Abstract
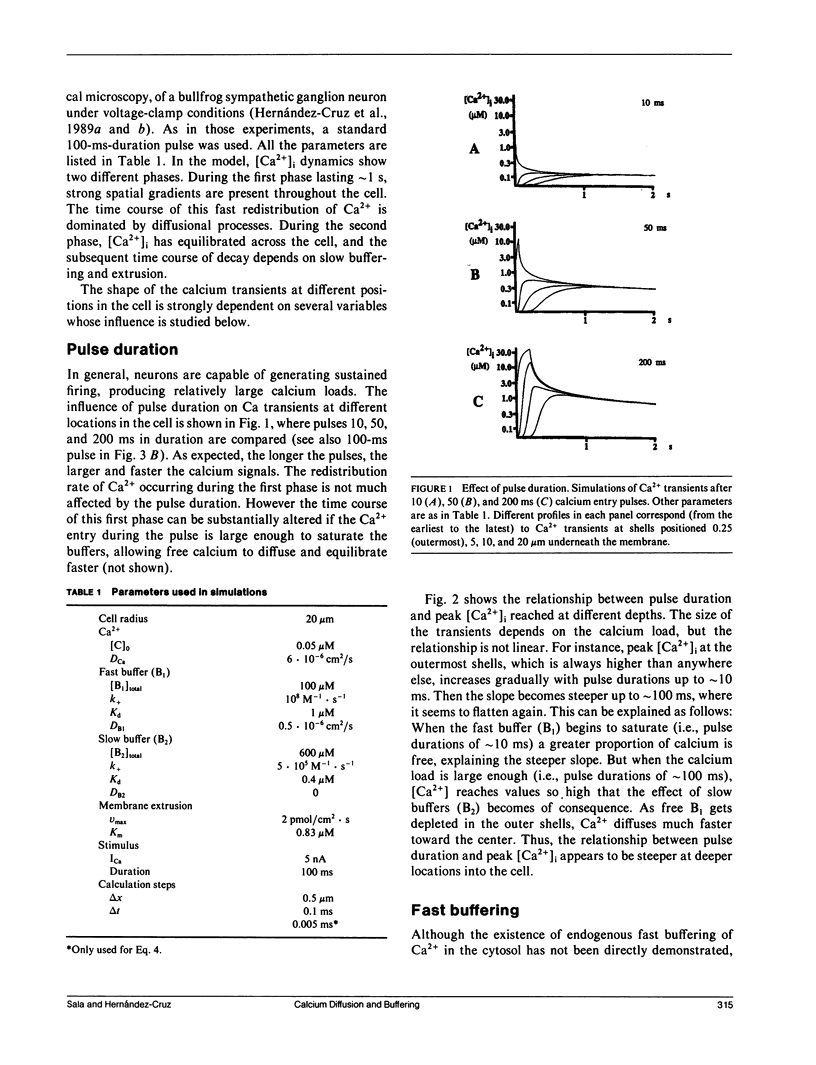
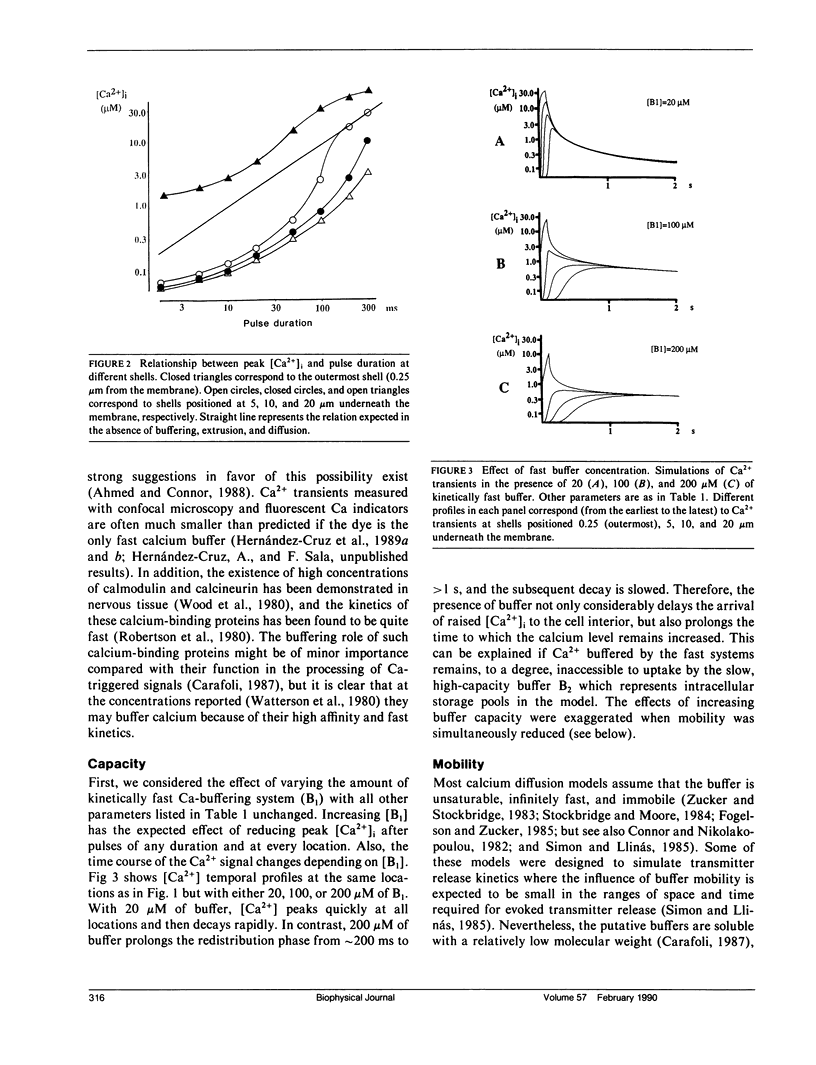
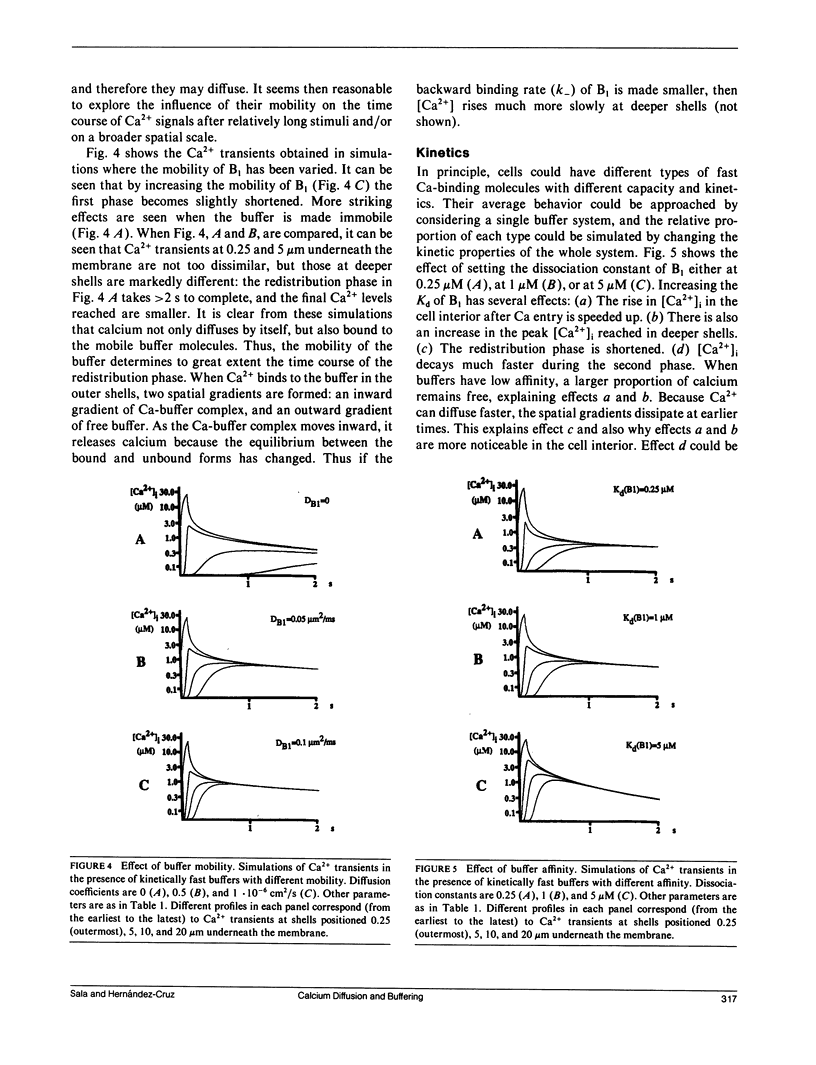
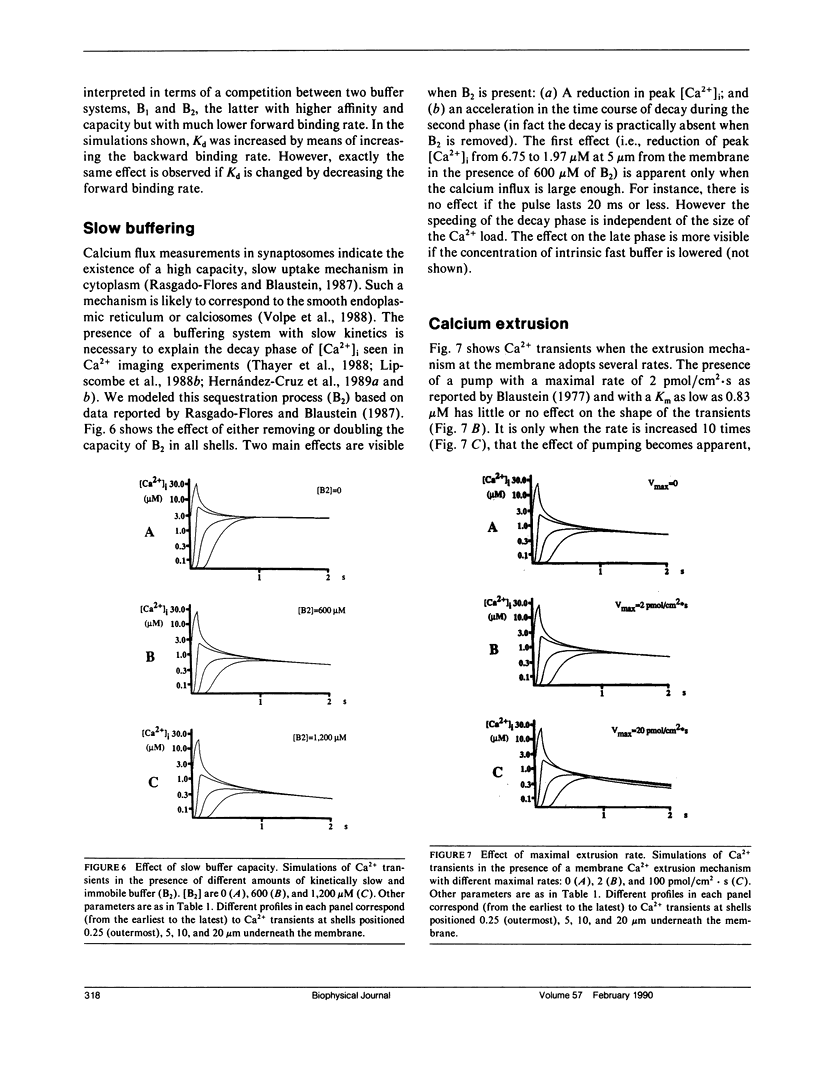
We have developed a calcium diffusion model for a spherical neuron which incorporates calcium influx and extrusion through the plasma membrane as well as three calcium buffer systems with different capacities, mobilities, and kinetics. The model allows us to calculate the concentration of any of the species involved at all locations in the cell and can be used to account for experimental data obtained with high-speed Ca imaging techniques. The influence of several factors on the Ca2+ transients is studied. The relationship between peak [Ca2+]i and calcium load is shown to be nonlinear and to depend on buffer characteristics. The time course of the Ca2+ signals is also shown to be dependent on buffer properties. In particular, buffer mobility strongly determines the size and time course of Ca2+ signals in the cell interior. The model predicts that the presence of exogenous buffer, such as fura-2, modifies the Ca2+ transients to a variable extent depending on its proportion relative to the natural, intrinsic buffers. The conclusions about natural calcium buffer properties that can be derived from Ca imaging experiments are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed Z., Connor J. A. Calcium regulation by and buffer capacity of molluscan neurons during calcium transients. Cell Calcium. 1988 Apr;9(2):57–69. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(88)90025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andresen M. C., Brown A. M., Yasui S. The role of diffusion in the photoresponse of an extraretinal photoreceptor of Aplysia. J Physiol. 1979 Feb;287:283–301. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft F. M., Stanfield P. R. Calcium dependence of the inactivation of calcium currents in skeletal muscle fibers of an insect. Science. 1981 Jul 10;213(4504):224–226. doi: 10.1126/science.213.4504.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Hodgkin A. L., Ridgway E. B. Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):709–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barish M. E., Thompson S. H. Calcium buffering and slow recovery kinetics of calcium-dependent outward current in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:201–219. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron G., Demaille J., Dutruge E. The distribution of parvalbumins in muscle and in other tissues. FEBS Lett. 1975 Aug 1;56(1):156–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Hodgkin A. L. The effect of cyanide on the efflux of calcium from squid axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):497–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Santiago E. M. Effects of internal and external cations and of ATP on sodium-calcium and calcium-calcium exchange in squid axons. Biophys J. 1977 Oct;20(1):79–111. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85538-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E. Intracellular calcium homeostasis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:395–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celio M. R. Parvalbumin in most gamma-aminobutyric acid-containing neurons of the rat cerebral cortex. Science. 1986 Feb 28;231(4741):995–997. doi: 10.1126/science.3945815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chad J. E., Eckert R. Calcium domains associated with individual channels can account for anomalous voltage relations of CA-dependent responses. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):993–999. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84244-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Calcium-induced release of calcium from the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):C1–14. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine A., Amos W. B., Durbin R. M., McNaughton P. A. Confocal microscopy: applications in neurobiology. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Aug;11(8):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelson A. L., Zucker R. S. Presynaptic calcium diffusion from various arrays of single channels. Implications for transmitter release and synaptic facilitation. Biophys J. 1985 Dec;48(6):1003–1017. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83863-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto S., Yamamoto K., Kuba K., Morita K., Kato E. Calcium localization in the sympathetic ganglion of the bullfrog and effects of caffeine. Brain Res. 1980 Nov 24;202(1):21–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble E., Koch C. The dynamics of free calcium in dendritic spines in response to repetitive synaptic input. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1311–1315. doi: 10.1126/science.3495885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L., Thomas M. V. Intracellular calcium accumulation during depolarization in a molluscan neurone. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:259–285. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Movements of labelled calcium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):253–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heizmann C. W. Parvalbumin, an intracellular calcium-binding protein; distribution, properties and possible roles in mammalian cells. Experientia. 1984 Sep 15;40(9):910–921. doi: 10.1007/BF01946439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. P., Timmerman M. P., Bagshaw C. R., Ashley C. C. The kinetics of calcium binding to fura-2 and indo-1. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 25;216(1):35–39. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80752-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao J. P., Tsien R. Y. Ca2+ binding kinetics of fura-2 and azo-1 from temperature-jump relaxation measurements. Biophys J. 1988 Apr;53(4):635–639. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83142-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. A study of synaptic transmission in the absence of nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):407–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M. G., Simon B. J., Szucs G., Schneider M. F. Simultaneous recording of calcium transients in skeletal muscle using high- and low-affinity calcium indicators. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):971–988. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83178-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konishi M., Olson A., Hollingworth S., Baylor S. M. Myoplasmic binding of fura-2 investigated by steady-state fluorescence and absorbance measurements. Biophys J. 1988 Dec;54(6):1089–1104. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83045-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Morita K., Nohmi M. Origin of calcium ions involved in the generation of a slow afterhyperpolarization in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Nov;399(3):194–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00656714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscombe D., Madison D. V., Poenie M., Reuter H., Tsien R. W., Tsien R. Y. Imaging of cytosolic Ca2+ transients arising from Ca2+ stores and Ca2+ channels in sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1988 Jul;1(5):355–365. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscombe D., Madison D. V., Poenie M., Reuter H., Tsien R. Y., Tsien R. W. Spatial distribution of calcium channels and cytosolic calcium transients in growth cones and cell bodies of sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2398–2402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Steinberg I. Z., Walton K. Relationship between presynaptic calcium current and postsynaptic potential in squid giant synapse. Biophys J. 1981 Mar;33(3):323–351. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84899-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. I., Curran T. Calcium as a modulator of the immediate-early gene cascade in neurons. Cell Calcium. 1988 Dec;9(5-6):303–311. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(88)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnas H., Hovav G., Parnas I. Effect of Ca2+ diffusion on the time course of neurotransmitter release. Biophys J. 1989 May;55(5):859–874. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82885-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusch M., Neher E. Rates of diffusional exchange between small cells and a measuring patch pipette. Pflugers Arch. 1988 Feb;411(2):204–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00582316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasgado-Flores H., Blaustein M. P. ATP-dependent regulation of cytoplasmic free calcium in nerve terminals. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jun;252(6 Pt 1):C588–C594. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.6.C588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Barrett P. Q. Calcium messenger system: an integrated view. Physiol Rev. 1984 Jul;64(3):938–984. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.3.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson S. P., Johnson J. D., Potter J. D. The time-course of Ca2+ exchange with calmodulin, troponin, parvalbumin, and myosin in response to transient increases in Ca2+. Biophys J. 1981 Jun;34(3):559–569. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84868-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. M., Llinás R. R. Compartmentalization of the submembrane calcium activity during calcium influx and its significance in transmitter release. Biophys J. 1985 Sep;48(3):485–498. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83804-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., Zucker R. S. Aequorin response facilitation and intracellular calcium accumulation in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:167–196. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockbridge N., Moore J. W. Dynamics of intracellular calcium and its possible relationship to phasic transmitter release and facilitation at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Neurosci. 1984 Mar;4(3):803–811. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-03-00803.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer S. A., Hirning L. D., Miller R. J. The role of caffeine-sensitive calcium stores in the regulation of the intracellular free calcium concentration in rat sympathetic neurons in vitro. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;34(5):664–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S., Coombs J. Spatial distribution of Ca currents in molluscan neuron cell bodies and regional differences in the strength of inactivation. J Neurosci. 1988 Jun;8(6):1929–1939. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-06-01929.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson D., Gorman A. L. Non-uniform Ca2+ buffer distribution in a nerve cell body. Nature. 1980 Aug 21;286(5775):816–817. doi: 10.1038/286816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y. Fluorescence measurement and photochemical manipulation of cytosolic free calcium. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):419–424. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe P., Krause K. H., Hashimoto S., Zorzato F., Pozzan T., Meldolesi J., Lew D. P. "Calciosome," a cytoplasmic organelle: the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive Ca2+ store of nonmuscle cells? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1091–1095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watterson D. M., Mendel P. A., Vanaman T. C. Comparison of calcium-modulated proteins from vertebrate brains. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2672–2676. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Fogarty K. E., Tsien R. Y., Fay F. S. Calcium gradients in single smooth muscle cells revealed by the digital imaging microscope using Fura-2. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):558–561. doi: 10.1038/318558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., Wallace R. W., Whitaker J. N., Cheung W. Y. Immunocytochemical localization of calmodulin and a heat-labile calmodulin-binding protein (CaM-BP80) in basal ganglia of mouse brain. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jan;84(1):66–76. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S., Fogelson A. L. Relationship between transmitter release and presynaptic calcium influx when calcium enters through discrete channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):3032–3036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.3032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S., Stockbridge N. Presynaptic calcium diffusion and the time courses of transmitter release and synaptic facilitation at the squid giant synapse. J Neurosci. 1983 Jun;3(6):1263–1269. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-06-01263.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


