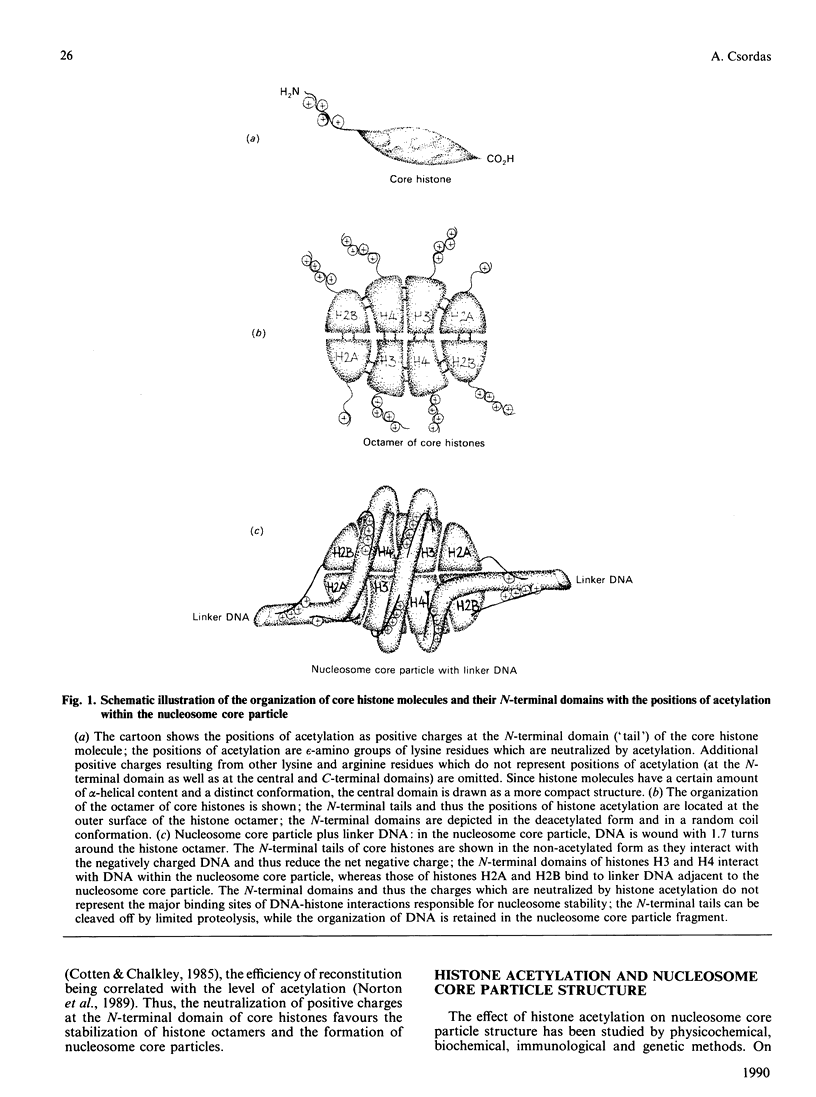
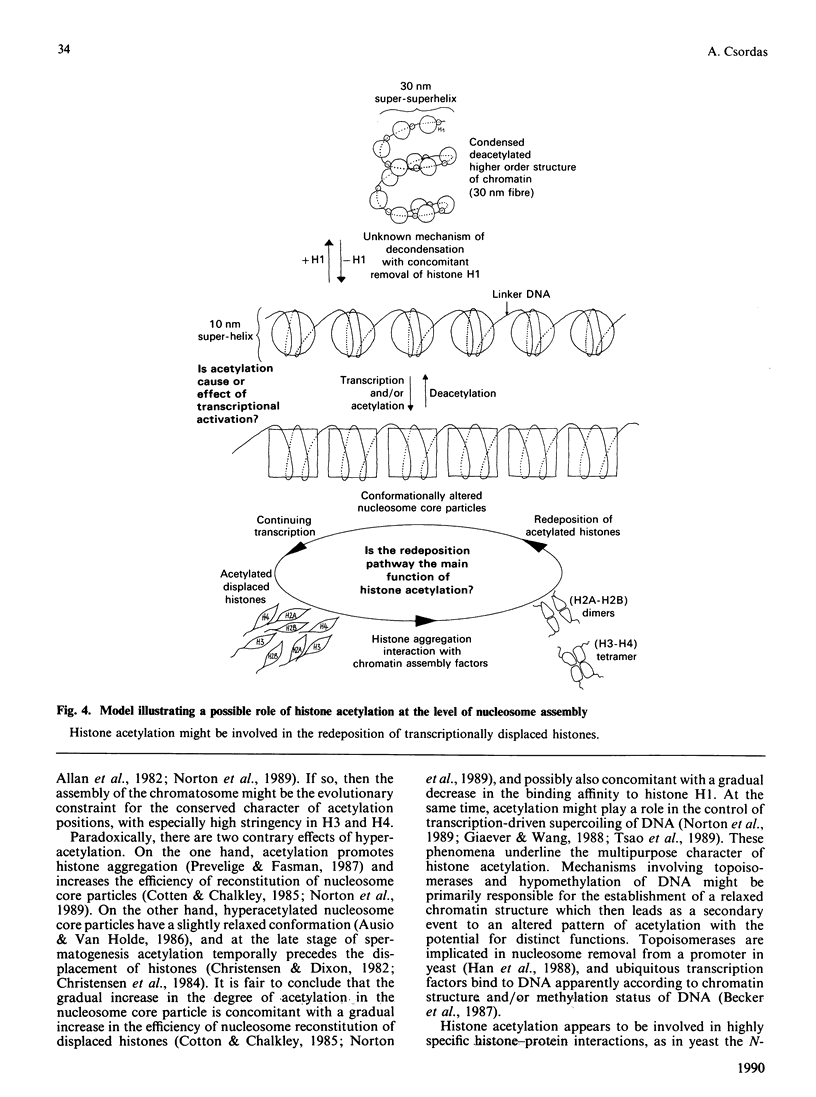
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLFREY V. G., FAULKNER R., MIRSKY A. E. ACETYLATION AND METHYLATION OF HISTONES AND THEIR POSSIBLE ROLE IN THE REGULATION OF RNA SYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 May;51:786–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.5.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan J., Cowling G. J., Harborne N., Cattini P., Craigie R., Gould H. Regulation of the higher-order structure of chromatin by histones H1 and H5. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):279–288. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan J., Harborne N., Rau D. C., Gould H. Participation of core histone "tails" in the stabilization of the chromatin solenoid. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):285–297. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allegra P., Sterner R., Clayton D. F., Allfrey V. G. Affinity chromatographic purification of nucleosomes containing transcriptionally active DNA sequences. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90698-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allis C. D., Chicoine L. G., Richman R., Schulman I. G. Deposition-related histone acetylation in micronuclei of conjugating Tetrahymena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8048–8052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almer A., Hörz W. Nuclease hypersensitive regions with adjacent positioned nucleosomes mark the gene boundaries of the PHO5/PHO3 locus in yeast. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2681–2687. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausio J., van Holde K. E. Histone hyperacetylation: its effects on nucleosome conformation and stability. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 25;25(6):1421–1428. doi: 10.1021/bi00354a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer B. W., Rhodes D. Eukaryotic RNA polymerase II binds to nucleosome cores from transcribed genes. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):482–488. doi: 10.1038/301482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. B., Ruppert S., Schütz G. Genomic footprinting reveals cell type-specific DNA binding of ubiquitous factors. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90639-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belikoff E., Wong L. J., Alberts B. M. Extensive purification of histone acetylase A, the major histone N-acetyl transferase activity detected in mammalian cell nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11448–11453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode J., Gómez-Lira M. M., Schröter H. Nucleosomal particles open as the histone core becomes hyperacetylated. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;130(3):437–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode J., Henco K., Wingender E. Modulation of the nucleosome structure by histone acetylation. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Sep;110(1):143–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boffa L. C., Gruss R. J., Allfrey V. G. Manifold effects of sodium butyrate on nuclear function. Selective and reversible inhibition of phosphorylation of histones H1 and H2A and impaired methylation of lysine and arginine residues in nuclear protein fractions. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9612–9621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonne-Andrea C., Harper F., Sobczak J., De Recondo A. M. Rat liver HMG1: a physiological nucleosome assembly factor. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1193–1199. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braddock G. W., Baldwin J. P., Bradbury E. M. Neutron-scattering studies of the structure of chromatin core particles in solution. Biopolymers. 1981 Feb;20(2):327–343. doi: 10.1002/bip.1981.360200206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brotherton T. W., Covault J., Shires A., Chalkley R. Only a small fraction of avian erythrocyte histone is involved in ongoing acetylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):5061–5073. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.5061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. L. A comparison of the turnover of alpha-N-acetylated and nonacetylated mouse L-cell proteins. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1447–1449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. L., Roberts W. K. Evidence that approximately eighty per cent of the soluble proteins from Ehrlich ascites cells are Nalpha-acetylated. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):1009–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhm J., Schlaeger E. J., Knippers R. Acetylation of nucleosomal histones in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Nov;112(2):353–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb07212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhm L., Briand G., Sautière P., Crane-Robinson C. Proteolytic digestion studies of chromatin core-histone structure. Identification of the limit peptides of histones H3 and H4. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep;119(1):67–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candido E. P., Dixon G. H. Trout testis cells. 3. Acetylation of histones in different cell types from developing trout testis. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 10;247(17):5506–5510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candido E. P., Reeves R., Davie J. R. Sodium butyrate inhibits histone deacetylation in cultured cells. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90305-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cano A., Pestaña A. Purification and properties of a histone acetyltransferase from Artemia salina, highly efficient with H1 histone. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun;97(1):65–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cary P. D., Crane-Robinson C., Bradbury E. M., Dixon G. H. Effect of acetylation on the binding of N-terminal peptides of histone H4 to DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Sep;127(1):137–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cary P. D., Moss T., Bradbury E. M. High-resolution proton-magnetic-resonance studies of chromatin core particles. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Sep 1;89(2):475–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12551.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Certa U., Colavito-Shepanski M., Grunstein M. Yeast may not contain histone H1: the only known 'histone H1-like' protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a mitochondrial protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):7975–7985. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.7975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalkley R., Shires A. The isolation of HTC variant cells which can replicate in butyrate. Changes in histone acetylation and tyrosine aminotransferase induction. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7698–7704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers S. A., Shaw B. R. Levels of histone H4 diacetylation decrease dramatically during sea urchin embryonic development and correlate with cell doubling rate. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13458–13463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. A., Allfrey V. G. Rapid and reversible changes in nucleosome structure accompany the activation, repression, and superinduction of murine fibroblast protooncogenes c-fos and c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5252–5256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chicoine L. G., Richman R., Cook R. G., Gorovsky M. A., Allis C. D. A single histone acetyltransferase from Tetrahymena macronuclei catalyzes deposition-related acetylation of free histones and transcription-related acetylation of nucleosomal histones. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):127–135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chicoine L. G., Schulman I. G., Richman R., Cook R. G., Allis C. D. Nonrandom utilization of acetylation sites in histones isolated from Tetrahymena. Evidence for functionally distinct H4 acetylation sites. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1071–1076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen M. E., Dixon G. H. Hyperacetylation of histone H4 correlates with the terminal, transcriptionally inactive stages of spermatogenesis in rainbow trout. Dev Biol. 1982 Oct;93(2):404–415. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen M. E., Rattner J. B., Dixon G. H. Hyperacetylation of histone H4 promotes chromatin decondensation prior to histone replacement by protamines during spermatogenesis in rainbow trout. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4575–4592. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton J. L., Bellard M., Chambon P. Biochemical evidence of variability in the DNA repeat length in the chromatin of higher eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4382–4386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotten M., Chalkley R. Hyperacetylated histones facilitate chromatin assembly in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 25;13(2):401–414. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotten M., Chalkley R. Purification of a novel, nucleoplasmin-like protein from somatic nuclei. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3945–3954. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02736.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotten M., Sealy L., Chalkley R. Massive phosphorylation distinguishes Xenopus laevis nucleoplasmin isolated from oocytes or unfertilized eggs. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5063–5069. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couppez M., Martin-Ponthieu A., Sautière P. Histone H4 from cuttlefish testis is sequentially acetylated. Comparison with acetylation of calf thymus histone H4. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2854–2860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousens L. S., Alberts B. M. Accessibility of newly synthesized chromatin to histone acetylase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3945–3949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousens L. S., Gallwitz D., Alberts B. M. Different accessibilities in chromatin to histone acetylase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1716–1723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csordas A., Multhaup I., Grunicke H. Transcription of chemically acetylated chromatin with homologous RNA polymerase B. Biosci Rep. 1984 Feb;4(2):155–163. doi: 10.1007/BF01120312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csordas A., Puschendorf B., Grunicke H. Increased acetylation of histones at an early stage of oestradiol-mediated gene activation in the liver of immature chicks. J Steroid Biochem. 1986 Jan;24(1):437–442. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(86)90097-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie J. R., Candido E. P. Acetylated histone H4 is preferentially associated with template-active chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3574–3577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie J. R., Candido E. P. DNase I sensitive chromatin is enriched in the acetylated species of histone H4. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 11;110(2):164–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie J. R., Saunders C. A., Walsh J. M., Weber S. C. Histone modifications in the yeast S. Cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3205–3216. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange R. J., Fambrough D. M., Smith E. L., Bonner J. Calf and pea histone IV. 3. Complete amino acid sequence of pea seedling histone IV; comparison with the homologous calf thymus histone. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5669–5679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange R. J., Fambrough D. M., Smith E. L., Bonner J. Calf and pea histone IV. II. The complete amino acid sequence of calf thymus histone IV; presence of epsilon-N-acetyllysine. