Abstract
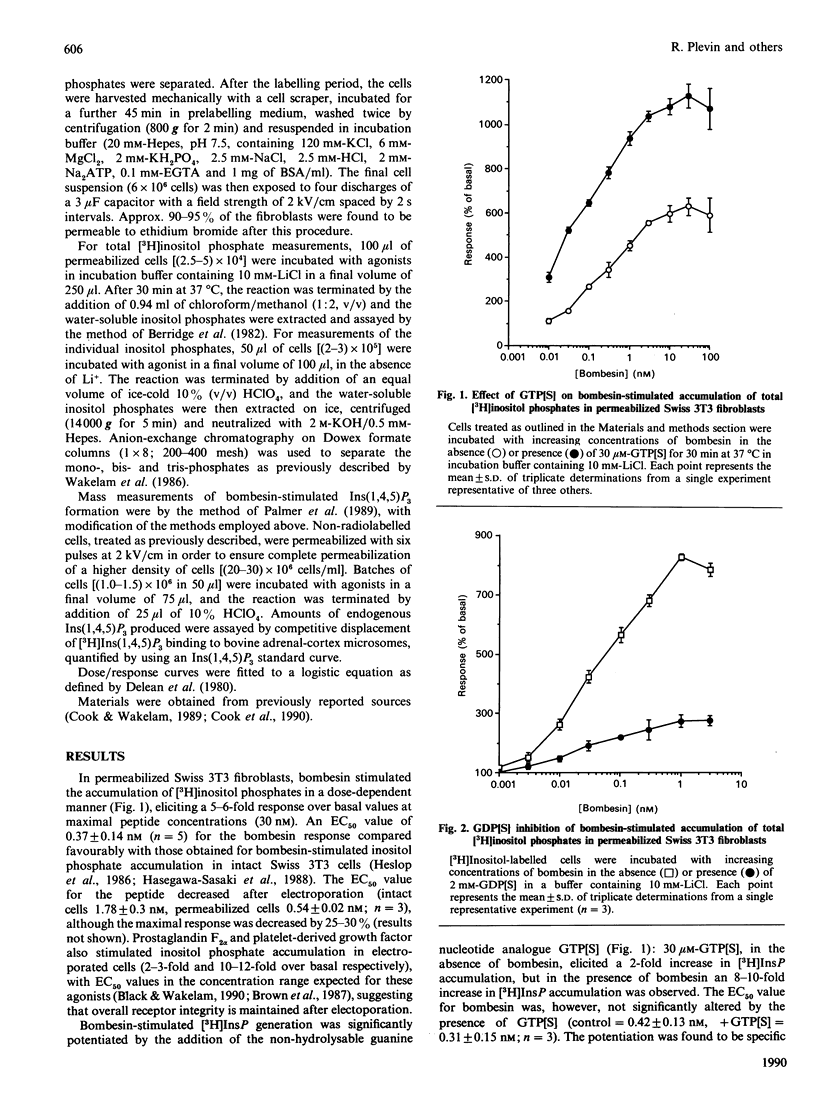
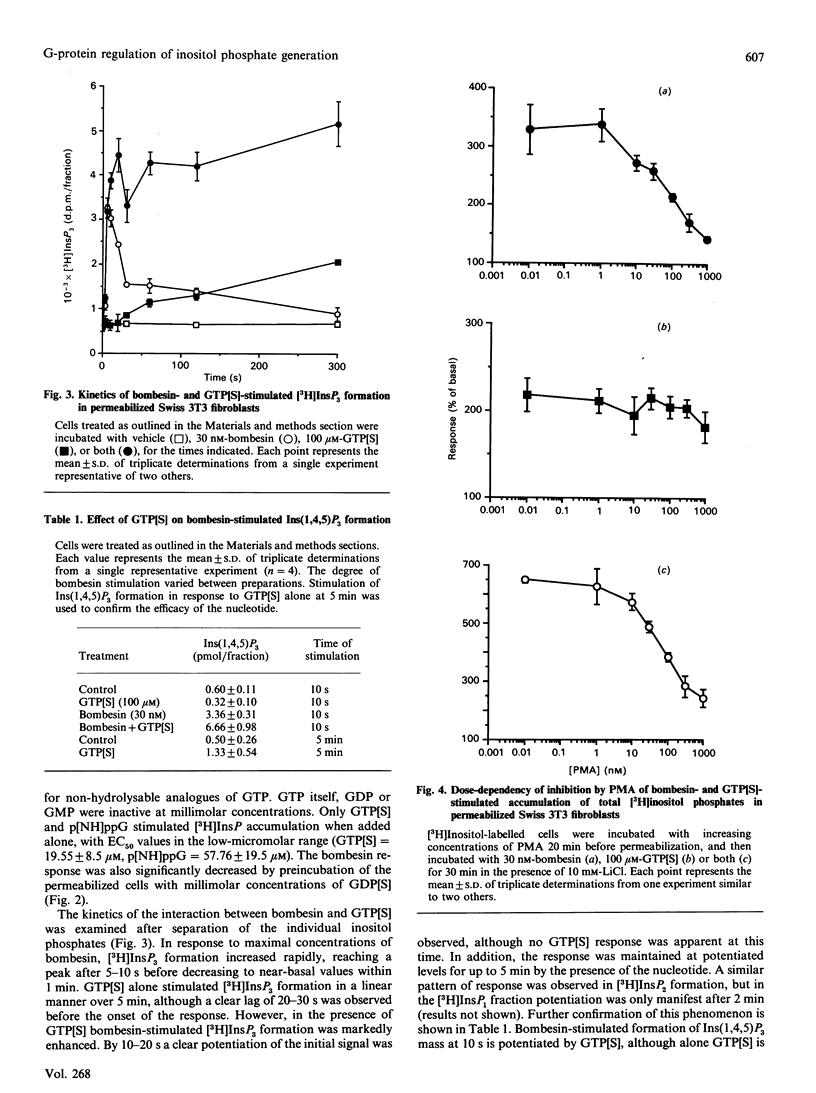
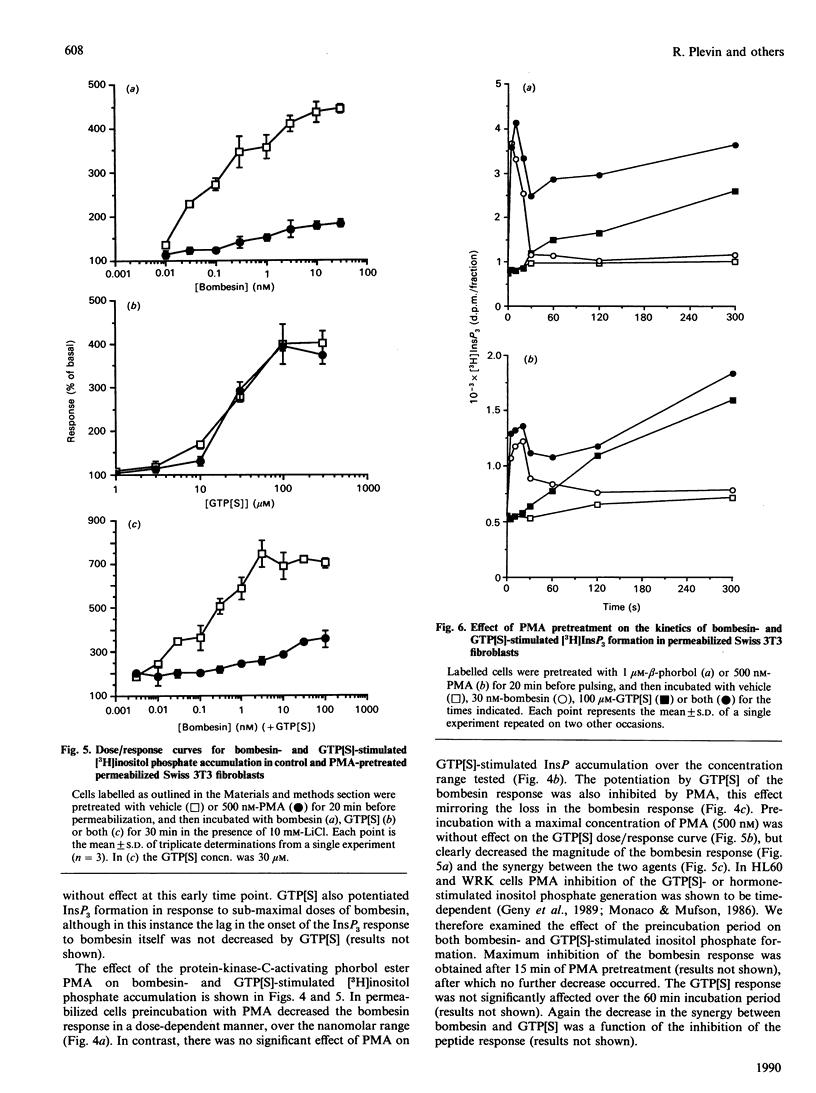
The stimulation of inositol phosphate generation by bombesin and GTP analogues was studied in Swiss 3T3 cells permeabilized by electroporation. Bombesin-stimulated inositol phosphate generation is potentiated by guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[S]) and inhibited by guanosine 5'-[beta-thio]diphosphate at all peptide concentrations tested, with no change in the EC50 value (concn. giving half-maximal response) for the agonist. Kinetic analysis showed that, although bombesin-stimulated [3H]InsP3 generation in [3H]inositol-labelled cells was rapid (maximal by 5-10 s), the response to GTP[S] alone displayed a distinct lag time of 20-30 s. This lag time was significantly decreased by the addition of bombesin, suggesting that in this system agonist-stimulated GTP/GDP exchange occurs. In addition, bombesin-stimulated generation of Ins(1,4,5)P3 mass at 10 s was enhanced by GTP[S] in the absence of a nucleotide response alone, a result consistent with this proposal. Pretreatment of the cells with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) resulted in a dose-dependent inhibition of bombesin-, but not GTP[S]-, stimulated inositol phosphate generation. Furthermore, although PMA pretreatment did not affect the lag time for InsP3 formation in response to GTP[S] alone, the degree of synergy between bombesin and the nucleotide was severely decreased at early time points. The results therefore demonstrate that the high-affinity bombesin receptor is coupled via a G-protein to phospholipase C in a manner consistent with a general model for receptor-G-protein interactions and that this coupling is sensitive to phosphorylation by protein kinase C.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Downes C. P., Hanley M. R. Lithium amplifies agonist-dependent phosphatidylinositol responses in brain and salivary glands. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):587–595. doi: 10.1042/bj2060587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black F. M., Wakelam M. J. Activation of inositol phospholipid breakdown by prostaglandin F2 alpha without any stimulation of proliferation in quiescent NIH-3T3 fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 15;266(3):661–667. doi: 10.1042/bj2660661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Downes C. P., Harden T. K. Kinetics of activation of phospholipase C by P2Y purinergic receptor agonists and guanine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):884–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Hepler J. R., Harden T. K. Hormone and growth factor receptor-mediated regulation of phospholipase C activity. