Abstract
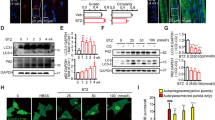
The ubiquitin-dependent proteasome system (UPS) is the major pathway responsible for selective nuclear and cytoplasmic protein degradation. Bortezomib, a boronic acid dipeptide, is a reversible 20S proteasome inhibitor used as novel anticancer drug, particularly in the treatment of multiple myeloma and certain lymphomas. Bortezomib-induced peripheral neuropathy (BIPN) is a widely recognized dose-limiting neurotoxicity of this proteasome inhibitor, which causes a significant negative impact on the quality of life. The pathogenic mechanisms underlying bortezomib neurotoxicity are little known. In this study a rat was used as our animal model to investigate the bortezomib-induced nuclear changes in dorsal root ganglia (DRG) neurons. Our results indicate that this neuronal population is an important target of bortezomib neurotoxicity. Nuclear changes include accumulation of ubiquitin–protein conjugates, reduction of transcriptional activity, and nuclear retention of poly(A) RNAs in numerous spherical or ring-shaped dense granules. They also contained the RNA-binding proteins PABPN1 (poly(A) binding protein nuclear 1) and Sam68, but lacked the mRNA nuclear export factors REF and Y14. At the cytoplasmic level, most neurons exhibited chromatolysis, supporting the inhibition of mRNA translation. Our results indicate that bortezomib interferes with transcription, nuclear processing and transport, and cytoplasmic translation of mRNAs in DRG neurons. They also support that this neuronal dysfunction is an essential pathogenic mechanism in the BIPN, which is characterized by sensory impairment including sensory ataxia.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams J (2004) The development of proteasome inhibitors as anticancer drugs. Cancer Cell 5:417–421
Alves-Rodrigues A, Gregory L, Figueiredo-Pereira ME (1998) Ubiquitin, cellular inclusions and their role in neurodegeneration. Trends Neurosci 21:517–520
Anderson P, Kedersha N (2006) RNA granules. J Cell Biol 172:803–808
Berciano MT, Villagra NT, Ojeda JL, Navascues J, Gomes A, Lafarga M, Carmo-Fonseca M (2004) Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy-like nuclear inclusions are present in normal magnocellular neurosecretory neurons of the hypothalamus. Hum Mol Genet 13:829–838
Berciano MT, Novell M, Villagra NT, Casafont I, Bengoechea R, Val-Bernal JF, Lafarga M (2007) Cajal body number and nucleolar size correlate with the cell body mass in human sensory ganglia neurons. J Struct Biol 158:410–420
Biamonti G (2004) Nuclear stress bodies: a heterochromatin affair? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:493–498
Biggiogera M, Fakan S (1998) Fine structural specific visualization of RNA on ultrathin sections. J Histochem Cytochem 46:389–395
Biggiogera M, Cisterna B, Spedito A, Vecchio L, Malatesta M (2008) Perichromatin fibrils as early markers of transcriptional alterations. Differentiation 76:57–65
Bigotte L, Arvidson B, Olsson Y (1982) Cytofluorescence localization of adriamycin in the nervous system. II. Distribution of the drug in the somatic and autonomic peripheral nervous systems of normal adult mice after intravenous injection. Acta Neuropathol 57:130–136
Carman GG, Mitchell HH (1926) Estimation of the surface area of the white rat. Am J Physiol 76:380–384
Carter KC, Taneja KL, Lawrence JB (1991) Discrete nuclear domains of poly(A) RNA and their relationship to the functional organization of the nucleus. J Cell Biol 115:1191–1202
Casafont I, Navascues J, Pena E, Lafarga M, Berciano MT (2006) Nuclear organization and dynamics of transcription sites in rat sensory ganglia neurons detected by incorporation of 5′-fluorouridina into nascent RNA. Neuroscience 140:453–462
Cavaletti G, Gilardini A, Canta A, Rigamonti L, Rodriguez-Menendez V, Ceresa C, Marmiroli P, Bossi M, Oggioni N, D′Incalci M, De Coster R (2007) Bortezomib-induced peripheral neurotoxicity: a neurophysiological and pathological study in the rat. Exp Neurol 204:317–325
Chen T, Boisvert FM, Bazzet-Jones DP, Richard S (1999) A role for the GSG domain in localizing Sam68 to novel nuclear structures in cancer cells. Mol Biol Cell 10:3015–3033
Chiodi I, Biggiogera M, Denegri M, Corioni M, Weighardt F, Cobianchi F, Riva S, Biamonti G (2000) Structure and dynamics of hnRNP-labelled nuclear bodies induced by stress treatments. J Cell Sci 113:4043–4053
