Abstract
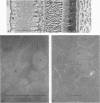
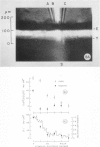
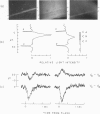
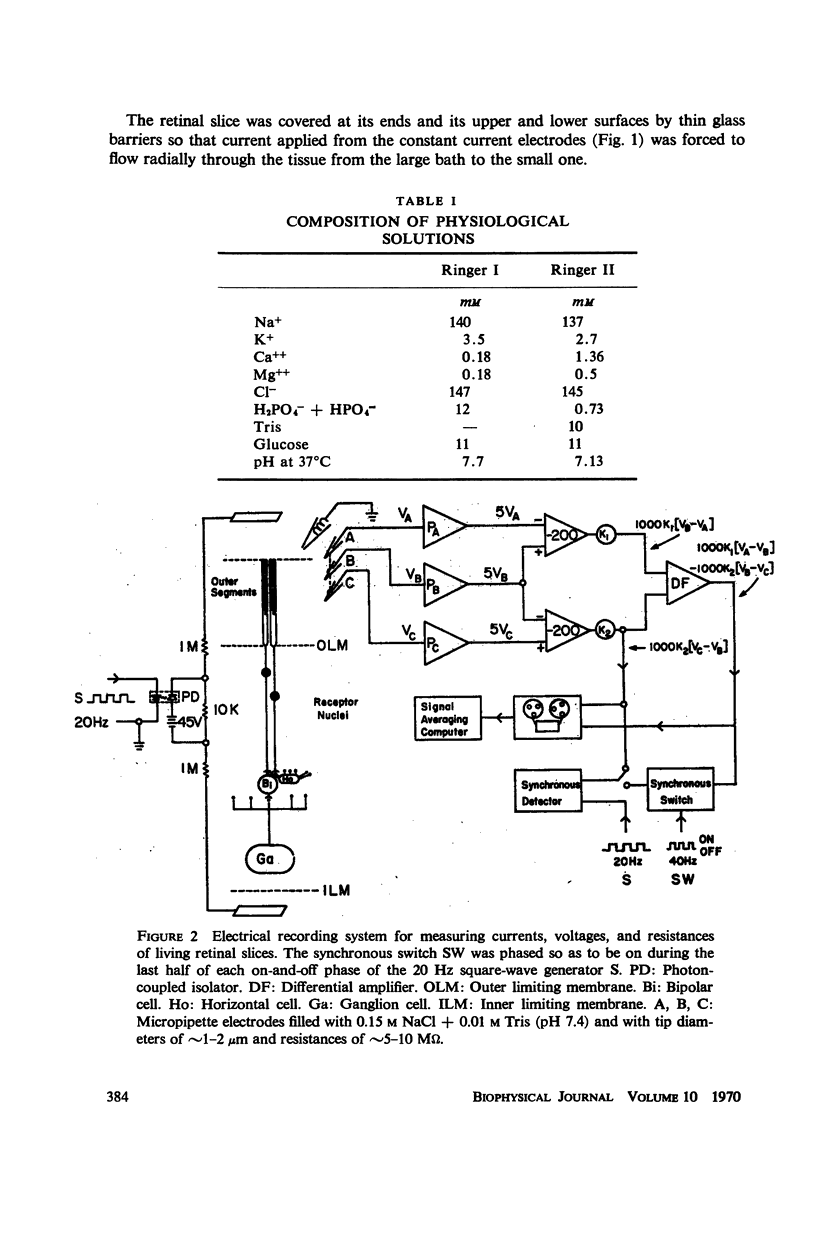
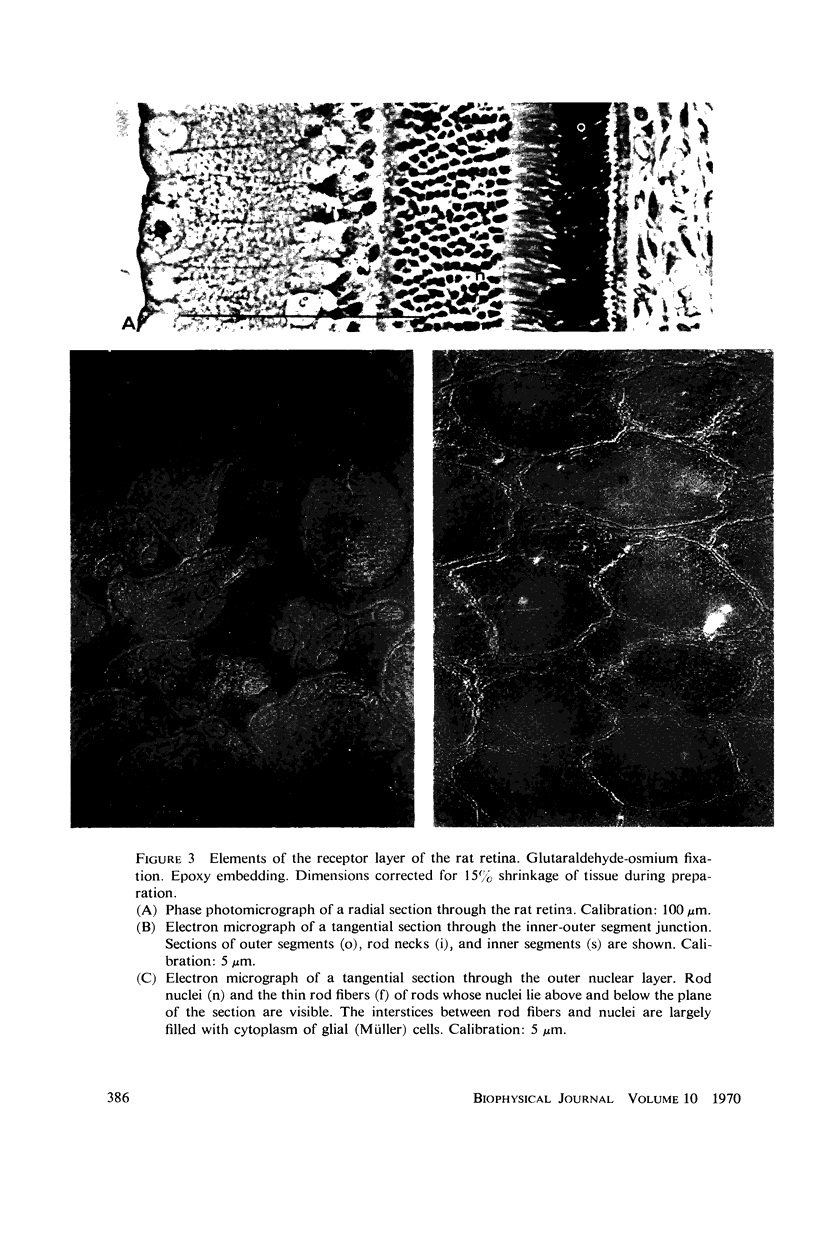
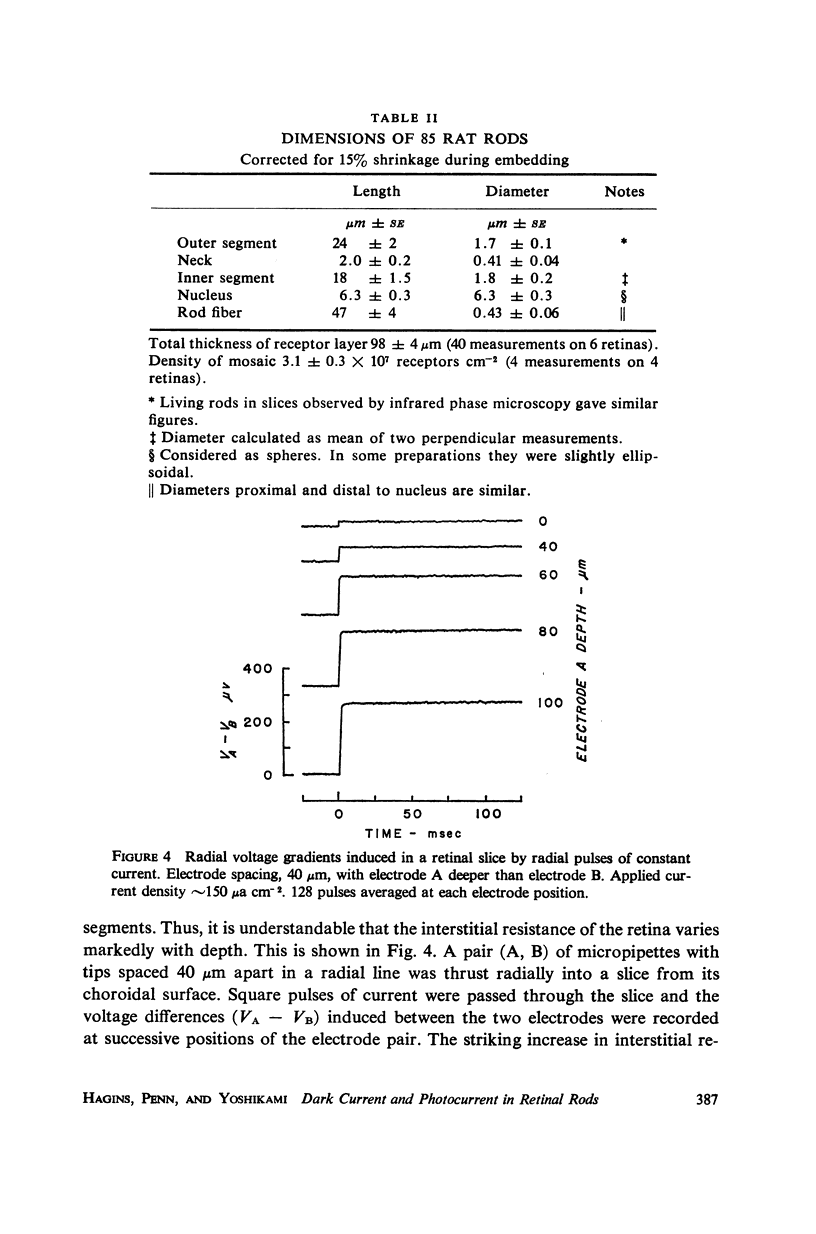
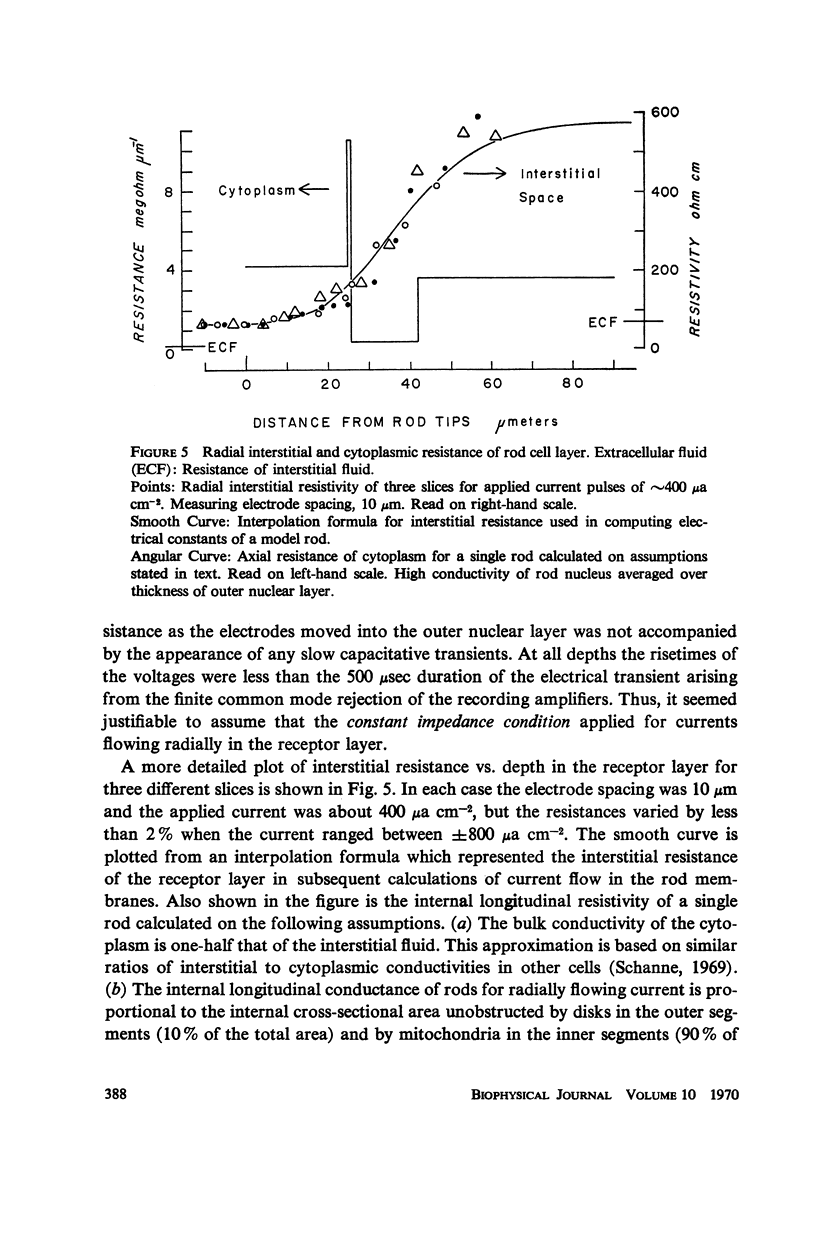
The interstitial voltages, currents, and resistances of the receptor layer of the isolated rat retina have been investigated with arrays of micropipette electrodes inserted under direct visual observation by infrared microscopy. In darkness a steady current flows inward through the plasma membrane of the rod outer segments. It is balanced by equal outward current distributed along the remainder of each rod. Flashes