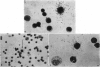
Abstract
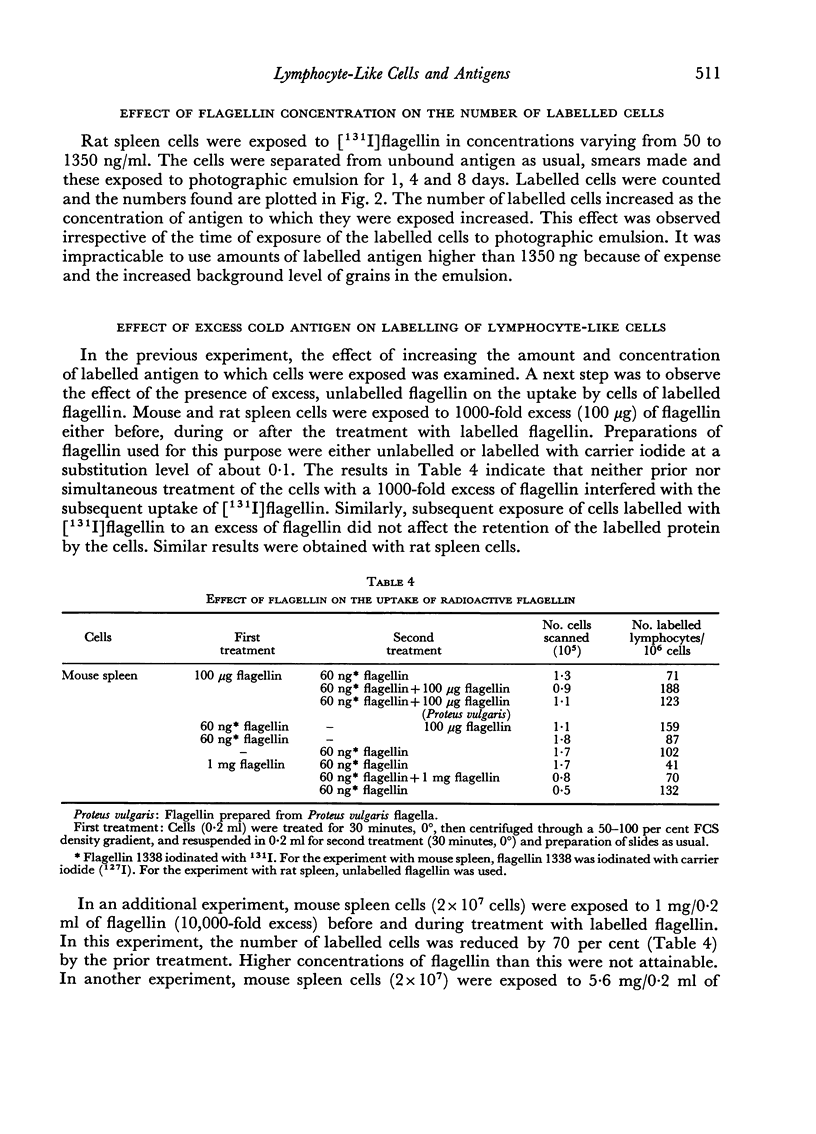
Labelled bacterial flagellin and haemocyanin reacted with lymphocyte-like cells from several rat and mouse tissues. This reaction occurred at low temperatures and in the presence of sodium azide, conditions which inhibited uptake of labelled proteins by phagocytic cells. The reactive cells took up at least 40,000 molecules of labelled flagellin, and appeared to have a much greater capacity, since pretreatment with 10,000 times this amount of flagellin was required to inhibit the reaction.
