Abstract
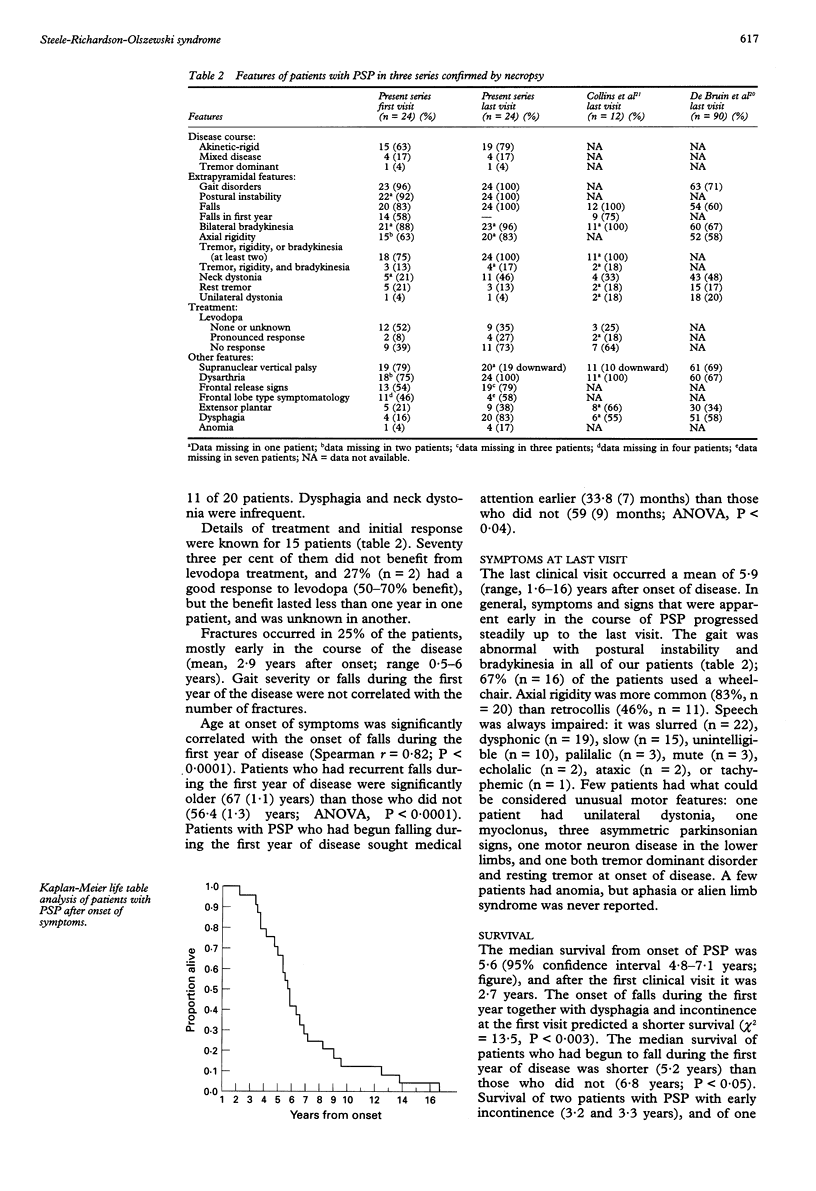
OBJECTIVE--To analyse the natural history of progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP or Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome) and clinical predictors of survival in 24 patients with PSP confirmed by necropsy, who fulfilled the NINDS criteria for a neuropathological diagnosis of typical PSP. METHODS--Patients were selected from the research and clinical files of seven medical centres involving tertiary centres of Austria, England, France, and the United States. Clinical features were analysed in detail. The patients' mean age at onset of PSP was 63 (range 45-73) years. RESULTS--The most frequent clinical features (occurring in at least 75% of the patients) were early postural instability and falls, vertical supranuclear palsy, akinetic-rigid predominant parkinsonian disorder characterised by symmetric bradykinesia and axial rigidity unrelieved by levodopa, pseudobulbar palsy, and frontal release signs. Occasionally, segmental dystonia or myoclonus were described, but neither aphasia nor alien limb syndrome was reported. Fractures occurred in 25% of the patients but were unrelated to the severity of the gait or to the presence of falls. Median survival time was 5.6 (range 2-16.6) years. Onset of falls during the first year, early dysphagia, and incontinence predicted a shorter survival time. Age at onset, sex, early onset of dementia, vertical supranuclear palsy, or axial rigidity had no effect on prognosis of survival. Pneumonia was the most common immediate cause of death. PSP was most often clinically misdiagnosed as Parkinson's disease. Errors in diagnosis suggest that PSP is underdiagnosed. CONCLUSION--Progressive onset of early postural instability with falls or supranuclear vertical palsy in the fifth decade, should suggest the diagnosis of PSP. Onset of falls during the first year are emphasised, as they could lead to an early diagnosis and influence the prognosis of patients with PSP. Whether appropriate treatment of the dysphagia could prolong the survival of PSP patients needs to be explored.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amarenco P., Roullet E., Hannoun L., Marteau R. Progressive supranuclear palsy as the sole manifestation of systemic Whipple's disease treated with pefloxacine. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1991 Dec;54(12):1121–1122. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.54.12.1121-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Shlomo Y., Marmot M. G. Survival and cause of death in a cohort of patients with parkinsonism: possible clues to aetiology? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1995 Mar;58(3):293–299. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.58.3.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks D. J. PET studies in progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1994;42:119–134. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-6641-3_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brusa A., Mancardi G. L., Bugiani O. Progressive supranuclear palsy 1979: an overview. Ital J Neurol Sci. 1980 Oct;1(4):205–222. doi: 10.1007/BF02336701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burn D. J., Sawle G. V., Brooks D. J. Differential diagnosis of Parkinson's disease, multiple system atrophy, and Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome: discriminant analysis of striatal 18F-dopa PET data. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1994 Mar;57(3):278–284. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.57.3.278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Ahlskog J. E., Parisi J. E., Maraganore D. M. Progressive supranuclear palsy: neuropathologically based diagnostic clinical criteria. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1995 Feb;58(2):167–173. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.58.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colosimo C., Albanese A., Hughes A. J., de Bruin V. M., Lees A. J. Some specific clinical features differentiate multiple system atrophy (striatonigral variety) from Parkinson's disease. Arch Neurol. 1995 Mar;52(3):294–298. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1995.00540270090024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel S. E., de Bruin V. M., Lees A. J. The clinical and pathological spectrum of Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome (progressive supranuclear palsy): a reappraisal. Brain. 1995 Jun;118(Pt 3):759–770. doi: 10.1093/brain/118.3.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. H., Bergeron C., McLachlan D. R. Atypical presentation of progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol. 1985 Apr;17(4):337–343. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bruin V. M., Lees A. J. Subcortical neurofibrillary degeneration presenting as Steele-Richardson-Olszewski and other related syndromes: a review of 90 pathologically verified cases. Mov Disord. 