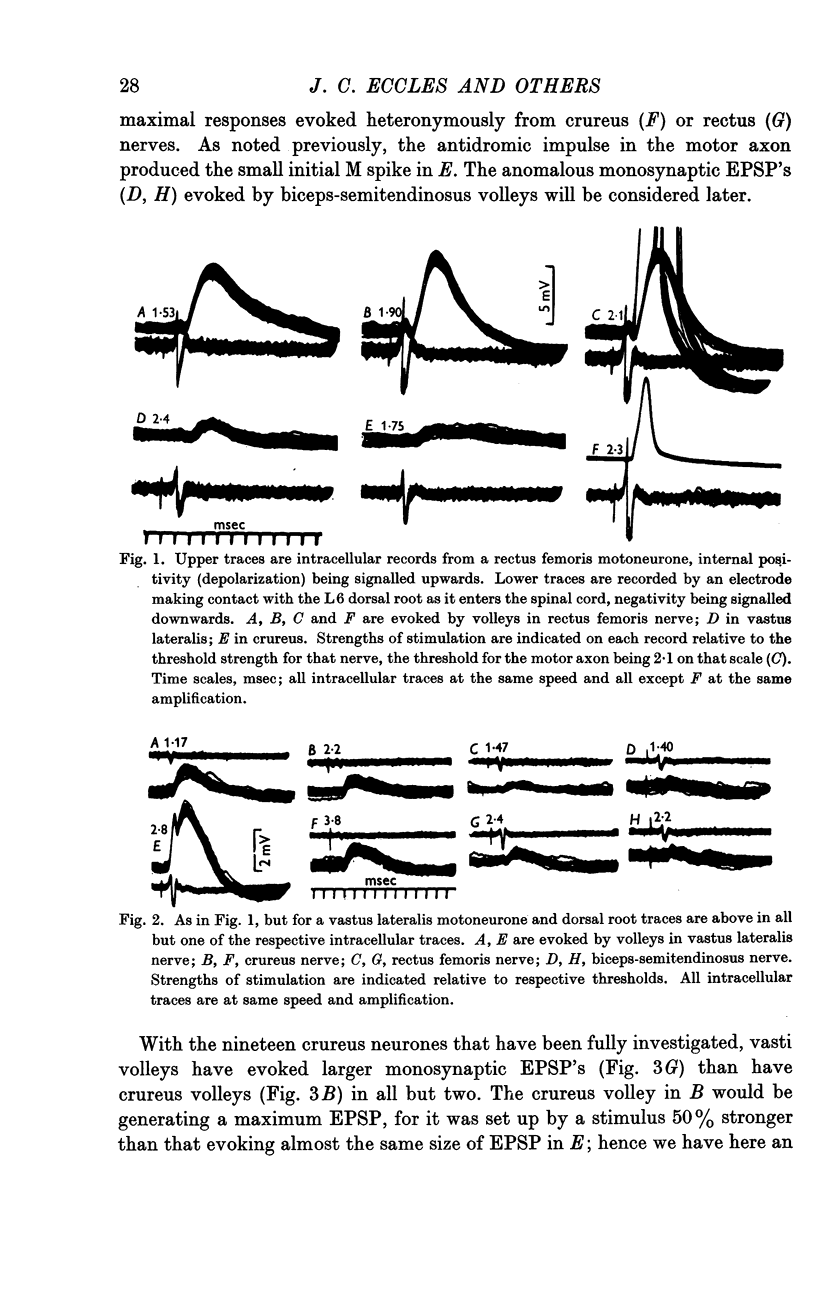
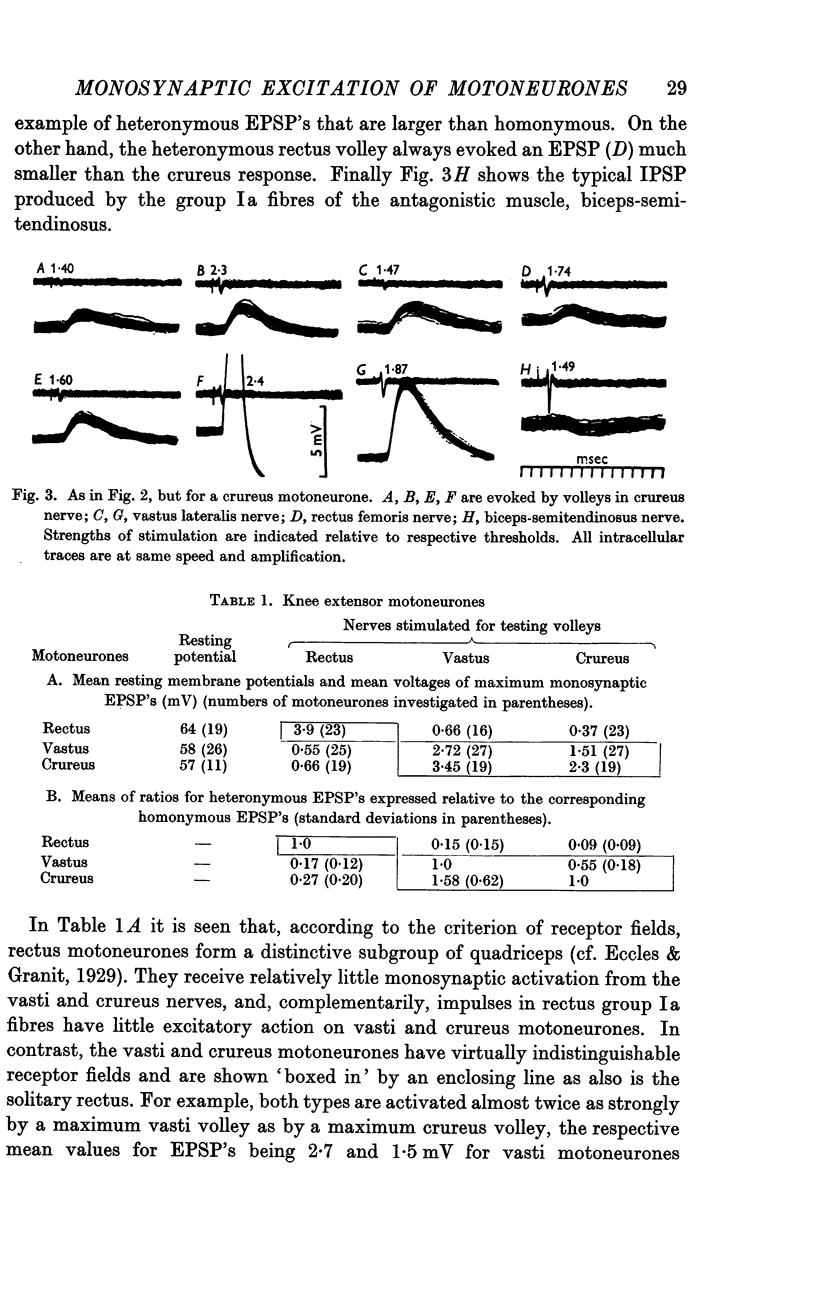
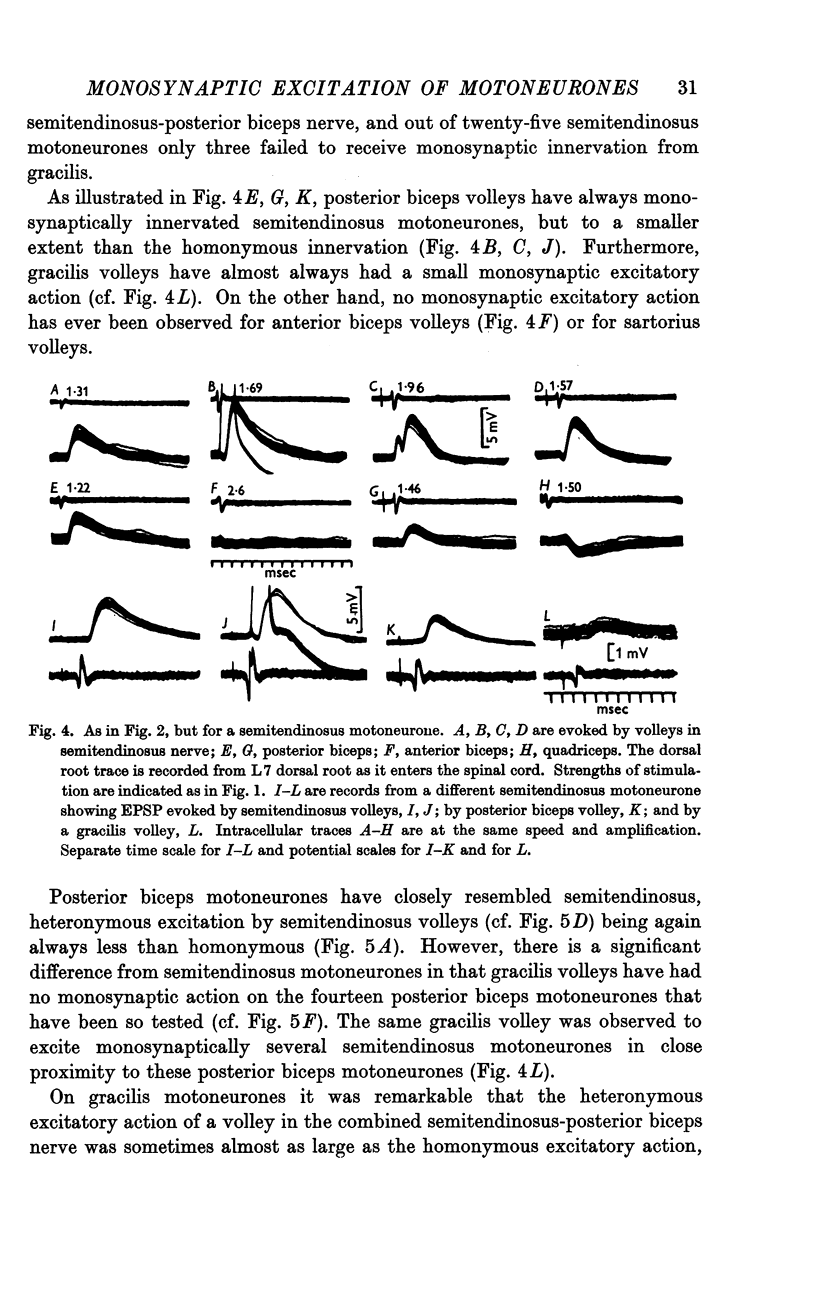
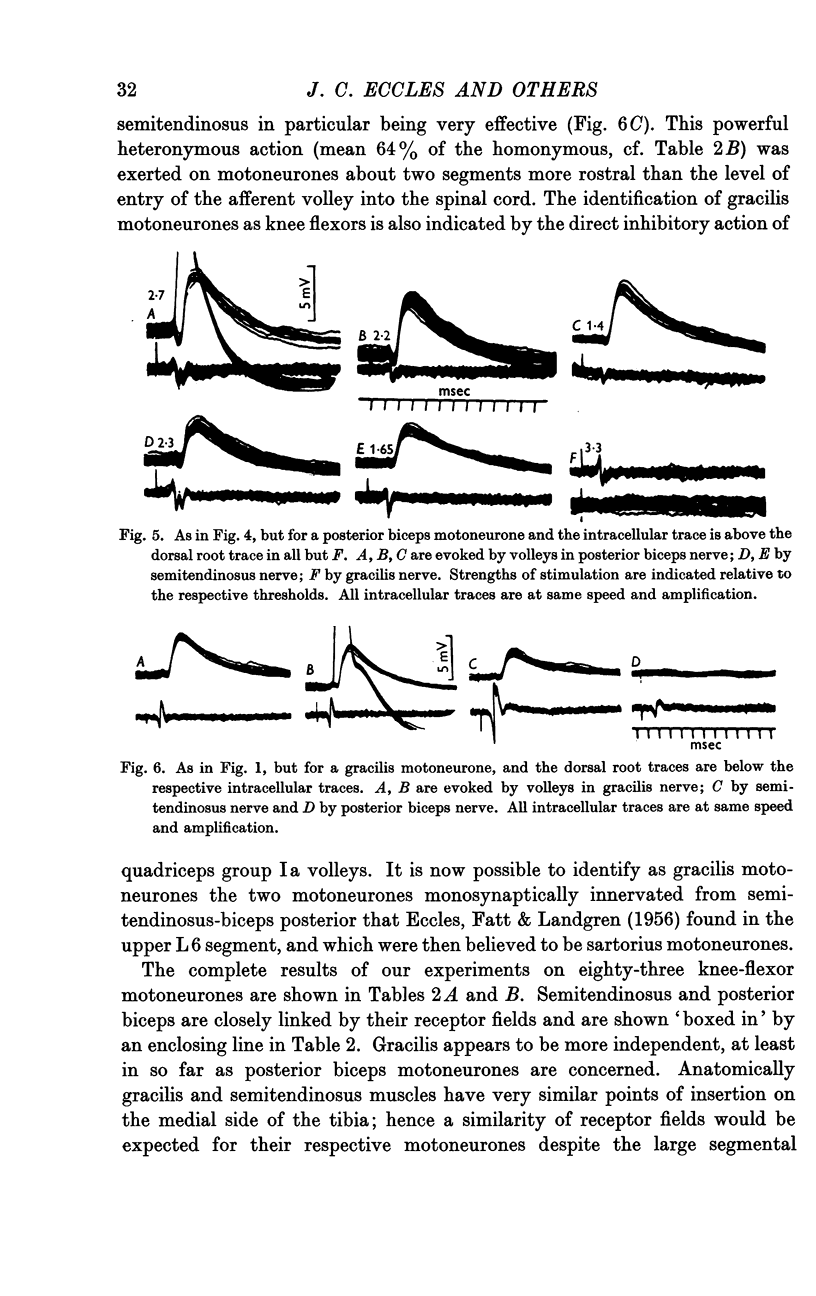
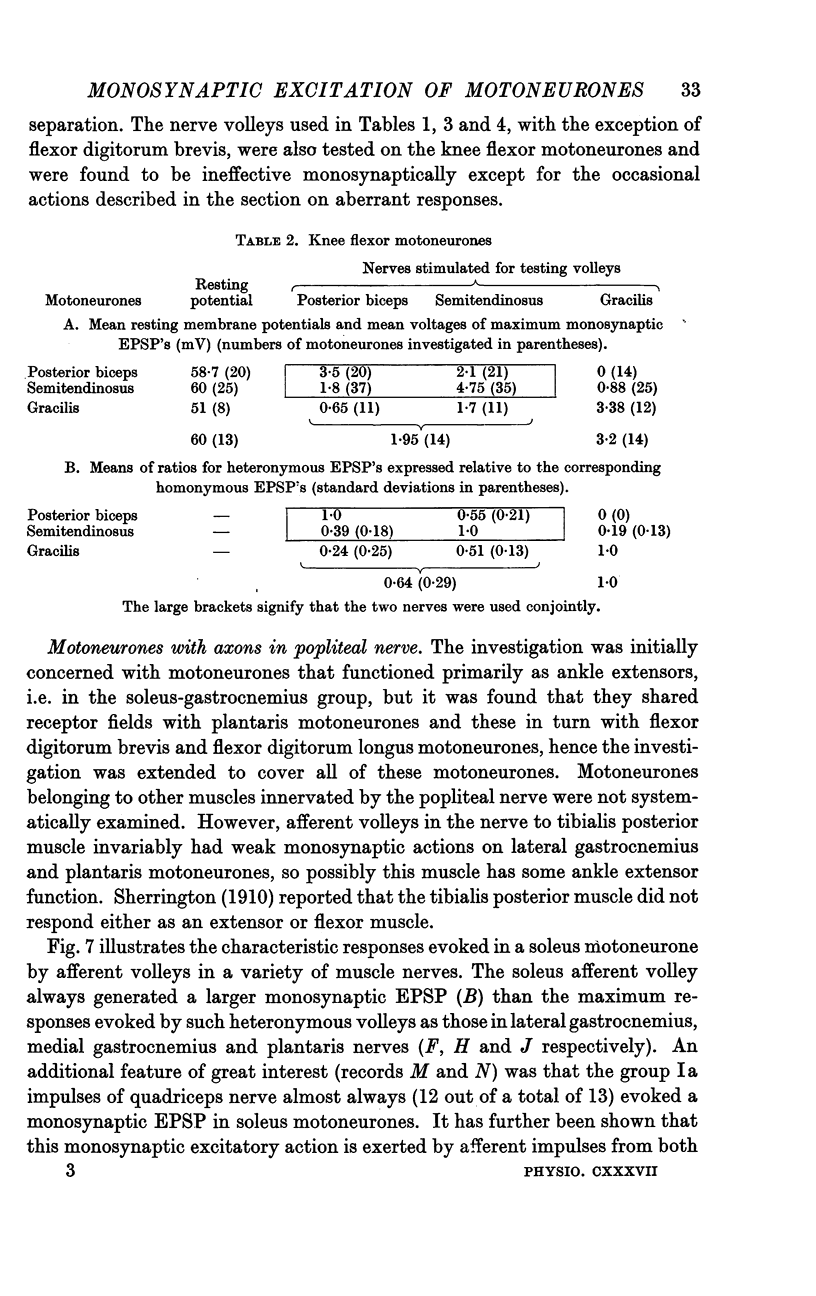
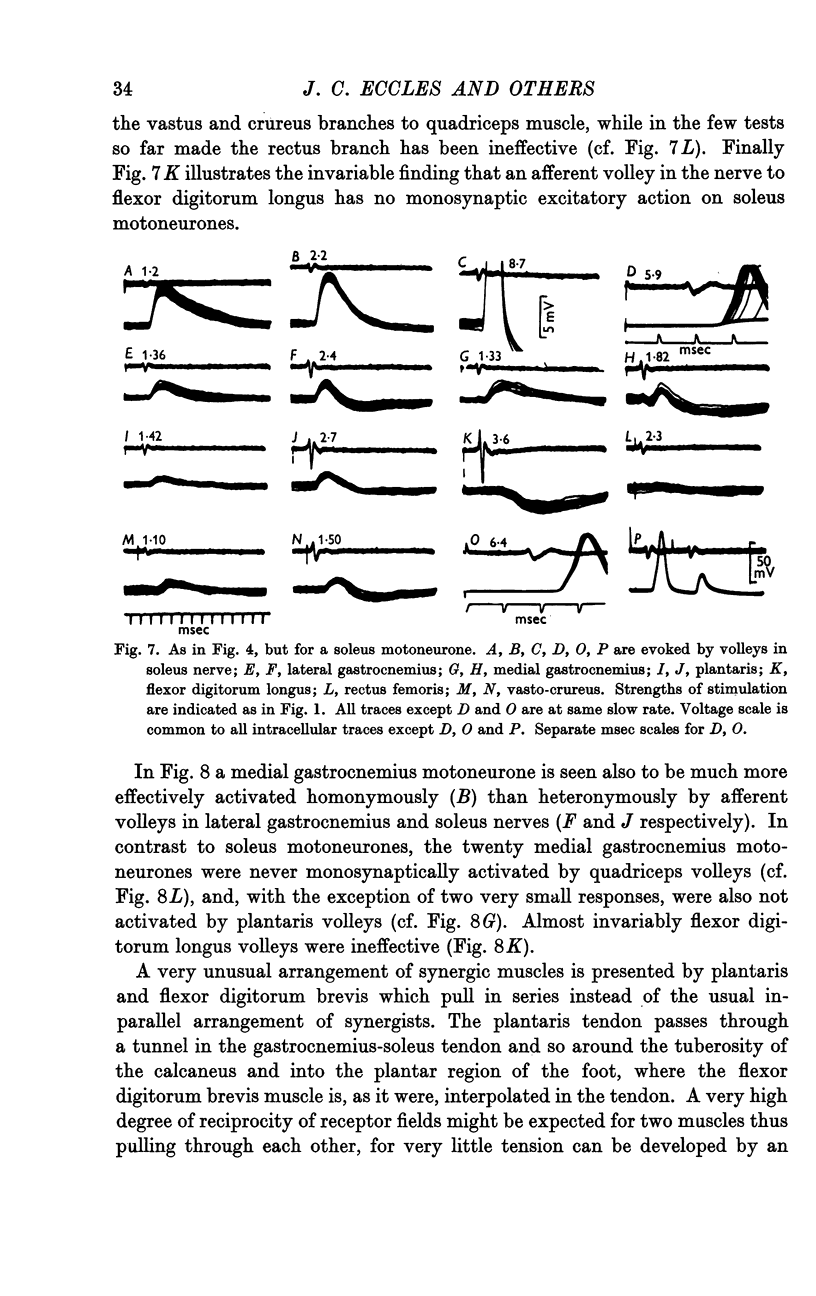
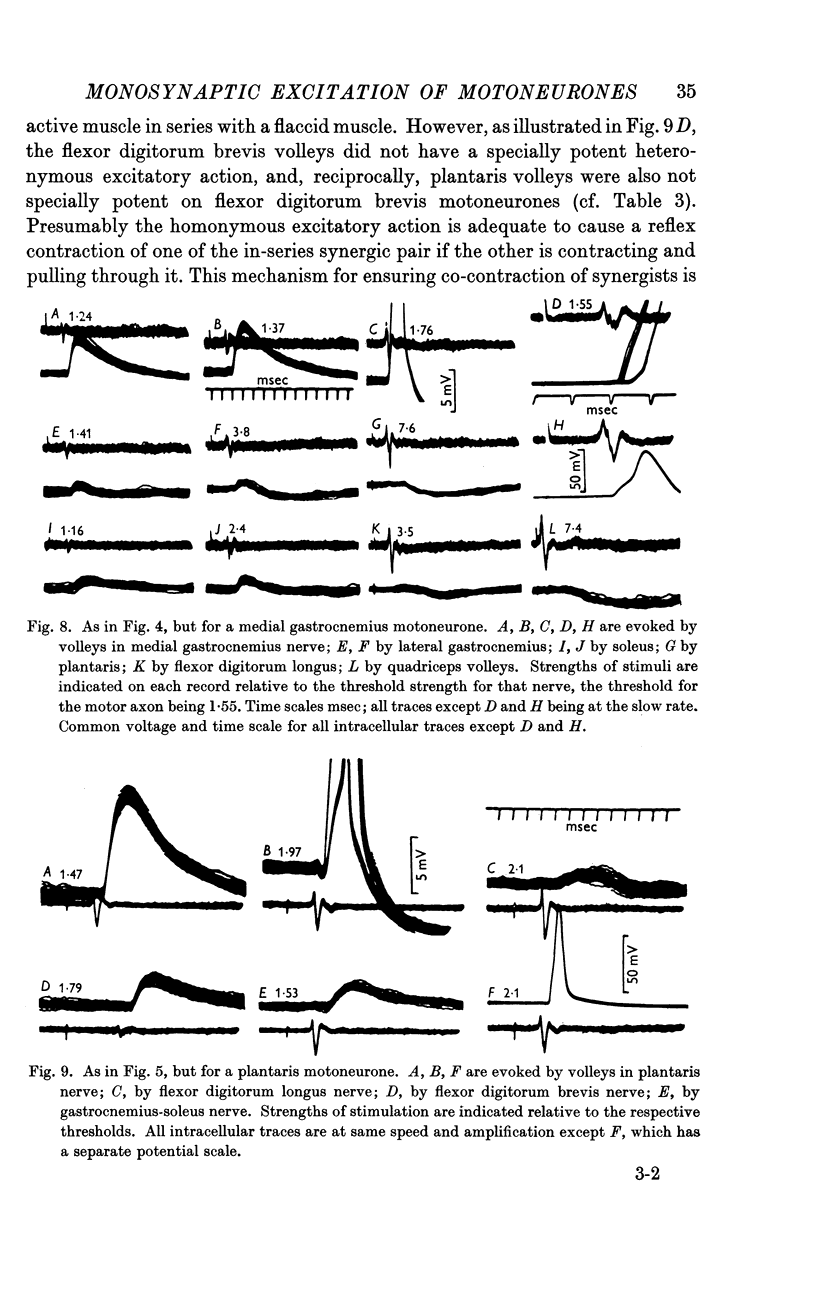
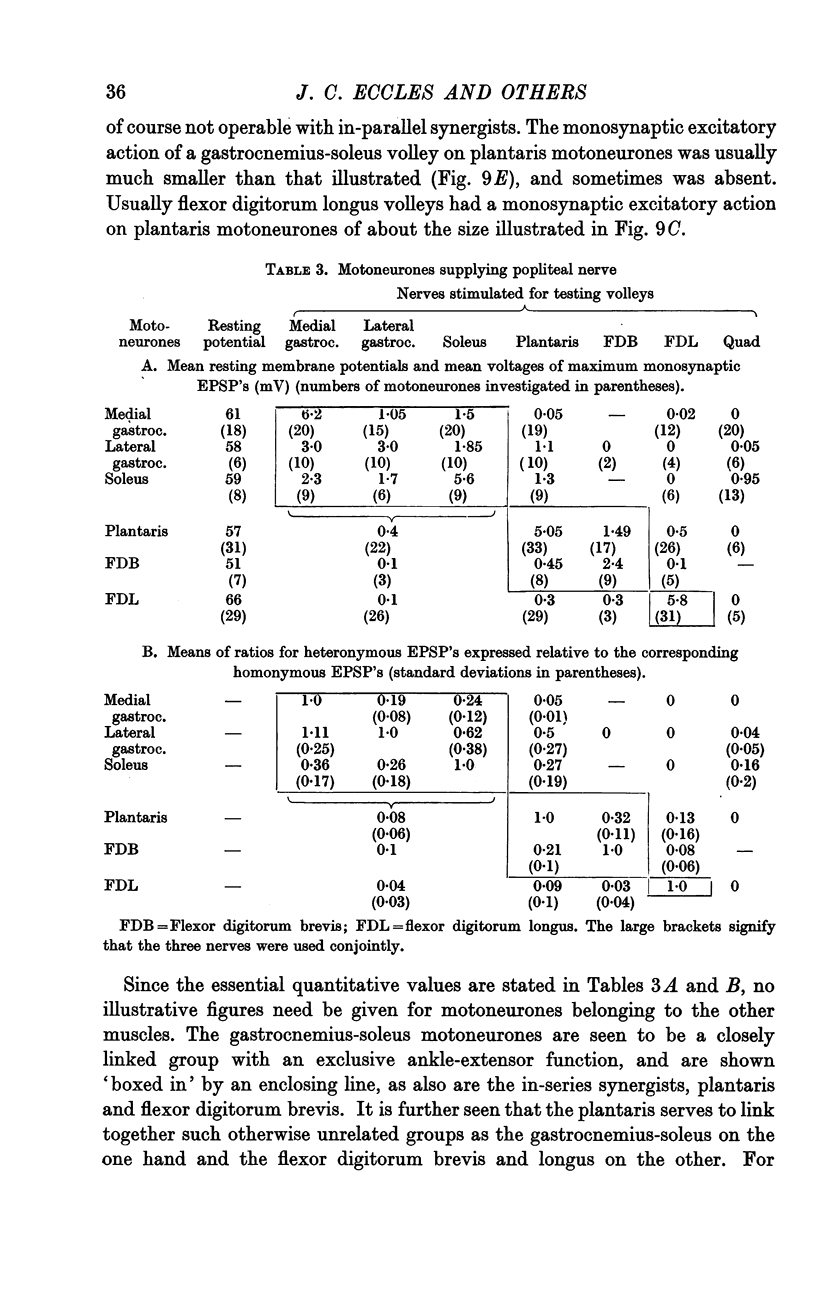
Full text
PDF

















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALVORD E. C., Jr, FUORTES M. G. Reflex activity of extensor motor units following muscular afferent excitation. J Physiol. 1953 Nov 28;122(2):302–321. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARAKI T., OTANI T. Response of single motoneurons to direct stimulation in toad's spinal cord. J Neurophysiol. 1955 Sep;18(5):472–485. doi: 10.1152/jn.1955.18.5.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK L. G., COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C. Intracellular recording from antidromically activated motoneurones. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):429–461. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK L. G., COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C. The recording of potentials from motoneurones with an intracellular electrode. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):431–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN L. A. Localization of stretch reflex. J Neurophysiol. 1953 May;16(3):272–285. doi: 10.1152/jn.1953.16.3.272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. Excitatory synaptic action in motoneurones. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):374–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. The electrical properties of the motoneurone membrane. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):291–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. The specific ionic conductances and the ionic movements across the motoneuronal membrane that produce the inhibitory post-synaptic potential. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):326–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., FATT P., KOKETSU K. Cholinergic and inhibitory synapses in a pathway from motor-axon collaterals to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1954 Dec 10;126(3):524–562. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., FATT P., LANDGREN S. Central pathway for direct inhibitory action of impulses in largest afferent nerve fibres to muscle. J Neurophysiol. 1956 Jan;19(1):75–98. doi: 10.1152/jn.1956.19.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., FATT P., LANDGREN S., WINSBURY G. J. Spinal cord potentials generated by volleys in the large muscle afferents. J Physiol. 1954 Sep 28;125(3):590–606. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C. The central action of antidromic impulses in motor nerve fibres. Pflugers Arch. 1955;260(5):385–415. doi: 10.1007/BF00363548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELDRED E., GRANIT R., MERTON P. A. Supraspinal control of the muscle spindles and its significance. J Physiol. 1953 Dec 29;122(3):498–523. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp005017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles J. C. Crossed extensor reflexes and their interaction. J Physiol. 1929 Feb 28;67(1):97–118. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1929.sp002556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., HOLMGREN B., MERTON P. A. The two routes for excitation of muscle and their subservience to the cerebellum. J Physiol. 