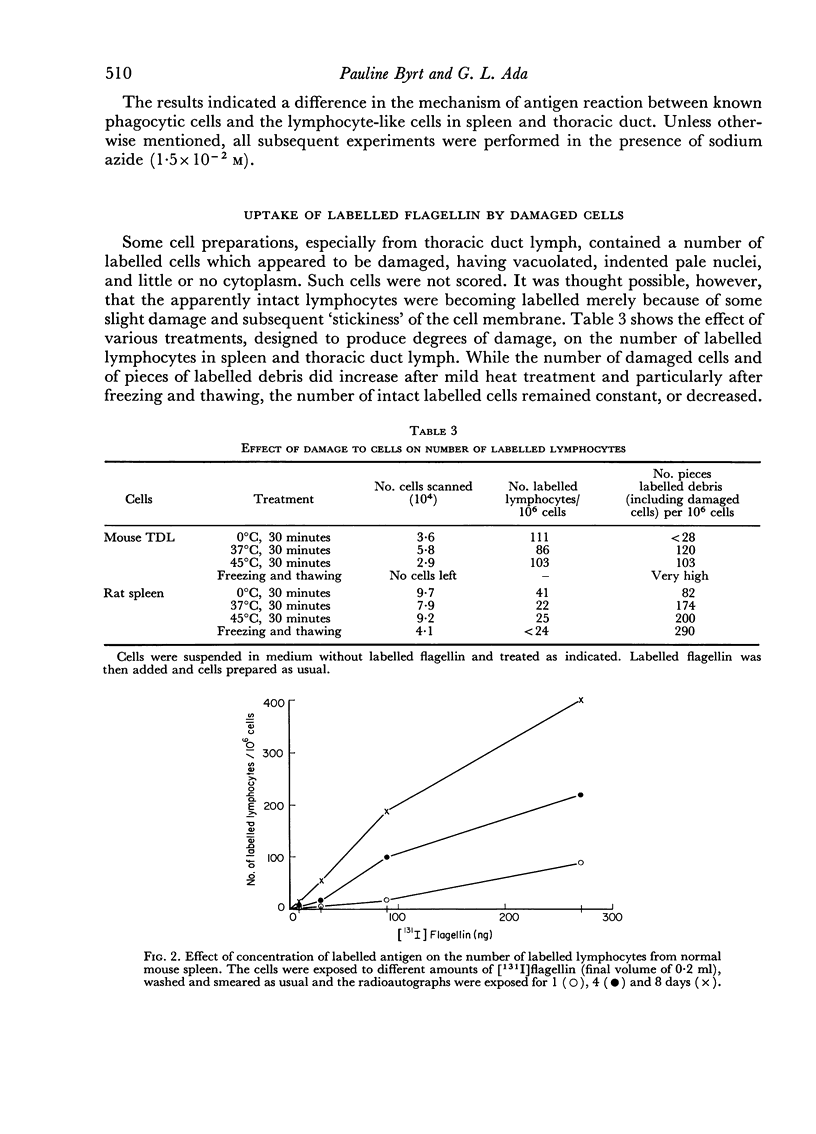
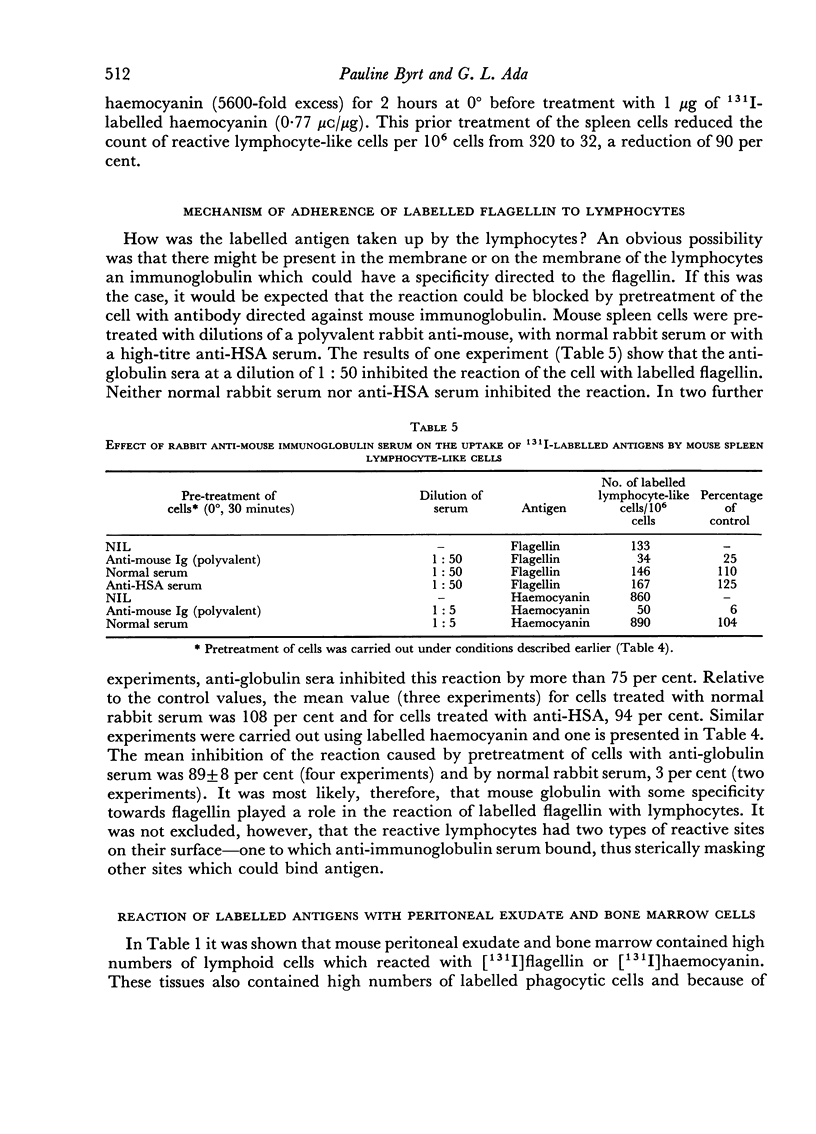
The flagellin and haemocyanin were firmly bound to the cells, possibly to immunoglobulin at the cell surface, since prior treatment with antisera directed against mouse immunoglobulin inhibited the reaction with lymphocytes from mouse spleen and peritoneal exudate. The number of reactive cells in spleen was proportional to the concentration of labelled protein. At a given concentration of labelled protein, however, the number of reactive lymphocytes was characteristic of each tissue. Spleen, lymph node and thoracic duct lymph contained a similar proportion of reactive lymphocyte-like cells, peritoneal exudate contained more, and thymus contained few if any such cells. Bone marrow contained a high proportion of reactive lymphoid cells which apparently reacted in a non-specific manner, since the uptake of labelled protein by these cells was not inhibited by anti-immunoglobulin serum.
Full text
PDF



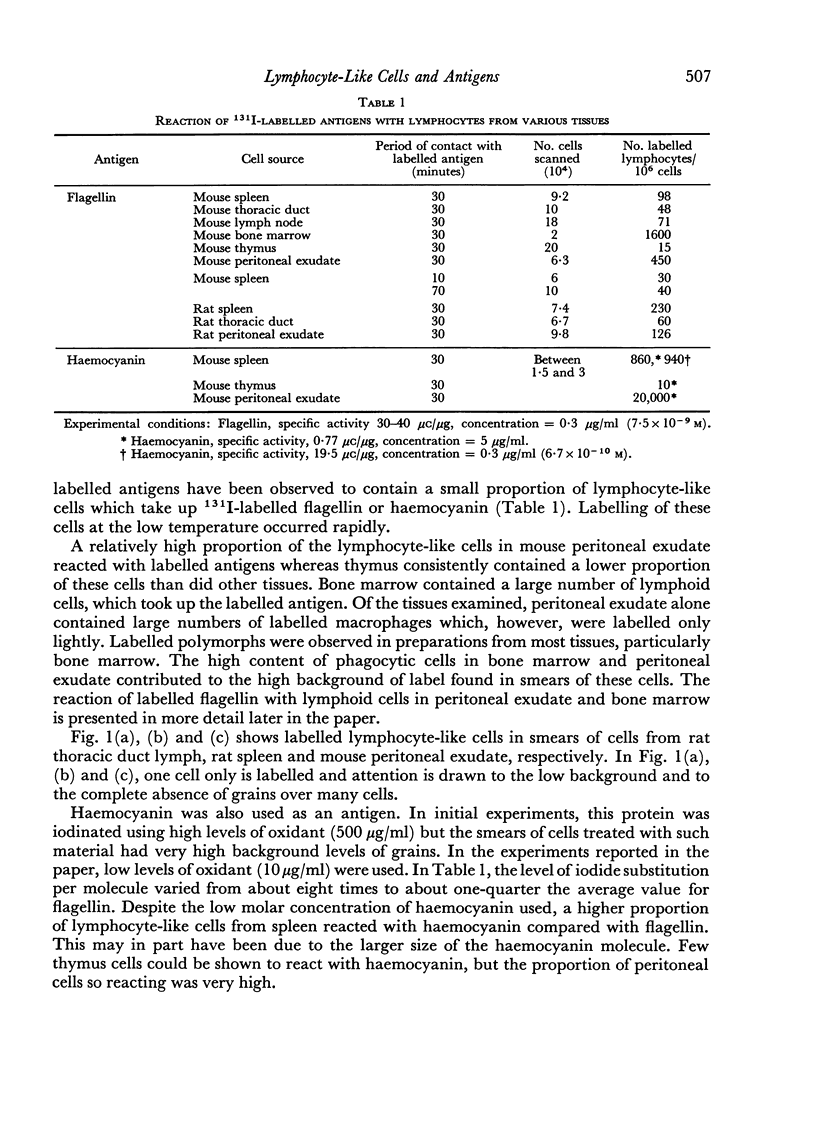
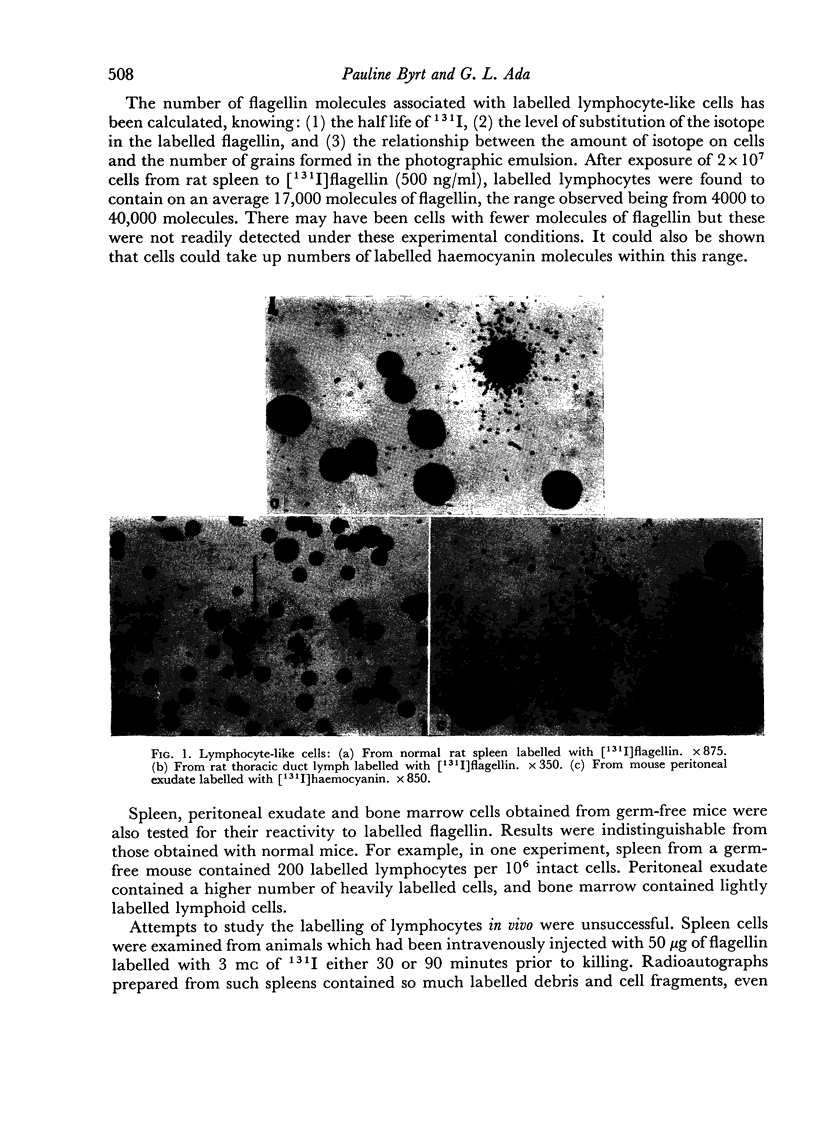
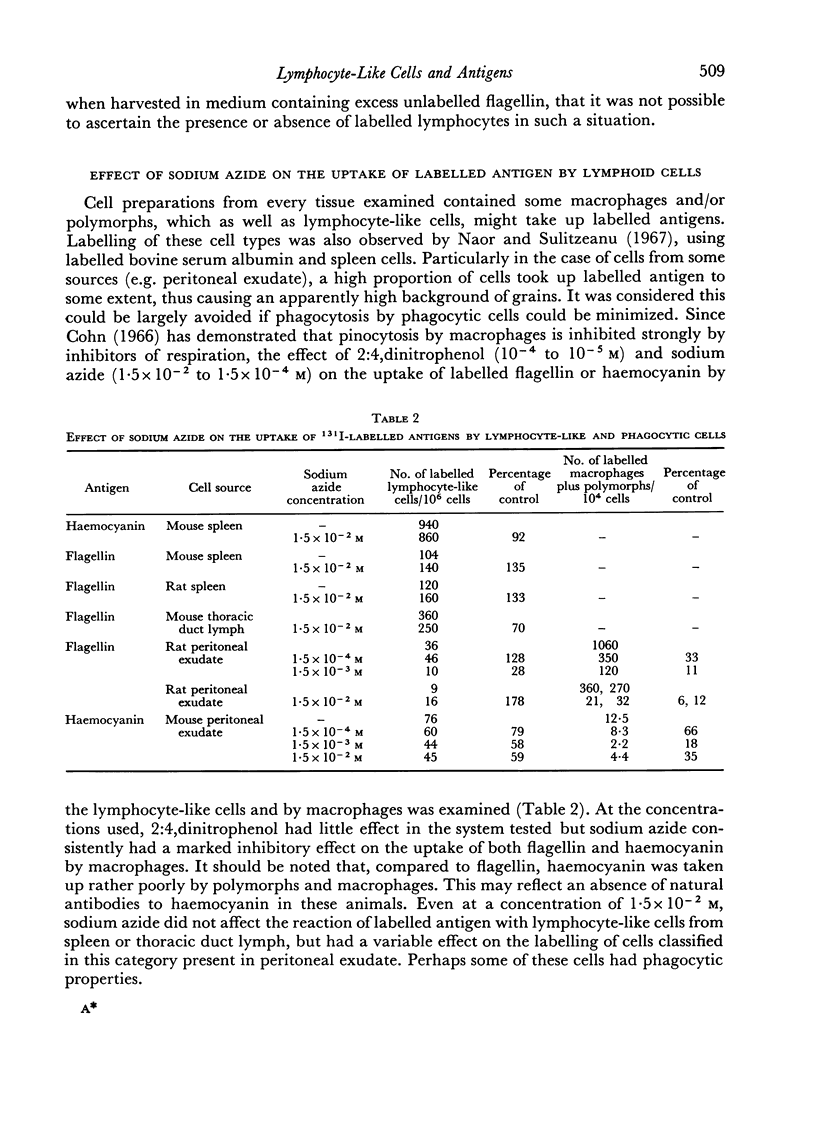