1994 Jul;9(4):381–389. doi: 10.1002/mds.870090402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubas F., Gray F., Escourolle R. Maladie de Steele-Richardson-Olszewski sans ophtalmoplégie. Six cas anatomo-cliniques. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1983;139(6-7):407–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubinsky R. M., Jankovic J. Progressive supranuclear palsy and a multi-infarct state. Neurology. 1987 Apr;37(4):570–576. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.4.570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg M. J., Knebl J., Tully J., Segall L. Aspiration and the elderly. Dysphagia. 1990;5(2):61–71. doi: 10.1007/BF02412646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster N. L., Gilman S., Berent S., Sima A. A., D'Amato C., Koeppe R. A., Hicks S. P. Progressive subcortical gliosis and progressive supranuclear palsy can have similar clinical and PET abnormalities. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992 Aug;55(8):707–713. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.55.8.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster N. L., Gilman S., Berent S., Sima A. A., D'Amato C., Koeppe R. A., Hicks S. P. Progressive subcortical gliosis and progressive supranuclear palsy can have similar clinical and PET abnormalities. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992 Aug;55(8):707–713. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.55.8.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing M., Olson D. A., Watts R. L., Mirra S. S. Progressive supranuclear palsy: neuropathologic and clinical heterogeneity. Neurology. 1994 Jun;44(6):1015–1024. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.6.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghika J., Tennis M., Growdon J., Hoffman E., Johnson K. Environment-driven responses in progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neurol Sci. 1995 May;130(1):104–111. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(95)00015-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibb W. R., Luthert P. J., Marsden C. D. Corticobasal degeneration. Brain. 1989 Oct;112(Pt 5):1171–1192. doi: 10.1093/brain/112.5.1171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golbe L. I., Davis P. H., Schoenberg B. S., Duvoisin R. C. Prevalence and natural history of progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology. 1988 Jul;38(7):1031–1034. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.7.1031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauw J. J., Daniel S. E., Dickson D., Horoupian D. S., Jellinger K., Lantos P. L., McKee A., Tabaton M., Litvan I. Preliminary NINDS neuropathologic criteria for Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome (progressive supranuclear palsy). Neurology. 1994 Nov;44(11):2015–2019. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.11.2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankovic J., Rajput A. H., Golbe L. I., Goodman J. C. What is it? Case 1, 1993: parkinsonism, dysautonomia, and ophthalmoparesis. Mov Disord. 1993 Oct;8(4):525–532. doi: 10.1002/mds.870080420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kircher T., Nelson J., Burdo H. The autopsy as a measure of accuracy of the death certificate. N Engl J Med. 1985 Nov 14;313(20):1263–1269. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198511143132005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang A. E., Bergeron C., Pollanen M. S., Ashby P. Parietal Pick's disease mimicking cortical-basal ganglionic degeneration. Neurology. 1994 Aug;44(8):1436–1440. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.8.1436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litvan I., Hauw J. J., Bartko J. J., Lantos P. L., Daniel S. E., Horoupian D. S., McKee A., Dickson D., Bancher C., Tabaton M. Validity and reliability of the preliminary NINDS neuropathologic criteria for progressive supranuclear palsy and related disorders. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1996 Jan;55(1):97–105. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199601000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher E. R., Lees A. J. The clinical features and natural history of the Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome (progressive supranuclear palsy). Neurology. 1986 Jul;36(7):1005–1008. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.7.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masliah E., Hansen L. A., Quijada S., DeTeresa R., Alford M., Kauss J., Terry R. Late onset dementia with argyrophilic grains and subcortical tangles or atypical progressive supranuclear palsy? Ann Neurol. 1991 Apr;29(4):389–396. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo H., Takashima H., Kishikawa M., Kinoshita I., Mori M., Tsujihata M., Nagataki S. Pure akinesia: an atypical manifestation of progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1991 May;54(5):397–400. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.54.5.