Abstract
K1 is the first open reading frame encoded by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) and lies positionally to the immediate right of the terminal repeats. K1 is a transmembrane glycoprotein having a functional immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) capable of activating B-cell receptor signaling. K1 is expressed mostly during the lytic cycle of the virus and its promoter lies within the terminal repeat which contains the binding sites for latency-associated nuclear antigen (LANA). The K1 promoter (K1p) having LANA binding sites assayed by reporter assay demonstrated that LANA is capable of down-regulating K1 promoter transcriptional activity. However, the KSHV replication transcription activator RTA up-regulates K1p transcriptional activity. The promoter deleted of LANA binding sites showed loss in LANA-mediated down-regulation but was unaffected for RTA-mediated up-regulation. Increasing amounts of RTA rescued LANA-mediated repression of K1p transcriptional activity in cotransfection experiments. Reporter assay data suggest that LANA binding to its cognate sequence is critical for LANA-mediated repression of K1p as a LANA construct lacking the DNA binding domain was unable to repress K1p transcription. Additionally, KSHV primary infection experiments suggest that K1 is expressed during early infection but is repressed on the establishment of latency and so follows an expression profile similar to that of RTA during infection. Analysis of the promoter sequence revealed the presence of Oct-1 transcription factor binding sites within the −116 to +76 region. Mutational analysis of the Oct-1 sites abolished RTA-mediated transcriptional activation, suggesting that RTA up-regulates K1p transcription through binding to this transcription factor.
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), also known as human herpesvirus 8, is the causative agent of Kaposi's sarcoma, a complex endothelial neoplasm predominantly seen in AIDS patients (6, 7, 18, 49). KSHV has also been shown to be present in primary effusion lymphoma and multicentric Castleman's disease, rare B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders (5, 13, 44, 50). KSHV was initially identified from a Kaposi's sarcoma biopsy specimen using representation difference analysis. Sequence comparison identified a new virus having strong similarity to herpesvirus saimiri, a gammaherpesvirus subfamily member (7, 8). KSHV, like other herpesviruses, establishes both lytic and latent infections but predominantly persists latently in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated tumors and primary effusion lymphoma with the expression of an array of limited genes (3, 14, 24, 25, 51, 60).
K1, which is predominantly expressed during lytic infection (26), is the positional equivalent to herpesvirus saimiri transformation protein, R1 of rhesus rhadinovirus, and Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) (11, 15, 23). KSHV, besides having a strong resemblance to herpesvirus saimiri, did not show similarity in amino acid sequence or structural organization to herpesvirus saimiri transformation protein but could replace its functional properties in terms of immortalization of rodent fibroblasts (33, 34, 55). Additionally, K1 transgenic mice have been shown to develop plasmablastic lymphoma with the feature of spindle cells (42).
K1 is a 46-kDa transmembrane glycoprotein with an N-terminal signal sequence, an extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain, and a C-terminal cytoplasmic tail containing an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) capable of activating signaling pathways (26, 33, 34, 57, 61). K1 protein is related to the immunoglobulin receptor family and has similarity to the B-cell receptor (33). K1 is constitutively active through oligomerization via conserved, extracellular cysteine residues leading to the phosphorylation of the ITAM and recruitment of the major B-cell kinase Syk for the phosphorylation of cellular proteins, mobilization of intracellular calcium, and activation of transcription factors such as NFAT and AP-1 (21, 27, 28, 30, 33, 38, 58). The amino-terminal domain of K1 interacts with the μ chain of the B-cell receptor complex leading to the inhibition of intracellular transport of B-cell receptor and resulting in retaining B-cell receptor complexes in the endoplasmic reticulum, preventing their intracellular transport to the cell surface which implies a role for K1 in the survival of KSHV-infected cells (26, 30, 32).
The expression profile of K1 during the KSHV life cycle in not restricted to only the lytic cycle. Previous studies performed by Lagunoff and Ganem demonstrate that a 1.3-kb transcript is expressed only when BCBL-1 cells were induced with tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate (26), whereas Samaniego et al. have shown the presence of a 1.3- and a 3-kb K1 transcript in uninduced BC-3 cells as well as their up-regulation in tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate-induced BC-3 cells (47). The K1 transcript has also been detected in Kaposi's sarcoma tumors as well as in multicentric Castleman's disease tissues (39, 47).
Northern hybridization and microarray data analyzing KSHV's transcriptional program during lytic reactivation in primary effusion lymphomas and real-time PCR analysis indicate that K1 expression was up-regulated during the lytic cycle (16, 22, 25, 40, 48). However, analysis of gene clusters based on transcriptional program groups K1 with the latency-associated nuclear antigen (LANA) gene cluster of Orf73, Orf72 (cyclin), and Orf71 (vFLIP) (16). Based on the previous data it is believed that K1 is clearly up-regulated during the lytic cycle but there is a possibility of a low level of K1 expression during latent infection. A previous published report shows that ITAM-dependent signaling by K1 can boost lytic reactivation in KSHV-infected primary effusion lymphoma cells, determined by introducing K1 mutants into BCBL-1 cells, which diminished lytic cycle gene expression (27). Therefore it is believed that K1 might have multiple roles in cellular signal transduction and viral lytic reactivation (27).
Since the expression of K1 was mostly up-regulated during the lytic cycle Bowser et al. evaluated the role of RTA on a K1 promoter cloned by PCR amplification of K1p spanning the −325 to +76 region including part of the terminal repeat sequences (4). In this report we have evaluated the effect of LANA on K1p activity by cloning the promoter region including the LANA binding sequence. We demonstrate that the K1 promoter element was down-regulated in the presence of LANA, which explains the reduced or minimal levels of K1 during latent infection. We have further demonstrated that RTA can rescue LANA-mediated down-regulation of K1p in a dose-responsive manner and thus may contribute to control the lytic reactivation of KSHV.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Promoter cloning and plasmids.
We digested previously described cosmid Z6 with BamHI and NotI and precisely excised a 2,315-bp band which includes the region of the first terminal repeat and the entire K1 open reading frame (ORF) (9, 45). The fragment was cloned into pBSpuro, resulting in pBSpuroB, which was further digested to remove the K1 ORF region with PstI (enzyme site immediately after translation start site) and BamHI. The plasmid was end blunted and ligated to generate pBSpuroBB containing the K1 promoter region. The K1 promoter region (−650 to +76), including the untranslated region, was excised by NotI, followed by end-filling and HindIII digestion. This fragment was cloned into the pGL3basic vector that had been digested with BglII, end filled to blunt the site using the Klenow fragment, and then digested with HindIII, generating pGL3B K1p(−650 to +76) (Fig. 1A).
FIG. 1.
LANA down-regulates K1 promoter transcriptional activity. A. Strategy for cloning K1p into pGL3B. The NotI-BamHI fragment of cosmid Z6 containing K1 and the terminal repeat was excised and cloned into BSpuro at the indicated sites, generating pBSpuroB. The coding sequence of K1 was deleted by digesting with BamHI and PstI followed by blunting both ends and religating it to make pBSpuroBB. K1p was excised from pBSpuroBB by digesting with NotI followed by blunting and digesting with HindIII. The excised fragment was cloned into pGL3B at the BglII (blunted) and HindIII sites. B. Schematic of K1p(−650 to +76) and LBS-deleted K1p(−350 to +76), generated by digesting pGL3BK1p with SmaI to remove the LBS region followed by religation of the remaining vector. C. LANA down-regulates K1p(−650 to +76) activity. pGL3B K1p(−650 to +76) was cotransfected with increasing amounts of LANA (5, 10, and 15 μg) into 293 cells. At 24 h posttransfection cells were lysed and assayed for luciferase activity. Increasing amounts of LANA showed down-regulation of K1p, whereas increasing amounts of RTA (5, 10, and 15 μg) up-regulated the promoter. Increasing amounts of LANA and RTA were detected in the respective cell lysates by Western blotting using anti-Myc antibody. D. LBS-deleted K1p(−350 to +76) is unaffected by LANA-mediated down-regulation. Increasing amounts of LANA and RTA were cotransfected with K1p ΔLBS and assayed for luciferase activity. Increasing amounts of LANA show slight up-regulation of K1p, whereas RTA showed a similar up-regulatory effect on full-length K1p. E. LANA down-regulates full-length K1p(−650 to +76), whereas RTA up-regulates the promoter in BJAB cells in a dose-dependent manner, similar to 293 cells. F. LANA and RTA show similar effects on LBS-deleted K1p(−350 to +76) transcriptional activity in BJAB cells.
