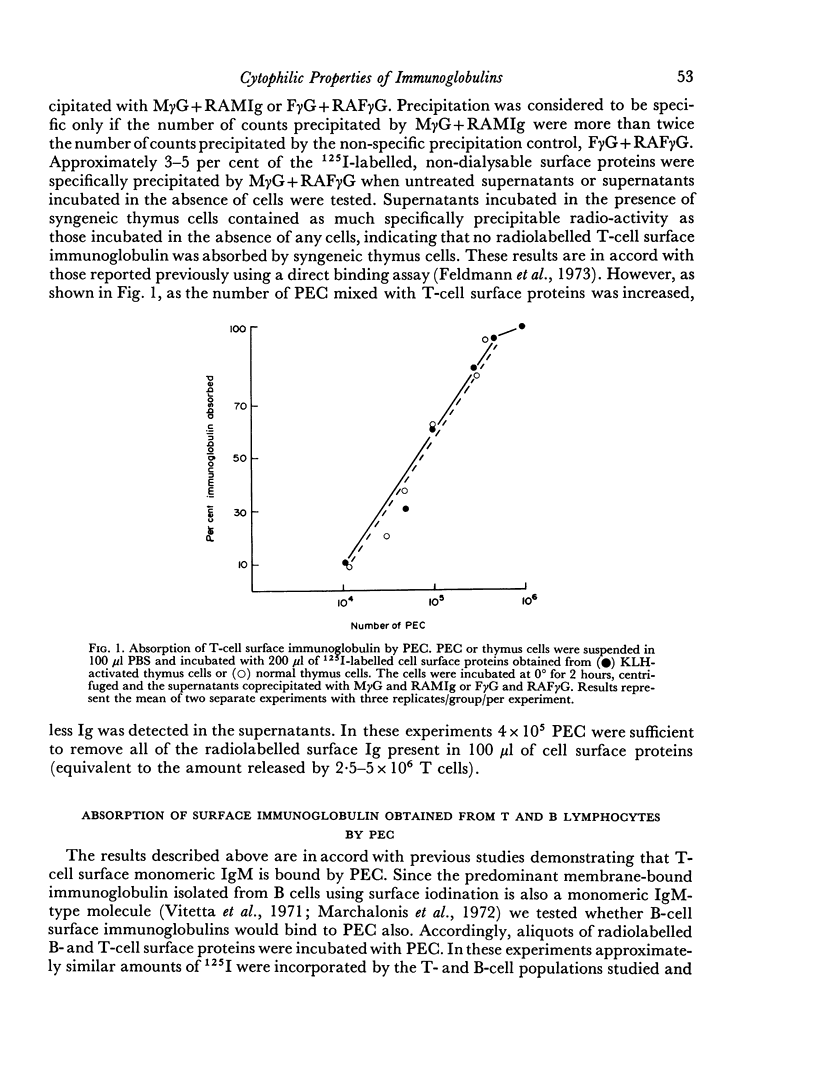
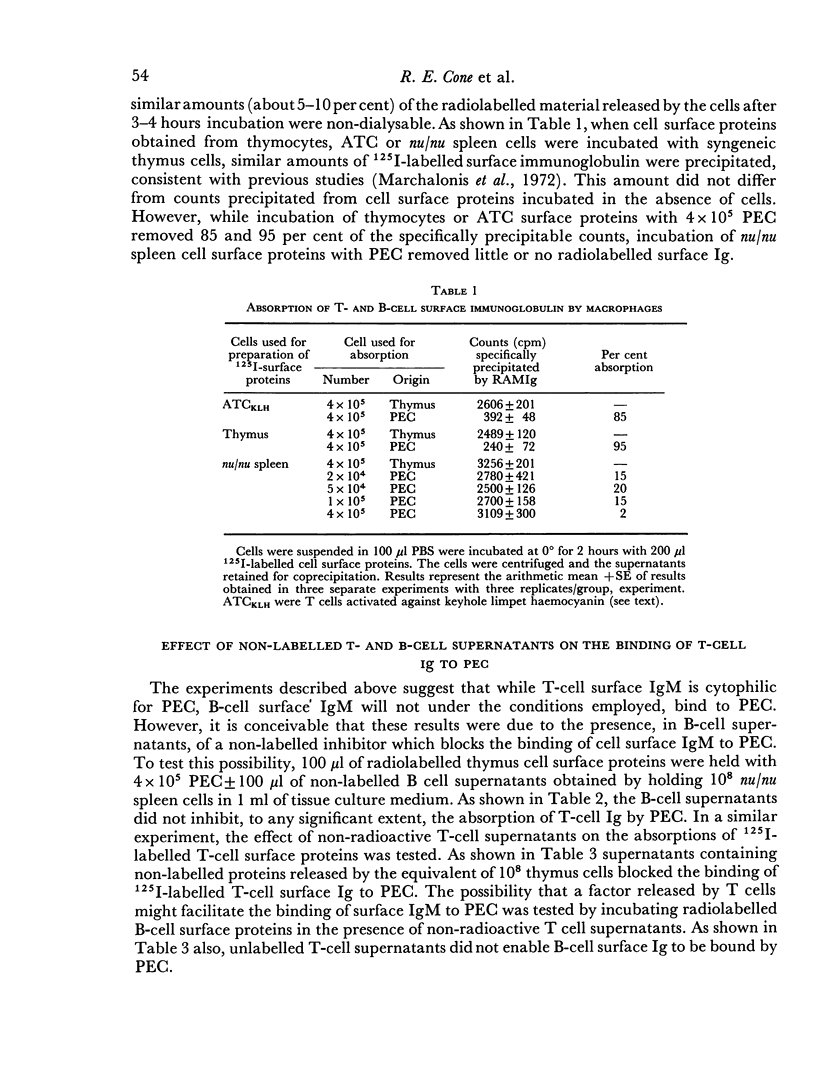
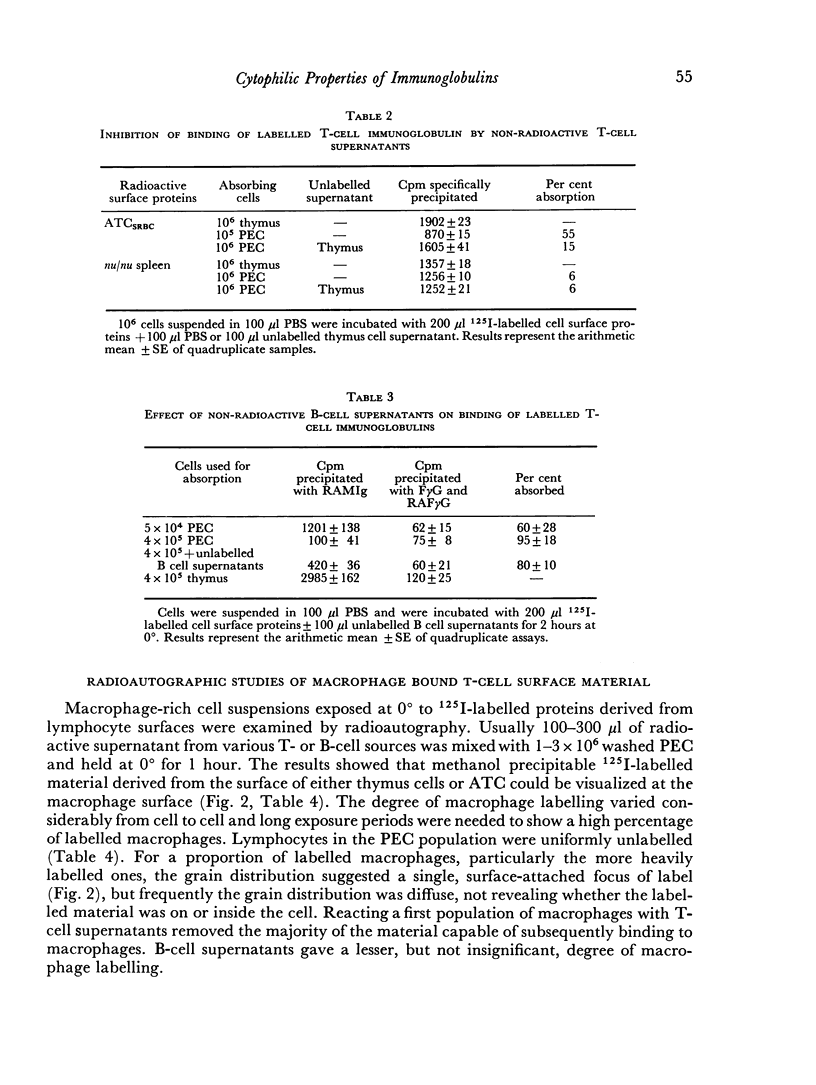
Abstract
The cytophilic properties of released surface immunoglobulins of normal thymus lymphocytes and of activated thymus-derived lymphocytes (ATC) were analysed by lactoperoxidase-catalysed radioiodination in conjunction with immunological and autoradiographic techniques. Immunoglobulin from both normal T cells and ATC was cytophilic for macrophages (peritoneal exudate cells), but showed no detectable capacity to bind to either T lymphocytes or to bone-marrow-derived lymphocytes (B cells). Under the operative experimental conditions surface immunoglobulin of B cells did not show appreciable binding to macrophages. These results support the feasibility of models of collaboration between T cells and B cells which involve a soluble antigen-specific collaborative factor (T-cell Ig complexed with antigen) and show an obligatory requirement for macrophages.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bankhurst A. D., Warner N. L., Sprent J. Surface immunoglobulins on thymus and thymus-derived lymphoid cells. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):1005–1015. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berken A., Benacerraf B. Sedimentation properties of antibody cytophilic for macrophages. J Immunol. 1968 Jun;100(6):1219–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. E., Marchalonis J. J., Rolley R. T. Lymphocyte membrane dynamics. Metabolic release of cell surface proteins. J Exp Med. 1971 Dec 1;134(6):1373–1384. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.6.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M. Cell interactions in the immune response in vitro. V. Specific collaboration via complexes of antigen and thymus-derived cell immunoglobulin. J Exp Med. 1972 Oct 1;136(4):737–760. