Abstract
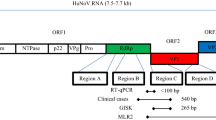
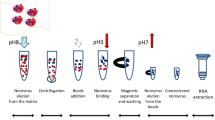
Raspberries have lately caused several human norovirus (HuNoV) outbreaks in Europe. In this study, we developed and evaluated for HuNoV reverse transcription (RT)-PCR detection in frozen raspberries extraction methods that have equal sensitivity but are less time-consuming than widely used methods based on polyethylene glycol (PEG) precipitation and chloroform–butanol purification. One method was applied to stored frozen raspberries linked to previous HuNoV outbreaks and berries on sale. In the virus elution-based Method 1, sparkling water eluted viruses most efficiently from the berries. Method 2, based on direct nucleic acid extraction with minor PEG supplement, yielded the highest number of positive findings (4 out of 9) at low virus concentration level of 100 genome copies HuNoV genogroup II per 25 g raspberries. Both methods showed approximately equal sensitivity to a method including PEG precipitation and chloroform–butanol purification. Two naturally contaminated berry samples linked to HuNoV outbreaks in 2006 and 2009 were still positive for HuNoV genogroup I, but all berry products purchased from a local store remained negative for HuNoV. In conclusion, this study presents two efficient and rapid methods which can be used in urgent HuNoV outbreak investigations, since the results of the virus analysis are available in a few hours.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, A. D., Garrett, V. D., Sobel, J., Monroe, S. S., Frankhauser, R. L., Schwab, K. J., et al. (2001). Multistate outbreak of norwalk-like virus gastroenteritis associated with a common carter. American Journal of Epidemiology, 154(11), 1013–1019.
Baert, L., Mattison, K., Loisy-Hamon, F., Harlow, J., Martyres, A., Lebeau, B., et al. (2011). Review: Norovirus prevalence in Belgian, Canadian and French fresh produce: A threat to human health? International Journal of Food Microbiology, 151, 261–269.
Baert, L., Uyttendaele, M., & Debevere, J. (2008). Evaluation of viral extraction methods on a broad range of ready-to-eat foods with conventional and real-time RT-PCR for norovirus GII detection. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 123, 101–108.
Bitler, E., Matthews, J., Dickey, B., Eisenberg, J., & Leon, J. (2013). Norovirus outbreaks: A systematic review of commonly implicated transmission routes and vehicles. Epidemiology and Infection, 141, 1563–1571.
Bouwknegt, M., Verhaelen, K., Rzezutka, A., Kozyra, I., Maunula, L., von Bonsdorff, C.-H., et al. (2015). Quantitative farm-to-fork risk assessment model for norovirus and hepatitis A virus in European leafy green vegetable and berry fruit supply chains. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 198, 50–58.
Boxman, I., Tilburg, J., te Loeke, N., Vennema, H., de Boer, E., & Koopmans, M. (2007). An efficient and rapid method for recovery of norovirus from food associated with outbreaks of gastroenteritis. Journal of Food Protection, 70(2), 504–508.
Butot, S., Putallaz, T., & Sanchez, G. (2007). Procedure for rapid concentration and detection of enteric viruses from berries and vegetables. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73(1), 186–192.
Butot, S., Zuber, S., & Baert, L. (2014). Sample preparation prior to molecular amplification: Complexities and opportunities. Current Opinion on Virology, 4, 66–70.
Carter, M. J. (2005). Enterically infecting viruses: Pathogenicity, transmission and significance for food and waterborne infection. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 98, 1354–1380.
Cheong, S., Lee, C., Choi, W. C., Lee, C.-H., & Kim, S.-J. (2009). Concentration method for the detection of enteric viruses from large volumes of foods. Journal of Food Protection, 72(9), 2001–2005.
Cotterelle, B., Drougard, C., Rolland, J., Becamel, M., Boudon, M., Piende, S., et al. (2005). Outbreak of norovirus infection associated with the consumption of frozen raspberries, France, March 2005. Eurosurveillance, 10(17), 2690.