The promoter element deleted of the LANA binding sequence was generated by deleting the SmaI fragment from the above promoter and designated pGL3B K1p(−350 to +76). pGL3B K1p(−116 to +76) deleted of potential RTA binding sequence (interleukin-6 promoter region) was generated by digesting the above −350 to +76 construct with AscI, followed by blunting this site and digesting the vector backbone again with SmaI to remove the region of the promoter from −350 to −115. Self-ligation of the remainder of the vector yielded pGL3B K1p(−116 to +1). The promoter region from −116 to +76, including the untranslated region, was analyzed for transcription factor binding motifs using an online motif search tool (http://motif.genome.jp/). Oct-1 transcription factor binding sites were mutated by site-directed mutagenesis using PCR primers containing the desired mutations. All the clones were sequenced and confirmed for the presence of indicated mutations.
pA3M LANA and RTA Myc were used as expression vectors for LANA and RTA and were described previously (29, 37, 56). LANA mutants LANA N (amino acids 1 to 340), LANA C (amino acids 762 to 1162), and LANA ΔIR (amino acids 327 to 929 deleted) used in reporter assay were described previously (54).
pBSpuro was made by cloning the puro cassette at the SalI and ClaI sites of pBS (Stratagene). The expression vector containing K1p under control of its endogenous promoter, pBSpuroB, was made as described above. Plasmid pBSpuroB ΔLBS, with K1 gene expression under the control of endogenous K1p deleted of LANA binding sites (LBS), was generated by removing the NotI and SmaI fragment of pBSpuroB. pCDNA3.1 K1 was generated by PCR amplification using pBSpuroB as template DNA.
Cell lines.
BCBL-1 is a KSHV-positive primary effusion lymphoma cell line. BJAB, KSHV-negative cells were cultured in RPMI supplemented with 7% fetal bovine serum, 2 mM l-glutamine and penicillin-streptomycin (5 U/ml and 5 μg/ml, respectively). Human embryonic kidney 293 cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 2 mM l-glutamine, and penicillin-streptomycin (5 U/ml and 5 μg/ml, respectively).
Antibodies.
Myc-tagged proteins were detected using mouse hybridoma 9E10 described previously (56). Beta-actin was detected using rabbit anti-β-actin antibody (Cell Signaling, Beverly, MA). Lyn and phospho-Lyn (S507) were detected using specific antibodies (Cell Signaling, Beverly, MA).
Reporter assay.
Reporter assays were performed in 293 and BJAB B cells; 10 million 293 and BJAB cells were transfected using a Bio-Rad electroporater (Bio-Rad Laboratories); 5.0 μg of the indicated reporter plasmids was transfected along with indicated amounts of LANA and RTA expression vectors. pA3M empty vector was used as filler DNA. Transfection efficiencies were normalized using the green fluorescent protein-containing vector pEGFPC1 (Clontech Inc., Palo Alto, CA). At 24 h posttransfection cells were harvested, washed in phosphate-buffered saline and lysed in cell lysis buffer (Bio-vision); 50 μl of cell lysate was used for the reporter assay using a Luminometer LMX384 (Molecular Devices, CA).
A portion of the cell lysate was used for Western blotting. Transferred proteins were detected by Odyssey infrared scanning technology (LiCor, Lincoln, NE.) using Alexa Fluor 680 and Alexa Fluor 800 (Molecular Probes, Carlsbad, CA, and Rockland, Gilbertsville, PA, respectively). Empty vector pGL3B showed some up-regulation with RTA expression and therefore the fold change in reporter plasmid with RTA is normalized with the empty vector. All the transfections were done in duplicate and the results shown represent the mean of the data from three independent experiments.
Reporter assays were also performed by transfecting the above plasmids into 293 cells using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA); 300 ng of indicated reporter plasmids was transfected with 500 ng of LANA and RTA expression vectors using 1.0 μl of Lipofectamine as per the manufacturer's instructions. At 24 h posttransfection cells were harvested and subjected to the reporter assay and Western blot analysis.
Quantitation of K1 transcript.
pBSpuro, pBSpuroB (−650 to +76 K1p and ORF) and pBSpuroB ΔLBS (−350 to +76) was cotransfected into 10 million HEK293 or BJAB cells with LANA, RTA or both by electroporation; 36 h posttransfection cells were harvested and divided into two sets. The first set was for the isolation of total RNA and the second set was used for Western detection of Lyn, phospho-Lyn, and β-actin using specific antibodies. Lyn and phospho-Lyn were subsequently detected with Alexa Fluor 680 and Alexa Fluor 800 secondary antibodies using Odyssey Infra-Red scanning technology (LiCor, Lincoln, NE). Band intensities were quantified using Odyssey software v1.2 (LiCor, Lincoln, NE) and relative intensities were calculated considering lane 1 of each set as the reference.
Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. cDNA was synthesized using a first-strand cDNA synthesis kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) as per the manufacturer's recommendations. K1 gene-specific primers Forward (5′-CCAAACGGACGAAATGAAAC-3′) and Reverse (5′-ACGTGTGGTTGCATGGATTA-3′) were used for amplification and quantitation of K1 transcripts in synthesized cDNA. Amplification of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) with specific primers (Forward, 5′-TGCACCACCAACTGCTTAG-3′, and Reverse, 5′-GATGCAGGGATGATGTTC-3′) was used for the normalization of Ct values in different samples.
Amplification was performed using SYBR Green real-time master mix (MJ Research Inc., Waltham, MA), 1 mM each primer, and 1 μl of the cDNA product in a total volume of 20 μl. Thirty cycles of 1 min at 94°C, 1 min at 56°C, and 30 s at 72°C, followed by 5 min at 72°C, were performed in an MJ Research Opticon II thermal cycler (MJ Research Inc., Waltham, MA). Each cycle was followed by two plate reads, the first at 72°C and the second at 82°C. A melting curve analysis was performed to verify the specificity of the amplified product. K1 transcripts were calculated using pCDNA3.1 K1 purified plasmid as a standard. The experiment was done in triplicate and the data presented here are the means of two independent experiments.
Primary infection of HEK293 cells with KSHV in vitro.
KSHV was purified from BCBL-1 as described previously (29). Approximately 50 million cells were induced with 20 ng of tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate/ml and 1.5 mM sodium butyrate (Sigma, St. Louis, MO) for 5 days. Medium containing virion particles was centrifuged to remove cell debris, followed by filtering through 0.45-μm syringe filters. Virions were pelleted at 20,000 rpm for 2 h and resuspended in 1× phosphate-buffered saline; 10 million 293 cells were infected at the 25% confluent stage and cells were harvested at the indicated time points. Total RNA was extracted and used for cDNA synthesis using a first-strand cDNA synthesis kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). Gene-specific primers were used for the amplification of K1 used in the previous experiment. The LANA- and RTA-specific primers for real-time quantitation used were described previously (29). The values for the relative copies were calculated by the ΔΔCt method using the β-actin gene as the control. Each sample was analyzed in triplicate.
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay.
Oligonucleotides containing the Oct-1 site or mutated Oct-1 site were synthesized and annealed to the respective antisense strand by gradient cooling. The double-stranded DNA probe was filled in with α-32P-labeled dCTP, dATP, dGTP, and dTTP using the Klenow fragment (New England Biolabs, Beverly, MA). The labeled probes were purified on a Nuc Trap probe purification column (Stratagene Inc., La Jolla, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The total incorporation of [α-32P]dCTP was measured, and approximately 75,000 cpm of probe was used per reaction.
