Abstract
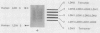
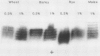
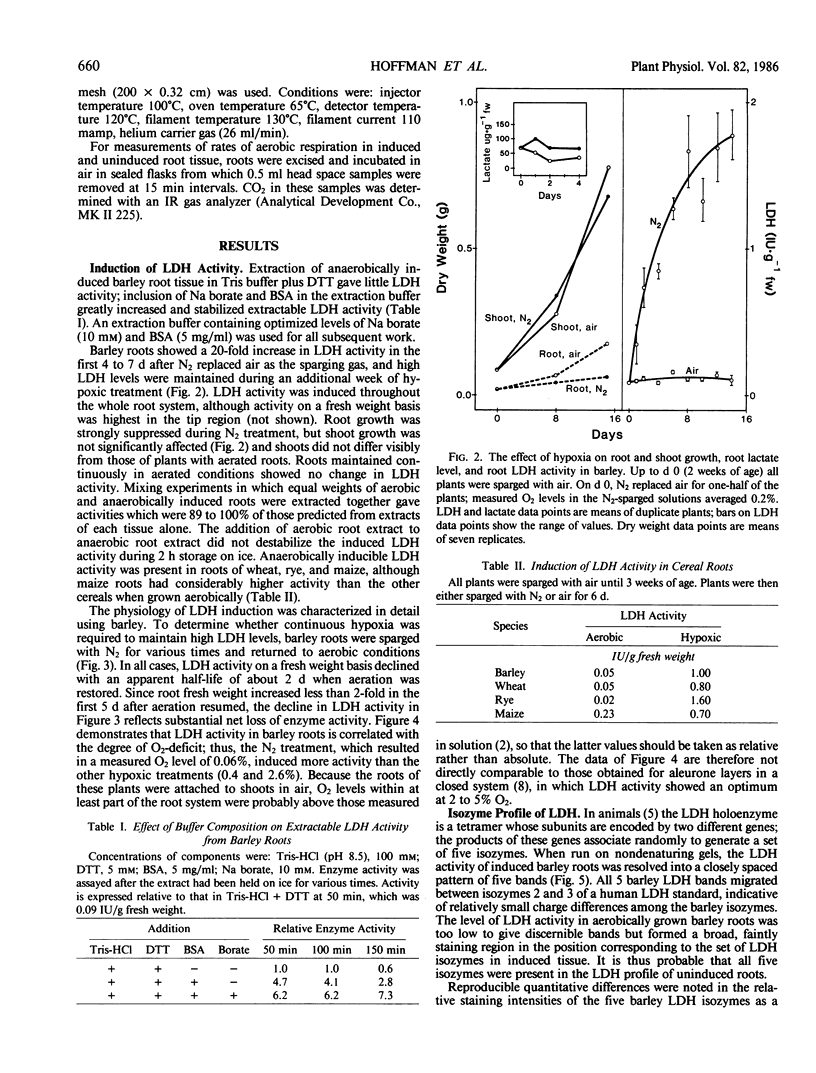
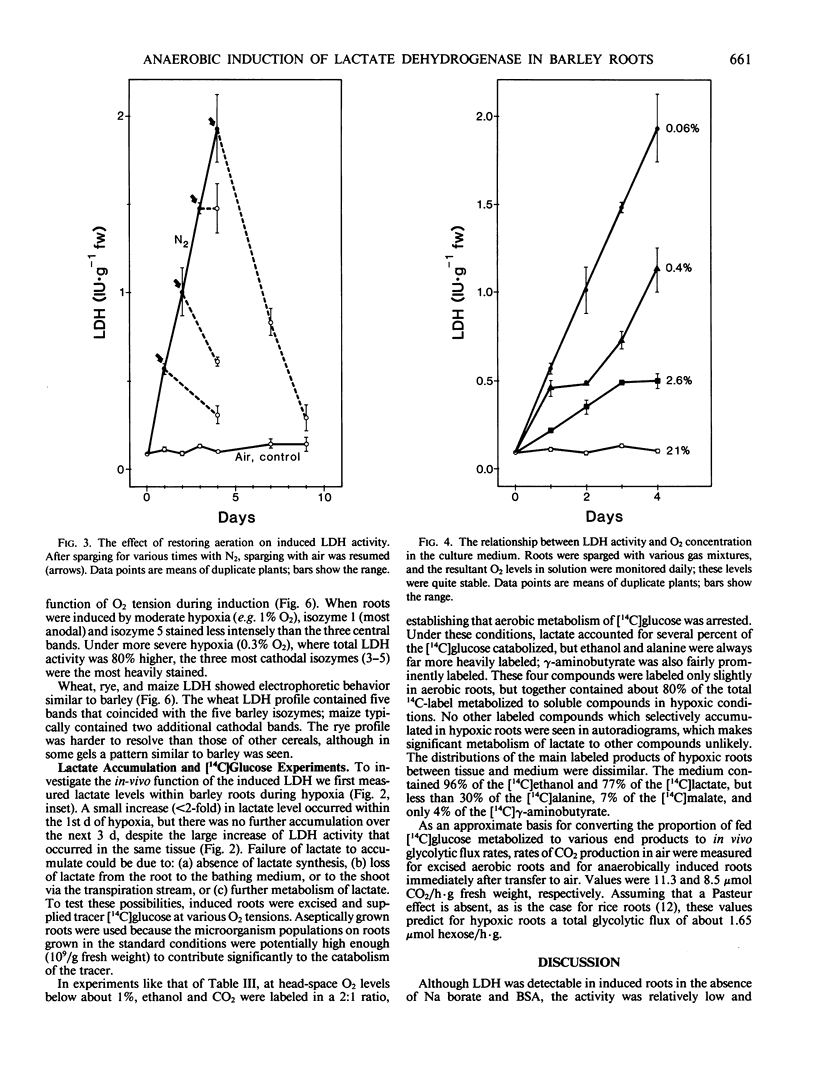
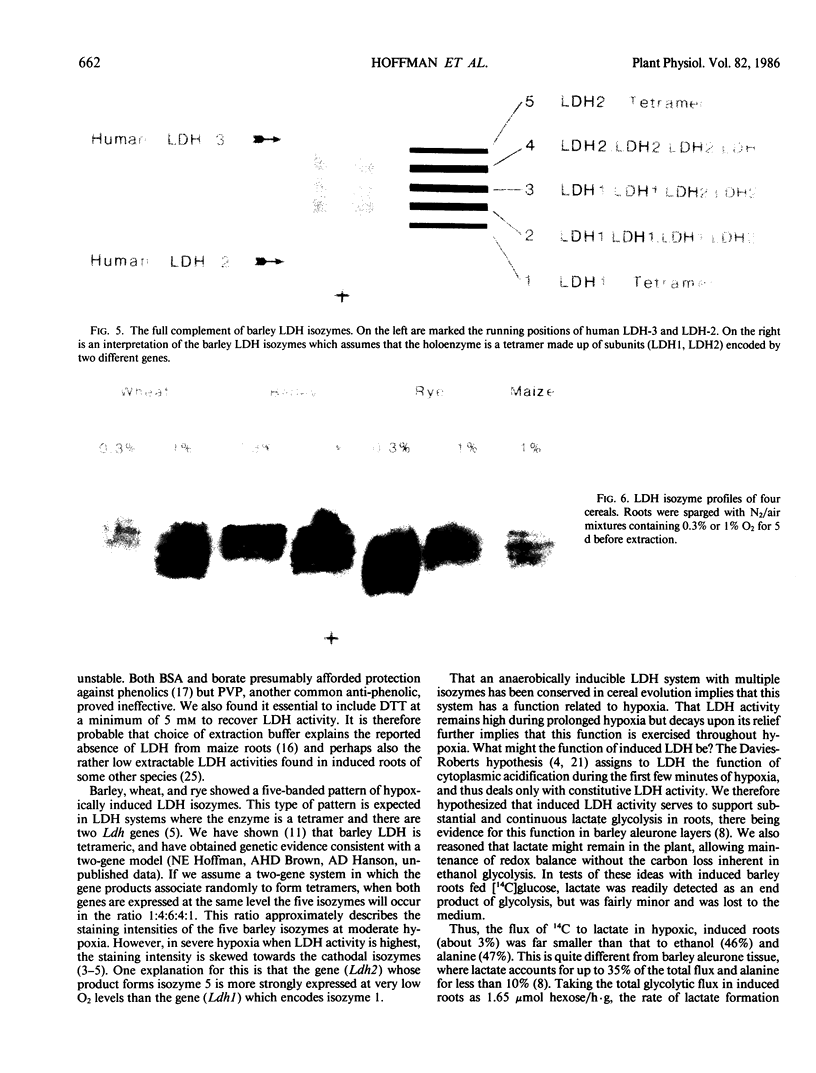
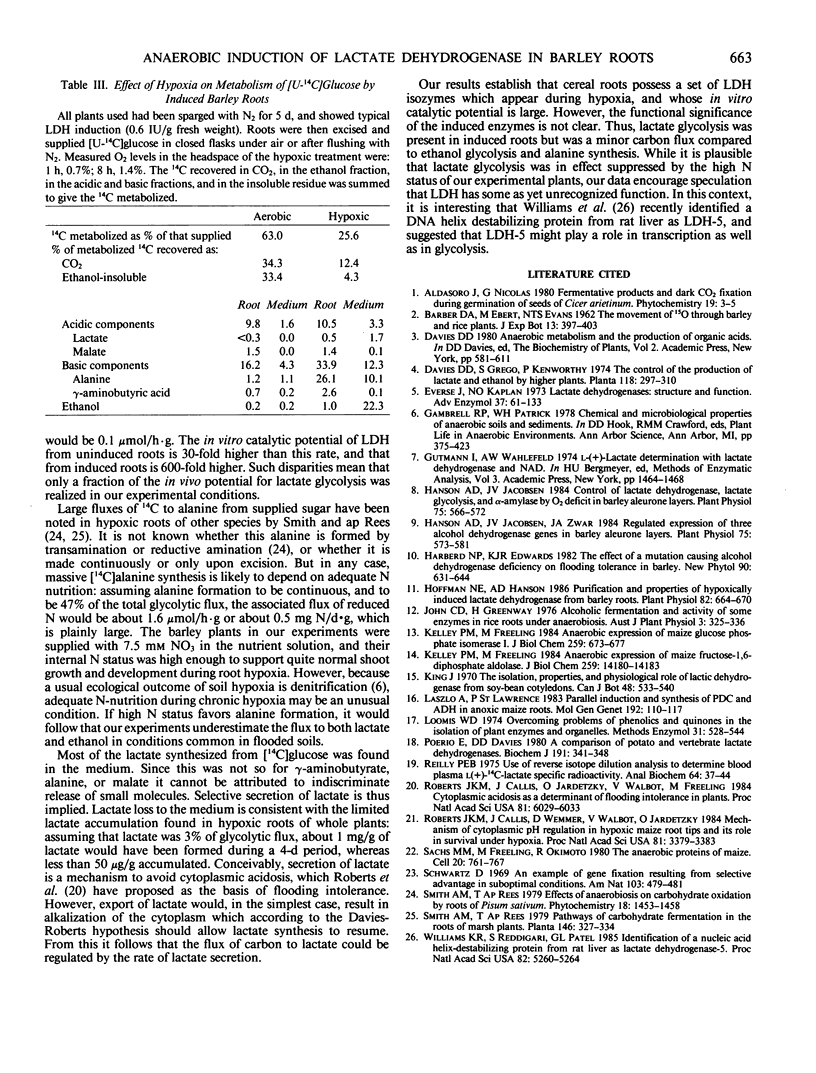
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity in attached roots of barley and other cereals increased up to 20-fold during several days of severe hypoxia, reaching a maximum of about 2 micromoles per minute per gram fresh weight. In barley, induction of LDH activity was significant at 2.6% O2 and greatest at 0.06%, the lowest O2 concentration tested. Upon return to aerobic conditions, induced LDH activity declined with an apparent half-life of 2 days. The isozyme profile of barley LDH comprised 5 bands, consistent with a tetrameric enzyme with subunits encoded by two different Ldh genes. Changes in staining intensity of the isozymes as a function of O2 level suggested that one Ldh gene was preferentially expressed in severe hypoxia. When tracer [U-14C]glucose was supplied to induced roots under hypoxic conditions, lactate acquired label, but much less than either ethanol or alanine. Most of the [14C] lactate was secreted into the medium, whereas most other labeled anionic products were retained in the root. Neither hypoxic induction of LDH, nor lactate secretion by induced roots, is predicted from the Davies-Roberts hypothesis, which holds that lactate glycolysis ceases soon after the onset of hypoxia due to acidosis brought about