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADA G. L., NOSSAL G. J., PYE J., ABBOT A. ANTIGENS IN IMMUNITY. I. PREPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF FLAGELLAR ANTIGENS FROM SALMONELLA ADELAIDE. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1964 Jun;42:267–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ADA G. L., NOSSAL G. J., PYE J. ANTIGENS IN IMMUNITY. III. DISTRIBUTION OF IODINATED ANTIGENS FOLLOWING INJECTION INTO RATS VIA THE HIND FOOTPADS. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1964 Jun;42:295–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ada G. L., Humphrey J. H., Askonas B. A., McDevitt H. O., Nossal G. J. Correlation of grain counts with radioactivity (125I and tritium) in autoradiography. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Mar;41(3):557–572. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(66)80106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERENBAUM M. C. The autoradiographic localization of intracellular antibody. Immunology. 1959 Jan;2(1):71–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYDEN S. V. CYTOPHILIC ANTIBODY IN GUINEA-PIGS WITH DELAYED-TYPE HYPERSENSITIVITY. Immunology. 1964 Jul;7:474–483. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn Z. A. The regulation of pinocytosis in mouse macrophages. I. Metabolic requirements as defined by the use of inhibitors. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):557–571. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGRAHAM J. S., BUSSARD A. APPLICATION OF A LOCALIZED HEMOLYSIN REACTION FOR SPECIFIC DETECTION OF INDIVIDUAL ANTIBODY-FORMING CELLS. J Exp Med. 1964 Apr 1;119:667–684. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.4.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JERNE N. K., NORDIN A. A. Plaque formation in agar by single antibody-producing cells. Science. 1963 Apr 26;140(3565):405–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy J. C., Till J. E., Siminovitch L., McCulloch E. A. The proliferative capacity of antigen-sensitive precursors of hemolytic plaque-forming cells. J Immunol. 1966 Jun;96(6):973–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKELA O., NOSSAL G. J. Bacterial adherence: a method for detecting antibody production by single cells. J Immunol. 