Nuclear extracts prepared from BCBL-1 cells were used as a source of Oct-1 transcription factor. In vitro-translated RTA prepared by the coupled in vitro transcription/translation system (TNT) of Promega Inc. (Madison, WI) according to the manufacturer's instructions was used in the indicated lanes. Anti-Oct-1 antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) was used for supershift analysis.
Nuclear extract (5.0 μg of total protein) was used for binding to the indicated probe in electrophoretic mobility shift assay reactions. Unlabeled competitor (100-fold) was added 5 min prior to the addition of radiolabeled probes; 1.0 μg of rabbit anti-Oct-1 was used to supershift the complex. The protein-DNA binding reaction mixture was incubated at 25°C for 15 minutes. The bound complex was loaded onto a 6.0% polyacrylamide gel containing 0.5× TBE (0.045 M Tris-borate, pH 8.2, 1 mM EDTA). The gel was resolved in 0.5× TBE for 4 h at 150 V, dried, and autoradiographed using a PhosphorImager plate (Molecular Dynamics, Inc.).
RESULTS
LANA down-regulates the K1 promoter in the reporter assay.
KSHV-encoded K1 is the first open reading frame shown to be expressed predominantly during the lytic cycle of the virus with the exception of low levels during latency (16, 26, 37). The role of K1 in tumorigenesis is clearly established by various laboratories but the regulation of K1 expression during latent and latent/lytic switch is not well understood (34, 42). One study done so far has demonstrated that the −125 to +76 region was sufficient and responsive to RTA expression (4), but did not explore the regulation of K1 expression during latent infection.
Sequence analysis of the K1 promoter region cloned from the Z6 cosmid revealed the presence of LANA binding sequence upstream of bp −325 previously described as a promoter (4). Since LANA is expressed in almost all KSHV-positive cells and important for tethering of the viral genome by binding to the LANA binding sequence (2, 10, 19, 20, 26), we hypothesized that LANA may have a role in regulation of K1 expression.
We digested cosmid Z6 of KSHV with BamHI and NotI and cloned K1p as described in the schematic (Fig. 1A). In order to determine the effect of LANA on K1p, we cotransfected pGL3B K1p(−650 to +76) with the LANA expression vector in HEK293 as well as in BJAB cells and assayed promoter activity as relative luciferase units. Reporter assays performed using pGL3B K1p(−650 to +76) with LANA showed a decrease in promoter activity which was further decreased in a dose-dependent manner with increasing LANA expression (Fig. 1C). LANA-dependent down-regulation of K1p was similarly observed in BJAB cells with increasing amounts of LANA (Fig. 1E). However, RTA, which was previously shown to up-regulate K1p (4), showed dose-dependent up-regulation of the full-length K1 promoter activity in both the 293 and BJAB cell lines (Fig. 1C and E).
LANA binding sequence in K1p is important for LANA-mediated down-regulation.
It has clearly been demonstrated that LANA binds to its cognate sequence within the terminal repeat with high affinity to at least one binding site, LBS1 (19). Therefore, we were interested in determining the effect of LANA on K1p deleted for the LANA binding sequence, pGL3B K1p ΔLBS (−350 to +76) (Fig. 1B). Cotransfection of reporter plasmid with the LANA expression vector did not show any down-regulation of the promoter activity in either of the cell lines tested, 293 or BJAB (Fig. 1D and F). Increasing amounts of LANA expression with the pGL3B K1p ΔLBS (−350 to +76) reporter plasmid revealed a small but noticeable up-regulation in promoter activity with increasing LANA expression (Fig. 1D and E). However, transcriptional activity of LBS-deleted K1p (pGL3B K1p ΔLBS) in the presence of RTA was similar to that on full-length K1p(−650 to +76) (Fig. 1D and E). LANA and RTA expression was detected using the anti-Myc antibody, as these expression plasmids were carboxyl- terminally fused with the Myc epitope.
RTA prevents LANA-mediated down-regulation of K1p transcriptional activity.
Our reporter assay data suggested that LANA can down-regulate K1 expression and it has been clearly shown that LANA is expressed in almost all infected cells during latent infection and tethers the viral genome to the host chromosomes (1, 9). Therefore, it is most likely that binding of LANA to its cognate sequence can repress K1 expression. In order to determine whether RTA is able to up-regulate K1 expression when LANA is bound to its cognate sequence we cotransfected pGL3B K1p(−650 to +76) along with constant amounts of LANA in the indicated lanes and increasing amounts of RTA. Reporter assays performed 24 h posttransfection with the cell lysates showed that RTA can prevent LANA-mediated repression of K1p and in fact was up-regulated with increasing RTA expression (Fig. 2A, lanes 3 and 4). Cotransfection of similar amounts of LANA and RTA with LBS-deleted K1p(−350 to +76) showed enhanced up-regulation in K1p, suggesting a cooperative effect of LANA and RTA on the truncated promoter (Fig. 2B). LANA and RTA in all these reporter assays were detected by Western blot using the anti-Myc antibody.
FIG. 2.
RTA reverses LANA-mediated down-regulation of K1p. pGL3B K1p(−650 to +76) was cotransfected into 293 cells with 10 μg of LANA (lane 2) and also with RTA at 5 and 10 μg in lanes 3 and 4, respectively. Increasing amounts of RTA reversed as well as up-regulated K1 promoter activity in a dose-dependent manner. LBS-deleted (−350 to +76) K1p showed synergistic effects of LANA and RTA on K1p transcriptional activity (lanes 3 and 4). Western blots show the expression of LANA and RTA in cotransfected cells. The blot was stripped and reprobed with anti-β-actin antibody to show equal protein loading.
Carboxyl terminus of LANA is sufficient for down-regulation of K1p(−650 to +76).
Previous studies have demonstrated that the C terminus of LANA contains the DNA binding domain; therefore we wanted to determine whether the binding domain by itself is sufficient for K1p down-regulation. Thus, we cotransfected different truncated mutants of LANA for the reporter assay along with full-length K1p(−650 to +76) as well as LBS-deleted K1p(−350 to +76). Our reporter assay data showed that the C terminus of LANA (amino acids 762 to 1162) had down-regulatory effects similar to those of full-length LANA, suggesting that the carboxyl terminus is sufficient to down-modulate K1p by binding to its cognate sequence of the promoter (Fig. 3A).
FIG. 3.
Carboxyl-terminal domain of LANA is the primary domain for K1p transcriptional modulation. A, pGL3B K1p(−650 to +1) was cotransfected with either full-length LANA or its truncations, LANA N (amino acids 1 to 340), LANA C (amino acids 762 to 1162), and LANA ΔIR (amino acids 327 to 929 deleted) into 293 cells. At 24 h posttruncation cells were harvested and assayed for luciferase activity. Full-length LANA (lane 2) and LANA C (lane 4) showed similar down-regulation of K1p activity, whereas the amino terminus (lane 3) and LANA ΔIR (lane 5) showed slight increases in promoter activity. B, LBS-deleted K1p was up-regulated by full-length LANA (lane 2), whereas LANA N (lane 3) and LANA C (lane 4) did not have much effect on this promoter. LANA deleted of the central glycine and glutamic amino acid residues had a slight up-regulatory effect on K1p (lane 5). The arrow indicates the expression of LANA and its truncation mutants in Myc Western blots.
The N terminus of LANA did not have any noticeable effect on transcriptional modulation, whereas the LANA truncation mutant deleted of the middle glycine/glutamic acid region (ΔIR; amino acids 327 to 929 deleted but containing both the amino- and carboxyl-terminal domains) up-regulated K1p (Fig. 3A). K1p deleted of the LBS (−350 to +76) upon transfection with LANA showed similar up-regulation in promoter activity, whereas neither the amino nor the carboxyl terminus of LANA was able to modulate its activity to any noticeable level above that of the control (Fig. 3B). The LANA truncation mutant (ΔIR) up-regulated the promoter like full-length LANA, suggesting that both the amino and carboxyl termini of LANA are important for up-regulation but binding of the LANA carboxyl terminus to the K1p region is important for down-regulation.
