Abstract
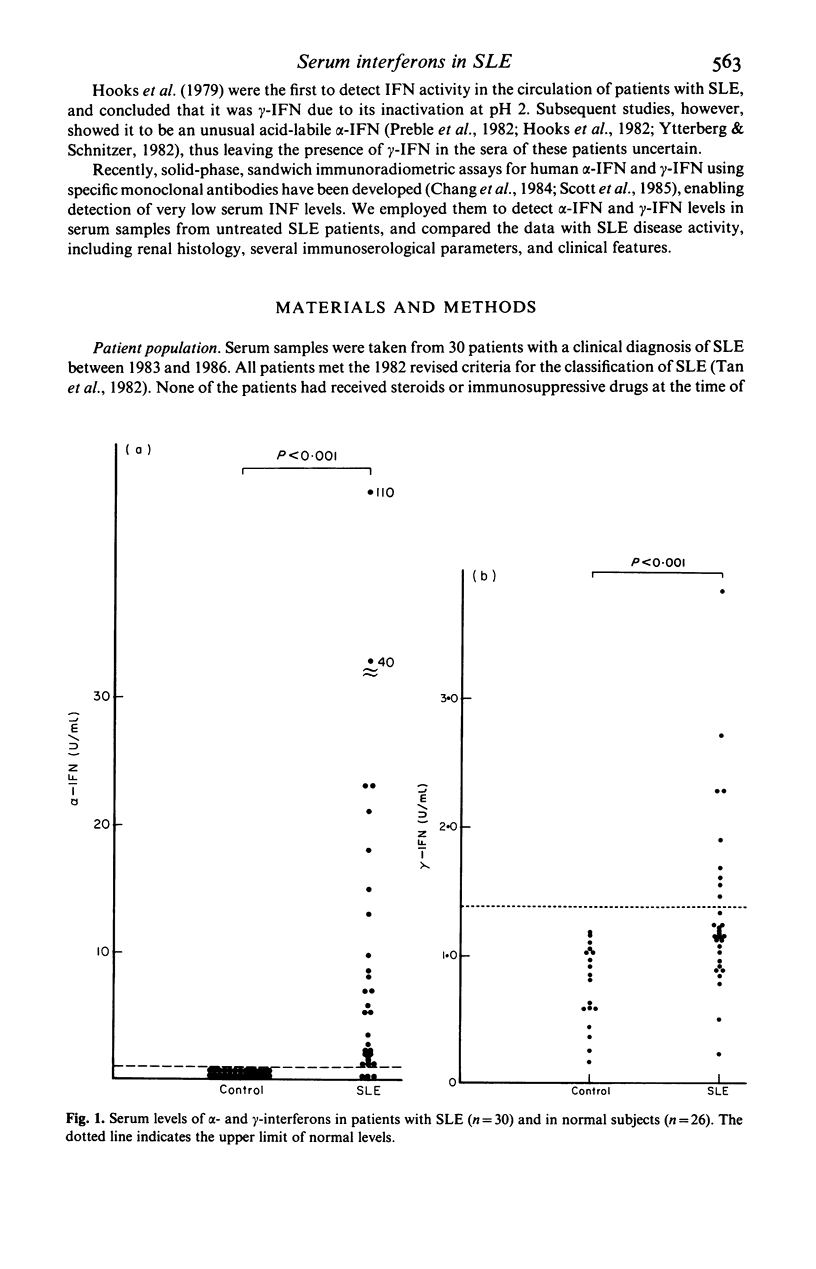
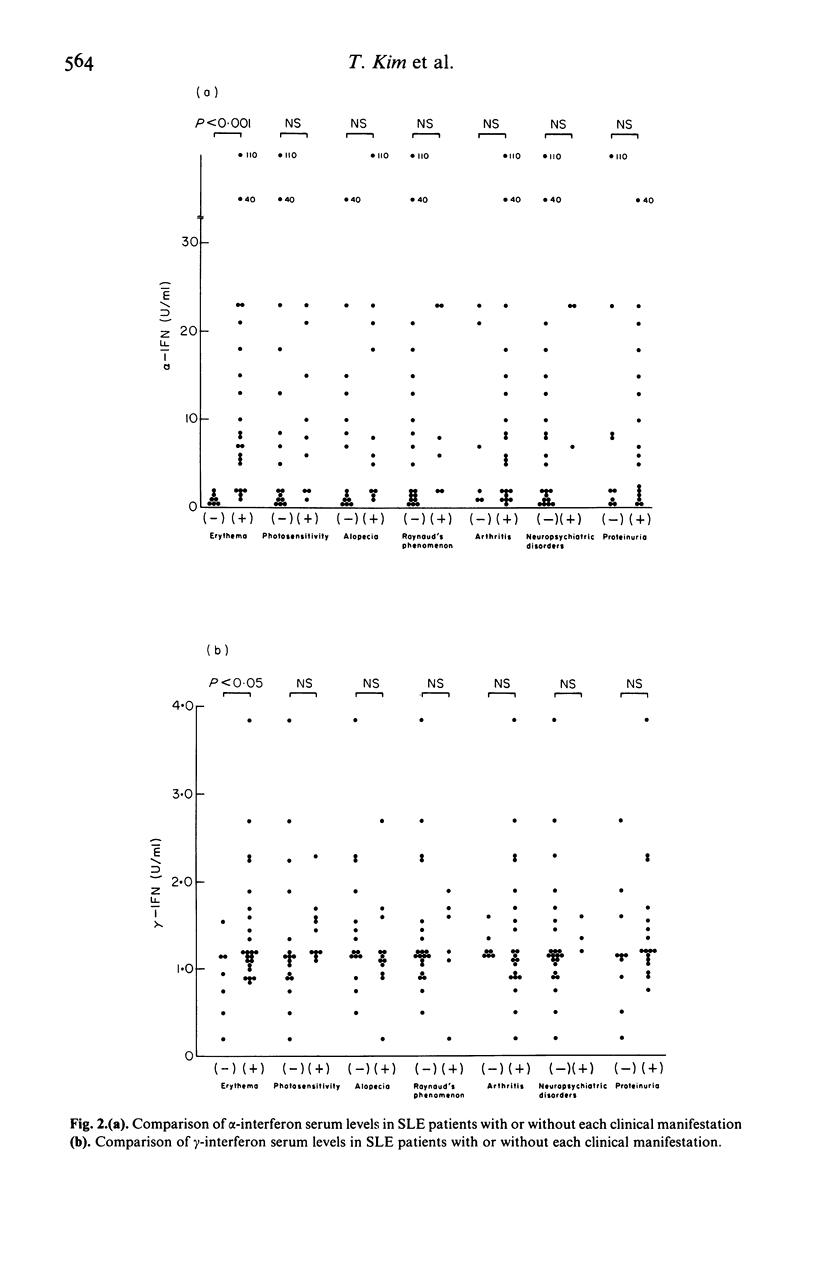
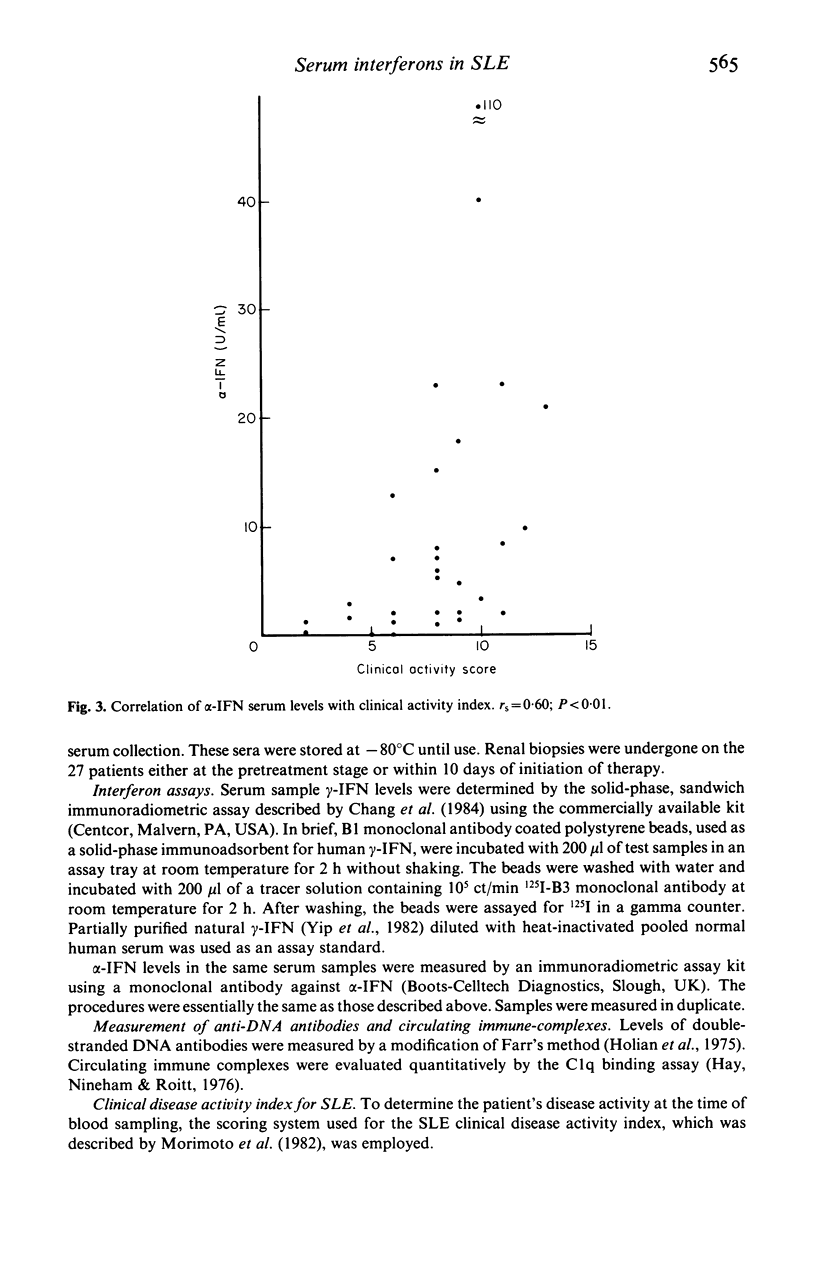
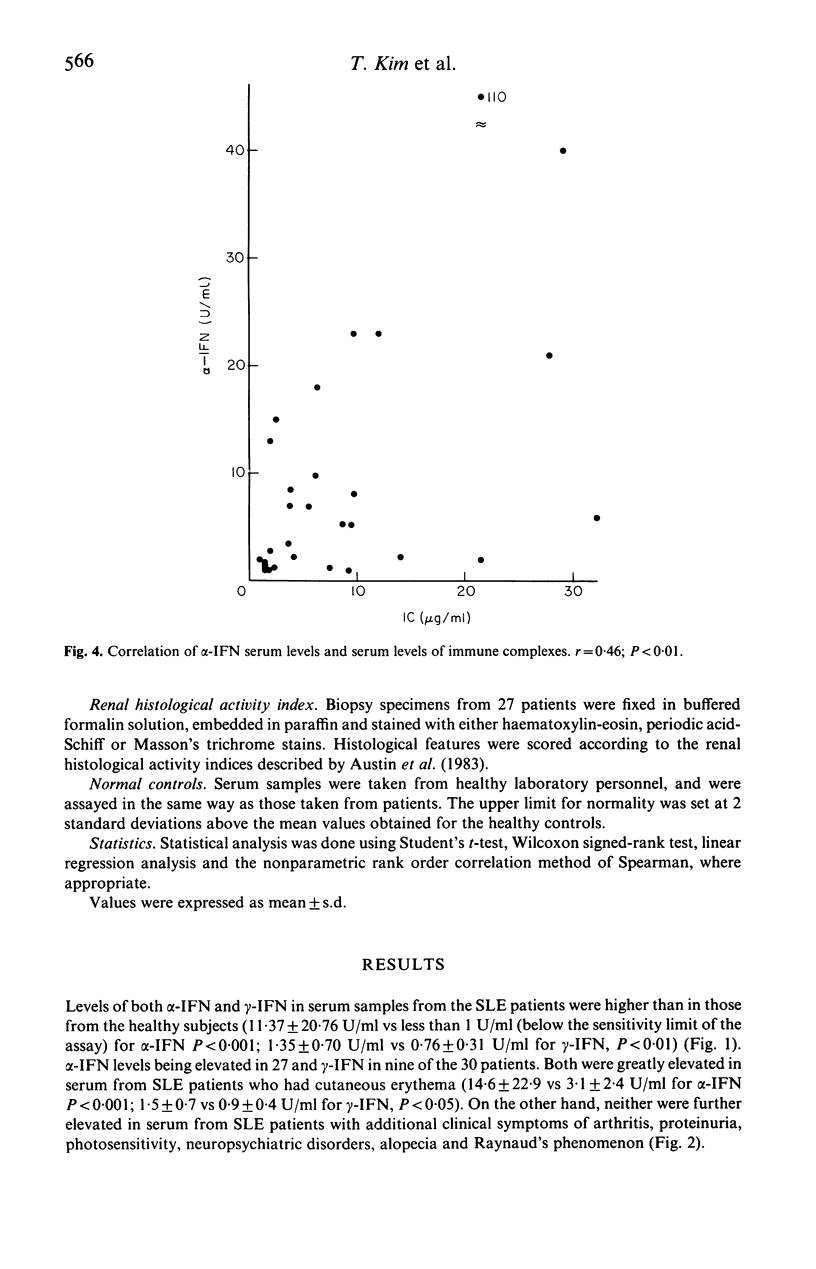
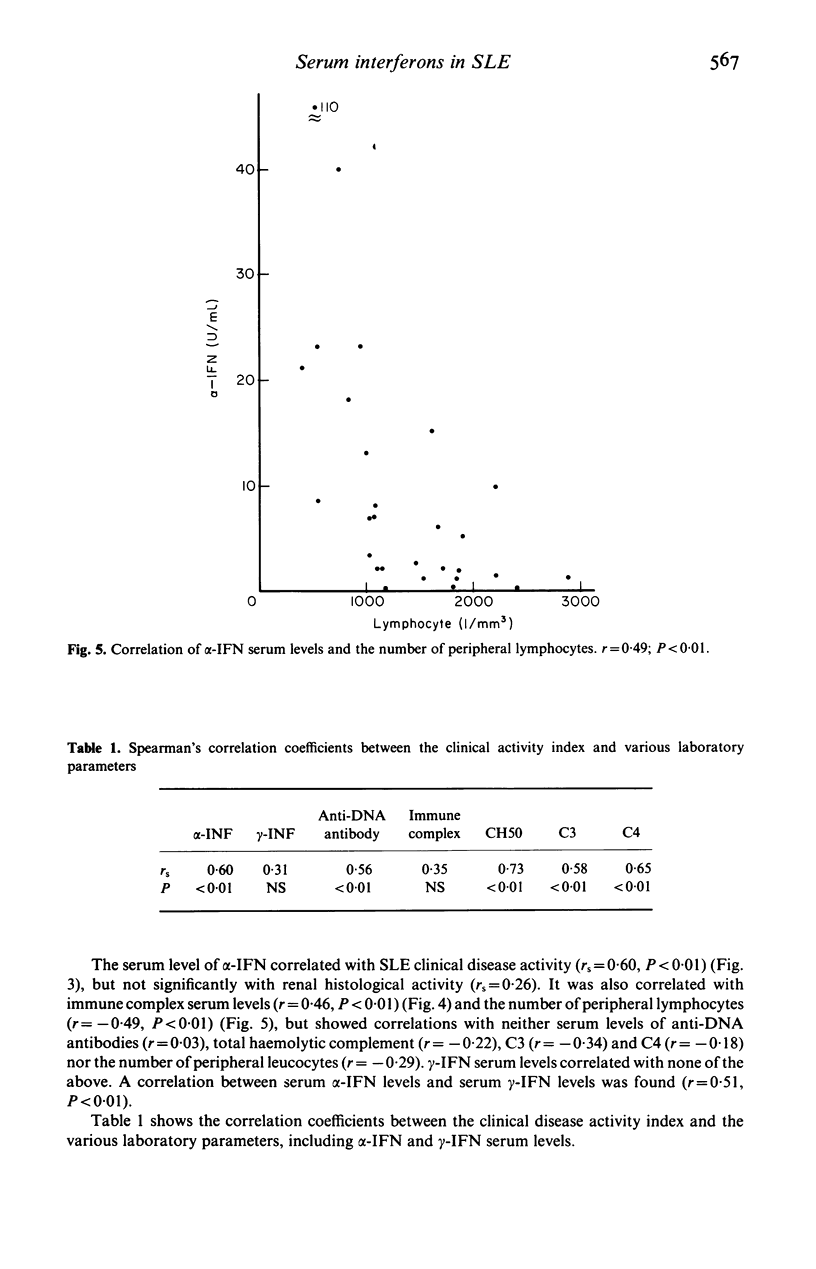
Serum levels of alpha (alpha) and gamma (gamma)-interferons (IFN) were measured in 30 patients with untreated systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) with a solid-phase, sandwich immunoradiometric assay using specific monoclonal antibodies. The serum levels of alpha-IFN were higher in patients with SLE than in normal subjects, and correlated with the clinical activity index (rs = 0.60, P less than 0.01), but not with renal histological activity. The serum level of alpha-IFN correlated with the serum level of immune complexes (r = 0.46, P less than 0.01) and the number of peripheral lymphocytes inversely (r = -0.49, P less than 0.01). Serum gamma-IFN levels were also higher in patients with SLE than in control subjects but no correlations were found between it and either clinical activity, renal histological activity or various laboratory parameters. Serum levels of both alpha-IFN and gamma-IFN were higher in SLE patients with erythema than in those without. These results suggested that serum levels of alpha-IFN were more closely related to clinical activity of SLE than were those of gamma-IFN, and that peripheral lymphocytes were probably not the source of the elevated serum IFN-alpha concentration.