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa H. ["Pure akinesia" and progressive supranuclear palsy]. No To Shinkei. 1993 Feb;45(2):113–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuwer M. R. Progressive supranuclear palsy despite normal eye movements. Arch Neurol. 1981 Dec;38(12):784–784. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1981.00510120084018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffenbach D. D., Layton D. D., Jr, Kearns T. P. Ocular manifestations in progressive supranuclear palsy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1972 Dec;74(6):1179–1184. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(72)90740-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn N. Parkinsonism--recognition and differential diagnosis. BMJ. 1995 Feb 18;310(6977):447–452. doi: 10.1136/bmj.310.6977.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revesz T., Daniel S. E., Lees A. J., Will R. G. A case of progressive subcortical gliosis associated with deposition of abnormal prion protein (PrP) J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1995 Jun;58(6):759–760. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.58.6.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinne J. O., Lee M. S., Thompson P. D., Marsden C. D. Corticobasal degeneration. A clinical study of 36 cases. Brain. 1994 Oct;117(Pt 5):1183–1196. doi: 10.1093/brain/117.5.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE J. C., RICHARDSON J. C., OLSZEWSKI J. PROGRESSIVE SUPRANUCLEAR PALSY. A HETEROGENEOUS DEGENERATION INVOLVING THE BRAIN STEM, BASAL GANGLIA AND CEREBELLUM WITH VERTICAL GAZE AND PSEUDOBULBAR PALSY, NUCHAL DYSTONIA AND DEMENTIA. Arch Neurol. 1964 Apr;10:333–359. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1964.00460160003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savoiardo M., Girotti F., Strada L., Ciceri E. Magnetic resonance imaging in progressive supranuclear palsy and other parkinsonian disorders. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1994;42:93–110. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-6641-3_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savoiardo M., Strada L., Girotti F., D'Incerti L., Sberna M., Soliveri P., Balzarini L. MR imaging in progressive supranuclear palsy and Shy-Drager syndrome. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1989 Jul-Aug;13(4):555–560. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198907000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld S. M., Golbe L. I., Sage J. I., Safer J. N., Duvoisin R. C. Computed tomographic findings in progressive supranuclear palsy: correlation with clinical grade. Mov Disord. 1987;2(4):263–278. doi: 10.1002/mds.870020404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Splaingard M. L., Hutchins B., Sulton L. D., Chaudhuri G. Aspiration in rehabilitation patients: videofluoroscopy vs bedside clinical assessment. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1988 Aug;69(8):637–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinetti M. E., Inouye S. K., Gill T. M., Doucette J. T. Shared risk factors for falls, incontinence, and functional dependence. Unifying the approach to geriatric syndromes. JAMA. 1995 May 3;273(17):1348–1353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinetti M. E., Speechley M. Prevention of falls among the elderly. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 20;320(16):1055–1059. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904203201606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenning G. K., Ben Shlomo Y., Magalhães M., Daniel S. E., Quinn N. P. Clinical features and natural history of multiple system atrophy. An analysis of 100 cases. Brain. 1994 Aug;117(Pt 4):835–845. doi: 10.1093/brain/117.4.835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Will R. G., Lees A. J., Gibb W., Barnard R. O. A case of progressive subcortical gliosis presenting clinically as Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 Sep;51(9):1224–1227. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.51.9.1224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winikates J., Jankovic J. Vascular progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1994;42:189–201. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-6641-3_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin V. M., Lees A. J., Daniel S. E. Diffuse Lewy body disease presenting with supranuclear gaze palsy, parkinsonism, and dementia: a case report. Mov Disord. 1992 Oct;7(4):355–358. doi: 10.1002/mds.870070410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Royen E., Verhoeff N. F., Speelman J. D., Wolters E. C., Kuiper M. A., Janssen A. G. Multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy. Diminished striatal D2 dopamine receptor activity demonstrated by 123I-IBZM single photon emission computed tomography. Arch Neurol. 1993 May;50(5):513–516. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1993.00540050063017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