LANA and RTA modulate K1 transcription level from the native endogenous viral promoter element.
We used pBSpuro B containing the entire K1p(−650 to +76) and its coding sequence for cotransfection with expression vectors of LANA, RTA, or both together into 293 and BJAB cells. Cells were harvested 36 h posttransfection for the isolation of total RNA followed by cDNA synthesis. Transcripts detected using real-time quantitative PCR showed almost 1.5-fold-reduced numbers of K1 transcripts in LANA- and pBSpuroB-cotransfected 293 cells (Fig. 4A, lanes 1 and 2). BJAB cells cotransfected with LANA and the above promoter (pBSpuroB) showed an almost twofold reduction in K1 transcripts at 36 h posttransfection (Fig. 4B, lanes 1 and 2). This corroborated our reporter assay data for both the 293 and BJAB cell lines. RTA, which was shown previously to up-regulate the K1 promoter as well as in our reporter assay, showed 1.5- to 2.5-fold increases in K1 transcript levels in 293 and BJAB cells, respectively. Cotransfection of the LANA and RTA expression vector together with pBSpuroB showed a moderate reduction in K1 transcripts which may be due to the antagonistic role of LANA on RTA-mediated K1p transcriptional up-regulation.
FIG. 4.
Coexpression of LANA and K1 driven by its native promoter showed down-regulation in K1 transcript level and Lyn phosphorylation. A, 293 and BJAB B cells. pBSpuroB containing the K1 ORF under the control of K1p(−650 to +76) was transfected alone (lane 1) and also cotransfected with either LANA (lane 2) or RTA (lane 3) or both LANA and RTA (lane 4). Total RNA extracted 36 h posttransfection and analyzed for K1 transcripts showed its reduction in LANA-expressing cells (lane 2) but elevation in RTA-expressing 293 as well as BJAB cells (lanes 3). LANA- and RTA-coexpressing cells also showed slight increases in K1 transcripts (lane 4). The level of phospho-Lyn was down-regulated in LANA-expressing cells (lane 2, relative density was 1.13 versus 0.87) relative to that in cells without LANA (lane 1, relative density was 1). In contrast, RTA showed slight up-regulation in phospho-Lyn levels (lane 3, relative density 1.25 versus 1.16), which was also slightly up-regulated in LANA- and RTA-expressing cells compared to the LANA only-expressing cells (lane 4). The native promoter deleted of LBS, pBSpuroB ΔLBS (−350 to +76), did not show LANA-mediated down-regulation of K1 transcript levels. Similarly, the level of phospho-Lyn was also not modulated in LANA-expressing cells (compare lanes 1 and 2, phospho-Lyn and Lyn panels). RTA, which showed increased K1 transcripts, showed slightly increased phospho-Lyn levels (lane 3, Lyn and phospho-Lyn panels). Lane 4 also showed modulation in phospho-Lyn levels. The pBSpuro empty vector showed very little or no change in Lyn and phospho-Lyn levels in cells transfected with LANA, RTA, or both, indicating moderate effects of these proteins on Lyn phosphorylation. LANA and RTA expression was detected using anti-Myc antibody. BJAB cells cotransfected with pBSpuroB and LANA showed reduced numbers of K1 transcripts as well as reduced levels of phospho-Lyn (lanes 1 and 2). RTA showed increased numbers of K1 transcripts as well as phospho-Lyn levels (lane 3). Cells transfected with both LANA and RTA showed similar slight modulations in Lyn phosphorylation in BJAB cells (lane 4). pBSpuroB ΔLBS showed enhanced Lyn phosphorylation in cells transfected with both LANA and RTA. The pBSpuro vector alone did not show much change in phospho-Lyn levels with LANA or RTA coexpression.
We also used LANA binding site-deleted K1p as the native viral promoter upstream of the K1 ORF and cotransfected it with LANA and RTA for detection of K1 transcripts. LANA-transfected 293 and BJAB cells showed moderate increases in K1 transcripts, whereas RTA transfection showed a significant (twofold) increase in the levels in both cell lines (Fig. 4A and B). Cotransfection of LANA and RTA together with LBS-deleted K1p showed significant increases in levels of K1 transcripts in 293 as well as BJAB cells, corroborating the reporter assay data. cDNA made from vector (pBSpuro)-transfected 293 and BJAB cells did not show any amplification using gene-specific primers for K1 (data not shown).
Further, we wanted to determine the phosphorylation state of Lyn in cells expressing K1 from its endogenous promoter and the effect of LANA and RTA on K1 expression and Lyn phosphorylation. K1 was previously shown to be increased in K1 transgenic mice (42). Protein extracted from 293 and BJAB cells cotransfected with pBSpuroB and LANA or RTA showed various levels of Lyn phosphorylation (relative band intensities are shown at the bottom of each band). Detection of phospho-Lyn in pBSpuroB- and LANA-transfected 293 as well as BJAB cells showed reduced levels of Lyn phosphorylation (Fig. 4A and B, relative change in band intensity of lanes 1 and 2 in the Lyn and phospho-Lyn panels). 293 and BJAB cells cotransfected with RTA and pBSpuroB showed a slight increase in the phosphorylation of Lyn which may be due to the increased K1 expression, thus corroborating the above data (Fig. 4A and B, relative change in band intensity of lanes 1 and 3 in the Lyn and phospho-Lyn panels). Expression of LANA and RTA along with pBSpuroB did not show a significant difference in phosphorylation of Lyn (Fig. 4A and B, lane 4 in the Lyn and phospho-Lyn panels).
The K1 gene under control of the deleted LBS (−350 to +76) promoter showed slight increases in the phosphorylation of Lyn upon cotransfection with either LANA or RTA compared to no LANA or RTA, suggesting that increased K1 might have enhanced the phosphorylation of Lyn (Fig. 4A and B, −350 to +76 panels, compare lane 1 with lanes 2 and 3). Expression of LANA and RTA together with the above promoter showed enhanced Lyn phosphorylation, corroborating the above data (Fig. 4A and B, lane 4). Transfection of LANA and RTA with the pBSpuro vector control in 293 and BJAB showed little or no change in relative levels of Lyn and phospho-Lyn in cells transfected with LANA, RTA, or both. This suggests that modulations in the phosphorylation of Lyn were due to the various levels of K1 expression. Expression of LANA and RTA was detected by Western blot analysis using anti-Myc antibodies. Blots were stripped and probed for β-actin as a control for protein loading.
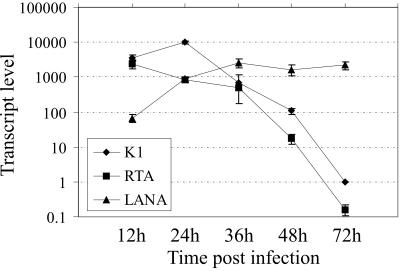
Levels of K1 transcript increase during early infection, followed by rapid reduction towards the establishment of latency.
We used purified BCBL-1 virions to infect 293 cells and followed the pattern of K1 transcripts levels during early infection up until 72 h. Total RNA was extracted from these infected cells at the indicated time points and detection of LANA, RTA and K1 transcripts levels is shown in Fig. 5. The expression levels of K1 peaked at 24 h, followed by a steady decline observed until 72 h postinfection. The LANA levels were increased by 12 h and remained at a high level after 24 h of infection. K1 and RTA mRNA levels were maintained at the same low level, likely due to the small subset of KSHV-infected cells which spontaneously undergo lytic replication. The rapid decrease in the levels of K1 and RTA transcripts is likely due to LANA activating its own expression and repressing transcriptional activity of the lytic genes.
FIG. 5.
KSHV-infected 293 cells show high K1 transcript levels during early infection and reduced levels towards the progression of latency. 293 cells infected with KSHV wild-type BCBL-1 virus showed similar relative copy numbers of K1 and RTA. The expression levels for K1 peaked at 24 h, followed by a steady decline in levels up to 72 h. The LANA levels were increased by 12 h and remained high after 24 h postinfection.
