Abstract
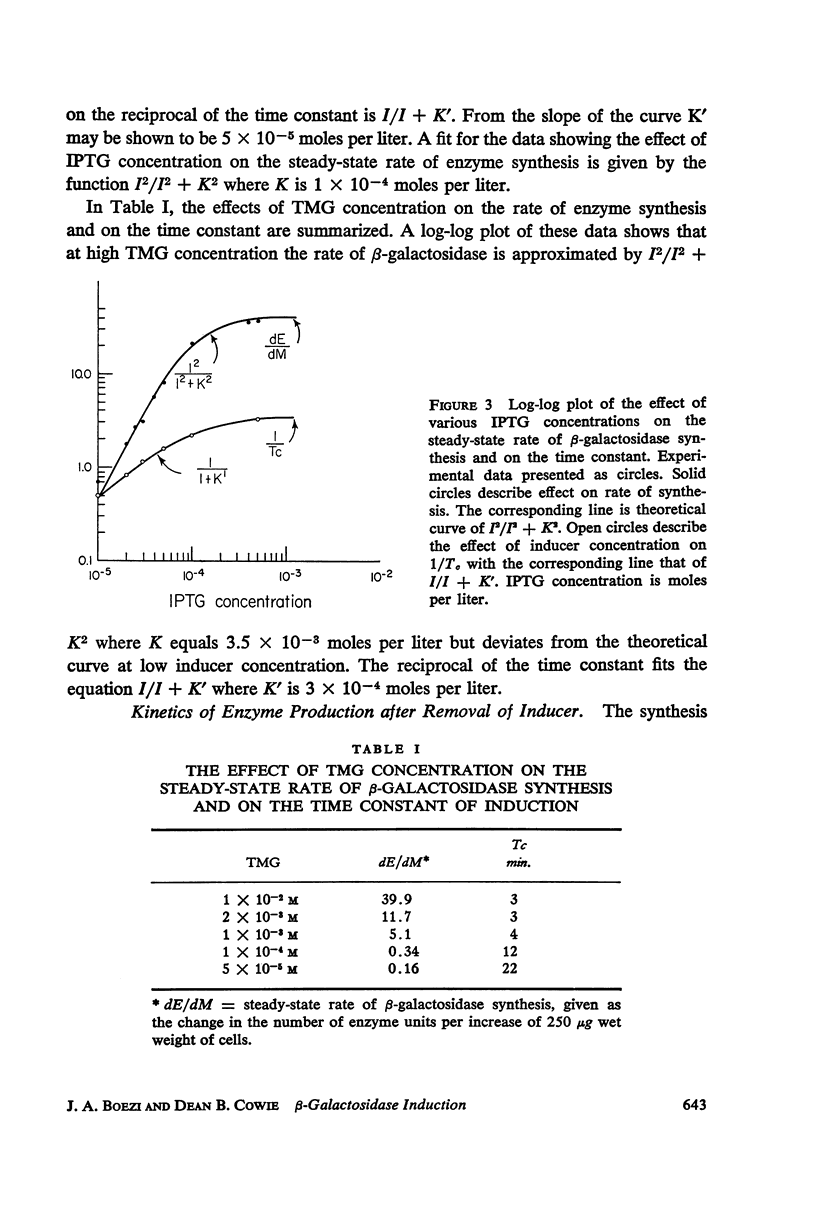
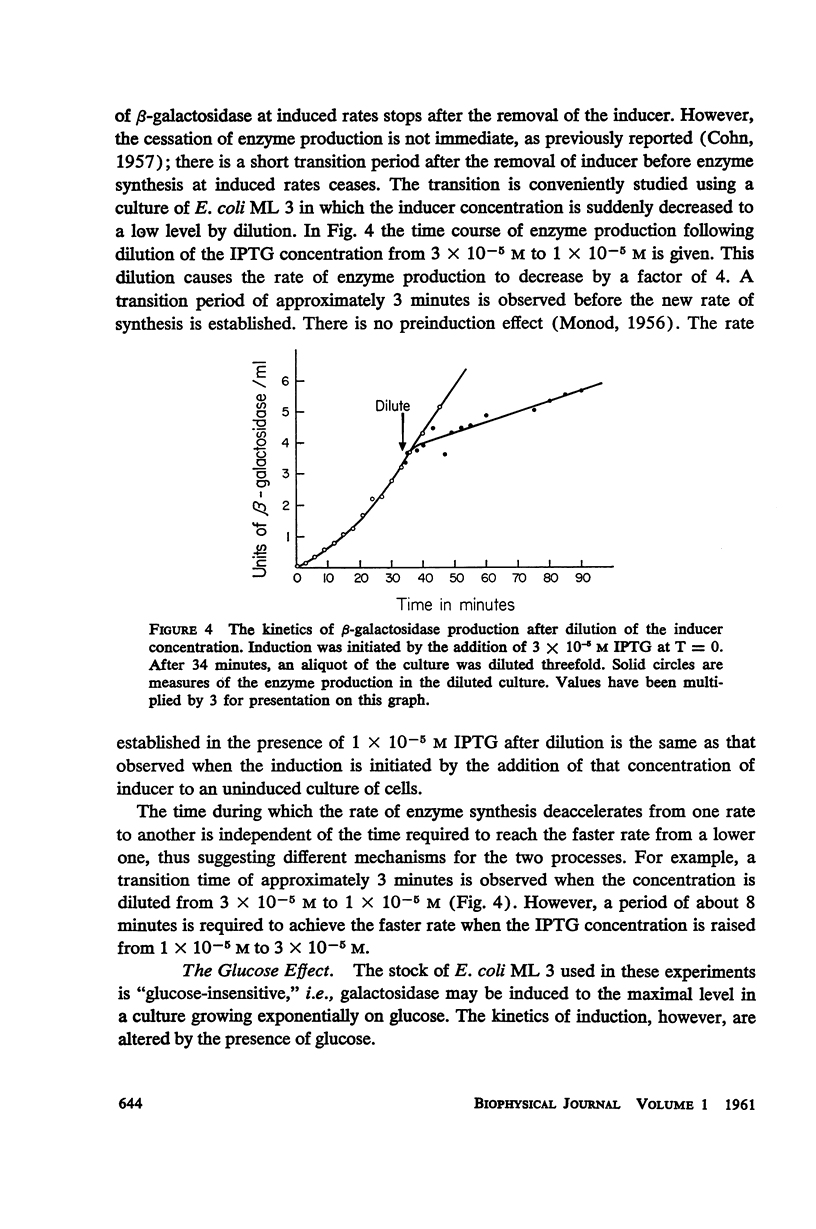
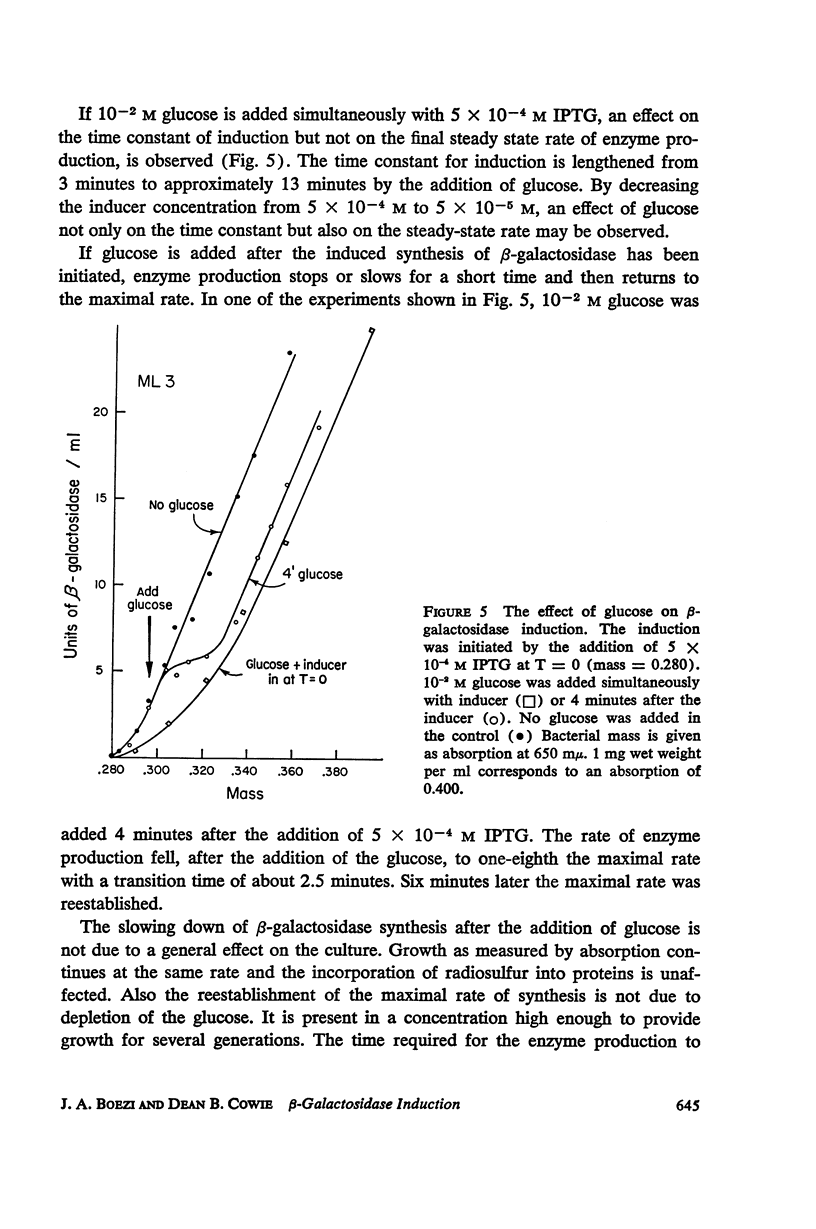
The kinetics of β-galactosidase induction in E. coli ML 3 have been studied. Following addition of inducer, the rate of enzyme synthesis accelerates from the uninduced to a steady-state rate. At saturating concentration of inducer the time constant (Tc) for this process is 2.5 to 3 minutes. With decreasing inducer concentration (I), increasing time constants are observed. I/I + K′ approximates I/Tc. The steady-state rate of β-galactosidase synthesis is approximated by I2/I2 + K2. K′ and K have been estimated for IPTG and TMG. The kinetics of β-galactosidase production after the removal of inducer by dilution or after the addition of glucose have been investigated. A transition time of 2.5 to 3 minutes is observed before enzyme synthesis slows or stops. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that the enzyme-forming unit is unstable.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COHN M., HORIBATA K. Analysis of the differentiation and of the heterogeneity within a population of Escherichia coli undergoing induced beta-galactosidase synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1959 Nov;78:613–623. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.5.613-623.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick A., Weiner M. ENZYME INDUCTION AS AN ALL-OR-NONE PHENOMENON. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1957 Jul 15;43(7):553–566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.43.7.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