1961 Oct;87:447–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Mitchell G. F., Weiss N. S. Cellular basis of the immunological defects in thymectomized mice. Nature. 1967 Jun 3;214(5092):992–997. doi: 10.1038/214992a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell G. F., Miller J. F. Immunological activity of thymus and thoracic-duct lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):296–303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naor D., Sulitzneau D. Binding of radioiodinated bovine serum albumin to mouse spleen cells. Nature. 1967 May 13;214(5089):687–688. doi: 10.1038/214687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick E., Feldman J. D. Autoradiographic plaques for the detection of antibody formation to soluble proteins by single cells. Science. 1967 May 19;156(3777):964–966. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3777.964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Playfair J. H., Papermaster B. W., Cole L. J. Focal antibody production by transferred spleen cells in irradiated mice. Science. 1965 Aug 27;149(3687):998–1000. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3687.998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELL S., GELL P. G. STUDIES ON RABBIT LYMPHOCYTES IN VITRO. I. STIMULATION OF BLAST TRANSFORMATION WITH AN ANTIALLOTYPE SERUM. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:423–440. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S., Gell P. G. Studies on rabbit lymphocytes in vitro. IV. Blast transformation of the lymphocytes from newborn rabbits induced by antiallotype serum to a paternal IgG allotype not present in the serum of the lymphocyte donors. J Exp Med. 1965 Nov 1;122(5):923–928. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.5.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhr J. W. Passive sensitization of lymphocytes and macrophages by antigen-antibody complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1599–1606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R., Schuit H. R., Hijmans W. The formation of immunoglobulins by human tissues in vitro. IV. Circulating lymphocytes in normal and pathological conditions. Immunology. 1966 Jul;11(1):29–40. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]