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.4.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan S. P. 'Nude', a new hairless gene with pleiotropic effects in the mouse. Genet Res. 1966 Dec;8(3):295–309. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300010168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg D. M., Jago G. R. The antibacterial action of lactoperoxidase. The nature of the bacterial inhibitor. Biochem J. 1970 May;117(4):779–790. doi: 10.1042/bj1170779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoy W. E., Nelson D. S. Studies on cytophilic antibodies. V. Alloantibodies cytophilic for mouse macrophages. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1969 Oct;47(5):525–539. doi: 10.1038/icb.1969.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J. An enzymic method for the trace iodination of immunoglobulins and other proteins. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):299–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1130299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J., Cone R. E., Atwell J. L. Isolation and partial characterization of lymphocyte surface immunoglobulins. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):956–971. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J., Cone R. E., Santer V. Enzymic iodination. A probe for accessible surface proteins of normal and neoplastic lymphocytes. Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(5):921–927. doi: 10.1042/bj1240921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Warner N. L., Lewis H., Sprent J. Quantitative features of a sandwich radioimmunolabeling technique for lymphocyte surface receptors. J Exp Med. 1972 Feb 1;135(2):405–428. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips-Quagliata J. M., Levine B. B., Quagliata F., Uhr J. W. Mechanisms underlying binding of immune complexes to macrophages. J Exp Med. 1971 Mar 1;133(3):589–601. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.3.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortman K. Physical procedures for the separation of animal cells. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1972;1:93–130. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.01.060172.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrasher S. G., Cohen S. Studies of the mechanism of binding of chemically modified cytophilic antibodies to macrophages. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):672–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tizard I. R. Macrophage cytophilic antibody in mice. Differentiation between antigen adherence due to these antibodies and opsoni adherence. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1969;36(4):332–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tizard I. R. Macrophage-cytophilic antibodies and the functions of macrophage-bound immunoglobulins. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Dec;35(4):365–378. doi: 10.1128/br.35.4.365-378.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Baur S., Uhr J. W. Cell surface immunoglobulin. II. Isolation and characterization of immunoglobulin from mouse splenic lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1971 Jul 1;134(1):242–264. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.1.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Uhr J. W. Release of cell surface immunoglobulin by mouse splenic lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1972 Feb;108(2):577–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]