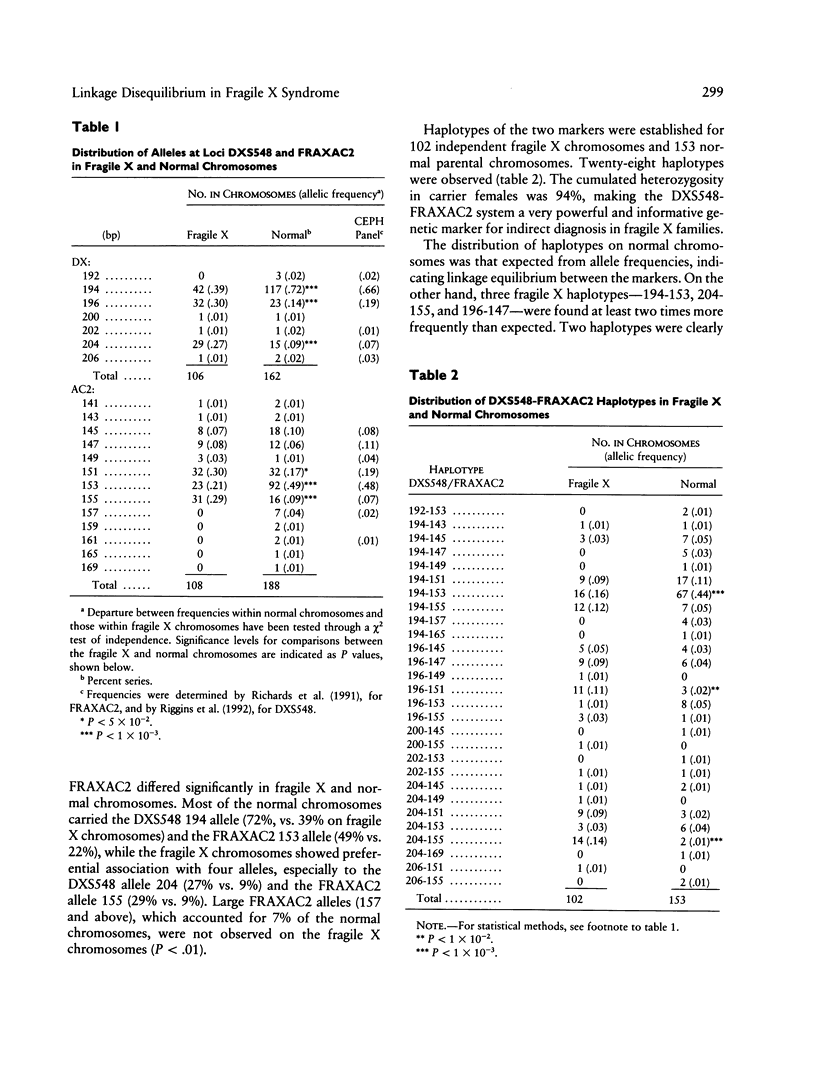
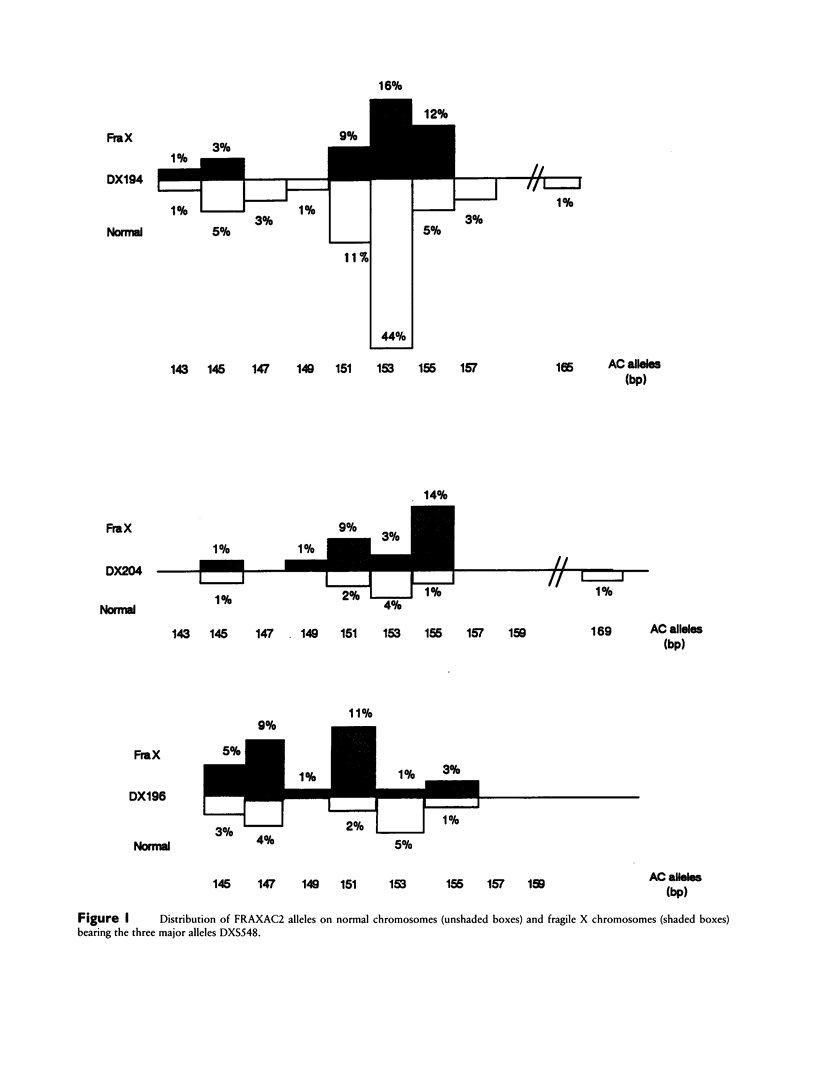
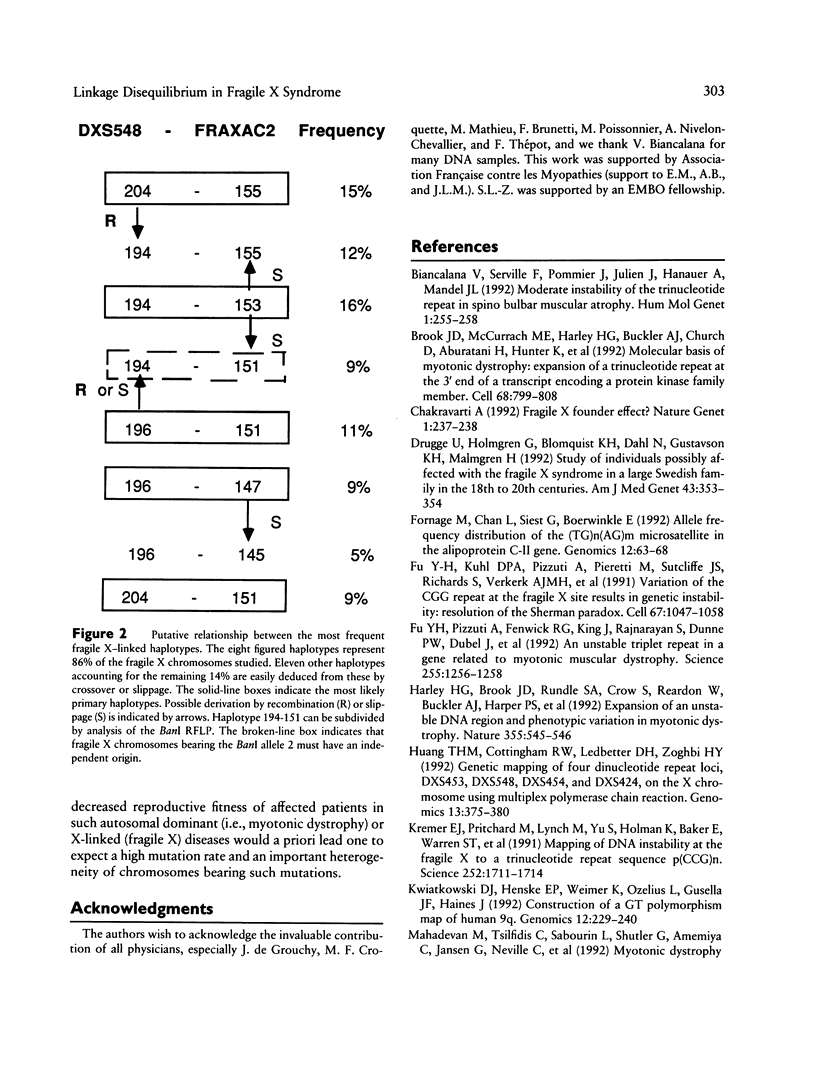
In order to investigate the origin of mutations responsible for the fragile X syndrome, two polymorphic CA repeats, one at 10 kb (FRAXAC2) and the other at 150 kb (DXS548) from the mutation target, were analyzed in normal and fragile X chromosomes. Contrary to observations made in myotonic dystrophy, fragile X mutations were not strongly associated with a single allele at the marker loci. However, significant differences in allelic and haplotypic distributions were observed between normal and fragile X chromosomes, indicating that a limited number of primary events may have been at the origin of most present-day fragile X chromosomes in Caucasian populations. We propose a putative scheme with six founder chromosomes from which most of the observed fragile X–linked haplotypes can be derived directly or by a single event at one of the marker loci, either a change of one repeat unit or a recombination between DXS548 and the mutation target. Such founder chromosomes may have carried a number of CGG repeats in an upper-normal range, from which recurrent multistep expansion mutations have arisen.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biancalana V., Serville F., Pommier J., Julien J., Hanauer A., Mandel J. L. Moderate instability of the trinucleotide repeat in spino bulbar muscular atrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):255–258. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.4.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook J. D., McCurrach M. E., Harley H. G., Buckler A. J., Church D., Aburatani H., Hunter K., Stanton V. P., Thirion J. P., Hudson T. Molecular basis of myotonic dystrophy: expansion of a trinucleotide (CTG) repeat at the 3' end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):799–808. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90154-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A. Fragile X founder effect? Nat Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):237–238. doi: 10.1038/ng0792-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drugge U., Holmgren G., Blomquist H. K., Dahl N., Gustavson K. H., Malmgren H. Study of individuals possibly affected with the fragile X syndrome in a large Swedish family in the 18th to 20th centuries. 