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Sep;10(9):360–364. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Blakeley D. M., Hamon M. H., Laurie M. S., Corps A. N. Protein kinase C-mediated negative-feedback inhibition of unstimulated and bombesin-stimulated polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in Swiss-mouse 3T3 cells. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):631–639. doi: 10.1042/bj2450631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J., Gilman A. G. G protein involvement in receptor-effector coupling. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2577–2580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo M. G., Vicentini L. M. Differential mechanisms of inositol phosphate generation at the receptors for bombesin and platelet-derived growth factor. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):665–668. doi: 10.1042/bj2620665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claro E., Garcia A., Picatoste F. Carbachol and histamine stimulation of guanine-nucleotide-dependent phosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat brain cortical membranes. Biochem J. 1989 Jul 1;261(1):29–35. doi: 10.1042/bj2610029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. J., Palmer S., Plevin R., Wakelam M. J. Mass measurement of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and sn-1,2-diacylglycerol in bombesin-stimulated Swiss 3T3 mouse fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):617–620. doi: 10.1042/bj2650617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. J., Wakelam M. J. Analysis of the water-soluble products of phosphatidylcholine breakdown by ion-exchange chromatography. Bombesin and TPA (12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate) stimulate choline generation in Swiss 3T3 cells by a common mechanism. Biochem J. 1989 Oct 15;263(2):581–587. doi: 10.1042/bj2630581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLean A., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E97–102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson K. M., Higashijima T., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. The influence of bound GDP on the kinetics of guanine nucleotide binding to G proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7393–7399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geny B., LePeuch C., Cost H., Basset M., Cockcroft S. Phorbol esters inhibit inositol phosphate and diacylglycerol formation in proliferating HL60 cells. Relationship to differentiation. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jun 20;233(2):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80434-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geny B., Stutchfield J., Cockcroft S. Phorbol ester inhibits polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase activity stimulated by either Ca2+, fluoride or GTP analogue in HL60 membranes and in permeabilized HL60 cells. Cell Signal. 