Ciechanover A, DiGiuseppe JA, Bercovich B, Orian A, Richter JD (1991) Degradation of nuclear oncoproteins by the ubiquitin system in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:139–143
Cioce M, Lamond AI (2005) Cajal Bodies: A long history of discovery. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21:105–131
Collins GA, Tansey WP (2006) The proteasome: a utility tool for transcription? Curr Opin Genet Dev 16:197–202
Dreyfuss G, Kim VN, Kataoka N (2002) Messenger-RNA-binding proteins and the messages they carry. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:195–205
Dubois E (1936) Basal metabolism in health and disease. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, pp 125–144
Filosto M, Rossi G, Pelizzari AM, Buzio S, Tentorio M, Broglio L, Mancuso M, Rinaldi M, Scarpelli M, Padovani A (2007) A high-dose bortezomib neuropathy with sensory ataxia and myelin involvement. J Neurol Sci 263:40–43
Fredj NB, Grange J, Sadoul R, Richard S, Goldberg Y, Boyer V (2004) Depolarization-induced translocation of the RNA-binding protein Sam68 to the dendrites of hippocampal neurons. J Cell Sci 117:1079–1090
Gall JC (2000) Cajal bodies: the first 100 years. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16:273–300
Grange J, Boyer V, Fabian-Fine R, Fredj NB, Sadoul R, Goldberg Y (2004) Somatodendritic localization and mRNA association of the splicing regulatory protein Sam68 in the hippocampus and cortex. J Neurosci Res 75:654–666
Hartmann AM, Nayler O, Schwaiger FW, Obermeier A, Stamm S (1999) The interaction and colocalization of Sam68 with the splicing-associated factor YT521-B in nuclear dots is regulated by the Src family kinase p59fyn. Mol Biol Cell 10:3909–3926
Henao-Mejia J, Liu Y, Park YW, Zhang J, Sanford J, He JJ (2009) Supression of HIV-1 nef translation by Sam68 mutant-induced stress granules and nef mRNA sequestration. Mol Cell 33:87–96
Jagannath S, Barlogie B, Berenson J, Siegel D, Irwin D, Richardson PG, Niesvizky R, Alexanian R, Limentani SA, Alsina M, Adams J, Kauffman M, Esseltine DL, Schenkein D, Anderson KC (2004) A phase 2 study of two doses of bortezomib in relapsed or refractory myeloma. Br J Haematol 127:165–172
Krause S, Fakan S, Weis K, Wahle E (1994) Immunodetection of poly (A)-binding protein II in the cell nucleus. Exp Cell Res 214:75–82
Kühn U, Wahle E (2004) Structure and function of poly(A) binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1678:67–84
Lafarga M, Berciano MT, Pena E, Mayo I, Castano JG, Bohmann D, Rodrigues JP, Tavanez JP, Carmo-Fonseca M (2002) Clastosome: a subtype of nuclear body enriched in 19S and 20S proteasomes, ubiquitin, and protein substrates of proteasome. Mol Biol Cell 13:2771–2782
Lamond AI, Spector DL (2003) Nuclear speckles: a model for nuclear organelles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:605–612
Landowski TH, Megli CJ, Nullmeyer KD, Lynch RM, Dorr RT (2005) Mitochondrial-mediated disregulation of Ca2+ is a critical determinant of Velcade (PS-341/bortezomib) cytotoxicity in myeloma cells lines. Cancer Res 65:3828–3836
Laroia G, Cuesta R, Brewer G, Scheneider RJ (1999) Control of mRNA decay by heat shock-ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Science 284:499–502
Laroia G, Sarkar B, Scheneider RJ (2002) Ubiquitin-dependent mechanisms regulates rapid turnover of AU-rich cytokine mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:1842–1846
Li J, Liu Y, Kim BO, He JJ (2002) Direct participation of Sam68, the 68-kilodalton Src-associated protein in mitosis, in the CRM1-mediated Rev nuclear export pathway. J Virol 76:8374–8382
Lukong KE, Richard S (2003) Sam68, the KH domain-containing superSTAR. Biochim Biophys Acta 1653:73–86
Matter N, Herrlich P, König H (2002) Signal-dependent regulation of splicing via phosphorylation of SAM68. Nature 420:691–695
Mazroui R, Di Marco S, Kaufman RJ, Gallouzi IE (2007) Inhibition of the ubiquitin-proteasome system induces stress granule formation. Mol Biol Cell 18:2603–2618
McConkey DJ, Zhu K (2008) Mechanisms of proteasome inhibitor action and resistance in cancer. Drug Resist Updat 11:164–179
Mengual E, Arizti P, Rodrigo J, Giménez-Amaya JM, Castaño JG (1996) Immunohistochemical distribution and electron microscopic subcellular localization of the proteasome in the rat CNS. J Neurosci 16:6331–6341