1992 Apr 15-May 1Am J Med Genet. 43(1-2):353–354. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornage M., Chan L., Siest G., Boerwinkle E. Allele frequency distribution of the (TG)n(AG)m microsatellite in the apolipoprotein C-II gene. Genomics. 1992 Jan;12(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90407-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Kuhl D. P., Pizzuti A., Pieretti M., Sutcliffe J. S., Richards S., Verkerk A. J., Holden J. J., Fenwick R. G., Jr, Warren S. T. Variation of the CGG repeat at the fragile X site results in genetic instability: resolution of the Sherman paradox. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1047–1058. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Pizzuti A., Fenwick R. G., Jr, King J., Rajnarayan S., Dunne P. W., Dubel J., Nasser G. A., Ashizawa T., de Jong P. An unstable triplet repeat in a gene related to myotonic muscular dystrophy. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1256–1258. doi: 10.1126/science.1546326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley H. G., Brook J. D., Rundle S. A., Crow S., Reardon W., Buckler A. J., Harper P. S., Housman D. E., Shaw D. J. Expansion of an unstable DNA region and phenotypic variation in myotonic dystrophy. Nature. 1992 Feb 6;355(6360):545–546. doi: 10.1038/355545a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. H., Cottingham R. W., Jr, Ledbetter D. H., Zoghbi H. Y. Genetic mapping of four dinucleotide repeat loci, DXS453, DXS458, DXS454, and DXS424, on the X chromosome using multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1992 Jun;13(2):375–380. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90256-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer E. J., Pritchard M., Lynch M., Yu S., Holman K., Baker E., Warren S. T., Schlessinger D., Sutherland G. R., Richards R. I. Mapping of DNA instability at the fragile X to a trinucleotide repeat sequence p(CCG)n. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1711–1714. doi: 10.1126/science.1675488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Henske E. P., Weimer K., Ozelius L., Gusella J. F., Haines J. Construction of a GT polymorphism map of human 9q. Genomics. 1992 Feb;12(2):229–240. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90370-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan M., Tsilfidis C., Sabourin L., Shutler G., Amemiya C., Jansen G., Neville C., Narang M., Barceló J., O'Hoy K. Myotonic dystrophy mutation: an unstable CTG repeat in the 3' untranslated region of the gene. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1253–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.1546325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. E., Macpherson J. N. Population genetics of the fragile-X syndrome: multiallelic model for the FMR1 locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4215–4217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Rousseau F., Heitz D., Kretz C., Devys D., Hanauer A., Boué J., Bertheas M. F., Mandel J. L. Instability of a 550-base pair DNA segment and abnormal methylation in fragile X syndrome. Science. 1991 May 24;252(5009):1097–1102. doi: 10.1126/science.252.5009.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet C., Heilig R., Hanauer A., Mandel J. L. Nonradioactive assay for new microsatellite polymorphisms at the 5' end of the dystrophin gene, and estimation of intragenic recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Aug;49(2):311–319. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. I., Holman K., Friend K., Kremer E., Hillen D., Staples A., Brown W. T., Goonewardena P., Tarleton J., Schwartz C. Evidence of founder chromosomes in fragile X syndrome. Nat Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):257–260. doi: 10.1038/ng0792-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. I., Holman K., Kozman H., Kremer E., Lynch M., Pritchard M., Yu S., Mulley J., Sutherland G. R. Fragile X syndrome: genetic localisation by linkage mapping of two microsatellite repeats FRAXAC1 and FRAXAC2 which immediately flank the fragile site. J Med Genet. 