1955 Oct 28;130(1):213–224. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., KAADA B. R. Influence of stimulation of central nervous structures on muscle spindles in cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1952;27(2-3):130–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1953.tb00930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R. Reflex self-regulation of muscle contraction and autogenetic inhibition. J Neurophysiol. 1950 Sep;13(5):351–372. doi: 10.1152/jn.1950.13.5.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRANIT R., STROM G. Autogenetic modulation of excitability of single ventral horn cells. J Neurophysiol. 1951 Mar;14(2):113–132. doi: 10.1152/jn.1951.14.2.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C. Monosynaptic reflex response of spinal motoneurons to graded afferent stimulation. J Gen Physiol. 1955 Jul 20;38(6):813–852. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.6.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C. The effect of stretch receptors from muscle on the discharge of motorneurons. J Physiol. 1952 Jul;117(3):359–379. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEFFERSON A., BENSON A. Some effects of post-tetanic potentiation of monosynaptic response of spinal cord of cat. J Neurophysiol. 1953 Jul;16(4):380–396. doi: 10.1152/jn.1953.16.4.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOB C. Monosynaptische Impulsübertragung zwischen Synergisten. Pflugers Arch. 1953;256(5):391–405. doi: 10.1007/BF00363686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONIG E. Uber die Wirkung antidromer Erregung auf den Eigenreflex von Katzen und Kaninchen. Pflugers Arch. 1952 Jul;225(4):339–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00370179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAPORTE Y., LLOYD D. P. C. Nature and significance of the reflex connections established by large afferent fibers of muscular origin. Am J Physiol. 1952 Jun;169(3):609–621. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1952.169.3.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLOYD D. P., HUNT C. C., McINTYRE A. K. Transmission in fractionated monosynaptic spinal reflex systems. J Gen Physiol. 1955 Jan 20;38(3):307–317. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.3.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLOYD D. P., McINTYRE A. K. Mono-synaptic reflex responses of individual motoneurons. J Gen Physiol. 1955 Jul 20;38(6):771–787. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.6.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLOYD D. P., McINTYRE A. K. Transmitter potentiality of homonymous and heteronymous monosynaptic reflex connections of individual motoneurons. J Gen Physiol. 1955 Jul 20;38(6):789–799. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.6.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL W. A statistical theory of monosynaptic input-output relations. J Cell Physiol. 1955 Dec;46(3):373–411. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030460302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS T. D. M. Reflex interaction of synergic extensor muscles of the cat hind limb. J Physiol. 1952 Jun;117(2):5p–6p. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrington C. S. Flexion-reflex of the limb, crossed extension-reflex, and reflex stepping and standing. J Physiol. 1910 Apr 26;40(1-2):28–121. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1910.sp001362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