Modem S, Badri KR, Holland TC, Reddy TR (2005) Sam68 is absolutely required for Rev function and HIV-1 production. Nucleic Acids Res 33:873–879
Nandi D, Tahiliani P, Kumar A, Chandu D (2006) The ubiquitin-proteasome system. J Biosci 31:137–155
Paronetto MP, Messina V, Bianchi E, Barchi M, Vogel G, Moretti C, Palombi F, Stefanini M, Geremia R, Richard S, Sette C (2009) Sam68 regulates translation of target mRNAs in male germ cells, necessary for mouse spermatogenesis. J Cell Biol 185:235–249
Pena E, Berciano MT, Fernandez R, Crespo P, Lafarga M (2000) Stress-induced activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in sensory ganglion neurons: accumulation in nuclear domains enriched in splicing factors and distribution in perichromatin fibrils. Exp Cell Res 10:179–191
Pena E, Berciano MT, Fernandez R, Ojeda JL, Lafarga M (2001) Neuronal body size correlates with the number of nucleoli and Cajal bodies, and with the organization of the splicing machinery in rat trigeminal ganglion neurons. J Comp Neurol 430:250–263
Rajan P, Gaughant L, Dalgliesh C, El-Sherif A, Robson CN, Leung HY, Elliott DJ (2008) Regulation of gene expression by the RNA-binding protein SAM68 in cancer. Biochem Soc Trans 36:505–507
Raska I, Ochs RL, Andrade LEC, Chan EKL, Burlingame R, Peebles C, Gruol D, Tan EM (1990) Association between the nucleolus and the coiled body. J Struct Biol 104:120–127
Richardson PG, Mitsiades C, Hideshima T, Anderson KC (2006a) Bortezomib: proteasome inhibition as an effective anticancer therapy. Annu Rev Med 57:33–47
Richardson PG, Briemberg H, Jagannath S, Wen PY, Barlogie B, Berenson J, Singhal S, Siegel DS, Irwin D, Schuster M, Srkalovic G, Alexanian R, Rajkumar SV, Limentani S, Alsina M, Orlowski RZ, Najarian K, Esseltine D, Anderson KC, Amato AA (2006b) Frequency, characteristics, and reversibility of peripheral neuropathy during treatment of advanced multiple myeloma with bortezomib. J Clin Oncol 24:3113–3120
Rouquette J, Kalland KH, Fakan S (2008) Visualization of RNA by electron microscopic in situ hybridization. In: Hancock R (ed) The nucleus: volume 2. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, pp 403–413
Shah MH, Young D, Kindler HL, Webb I, Kleiber B, Wright J, Grever M (2004) Phase II study of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (PS-341) in patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumors. Clin Cancer Res 10:6111–6118
Spector WS (1956) Handbook of biological data. W.B. Sanders Co., Philadelphia, p 175
Szutorisz H, Georgiou A, Tora L, Dillon N (2006) The proteasome restricts permissive transcription at tissue-specific gene loci in embryonic stem cells. Cell 127:1375–1388
Treier M, Staszewski LM, Bohmann D (1994) Ubiquitin-dependent c-Jun degradation in vivo is mediated by the delta domain. Cell 78:787–798
Woulfe J (2008) Nuclear bodies in neurodegenerative disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1783:2195–2206
Zimmermann J, Erdmann D, Lalande I, Grossenbacher R, Noorani M, Furst P (2000) Proteasome inhibitor induced gene expression profiles reveal overexpression of transcriptional regulators ATF3, GADD153 and MAD1. Oncogene 19:2913–2920
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Raquel García-Ceballos and Saray Pereda for technical assistance. We are also grateful to Prof. E. Wahle (University of Halle, Germany) for generously providing anti-PABPN1 rabbit serum, Dr. Stéphane Richard (McGill University, Canada) for anti-Sam68 (AD1) antibody, Prof. A. I. Lamond (University of Dundee, UK) for anti-coilin antibody (204.10), and Prof. M. Carmo-Fonseca (Institute of Molecular Medicine, Lisbon) for mouse polyclonal anti-PABPN1 antibody. This work was supported by the following grants: “Dirección General de Investigación” of Spain (BFU2008-00175), and “Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red sobre Enfermedades Neurodegenerativas (CIBERNED; CB06/05/0037)” from Spain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Casafont, I., Berciano, M.T. & Lafarga, M. Bortezomib Induces the Formation of Nuclear poly(A) RNA Granules Enriched in Sam68 and PABPN1 in Sensory Ganglia Neurons. Neurotox Res 17, 167–178 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9086-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9086-1