of light produce a photocurrent which transiently reduces the dark current with a waveform resembling the PII and a-wave components of the electroretinogram. The photocurrent is produced by a local action of light within 12 μm of its point of absorption in the outer segments. The quantum current gain of the photocurrent is greater than 106. The electrical space constant of rat rods is greater than 25 μm, so that the electrical effects of the photocurrent are large enough at the rod synapses to permit single absorbed photons to be detected by the visual system. The photocurrent is apparently the primary sensory consequence of light absorption by rhodopsin.
Full text
PDF






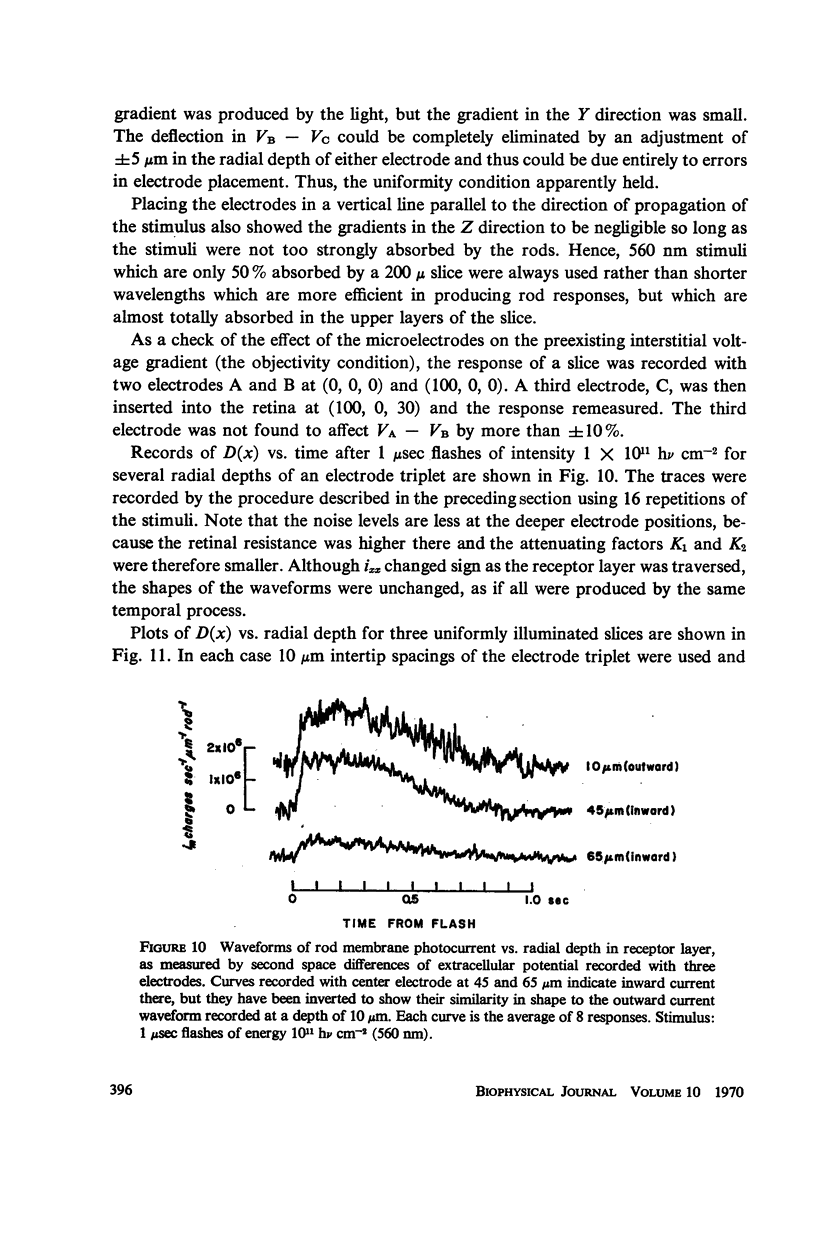
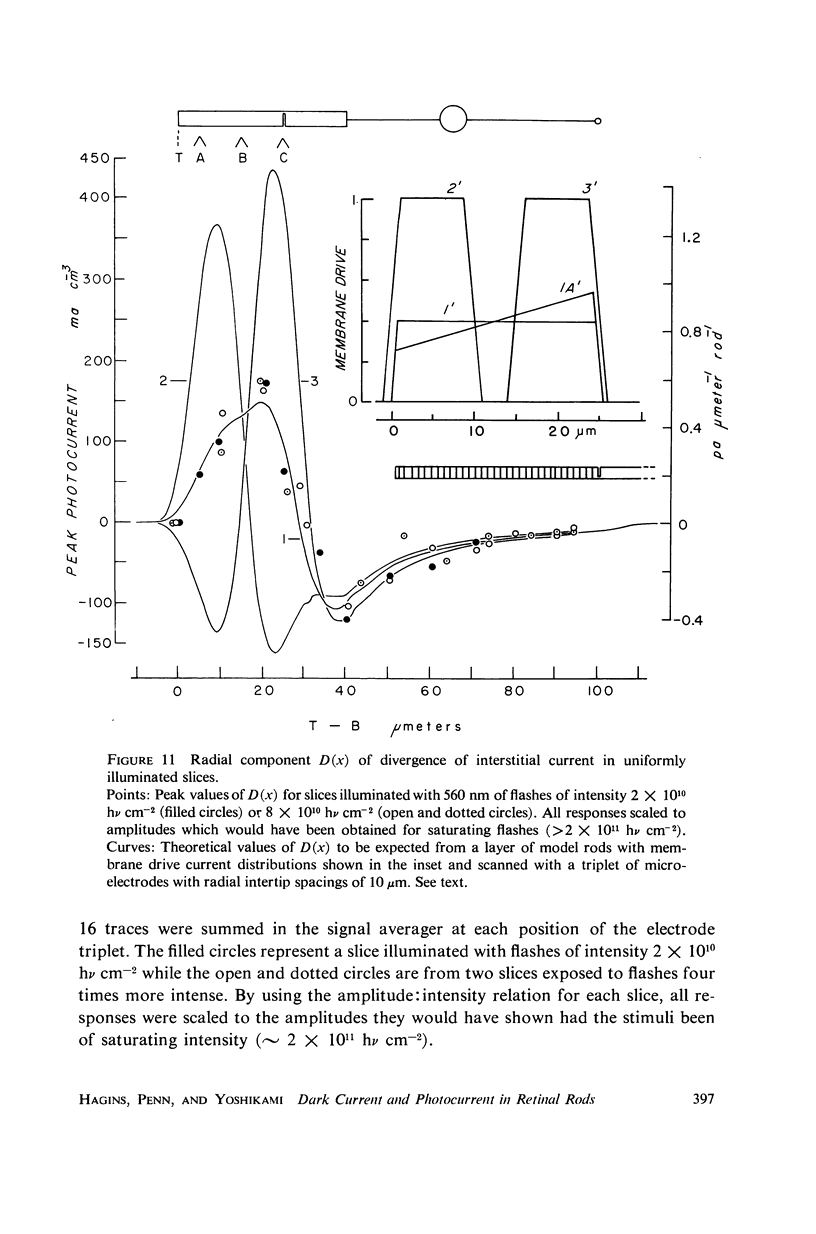

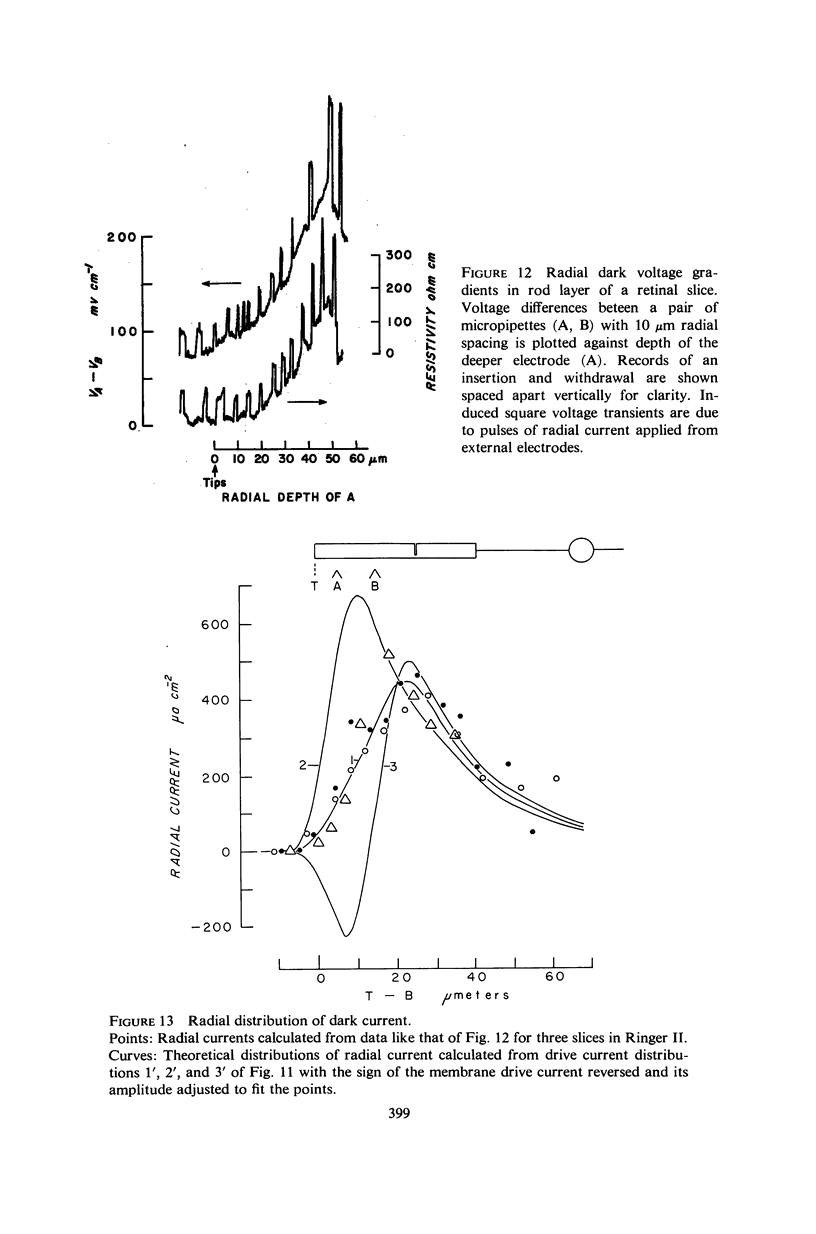
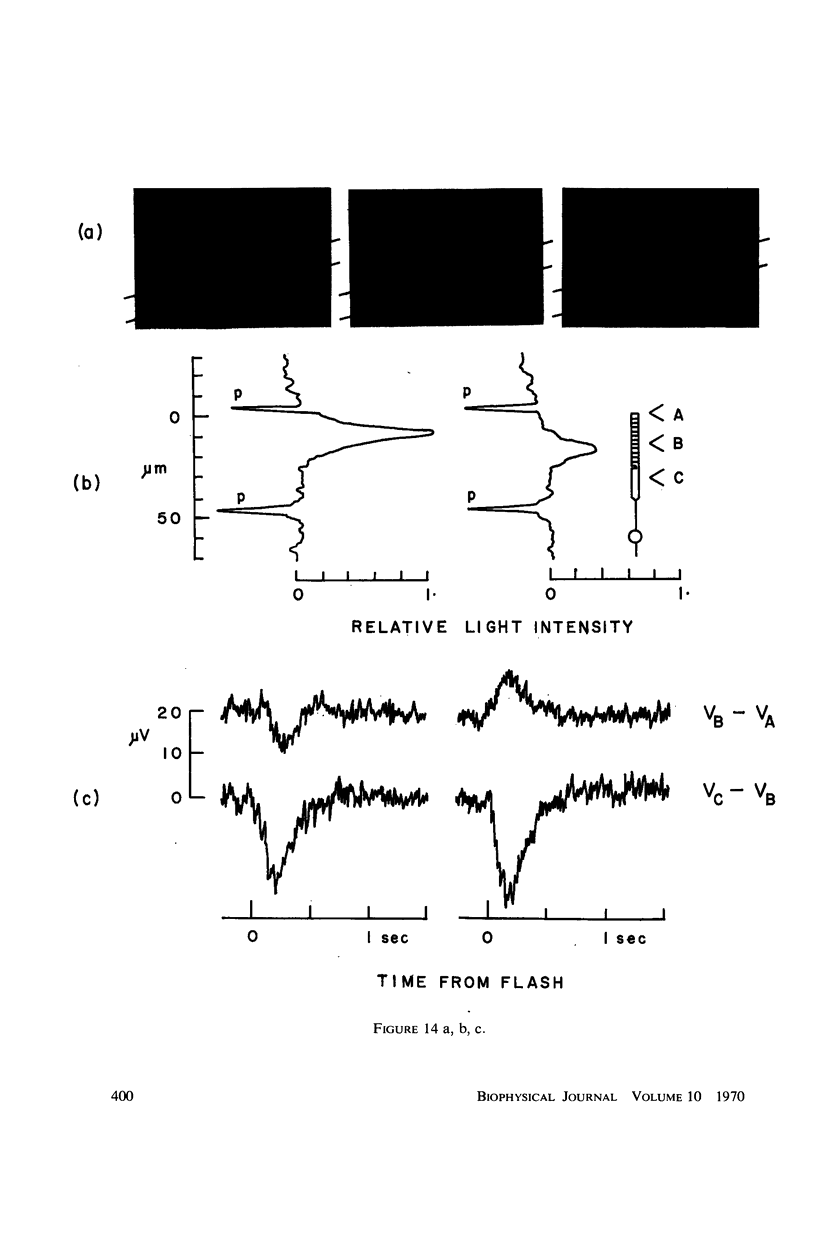











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRINDLEY G. S. Responses to illumination recorded by microelectrodes from the frog's retina. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):360–384. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortoff A. Localization of slow potential responses in the Necturus retina. Vision Res. 1964 Dec;4(11):627–635. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(64)90048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortoff A., Norton A. L. An electrical model of the vertebrate