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin H. A., 3rd, Muenz L. R., Joyce K. M., Antonovych T. A., Kullick M. E., Klippel J. H., Decker J. L., Balow J. E. Prognostic factors in lupus nephritis. Contribution of renal histologic data. Am J Med. 1983 Sep;75(3):382–391. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90338-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill F. R., Griffin D. B., Band H. A., Beverley P. C. Immune human lymphocytes produce an acid-labile alpha-interferon. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):1059–1063. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basham T. Y., Merigan T. C. Recombinant interferon-gamma increases HLA-DR synthesis and expression. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1492–1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., McKinney S., Liu V., Kung P. C., Vilcek J., Le J. Use of monoclonal antibodies as sensitive and specific probes for biologically active human gamma-interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5219–5222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernielewski J. M., Bagot M. Class II MHC antigen expression by human keratinocytes results from lympho-epidermal interactions and gamma-interferon production. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Nov;66(2):295–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer D. G., Rubinstein M. Spontaneous production of interferon-gamma and acid-labile interferon-alpha by subpopulations of human mononuclear cells. Cell Immunol. 1983 Oct 15;81(2):426–434. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90249-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujibayashi T., Hooks J. J., Notkins A. L. Production of interferon by immune lymphocytes exposed to herpes simplex virus-antibody complexes. J Immunol. 1975 Nov;115(5):1191–1193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Nineham L. J., Roitt I. M. Routine assay for the detection of immune complexes of known immunoglobulin class using solid phase C1q. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jun;24(3):396–400. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holian J., Griffiths I. D., Glass D. N., Maini R. N., Scott J. T. Human anti-DNA antibody: reference standards for diagnosis and management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Oct;34(5):438–443. doi: 10.1136/ard.34.5.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooks J. J., Jordan G. W., Cupps T., Moutsopoulos H. M., Fauci A. S., Notkins A. L. Multiple interferons in the circulation of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Apr;25(4):396–400. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooks J. J., Moutsopoulos H. M., Geis S. A., Stahl N. I., Decker J. L., Notkins A. L. Immune interferon in the circulation of patients with autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jul 5;301(1):5–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197907053010102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Farrar W. L. The role of a gamma interferon-like lymphokine in the activation of T cells for expression of interleukin 2 receptors. Cell Immunol. 