Coudray-Meunier, C., Fraisse, A., Martin-Latil, S., Guillier, L., Delannoy, S., Fach, P., et al. (2015). A comparative study of digital RT-PCR and RT-qPCR for quantification of hepatitis A virus and norovirus in lettuce and water samples. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 201, 17–26.
de Abreu Corrêa, A., & Miagostovich, M. P. (2013). Optimization of an adsorption-elution method with a negatively charged membrane to recover norovirus from lettuce. Food and Environmental Virology, 5, 144–149.
De Keuckelaere, A., Li, D., Deliens, B., Stals, A., & Uyttendaele, M. (2015). Batch testing for noroviruses in frozen raspberries. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 192, 43–50.
Dolin, R., Blacklow, N., DuPont, H., Buscho, R., Wyatt, R., Kasel, J., et al. (1972). Biological properties of norwalk agent of acute infectious nonbacterial gastroenteritis. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine, 140, 578–583.
Dubois, E., Agier, C., Traore, O., Hennechart, C., Merle, G., Cruciere, C., et al. (2002). Modified concentration method for the detection of enteric viruses on fruits and vegetables by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction or cell culture. Journal of Food Protection, 65(12), 1962–1969.
Dubois, E., Hennechart, C., Deboosere, N., Merle, G., Legeay, O., Burger, C., et al. (2006). Intra-laboratory validation of a concentration method adapted for the enumeration of infectious F-specific RNA coliphage, enterovirus, and hepatitis A virus from inoculated leaves of salad vegetables. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 108, 164–171.
European Commission (2014). RASFF, the rapid alert system for food and feed, 2013 Annual Report.
European Commission (2015). RASFF, the rapid Alert system for food and feed, 2014 Annual Report.
Falkenhorst, G., Krusell, L., Lisby, M., Madsen, S., Böttinger, B., & Mølbak, K. (2005). Imported frozen raspberries cause a series of norovirus outbreaks in Denmark, 2005. Eurosurveillance, 10(38), 2795.
Fraisse, A., Coudray-Meunier, C., Martin-Latil, S., Hennechart-Collette, C., Delannoy, S., Fach, P., et al. (2017). Digital RT-PCR method for hepatitis A virus and norovirus quantification in soft berries. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 243, 36–45.
Fraisse, A., Temmam, S., Deboosere, N., Guillier, L., Delobel, A., Maris, P., et al. (2011). Comparison of chlorine and peroxyacetic-based disinfectant to inactivate feline calicivirus, murine norovirus and hepatitis A VIRUS on lettuce. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 151, 98–104.
Fumian, T., Leite, J., Marin, V., & Miagostovich, M. (2009). A rapid procedure for detecting noroviruses from cheese and fresh lettuce. Journal of Virological Methods, 155, 39–43.
Guévremont, E., Brassard, J., Houde, A., Simard, C., & Trottier, Y.-L. (2006). Development of an extraction and concentration procedure and comparison of RT-PCR primer system for the detection of hepatitis A virus and norovirus GII in green onions. Journal of Virological Methods, 134, 130–135.
Hewitt, J., Rivera-Aban, M., & Greening, G. (2009). Evaluation of murine norovirus as a surrogate for human norovirus and hepatitis A virus in heat inactivation studies. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 107, 65–71.
Hjertqvist, M., Johansson, A., Svensson, N., Åbom, P.-E., Magnusson, C., Olsson, M., et al. (2006). Four outbreaks of norovirus gastroenteritis after consuming raspberries, Sweden, June–August 2006. Eurosurveillance, 11(36), 3038.
Jones, T. H., Brassard, J., Johns, M. W., & Gagne, M.-J. (2009). The effect of pre-treatment and sonication of centrifugal ultrafiltration devices on virus recovery. Journal of Virological Methods, 161, 199–204.
Kim, H.-Y., Kwak, I.-S., Hwang, I.-G., & Ko, G. P. (2008). Optimization of methods for detecting norovirus on various fruit. Journal of Virological Methods, 153, 104–110.