LBS-deleted K1p(−350 to +76) contains an interleukin-6 promoter-like RRE element.
Our reporter assay data indicated that LANA-mediated repression of K1p is due to the presence of its cognate sequence and most probably LANA binding to this region. We further looked to map the RTA-mediated responsive region on K1p. We aligned the −350 to +76 sequence of K1p with the sequence of known binding sites of RTA (12). In our sequence alignment analysis we found a region on K1p having significant similarity to the RTA response elements (RRE) present in the interleukin-6 promoter (Fig. 6).
FIG. 6.
K1p(−350 to +76) contains an RRE similar to the interleukin-6p RRE. Sequence alignment showed RRE elements in K1p (C). The deletion mutant lacking the RRE (−116 to +76) cotransfected with LANA and RTA was assayed for luciferase activity 24 h posttransfection. Comparison of relative luciferase units (RLU) did not show dramatic changes in the RRE-deleted mutant of K1p compared to full-length as well as LBS-deleted K1p (compare panel C with panels A and B). Western blots show expression of LANA and RTA in these cotransfected 293 cells.
In order to evaluate the effect of RTA, we made a mutant promoter by deleting the potential RRE element [K1p(−116 to +76)]. Reporter analysis with RTA revealed that the −116 to +76 region of the promoter was sufficient for RTA-mediated up-regulation, suggesting some other mechanism of RTA-mediated K1p activation (Fig. 6). Coexpression of LANA with the −116 to +76 promoter region showed a slight increase in promoter activity (Fig. 6). Full-length K1p(−650 to +76) and LBS-deleted K1p(−350 to +76) were used parallel to the −116 to +76 region in this experiment (Fig. 6). Expression of LANA and RTA was detected by Western blot analysis using anti-Myc antibody.
Sequence analysis of the −116 to +76 region of K1p revealed Oct-1 transcription factor binding sites.
In order to determine the specific transcription factor binding sites located within the −116 to +76 elements we scanned the indicated region which also includes the first start codon using a web-based motif search tool. The result revealed the presence of multiple Oct-1 transcription factor binding sites shown in Fig. 7A (Oct-1 binding sites shown are shown in expanded boxes).
FIG. 7.
Oct-1 sites are important for RTA-mediated up-regulation of K1p. A, Schematic showing the presence of Oct-1 transcription factor binding sites in the −116 to +76 region of K1p. B, C, and D, Oct-1 transcription factor binding sequences I, II, and III. The top strand is the sequence in K1p and the bottom strand is the mutated sequence incorporated by site-directed mutagenesis. E, K1p −116 to +76 with all Oct-1 sites mutated. Reporter assays performed in 293 cells with pGL3B K1p −116 to +76 (pGL3B-A), Oct-1 site I mutated (pGL3B-B), Oct-1 site II mutated (pGL3B-C), Oct-1 site III mutated (pGL3B-D), and all three Oct-1 sites mutated (pGL3B-E) with LANA and RTA. All Oct-1 site-mutated promoters had significantly reduced (80%) relative luciferase activity (E). The Oct-1-mutated promoters had different basic transcriptional activities which were normalized, and relative fold changes are plotted here. Representative Western blots show expression of LANA and RTA in the above transfections.
We mutated these potential Oct-1 transcription factor binding sites individually as well as all three together by site-directed mutagenesis (Fig. 7B, C, D, and E). Reporter analysis performed in 293 cells demonstrated that loss of the first Oct-1 site reduced RTA-mediated responsiveness to 50%, suggesting that this site contributes a significant amount of activity to the promoter (Fig. 7B, I Oct-1 mut). Mutation of the second Oct-1 site reduced RTA responsiveness to 30%, whereas mutation of the third Oct-1 site was unaffected by RTA-mediated up-regulation (Fig. 7C and D). Mutation of all three Oct-1 sites reduced the RTA-mediated responsiveness to 25%, suggesting that Oct-1 transcription factor binding sites contribute significantly to the RTA-mediated up-regulation of the K1 promoter (Fig. 7E). Representative Western blots for LANA and RTA expression are shown in Fig. 7F.
Sp1 transcription factor binding sites were not responsible for RTA-mediated up-regulation but important in LANA-mediated up-regulation.
Sequence-scanning analysis also demonstrated the presence of multiple Sp1 transcription factor binding sites within −116 to +76, similar to a previous report (4). We wanted to further determine whether these sites may in fact play a role in RTA-mediated up-regulation of the promoter. A deletion excising all Sp1 transcription factor binding sites was generated (Fig. 8). Reporter analysis of this construct performed in the presence of the RTA expression vector revealed that there was a negligible change in RTA-mediated responsiveness, suggesting that Sp1 sites were not the critical sites for modulation (Fig. 8). However, the low level of activation by LANA was abolished in the Sp1-deleted promoter construct, suggesting that LANA may have this activity through binding to Sp1 transcription factors. Deletion of Sp1 sites in the third Oct-1 mutated reporter construct (retaining the second Oct-1 site) −116 to +76 promoter region clearly demonstrated that most of the RTA-mediated response is due to the second Oct-1 transcription factor binding site (Fig. 8C).
FIG. 8.
Sp1 sites of K1p are not required for RTA-mediated up-regulation. Top panel, schematic of K1p(−116 to +76) and its Sp1-deleted mutants. The bottom panel shows relative luciferase activity detected 24 h posttransfection with the −116 to +76 promoter region (A), −116 to +76 Sp1 deleted (B), and −116 to +76 Oct-1 III mutated and Sp1 deleted (C). The Sp1-deleted promoter region did not show significant changes in relative luciferase units in either Sp1-deleted reporter plasmid (B or C). Representative Western blots show expression of LANA and RTA in the above transfections.
Oct-1 transcription factor binds to cis-acting elements within the K1p promoter region.
We performed electrophoretic mobility shift assays to demonstrate the binding of cellular Oct-1 to nucleotide sequences within K1p. We used oligonucleotide probes comprising the second Oct-1 site as well as a mutated site as the probe. Labeled probes were incubated with BCBL-1 cell nuclear extract which showed a specific shift in the mobility of probe (Fig. 9, lane 2). The shift in mobility was abolished using 100-fold specific unlabeled competitor, suggesting the specificity of binding (Fig. 9, lane 3). Mutated nonspecific unlabeled competitor was unable to abolish the Oct-1-specific shift, suggesting that the mutation in the Oct-1 site abolished binding of the Oct-1 transcription factor.
FIG. 9.
Oct-1 transcription factor binds to the Oct-1 site present in K1p(−116 to +76), demonstrated by electrophoretic mobility shift assay. Oligonucleotides encompassing the second octamer site labeled with 32P and incubated with BCBL-1 nuclear extract as a source of Oct-1 transcription factor retarded the mobility of the probe (compare lanes 1 and 2; the open circle in lane 1 shows where free probe ran off the gel). Addition of a 100-fold excess of specific unlabeled competitor (SCC) abolished the shift (lane 3), whereas a similar amount of unlabeled mutant probe competitor (MPCC, II Oct-1 mutant sequence) was unable to compete with the binding of Oct-1 transcription factor to the wild-type sequence (lane 4, open circle). Addition of rabbit anti-Oct-1 antibody (α-Oct-1) supershifted the DNA-Oct-1 complex (lane 5, solid triangle) whereas control immunoglobulin G was unable to modulate the shift (lane 6). Rabbit anti-Oct-1 did not show any binding to the probe on its own (lane 7). Addition of in vitro-translated RTA did not show any detectable level of the larger complex, suggesting weaker binding of Oct-1 and RTA (lane 8). Rabbit reticulocyte lysate was also unable to affect the mobility of the Oct-1-DNA complex (lane 9). In vitro-translated RTA did not show any binding to the probe (lane 10).