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 25;244(2):319–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilworth S. M., Black S. J., Laskey R. A. Two complexes that contain histones are required for nucleosome assembly in vitro: role of nucleoplasmin and N1 in Xenopus egg extracts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1009–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90587-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov S., Makarov V., Apostolova T., Pashev I. Structure of hyperacetylated chromatin: light scattering and flow linear dichroism study. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 3;197(1-2):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80329-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doenecke D., Gallwitz D. Acetylation of histones in nucleosomes. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Apr 30;44(2):113–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00226895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumuis-Kervabon A., Encontre I., Etienne G., Jauregui-Adell J., Méry J., Mesnier D., Parello J. A chromatin core particle obtained by selective cleavage of histones by clostripain. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1735–1742. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04418.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Honda B. M., Laskey R. A., Thomas J. O. Assembly of nucleosomes: the reaction involving X. laevis nucleoplasmin. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90474-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estepa I., Pestaña A. Isolation and partial characterization of three histone-specific acetyltransferases from Artemia. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 2;132(2):249–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07356.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G., McGhee J. D. Structure of the 30 nm chromatin fiber. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):375–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90456-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. T., Klug A. Solenoidal model for superstructure in chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1897–1901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch J. T., Lutter L. C., Rhodes D., Brown R. S., Rushton B., Levitt M., Klug A. Structure of nucleosome core particles of chromatin. Nature. 1977 Sep 1;269(5623):29–36. doi: 10.1038/269029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcea R. L., Alberts B. M. Comparative studies of histone acetylation in nucleosomes, nuclei, and intact cells. Evidence for special factors which modify acetylase action. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11454–11463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garel A., Axel R. Selective digestion of transcriptionally active ovalbumin genes from oviduct nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3966–3970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatewood J. M., Cook G. R., Balhorn R., Bradbury E. M., Schmid C. W. Sequence-specific packaging of DNA in human sperm chromatin. Science. 1987 May 22;236(4804):962–964. doi: 10.1126/science.3576213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaever G. N., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of intracellular DNA can occur in eukaryotic cells. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):849–856. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90140-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover C. V., Gorovsky M. A. Amino-acid sequence of Tetrahymena histone H4 differs from that of higher eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):585–589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Pleger G. L., Keevert J. B., Johmann C. A. Studies on histone fraction F2A1 in macro- and micronuclei of Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jun;57(3):773–781. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.3.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J. M., Butler P. J. Structure of transcriptionally-active chromatin subunits. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Sep;4(9):3155–3173. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.9.3155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoryev S. A., Krasheninnikov I. A. Transient unfolding of trypsin-digested chromatin core particles. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec;129(1):119–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07029.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimes S. R., Jr, Henderson N. Acetylation of rat testis histones H2B and TH2B. Dev Biol. 1984 Feb;101(2):516–521. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90165-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimes S. R., Jr, Henderson N. Hyperacetylation of histone H4 in rat testis spermatids. Exp Cell Res. 1984 May;152(1):91–97. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90232-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han M., Chang M., Kim U. J., Grunstein M. Histone H2B repression causes cell-cycle-specific arrest in yeast: effects on chromosomal segregation, replication, and transcription. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):589–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90237-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han M., Kim U. J., Kayne P., Grunstein M. Depletion of histone H4 and nucleosomes activates the PHO5 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2221–2228. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03061.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay C. W., Candido E. P. Histone deacetylase from HeLa cells: properties of the high molecular weight complex. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 20;22(26):6175–6180. doi: 10.1021/bi00295a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay C. W., Candido E. P. Histone deacetylase. Association with a nuclease resistant, high molecular weight fraction of HeLa cell chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3726–3734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbes T. R., Thorne A. W., Crane-Robinson C. A direct link between core histone acetylation and transcriptionally active chromatin. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1395–1402. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm R. P., Kneale G. G., Sauau P., Baldwin J. P., Bradbury E. M., Ibel K. Small angle neutron scattering studies of chromatin subunits in solution. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutcheon T., Dixon G. H., Levy-Wilson B. Transcriptionally active mononucleosomes from trout testis are heterogeneous in composition. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):681–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo-Kemenes T., Hörz W., Zachau H. G. Chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:89–121. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai B. S., Yau P., Baldwin J. P., Ibel K., May R. P., Bradbury E. M. Hyperacetylation of core histones does not cause unfolding of nucleosomes. Neutron scatter data accords with disc shape of the nucleosome. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8784–8792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip Y. T., Jackson V., Meier J., Chalkley R. The separation of transcriptionally engaged genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14044–14052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg I. Histones. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:159–191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson V., Shires A., Tanphaichitr N., Chalkley R. Modifications to histones immediately after synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 25;104(2):471–483. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90282-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiakuntorn Y., Mathias A. P. Effects of gene modulators on the acetylation of chromosomal proteins of rat liver slices. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Oct 15;102(3):811–817. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91610-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Matthews H. R., Littau V. C., Lothstein L., Bradbury E. M., Allfrey V. G. The structure of chromatin containing DNA complementary to 19 S and 26 S ribosomal RNA in active and inactive stages of Physarum polycephalum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Dec;191(2):537–560. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90392-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko Y. Epidermal growth factor enhances acetylation of nuclear proteins in cultured human liver cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb 16;762(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayne P. S., Kim U. J., Han M., Mullen J. R., Yoshizaki F., Grunstein M. Extremely conserved histone H4 N terminus is dispensable for growth but essential for repressing the silent mating loci in yeast. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):27–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim U. J., Han M., Kayne P., Grunstein M. Effects of histone H4 depletion on the cell cycle and transcription of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2211–2219. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03060.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Fortkamp E., Krohne G., Zentgraf H., Franke W. W. Co-existence of two different types of soluble histone complexes in nuclei of Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1166–1176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Franke W. W. Soluble acidic complexes containing histones H3 and H4 in nuclei of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):799–809. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90442-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Seiter A. Identification of domains involved in nuclear uptake and histone binding of protein N1 of Xenopus laevis. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1605–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02986.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A. From macromolecules to biological assemblies. Nobel Lecture, 8 December 1982. Biosci Rep. 1983 May;3(5):395–430. doi: 10.1007/BF01121953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A., Rhodes D., Smith J., Finch J. T., Thomas J. O. A low resolution structure for the histone core of the nucleosome. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):509–516. doi: 10.1038/287509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Structure of chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:931–954. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Franke W. W. A major soluble acidic protein located in nuclei of diverse vertebrate species. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Sep;129(1):167–189. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90341-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G. Immunological identification of the karyophilic, histone-binding proteins N1 and N2 in somatic cells and oocytes of diverse amphibia. Exp Cell Res. 1985 May;158(1):205–222. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90444-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruh J. Effects of sodium butyrate, a new pharmacological agent, on cells in culture. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Feb 5;42(2):65–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00222695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehl L., Lyness T., Dixon G. H., Levy-Wilson B. Distribution of high mobility group proteins among domains of trout testis chromatin differing in their susceptibility to micrococcal nuclease. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):1090–1095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Honda B. M., Mills A. D., Finch J. T. Nucleosomes are assembled by an acidic protein which binds histones and transfers them to DNA. Nature. 1978 Oct 5;275(5679):416–420. doi: 10.1038/275416a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D., Morris N. R. Assembly of SV40 chromatin in a cell-free system from Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P. R. Calf liver nuclear N-acetyltransferases. Purification and properties of two enzymes with both spermidine acetyltransferase and histone acetyltransferase activities. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 10;253(1):233–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P. R. Histone acetylation and hormone action. Early effects of aldosterone on histone acetylation in rat kidney. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;134(4):907–912. doi: 10.1042/bj1340907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P. R. Histone acetylation and hormone action. Early effects of oestradiol-17beta on histone acetylation in rat uterus. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(3):663–669. doi: 10.1042/bj1300663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P. R. Histone acetylation by cell-free preparations from rat uterus: in vitro stimulation by estradiol-17 beta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Apr 5;31(1):59–65. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M., Tatchell K. Chromatin core particle unfolding induced by tryptic cleavage of histones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jun;4(6):2039–2055. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.6.2039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohr D., Hereford L. Yeast chromatin is uniformly digested by DNase-I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4285–4288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch Y., LaPointe J. W., Kornberg R. D. Nucleosomes inhibit the initiation of transcription but allow chain elongation with the displacement of histones. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90561-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch Y., LaPointe J. W., Kornberg R. D. On the displacement of histones from DNA by transcription. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):743–744. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90128-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losa R., Brown D. D. A bacteriophage RNA polymerase transcribes in vitro through a nucleosome core without displacing it. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):801–808. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90338-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louie A. J., Dixon G. H. Synthesis, acetylation, and phosphorylation of histone IV and its binding to DNA during spermatogenesis in trout. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1975–1979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louie A. J., Dixon G. H. Synthesis, acetylation, and phosphorylation of histone IV and its binding to DNA during spermatogenesis in trout. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1975–1979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannironi C., D'Incalci M. Doxorubicin induces the acetylation of histone H1 in a human colon cancer cell line (LoVo/DX) selected for resistance to the drug, but not in the sensitive parental line (LoVo). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 30;155(3):1221–1229. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81270-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marian B., Wintersberger U. Modification of histones during the mitotic and meiotic cycle of yeast. FEBS Lett. 1982 Mar 8;139(1):72–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80490-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marushige K., Dixon G. H. Developmental changes in chromosomal composition and template activity during spermatogenesis in trout testis. Dev Biol. 1969 Apr;19(4):397–414. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(69)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marushige K., Dixon G. H. Transformation of trout testis chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 25;246(18):5799–5805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Oudet P., Wasylyk B., Chambon P. Effect of histone acetylation on structure and in vitro transcription of chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3523–3547. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D., Oudet P., Chambon P. Structure of transcribing chromatin. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1980;24:1–55. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60670-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Nucleosome structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1115–1156. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.005343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Nickol J. M., Felsenfeld G., Rau D. C. Histone hyperacetylation has little effect on the higher order folding of chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4065–4075. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Hager L., Palmiter R. D. Butyrate and related inhibitors of histone deacetylation block the induction of egg white genes by steroid hormones. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):469–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90357-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mende L. M., Waterborg J. H., Mueller R. D., Matthews H. R. Isolation, identification, and characterization of histones from plasmodia of the true slime mold Physarum polycephalum using extraction with guanidine hydrochloride. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 4;22(1):38–51. doi: 10.1021/bi00270a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills A. D., Laskey R. A., Black P., De Robertis E. M. An acidic protein which assembles nucleosomes in vitro is the most abundant protein in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. J Mol Biol. 1980 May 25;139(3):561–568. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90148-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris N. R. A comparison of the structure of chicken erythrocyte and chicken liver chromatin. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 1):627–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller S., Erard M., Burggraf E., Couppez M., Sautière P., Champagne M., Van Regenmortel M. H. Immunochemical detection of changes in chromatin subunits induced by histone H4 acetylation. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):939–944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01275.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A. The regulation of yeast mating-type chromatin structure by SIR: an action at a distance affecting both transcription and transposition. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):567–578. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90253-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. A. Histone acetylation in baker's yeast. Maintenance of the hyperacetylated configuration in log phase protoplasts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1565–1568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D., Perry M. E., Chalkley R. A correlation between nucleosome spacer region susceptibility to DNase I and histone acetylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Feb;6(2):561–574. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.2.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton V. G., Imai B. S., Yau P., Bradbury E. M. Histone acetylation reduces nucleosome core particle linking number change. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):449–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90920-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa Y., Quagliarotti G., Jordan J., Taylor C. W., Starbuck W. C., Busch H. Structural analysis of the glycine-rich, arginine-rich histone. 3. Sequence of the amino-terminal half of the molecule containing the modified lysine residues and the total sequence. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4387–4392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohe Y., Iwai K. Human spleen histone H3. Isolation and amino acid sequence. J Biochem. 1981 Oct;90(4):1205–1211. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliva R., Bazett-Jones D., Mezquita C., Dixon G. H. Factors affecting nucleosome disassembly by protamines in vitro. Histone hyperacetylation and chromatin structure, time dependence, and the size of the sperm nuclear proteins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17016–17025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliva R., Mezquita C. Histone H4 hyperacetylation and rapid turnover of its acetyl groups in transcriptionally inactive rooster testis spermatids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8049–8059. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS D. M. The presence of acetyl groups of histones. Biochem J. 1963 May;87:258–263. doi: 10.1042/bj0870258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palter K. B., Alberts B. M. The use of DNA-cellulose for analyzing histone-DNA interactions. Discovery of nucleosome-like histone binding to single-stranded DNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11160–11169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardon J. F., Worcester D. L., Wooley J. C., Cotter R. I., Lilley D. M., Richards R. M. The structure of the chromatin core particle in solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Sep;4(9):3199–3214. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.9.3199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasqualini J. R., Cosquer-Clavreul C., Gelly C. Rapid modulation by progesterone and tamoxifen of estradiol effects on nuclear histone acetylation in the uterus of the fetal guinea pig. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 20;739(1):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M., Chalkley R. The effect of histone hyperacetylation on the nuclease sensitivity and the solubility of chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3313–3318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesis K. H., Matthews H. R. Histone acetylation in replication and transcription: turnover at specific acetylation sites in histone H4 from Physarum polycephalum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Dec;251(2):665–673. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90376-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogo B. G., Allfrey V. G., Mirsky A. E. RNA synthesis and histone acetylation during the course of gene activation in lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Apr;55(4):805–812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.4.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogo B. G., Pogo A. O., Allfrey V. G., Mirsky A. E. Changing patterns of histone acetylation and RNA synthesis in regeneration of the liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Apr;59(4):1337–1344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.4.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prevelige P. E., Jr, Fasman G. D. Structural studies of acetylated and control inner core histones. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2944–2955. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reczek P. R., Weissman D., Hüvös P. E., Fasman G. D. Sodium butyrate induced structural changes in HeLa cell chromatin. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 2;21(5):993–1002. doi: 10.1021/bi00534a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R. Transcriptionally active chromatin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 10;782(4):343–393. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renz M., Nehls P., Hozier J. Histone H1 involvement in the structure of the chromosome fiber. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):245–252. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J., Finch J. T., Rushton B., Rhodes D., Klug A. Structure of the nucleosome core particle at 7 A resolution. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):532–537. doi: 10.1038/311532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridsdale J. A., Davie J. R. Chicken erythrocyte polynucleosomes which are soluble at physiological ionic strength and contain linker histones are highly enriched in beta-globin gene sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1081–1096. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs M. G., Whittaker R. G., Neumann J. R., Ingram V. M. n-Butyrate causes histone modification in HeLa and Friend erythroleukaemia cells. Nature. 1977 Aug 4;268(5619):462–464. doi: 10.1038/268462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein P., Sealy L., Marshall S., Chalkley R. Cellular protein synthesis and inhibition of cell division are independent of butyrate-induced histone hyperacetylation. Nature. 1979 Aug 23;280(5724):692–693. doi: 10.1038/280692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Carrillo A., Wangh L. J., Allfrey V. G. Processing of newly synthesized histone molecules. Science. 