photoreceptor cell. Vision Res. 1967 Mar;7(3):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(67)90089-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortoff A., Norton A. L. Simultaneous recording of photoreceptor protentials and the P-3 component of the ERG. Vision Res. 1965 Oct;5(9):527–533. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(65)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. T. The eclectroretinogram: its components and their origins. Vision Res. 1968 Jun;8(6):633–677. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(68)90041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byzov A. L. Functional properties of different cells in the retina of cold-blooded vertebrates. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1965;30:547–558. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1965.030.01.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derksen H. E., Verveen A. A. Fluctuations of resting neural membrane potential. Science. 1966 Mar 18;151(3716):1388–1389. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3716.1388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagins W. A. Electrical signs of information flow in photoreceptors. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1965;30:403–418. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1965.030.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko A., Hashimoto H. Recording site of the single cone response determined by an electrode marking technique. Vision Res. 1967 Nov;7(11):847–851. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(67)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasansky A., De Fisch F. W. Potential, current, and ionic fluxes across the isolated retinal pigment epithelium and choriod. J Gen Physiol. 1966 May;49(5):913–924. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.5.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman P. A., Entine G. Visual pigments of frog and tadpole (Rana pipiens). Vision Res. 1968 Jul;8(7):761–775. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(68)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson S. E., Crescitelli F. Changes in ultrastructure and electroretinogram of bullfrog retina during development. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Apr;27(2):45–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn R. D., Hagins W. A. Signal transmission along retinal rods and the origin of the electroretinographic a-wave. Nature. 1969 Jul 12;223(5202):201–204. doi: 10.1038/223201a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda J., Nosaki H., Tomita T. Light-induced resistance changes in single photoreceptors of Necturus and Gekko. Vision Res. 1969 Apr;9(4):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(69)90134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]