Oct-1-specific binding was further confirmed by using anti-Oct-1 antibody to supershift the Oct-1-DNA complex (Fig. 9, lane 5). Nonspecific immunoglobulin G antibody did not have any effect on the mobility of the Oct-1-DNA complex and Oct-1-specific antibody by itself did not show any binding to DNA (Fig. 9, lanes 6 and 7, respectively). Addition of in vitro-translated RTA to the Oct-1-DNA complex did not show any change in the mobility of the complex, suggesting that RTA does not have a strong affinity for Oct-1 bound to DNA. Similar amounts of rabbit reticulocyte lysate were also unable to modulate the shift in mobility. In vitro-translated RTA by itself also did not bind to the probes (Fig. 9, lane 10). Thus, the activity of K1p mediated by RTA is most likely occurring through the specific Oct-1 sites by the interaction of Oct-1 and RTA, or by recruitment of additional activators and coactivators. Further studies to elucidate this possibility are ongoing.
DISCUSSION
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus persists episomally in infected cells by tethering the viral genome to the host chromosome (1, 9). During latent infection only a small subset of genes important for maintaining viral latency by modulating various cellular pathways are expressed (3, 14, 24, 25, 51, 60). Latency-associated nuclear antigen is one of the prominent proteins detected in all forms of latency and shown to be critical for maintenance of latency (1, 9, 17, 25, 43). K1, a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed mostly during lytic infection, contains an extracellular domain and a C-terminal cytoplasmic tail immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (26, 33, 34, 57, 61). Phosphorylation of the tyrosine residue in ITAM motifs leads to the phosphorylation and activation of cellular Src homology 2 (SH2)-containing signaling proteins Lyn, Syk, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-p85, phospholipase Cγ2, Ras-GAP, Vav, SH2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatases 1 and 2, and Grab2 (21, 27, 28, 30, 33, 38, 58). Recently, Lee et al. have shown that K1 protein efficiently interacts with a number of cellular Src homology 2-containing signaling proteins through its ITAM and up-regulates signal transduction and intracellular calcium mobilization and NFAT activation (31). The activation of signal transduction by K1 within the host cells favors efficient viral lytic replication (38).
Cloning and sequence analysis of the NotI-BamHI fragment of cosmid Z6 revealed the presence of LANA binding sequences in the K1p region which was not previously explored for K1 expression (4). However, terminal-repeat-mediated transcriptional activity has been shown to be repressed by LANA expression (35). Also, K1 mRNA has been detected at low levels in latently infected primary effusion lymphoma cell lines (16). Our reporter assay data for the full-length promoter (−650 to +76) compared to LBS-deleted K1p showed a small increase in K1p activity compared to the wild type with LANA, suggesting that binding of LANA to its cognate sequence contributes to the down-modulation of K1p transcription. This may partially explain why K1 mRNA is at very low levels during latent infection as LANA binds to its cognate sequence to tether the viral genome to the host chromosomes (55).
It would be interesting to see the levels of K1 mRNA in primary effusion lymphoma cell lines lacking LANA using small interfering RNA or binding of LANA to its cognate sequence with the use of the dominant negative LANA carboxyl terminus. However, knocking down LANA may not be conclusive for K1 expression because LANA depletion leads to the expression of RTA and related genes and RTA by itself has been shown to up-regulate K1p (4, 29). Thus, the up-regulation of K1p transcriptional activity in LANA-depleted primary effusion lymphoma cell lines will be mainly because of RTA.
Binding of LANA to the LBS is likely to be the primary reason for its repressive activity, as LANA lacking the DNA binding domain did not repress K1p. Additionally, the C terminus of LANA, which is the binding domain for DNA, repressed K1p as full-length LANA did, confirming our hypothesis. Surprisingly, LANA containing both the amino and carboxyl termini fused in frame (LANA ΔIR) was unable to repress K1p transcriptional activity in our reporter assays even though this contained the DNA binding domain. This may be due the fact that LANA lacking glutamine and glutamic acid residues has been demonstrated to have higher transcriptional activity than full-length LANA (54, 59). Thus, the repressive effect due to the binding of LANA-C may be overridden by increased transcription regulation by LANA ΔIR (Fig. 4).
The effect of LANA on the transcriptional activity of K1p was further confirmed by using the K1 ORF under the control of its own promoter and determining the copies of K1 mRNA. This corroborated the luciferase reporter assay data showing that LANA reduced the transcription of the K1 gene. Additionally, RTA-mediated up-regulation of K1p transcription was confirmed at the mRNA level and was unaffected by deletion of the LBS sequence from the promoter region, unlike LANA, which lost its repression ability in the LBS-deleted promoter region.
Increased transcriptional activity of K1p and thus enhanced K1 expression was further confirmed by looking at levels of cellular Src homology 2-containing signaling protein Lyn. Increased K1 expression has been shown to induce phosphorylation and activation of cellular Src homology 2-containing signaling protein Lyn and other cellular signaling kinases (38, 41). Analysis of active phospho-Lyn levels in 293 and BJAB cells in the presence of LANA and RTA along with the K1 ORF under the control of its own promoter showed modulation in phospho-Lyn levels. The reduction in phospho-Lyn levels is most likely due to the reduced levels of K1 expression as there were no significant changes in phospho-Lyn levels in the cells expressing LANA only.
Reduced levels of phospho-Lyn may repress the downstream signaling activities, including phospholipase Cγ/Ca2+ pathway activation, thus establishing latency (38). However, previous studies have demonstrated ITAM tyrosine phosphorylation-independent Syc phosporylation and NFAT reporter activation, suggesting that Syc is not the only effector of K1 signal transduction (28, 38). Additionally, K1-transgenic mice have been shown to have increased active Lyn kinase but not Syc kinase in splenic B lymphocytes, supportive for Syc-independent phosphorylation of Lyn (38, 42). In contrast to LANA, RTA showed increased levels of active phospho-Lyn and thus possible enhancement of the lytic cycle (38).
Detection of increased phospho-Lyn levels in LANA- and RTA-coexpressing cells with the homologous promoter-driven K1 gene suggests that RTA has strong up-regulatory effects, thus preventing LANA-mediated down-regulation, which corroborates the reporter assay data. Interestingly, we have observed reduced levels of LANA in RTA-expressing cells even though they were expressed from the same heterologous promoter. Therefore one might argue that RTA-mediated rescue may be due to degradation or reduced amounts of LANA in the cells. This needs to be further addressed by exploring the stability of LANA in the presence of RTA.
Our infection assay and time course detection of K1 mRNA demonstrated that K1 transcripts can be detected at about the same time as RTA and the level is suppressed with the persistence of infection, similar to previous observations (37, 40). This indicates that K1 might be playing an important role during initial lytic replication for the establishment of latency by mediating signaling of a productive infection (38). K1 might also be important for signaling to produce cytokines which mediate paracrine effects, thus influencing neighboring uninfected as well as infected cells and KSHV-associated pathogenesis (38). During the progression of latency, LANA mRNA increases, producing sufficient molecules for tethering the viral genome and thereby influencing the activity at the K1 promoter.
This study as well as previous studies have shown that RTA can modulate K1p (4). However, we were interested in delineating the promoter region responsive to RTA. Our reporter deletion analysis showed that the −116 to +76 region of the promoter was sufficient for RTA-mediated up-regulation. Interestingly, a previous study has also demonstrated that the −125 to +76 region of the promoter was efficiently modulated by RTA in various cell lines (4). Sequence analysis of the −116 to +76 region, which includes untranslated sequence up to the translation start site, revealed the presence of Oct-1 transcription factor binding sites as well as multiple sites for Sp1 transcription factor binding (4).
Oct-1 belongs to the POU family and both Oct-1 and -2 can specifically interact with the octamer binding sequence ATGCAAAT (53). Since Oct-1 was shown previously to be the important transcription factor binding site in the RTA promoter region responsible for RTA-mediated autoregulation (46), we focused on addressing their role by mutating these binding sites. The promoter region (−116 to +76) mutated for the Oct-1 site showed a marked decrease in RTA responsiveness, suggesting that binding of Oct-1 is important for RTA-mediated up-regulation. This again did not clearly demonstrate whether up-regulation is due to direct tight binding of RTA to Oct-1 or a likely weaker binding shown for RTA (46).