1975 Oct 10;190(4210):117–128. doi: 10.1126/science.1166303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Carrillo A., Wangh L. J., Littau V. C., Allfrey V. G. Changes in histone acetyl content and in nuclear non-histone protein composition of avian erythroid cells at different stages of maturation. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 25;249(22):7358–7368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savić A., Richman P., Williamson P., Poccia D. Alterations in chromatin structure during early sea urchin embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3706–3710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröter H., Gómez-Lira M. M., Plank K. H., Bode J. The extent of histone acetylation induced by butyrate and the turnover of acetyl groups depend on the nature of the cell line. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(1):21–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster T., Han M., Grunstein M. Yeast histone H2A and H2B amino termini have interchangeable functions. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):445–451. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90330-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealy L., Chalkley R. DNA associated with hyperacetylated histone is preferentially digested by DNase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jun;5(6):1863–1876. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.6.1863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealy L., Chalkley R. Modification of histones immediately following synthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Oct 1;197(1):78–82. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90221-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealy L., Chalkley R. The effect of sodium butyrate on histone modification. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):115–121. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealy L., Cotten M., Chalkley R. Xenopus nucleoplasmin: egg vs. oocyte. Biochemistry. 1986 May 20;25(10):3064–3072. doi: 10.1021/bi00358a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Structure of chromatin containing extensively acetylated H3 and H4. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90219-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Structure of the chromatosome, a chromatin particle containing 160 base pairs of DNA and all the histones. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 12;17(25):5524–5531. doi: 10.1021/bi00618a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling L., Klug A. X-ray studies on "native" chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 15;112(2):253–263. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srebreva L., Zlatanova J., Miloshev G., Tsanev R. Immunological evidence for the existence of H1-like histone in yeast. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jun 1;165(2):449–454. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein A. DNA wrapping in nucleosomes. The linking number problem re-examined. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 24;8(20):4803–4820. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.20.4803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterner R., Boffa L. C., Chen T. A., Allfrey V. G. Cell cycle-dependent changes in conformation and composition of nucleosomes containing human histone gene sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4375–4391. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterner R., Vidali G., Allfrey V. G. Studies of acetylation and deacetylation in high mobility group proteins. Identification of the sites of acetylation in HMG-1. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11577–11583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterner R., Vidali G., Allfrey V. G. Studies of acetylation and deacetylation in high mobility group proteins. Identification of the sites of acetylation in high mobility group proteins 14 and 17. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8892–8895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suau P., Kneale G. G., Braddock G. W., Baldwin J. P., Bradbury E. M. A low resolution model for the chromatin core particle by neutron scattering. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Nov;4(11):3769–3786. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.11.3769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung M. T., Dixon G. H. Modification of histones during spermiogenesis in trout: a molecular mechanism for altering histone binding to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1616–1623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sures I., Gallwitz D. Histone-specific acetyltransferases from calf thymus. Isolation, properties, and substrate specificity of three different enzymes. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 4;19(5):943–951. doi: 10.1021/bi00546a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaku F., Nakao K., Ono T., Terayama H. Changes in histone acetylation and RNA synthesis in the spleen of polycythemic mouse after erythropoietin injection. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Dec 16;195(2):396–400. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90646-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanphaichitr N., Sobhon P., Taluppeth N., Chalermisarachai P. Basic nuclear proteins in testicular cells and ejaculated spermatozoa in man. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Dec;117(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Koller T., Klug A. Involvement of histone H1 in the organization of the nucleosome and of the salt-dependent superstructures of chromatin. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):403–427. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis G. H., Colavito-Shepanski M., Grunstein M. Extensive purification and characterization of chromatin-bound histone acetyltransferase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14406–14412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao Y. P., Wu H. Y., Liu L. F. Transcription-driven supercoiling of DNA: direct biochemical evidence from in vitro studies. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90989-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanfleteren J. R., Van Bun S. M., Van Beeumen J. J. The primary structure of histone H2A from the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):297–300. doi: 10.1042/bj2430297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vavra K. J., Allis C. D., Gorovsky M. A. Regulation of histone acetylation in Tetrahymena macro- and micronuclei. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2591–2598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vavra K. J., Colavito-Shepanski M., Gorovsky M. A. Histone acetylation and the deoxyribonuclease I sensitivity of the Tetrahymena ribosomal gene. Biochemistry. 1982 Apr 13;21(8):1772–1781. doi: 10.1021/bi00537a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidali G., Boffa L. C., Bradbury E. M., Allfrey V. G. Butyrate suppression of histone deacetylation leads to accumulation of multiacetylated forms of histones H3 and H4 and increased DNase I sensitivity of the associated DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2239–2243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Holt C., Strickland W. N., Brandt W. F., Strickland M. S. More histone structures. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 15;100(2):201–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80337-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis J. W., Rykowski M., Grunstein M. Yeast histone H2B containing large amino terminus deletions can function in vivo. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):711–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterborg J. H., Fried S. R., Matthews H. R. Acetylation and methylation sites in histone H4 from Physarum polycephalum. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Nov 2;136(2):245–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07734.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterborg J. H., Matthews H. R. Patterns of histone acetylation in Physarum polycephalum. H2A and H2B acetylation is functionally distinct from H3 and H4 acetylation. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jul 16;142(2):329–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Groudine M. Chromosomal subunits in active genes have an altered conformation. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):848–856. doi: 10.1126/science.948749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. The nucleosome repeat length increases during erythropoiesis in the chick. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Apr;5(4):1179–1188. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.4.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Van Lente F. Dissection of chromosome structure with trypsin and nucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4249–4253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S. T. Properties of active nucleosomes as revealed by HMG 14 and 17 chromatography. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 25;10(6):2017–2042. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.6.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Augustine R., Schulman H. Calcium-dependent phosphorylation of histone H3 in butyrate-treated HeLa cells. Nature. 1980 Sep 4;287(5777):74–76. doi: 10.1038/287074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Simpson R. T. Localization of the sites along nucleosome DNA which interact with NH2-terminal histone regions. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6516–6520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Stein A. Folding of DNA by histones which lack their NH2-terminal regions. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3857–3861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widom J., Klug A. Structure of the 300A chromatin filament: X-ray diffraction from oriented samples. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegand R. C., Brutlag D. L. Histone acetylase from Drosophila melanogaster specific for H4. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4578–4583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodland H. R. The modification of stored histones H3 and H4 during the oogenesis and early development of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1979 Feb;68(2):360–370. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90210-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Abmayr S. M., Cromlish W. A., Roeder R. G. Transcriptional regulation by the immediate early protein of pseudorabies virus during in vitro nucleosome assembly. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Roeder R. G. Binding of transcription factor TFIID to the major late promoter during in vitro nucleosome assembly potentiates subsequent initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):613–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wouters-Tyrou D., Martin-Ponthieu A., Sautiere P., Biserte G. Acetylation of histone H4 in chicken erythrocyte and cuttle-fish testis chromatin. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 15;128(2):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80079-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Nishioka D., Bonner W. M. Differential conservation of histone 2A variants between mammals and sea urchins. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):426–431. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau P., Thorne A. W., Imai B. S., Matthews H. R., Bradbury E. M. Thermal denaturation studies of acetylated nucleosomes and oligonucleosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec 15;129(2):281–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07050.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang D. E., Nelson D. A. Histone acetylation in chicken erythrocytes. Rates of acetylation and evidence that histones in both active and potentially active chromatin are rapidly modified. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 15;250(1):233–240. doi: 10.1042/bj2500233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang D., Nelson D. A. Histone acetylation in chicken erythrocytes. Estimation of the percentage of sites actively modified. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):857–862. doi: 10.1042/bj2400857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]