1983 Jan;75(1):154–159. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley V. E., Fiers W., Strom T. B. Cloned human interferon-gamma, but not interferon-beta or -alpha, induces expression of HLA-DR determinants by fetal monocytes and myeloid leukemic cell lines. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):240–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knop J., Stremmer R., Neumann C., De Maeyer E., Macher E. Interferon inhibits the suppressor T cell response of delayed-type hypersensitivity. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):757–759. doi: 10.1038/296757a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Sano H., Abe T., Homma M., Steinberg A. D. Correlation between clinical activity of systemic lupus erythematosus and the amounts of DNA in DNA/anti-DNA antibody immune complexes. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):1960–1965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neighbour P. A., Grayzel A. I. Interferon production of vitro by leucocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Sep;45(3):576–582. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preble O. T., Black R. J., Friedman R. M., Klippel J. H., Vilcek J. Systemic lupus erythematosus: presence in human serum of an unusual acid-labile leukocyte interferon. Science. 1982 Apr 23;216(4544):429–431. doi: 10.1126/science.6176024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preble O. T., Rothko K., Klippel J. H., Friedman R. M., Johnston M. I. Interferon-induced 2'-5' adenylate synthetase in vivo and interferon production in vitro by lymphocytes from systemic lupus erythematosus patients with and without circulating interferon. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):2140–2146. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schattner A. Lymphopenia in systemic lupus erythematosus: possible role of interferon. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Nov;26(11):1415–1415. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott G. M., Robinson J. A., Secher D. S., Ashburner C. M., Abbott S. R. Measurement of interferon from in vitro stimulated lymphocytes by bioassay and monoclonal antibody-based immunoassay. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jul;66(Pt 7):1621–1625. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-7-1621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibbitt W. L., Jr, Gibbs D. L., Kenny C., Bankhurst A. D., Searles R. P., Ley K. D. Relationship between circulating interferon and anti-interferon antibodies and impaired natural killer cell activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Jun;28(6):624–629. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strannegård O., Hermodsson S., Westberg G. Interferon and natural killer cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Nov;50(2):246–252. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targan S., Stebbing N. In vitro interactions of purified cloned human interferons on NK cells: enhanced activation. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):934–935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsokos G. C., Rook A. H., Djeu J. Y., Balow J. E. Natural killer cells and interferon responses in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Nov;50(2):239–245. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valle M. J., Jordan G. W., Haahr S., Merigan T. C. Characteristics of immune interferon produced by human lymphocyte cultures compared to other human interferons. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):230–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Clark-Lewis I., McKimm-Breschkin L., Harris A. W., Schrader J. W. Interferon-gamma induces enhanced expression of Ia and H-2 antigens on B lymphoid, macrophage, and myeloid cell lines. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):788–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ytterberg S. R., Schnitzer T. J. Serum interferon levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Apr;25(4):401–406. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlotnik A., Shimonkevitz R. P., Gefter M. L., Kappler J., Marrack P. Characterization of the gamma-interferon-mediated induction of antigen-presenting ability in P388D1 cells. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2814–2820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