The herpes simplex virus type 1 VP16 and varicella-zoster virus ORF10 proteins form a tight complex easily detected by electrophoretic mobility shift assay, with Oct-1 for activation of the target genes (36, 52). However, RTA has been shown to up-regulate genes even without forming a tight complex with Oct-1 (46). Sequence analysis showed that the Oct-1 sites identified have approximately 80% similarity to the Oct-1 consensus sequence and are bound by Oct-1 transcription factors. Therefore these sites may be critical to or contribute a major portion of K1 up-regulation.
In conclusion, the LANA binding sites of K1p are important for limited expression of K1 during latent infection as well as during the latent/lytic switch. RTA reverses the LANA-mediated repression of K1p and up-regulates K1 and its mediated signaling, thus contributing to the enhancement of lytic replication (Fig. 10).
FIG. 10.
Regulation of K1 expression during latent and lytic replication cycles. LANA tethers the viral genome to the host chromosome through binding to its cognate sequence within the terminal repeat (TR) (2, 10). Binding of LANA to the terminal repeat promoter region of K1 down-regulates K1 expression and therefore down-regulates K1-mediated signaling and thus helps in maintaining latency. On the onset of lytic replication, the immediate-early gene RTA reverses LANA-mediated down-regulation of K1p partly through Oct-1 binding sites, thus elevating K1 levels. Up-regulation of K1 most likely leads to up-regulation of downstream K1-interacting kinases, including a number of cellular Src homology 2-containing proteins, leading to the up-regulation of downstream signaling and intracellular calcium mobilization and NFAT activation, which favors viral lytic replication (31, 38).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Public Health service grants NCI CA072510 and CA091792, NIDCR DE01436, and DE017335 (E.S.R.). E.S.R. is a scholar of the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society of America.
We thank Bernadine Akukwe, BGS summer intern, for technical assistance.
REFERENCES
- 1.Ballestas, M. E., P. A. Chatis, and K. M. Kaye. 1999. Efficient persistence of extrachromosomal KSHV DNA mediated by latency-associated nuclear antigen. Science 284:641-644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ballestas, M. E., and K. M. Kaye. 2001. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency-associated nuclear antigen 1 mediates episome persistence through cis-acting terminal repeat (TR) sequence and specifically binds TR DNA. J. Virol. 75:3250-3258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Boshoff, C., D. Whitby, T. Hatziioannou, C. Fisher, J. van der Walt, A. Hatzakis, R. Weiss, and T. Schulz. 1995. Kaposi's-sarcoma-associated herpesvirus in HIV-negative Kaposi's sarcoma. Lancet 345:1043-1044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bowser, B. S., S. M. DeWire, and B. Damania. 2002. Transcriptional regulation of the K1 gene product of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. J. Virol. 76:12574-12583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cesarman, E., Y. Chang, P. S. Moore, J. W. Said, and D. M. Knowles. 1995. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 332:1186-1191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chang, Y. 1997. Kaposi's sarcoma and Kaposi's sarcoma associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus 8): where are we now? J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 89:1829-1831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chang, Y., E. Cesarman, M. S. Pessin, F. Lee, J. Culpepper, D. M. Knowles, and P. S. Moore. 1994. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Science 266:1865-1869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chang, Y., and P. S. Moore. 1996. Kaposi's sarcoma (KS)-associated herpesvirus and its role in KS. Infect. Agents Dis. 5:215-222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cotter, M. A., II, and E. S. Robertson. 1999. The latency-associated nuclear antigen tethers the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus genome to host chromosomes in body cavity-based lymphoma cells. Virology 264:254-264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cotter, M. A., II, C. Subramanian, and E. S. Robertson. 2001. The Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency-associated nuclear antigen binds to specific sequences at the left end of the viral genome through its carboxy-terminus. Virology 291:241-259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Damania, B., M. Li, J. K. Choi, L. Alexander, J. U. Jung, and R. C. Desrosiers. 1999. Identification of the R1 oncogene and its protein product from the rhadinovirus of rhesus monkeys. J. Virol. 73:5123-5131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Deng, H., M. J. Song, J. T. Chu, and R. Sun. 2002. Transcriptional regulation of the interleukin-6 gene of human herpesvirus 8 (Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus). J. Virol. 76:8252-8264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Dupin, N., T. L. Diss, P. Kellam, M. Tulliez, M. Q. Du, D. Sicard, R. A. Weiss, P. G. Isaacson, and C. Boshoff. 2000. HHV-8 is associated with a plasmablastic variant of Castleman disease that is linked to HHV-8-positive plasmablastic lymphoma. Blood 95:1406-1412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dupin, N., C. Fisher, P. Kellam, S. Ariad, M. Tulliez, N. Franck, E. van Marck, D. Salmon, I. Gorin, J. P. Escande, R. A. Weiss, K. Alitalo, and C. Boshoff. 1999. Distribution of human herpesvirus-8 latently infected cells in Kaposi's sarcoma, multicentric Castleman's disease, and primary effusion lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96:4546-4551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Eliopoulos, A. G., and L. S. Young. 2001. LMP1 structure and signal transduction. Semin. Cancer Biol. 11:435-444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fakhari, F. D., and D. P. Dittmer. 2002. Charting latency transcripts in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus by whole-genome real-time quantitative PCR. J. Virol. 76:6213-6223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Friborg, J., Jr., W. Kong, M. O. Hottiger, and G. J. Nabel. 1999. p53 inhibition by the LANA protein of KSHV protects against cell death. Nature 402:889-894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ganem, D. 1997. KSHV and Kaposi's sarcoma: the end of the beginning? Cell 91:157-160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Garber, A. C., J. Hu, and R. Renne. 2002. Latency-associated nuclear antigen (LANA) cooperatively binds to two sites within the terminal repeat, and both sites contribute to the ability of LANA to suppress transcription and to facilitate DNA replication. J. Biol. Chem. 277:27401-27411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Garber, A. C., M. A. Shu, J. Hu, and R. Renne. 2001. DNA binding and modulation of gene expression by the latency-associated nuclear antigen of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. J. Virol. 75:7882-7892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jain, J., P. G. McCaffrey, Z. Miner, T. K. Kerppola, J. N. Lambert, G. L. Verdine, T. Curran, and A. Rao. 1993. The T-cell transcription factor NFATp is a substrate for calcineurin and interacts with Fos and Jun. Nature 365:352-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jenner, R. G., M. M. Alba, C. Boshoff, and P. Kellam. 2001. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latent and lytic gene expression as revealed by DNA arrays. J. Virol. 75:891-902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jung, J. U., J. K. Choi, A. Ensser, and B. Biesinger. 1999. Herpesvirus saimiri as a model for gammaherpesvirus oncogenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 9:231-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kedes, D. H., E. Operskalski, M. Busch, R. Kohn, J. Flood, and D. Ganem. 1996. The seroepidemiology of human herpesvirus 8 (Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus): distribution of infection in KS risk groups and evidence for sexual transmission. Nat. Med. 2:918-924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Krishnan, H. H., P. P. Naranatt, M. S. Smith, L. Zeng, C. Bloomer, and B. Chandran. 2004. Concurrent expression of latent and a limited number of lytic genes with immune modulation and antiapoptotic function by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus early during infection of primary endothelial and fibroblast cells and subsequent decline of lytic gene expression. J. Virol. 78:3601-3620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lagunoff, M., and D. Ganem. 1997. The structure and coding organization of the genomic termini of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Virology 236:147-154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lagunoff, M., D. M. Lukac, and D. Ganem. 2001. Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif-dependent signaling by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K1 protein: effects on lytic viral replication. J. Virol. 75:5891-5898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lagunoff, M., R. Majeti, A. Weiss, and D. Ganem. 1999. Deregulated signal transduction by the K1 gene product of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96:5704-5709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lan, K., D. A. Kuppers, S. C. Verma, N. Sharma, M. Murakami, and E. S. Robertson. 