1989;1(2):165–172. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden T. K., Hawkins P. T., Stephens L., Boyer J. L., Downes C. P. Phosphoinositide hydrolysis by guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate-activated phospholipase C of turkey erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 1;252(2):583–593. doi: 10.1042/bj2520583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa-Sasaki H., Lutz F., Sasaki T. Pathway of phospholipase C activation initiated with platelet-derived growth factor is different from that initiated with vasopressin and bombesin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):12970–12976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heslop J. P., Blakeley D. M., Brown K. D., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J. Effects of bombesin and insulin on inositol (1,4,5)trisphosphate and inositol (1,3,4)trisphosphate formation in Swiss 3T3 cells. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):703–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90513-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Gilman A. G., Watanabe Y., Bauer S., Jakobs K. H. Protein kinase C phosphorylates the inhibitory guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory component and apparently suppresses its function in hormonal inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):431–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Cotecchia S., Lomasney J. W., DeBernardis J. F., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Phorbol esters promote alpha 1-adrenergic receptor phosphorylation and receptor uncoupling from inositol phospholipid metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5651–5655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco M. E., Mufson R. A. Phorbol ester inhibition of the hormone-stimulated phosphoinositide cycle in WRK-1 cells. Biochem J. 1986 May 15;236(1):171–175. doi: 10.1042/bj2360171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orellana S., Solski P. A., Brown J. H. Guanosine 5'-O-(thiotriphosphate)-dependent inositol trisphosphate formation in membranes is inhibited by phorbol ester and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1638–1643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer S., Hughes K. T., Lee D. Y., Wakelam M. J. Development of a novel, Ins(1,4,5)P3-specific binding assay. Its use to determine the intracellular concentration of Ins(1,4,5)P3 in unstimulated and vasopressin-stimulated rat hepatocytes. Cell Signal. 1989;1(2):147–156. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(89)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris S., Pouysségur J. Pertussis toxin inhibits thrombin-induced activation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis and Na+/H+ exchange in hamster fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):55–60. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04177.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Bauer C. Different effects of phorbol ester on angiotensin II- and stable GTP analogue-induced activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in membranes isolated from rat renal mesangial cells. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):209–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2480209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse S. E., Sasson J. P. Mass changes in myoinositol trisphosphate in human platelets stimulated by thrombin. Inhibitory effects of phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8657–8660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Uhing R. J., Snyderman R. Nucleotide regulatory protein-mediated activation of phospholipase C in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes is disrupted by phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6121–6127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W., Blakeley D. M., Corps A. N., Berridge M. J., Brown K. D. Effects of pertussis toxin on growth factor-stimulated inositol phosphate formation and DNA synthesis in Swiss 3T3 cells. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 1;249(3):917–920. doi: 10.1042/bj2490917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhing R. J., Prpic V., Jiang H., Exton J. H. Hormone-stimulated polyphosphoinositide breakdown in rat liver plasma membranes. Roles of guanine nucleotides and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2140–2146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Murphy G. J., Hruby V. J., Houslay M. D. Activation of two signal-transduction systems in hepatocytes by glucagon. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):68–71. doi: 10.1038/323068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojcikiewicz R. J., Lambert D. G., Nahorski S. R. Regulation of muscarinic agonist-induced activation of phosphoinositidase C in electrically permeabilized SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells by guanine nucleotides. J Neurochem. 1990 Feb;54(2):676–685. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01924.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary I., Rozengurt E. High-affinity receptors for peptides of the bombesin family in Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7616–7620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