1991 Dec;28(12):818–823. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.12.818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggins G. J., Sherman S. L., Oostra B. A., Sutcliffe J. S., Feitell D., Nelson D. L., van Oost B. A., Smits A. P., Ramos F. J., Pfendner E. Characterization of a highly polymorphic dinucleotide repeat 150 KB proximal to the fragile X site. 1992 Apr 15-May 1Am J Med Genet. 43(1-2):237–243. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau F., Heitz D., Biancalana V., Blumenfeld S., Kretz C., Boué J., Tommerup N., Van Der Hagen C., DeLozier-Blanchet C., Croquette M. F. Direct diagnosis by DNA analysis of the fragile X syndrome of mental retardation. N Engl J Med. 1991 Dec 12;325(24):1673–1681. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199112123252401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smits A., Smeets D., Hamel B., Dreesen J., van Oost B. High prevalence of the fra(X) syndrome cannot be explained by a high mutation rate. 1992 Apr 15-May 1Am J Med Genet. 43(1-2):345–352. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tejada I., Mornet E., Biancalana V., Oberlé I., Boué J., Mandel J. L., Boué A. Direct DNA analysis of fragile X syndrome in Spanish pedigrees. 1992 Apr 15-May 1Am J Med Genet. 43(1-2):282–290. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkerk A. J., Pieretti M., Sutcliffe J. S., Fu Y. H., Kuhl D. P., Pizzuti A., Reiner O., Richards S., Victoria M. F., Zhang F. P. Identification of a gene (FMR-1) containing a CGG repeat coincident with a breakpoint cluster region exhibiting length variation in fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):905–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90397-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S., Mulley J., Loesch D., Turner G., Donnelly A., Gedeon A., Hillen D., Kremer E., Lynch M., Pritchard M. Fragile-X syndrome: unique genetics of the heritable unstable element. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 May;50(5):968–980. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