2005. Induction of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency-associated nuclear antigen by the lytic transactivator RTA: a novel mechanism for establishment of latency. J. Virol. 79:7453-7465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lee, B. S., X. Alvarez, S. Ishido, A. A. Lackner, and J. U. Jung. 2000. Inhibition of intracellular transport of B cell antigen receptor complexes by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K1. J Exp. Med. 192:11-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lee, B. S., S. H. Lee, P. Feng, H. Chang, N. H. Cho, and J. U. Jung. 2005. Characterization of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K1 signalosome. J. Virol. 79:12173-12184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lee, B. S., M. Paulose-Murphy, Y. H. Chung, M. Connlole, S. Zeichner, and J. U. Jung. 2002. Suppression of tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate-induced lytic reactivation of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus by K1 signal transduction. J. Virol. 76:12185-12199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lee, H., J. Guo, M. Li, J. K. Choi, M. DeMaria, M. Rosenzweig, and J. U. Jung. 1998. Identification of an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif of K1 transforming protein of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18:5219-5228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lee, H., R. Veazey, K. Williams, M. Li, J. Guo, F. Neipel, B. Fleckenstein, A. Lackner, R. C. Desrosiers, and J. U. Jung. 1998. Deregulation of cell growth by the K1 gene of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Nat. Med. 4:435-440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lim, C., H. Sohn, D. Lee, Y. Gwack, and J. Choe. 2002. Functional dissection of latency-associated nuclear antigen 1 of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus involved in latent DNA replication and transcription of terminal repeats of the viral genome. J. Virol. 76:10320-10331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Moriuchi, H., M. Moriuchi, and J. I. Cohen. 1995. Proteins and cis-acting elements associated with transactivation of the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) immediate-early gene 62 promoter by VZV open reading frame 10 protein. J. Virol. 69:4693-4701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nakamura, H., M. Lu, Y. Gwack, J. Souvlis, S. L. Zeichner, and J. U. Jung. 2003. Global changes in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated virus gene expression patterns following expression of a tetracycline-inducible Rta transactivator. J. Virol. 77:4205-4220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Nicholas, J. 2003. Human herpesvirus-8-encoded signalling ligands and receptors. J. Biomed. Sci. 10:475-489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nishi, J., K. Arimura, A. Utsunomiya, S. Yonezawa, K. Kawakami, N. Maeno, O. Ijichi, N. Ikarimoto, M. Nakata, I. Kitajima, T. Fukushige, H. Takamatsu, K. Miyata, and I. Maruyama. 1999. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in sera and lymph nodes of the plasma cell type of Castleman's disease. Br. J. Haematol. 104:482-485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Paulose-Murphy, M., N. K. Ha, C. Xiang, Y. Chen, L. Gillim, R. Yarchoan, P. Meltzer, M. Bittner, J. Trent, and S. Zeichner. 2001. Transcription program of human herpesvirus 8 (Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus). J. Virol. 75:4843-4853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Prakash, O., O. R. Swamy, X. Peng, Z. Y. Tang, L. Li, J. E. Larson, J. C. Cohen, J. Gill, G. Farr, S. Wang, and F. Samaniego. 2005. Activation of Src kinase Lyn by the Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K1 protein: implications for lymphomagenesis. Blood 105:3987-3994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Prakash, O., Z. Y. Tang, X. Peng, R. Coleman, J. Gill, G. Farr, and F. Samaniego. 2002. Tumorigenesis and aberrant signaling in transgenic mice expressing the human herpesvirus-8 K1 gene. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 94:926-935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Radkov, S. A., P. Kellam, and C. Boshoff. 2000. The latent nuclear antigen of Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus targets the retinoblastoma-E2F pathway and with the oncogene Hras transforms primary rat cells. Nat. Med. 6:1121-1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Renne, R., W. Zhong, B. Herndier, M. McGrath, N. Abbey, D. Kedes, and D. Ganem. 1996. Lytic growth of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus 8) in culture. Nat. Med. 2:342-346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Russo, J. J., R. A. Bohenzky, M. C. Chien, J. Chen, M. Yan, D. Maddalena, J. P. Parry, D. Peruzzi, I. S. Edelman, Y. Chang, and P. S. Moore. 1996. Nucleotide sequence of the Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (HHV8). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93:14862-14867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sakakibara, S., K. Ueda, J. Chen, T. Okuno, and K. Yamanishi. 2001. Octamer-binding sequence is a key element for the autoregulation of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF50/Lyta gene expression. J. Virol. 75:6894-6900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Samaniego, F., S. Pati, J. E. Karp, O. Prakash, and D. Bose. 2001. Human herpesvirus 8 K1-associated nuclear factor-kappa B-dependent promoter activity: role in Kaposi's sarcoma inflammation? J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 28:15-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sarid, R., J. S. Wiezorek, P. S. Moore, and Y. Chang. 1999. Characterization and cell cycle regulation of the major Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus 8) latent genes and their promoter. J. Virol. 73:1438-1446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Schulz, T. F. 1998. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus-8). J. Gen. Virol. 79:1573-1591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Soulier, J., L. Grollet, E. Oksenhendler, P. Cacoub, D. Cazals-Hatem, P. Babinet, M. F. d'Agay, J. P. Clauvel, M. Raphael, L. Degos, et al. 1995. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in multicentric Castleman's disease. Blood 86:1276-1280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Staskus, K. A., W. Zhong, K. Gebhard, B. Herndier, H. Wang, R. Renne, J. Beneke, J. Pudney, D. J. Anderson, D. Ganem, and A. T. Haase. 1997. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus gene expression in endothelial (spindle) tumor cells. J. Virol. 71:715-719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Stern, S., M. Tanaka, and W. Herr. 1989. The Oct-1 homoeodomain directs formation of a multiprotein-DNA complex with the HSV transactivator VP16. Nature 341:624-630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sturm, R. A., G. Das, and W. Herr. 1988. The ubiquitous octamer-binding protein Oct-1 contains a POU domain with a homeo box subdomain. Genes Dev. 2:1582-1599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Verma, S. C., S. Borah, and E. S. Robertson. 2004. Latency-associated nuclear antigen of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus up-regulates transcription of human telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter through interaction with transcription factor Sp1. J. Virol. 78:10348-10359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Verma, S. C., and E. S. Robertson. 2003. Molecular biology and pathogenesis of Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 222:155-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Verma, S. C., and E. S. Robertson. 2003. ORF73 of herpesvirus saimiri strain C488 tethers the viral genome to metaphase chromosomes and binds to cis-acting DNA sequences in the terminal repeats. J. Virol. 77:12494-12506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Weck, K. E., S. S. Kim, H. I. Virgin, and S. H. Speck. 1999. Macrophages are the major reservoir of latent murine gammaherpesvirus 68 in peritoneal cells. J. Virol. 73:3273-3283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Weiss, A., and D. R. Littman. 1994. Signal transduction by lymphocyte antigen receptors. Cell 76:263-274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Wong, L. Y., G. A. Matchett, and A. C. Wilson. 2004. Transcriptional activation by the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency-associated nuclear antigen is facilitated by an N-terminal chromatin-binding motif. J. Virol. 78:10074-10085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Zhong, W., H. Wang, B. Herndier, and D. Ganem. 1996. Restricted expression of Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus 8) genes in Kaposi sarcoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93:6641-6646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Zong, J. C., D. M. Ciufo, D. J. Alcendor, X. Wan, J. Nicholas, P. J. Browning, P. L. Rady, S. K. Tyring, J. M. Orenstein, C. S. Rabkin, I. J. Su, K. F. Powell, M. Croxson, K. E. Foreman, B. J. Nickoloff, S. Alkan, and G. S. Hayward. 1999. High-level variability in the ORF-K1 membrane protein gene at the left end of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus genome defines four major virus subtypes and multiple variants or clades in different human populations. J. Virol. 73:4156-4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]