by lactate accumulation in the cytoplasm. These results imply a functional significance for LDH beyond that assigned it in this hypothesis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Everse J., Kaplan N. O. Lactate dehydrogenases: structure and function. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1973;37:61–133. doi: 10.1002/9780470122822.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson A. D., Jacobsen J. V. Control of lactate dehydrogenase, lactate glycolysis, and alpha-amylase by o(2) deficit in barley aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):566–572. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson A. D., Jacobsen J. V., Zwar J. A. Regulated expression of three alcohol dehydrogenase genes in barley aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):573–581. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman N. E., Hanson A. D. Purification and properties of hypoxically induced lactate dehydrogenase from barley roots. Plant Physiol. 1986 Nov;82(3):664–670. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley P. M., Freeling M. Anaerobic expression of maize fructose-1,6-diphosphate aldolase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14180–14183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley P. M., Freeling M. Anaerobic expression of maize glucose phosphate isomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):673–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. D. Overcoming problems of phenolics and quinones in the isolation of plant enzymes and organelles. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:528–544. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poerio E., Davies D. D. A comparison of potato and vertebrate lactate dehydrogenases. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):341–348. doi: 10.1042/bj1910341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly P. E. Use of reverse isotope diluation analysis to determine blood plasma L(+)-14C-lactate specific radioactivity. Anal Biochem. 1975 Mar;64(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. K., Callis J., Jardetzky O., Walbot V., Freeling M. Cytoplasmic acidosis as a determinant of flooding intolerance in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6029–6033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. K., Callis J., Wemmer D., Walbot V., Jardetzky O. Mechanisms of cytoplasmic pH regulation in hypoxic maize root tips and its role in survival under hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3379–3383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs M. M., Freeling M., Okimoto R. The anaerobic proteins of maize. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):761–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. R., Reddigari S., Patel G. L. Identification of a nucleic acid helix-destabilizing protein from rat liver as lactate dehydrogenase-5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5260–5264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]