Kokkinos, P., Kozyra, I., Lazic, S., Bouwknegt, M., Rutjes, S., Willem, K., et al. (2012). Harmonised investigation of the occurrence of human enteric viruses in the leafy green vegetable supply chain in three European countries. Food and Environmental Virology, 4, 179–191.
Le Guyader, F. S., Mittelholzer, C., Haugarreau, L., Hedlund, K.-O., Alsterlund, R., Pommepuy, M., et al. (2004). Detection of noroviruses in raspberries associated with a gastroenteritis outbreak. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 97, 179–186.
Lee, H.-M., Kwon, J., Choi, J.-S., Lee, K.-H., Yang, S., Ko, S.-M., et al. (2013). Rapid detection of norovirus from fresh lettuce using immunomagnetic separation and a quantum dots assay. Journal of Food Protection, 76(4), 707–711.
Mathijs, E., Stals, A., Baert, L., Botteldoorn, N., Denayer, S., Mauroy, A., et al. (2012). A review of known and hypothetical transmission routes for noroviruses. Food and Environmental Virology, 4, 131–152.
Matthews, J., Dickey, B., Miller, R., Felzer, J., Dawson, B., Lee, A., et al. (2012). The epidemiology of published norovirus outbreaks: A systematic review of risk factors associated with attack rate and genogroup. Epidemiology and Infection, 140, 1161–1172.
Maunula, L., Kaupke, A., Vasickova, P., Söderberg, K., Kozyra, I., Lazic, S., et al. (2013). Tracking enteric viruses in the European berry fruit supply chain. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 167, 177–185.
Maunula, L., Roivainen, M., Keränen, M., Mäkelä, S., Söderberg, K., Summa, M., et al. (2009). Detection of human norovirus from frozen raspberries in a cluster of gastroenteritis outbreaks. Eurosurveillance, 14(49), 19435.
Mokhtari, A., & Jaykus, L.-A. (2009). Quantitative exposure model for the transmission of norovirus in retail food preparation. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 133, 38–47.
Morillo, S., Luchs, A., Cilli, A., & Timenetsky, M. (2012). Rapid detection of norovirus in naturally contaminated food: Foodborne gastroenteritis outbreak on a Cruise Ship in Brazil, 2010. Food and Environmental Virology, 4, 124–129.
Park, H., Kim, M., & Ko, G. (2010). Evaluation of various methods for recovering human norovirus and murine norovirus from vegetables and ham. Journal of Food Protection, 73(9), 1651–1657.
Perrin, A., Loutreul, J., Boudaud, N., Bertrand, I., & Ganzer, C. (2015). Rapid, simple and efficient method for detection of viral genomes on raspberries. Journal of Virological Methods, 224, 95–101.
Rönnqvist, M., Aho, E., Mikkelä, A., Ranta, J., Tuominen, P., Rättö, M., et al. (2014). Norovirus transmission between hands, gloves, utensils, and fresh produce during simulated food handling. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 80(17), 5403–5410.
Rutjes, S. A., Lodder-Verschoor, F., van der Poel, W. H. M., van Duijnhoven, Y. T. H. P., & de Roda, Husman A. M. (2006). Detection of noroviruses in foods: A study on virus extraction procedures in foods implicated in outbreaks of human gastroenteritis. Journal of Food Protection, 69(8), 1949–1956.
Rzezutka, A., Alotaibi, M., D’Agostino, M., & Cook, N. (2005). A centrifugation-based method for extraction of norovirus from raspberries. Journal of Food Protection, 68(9), 1923–1925.
Sarvikivi, E., Roivainen, M., Maunula, L., Niskanen, T., Korhonen, T., Lappalainen, M., et al. (2012). Multiple norovirus outbreaks linked to imported frozen raspberries. Epidemiology and Infection, 140, 260–267.
Schwab, K., Neill, F., Fankhauser, R., Daniels, N., Monroe, S., Bergmire-Sweat, D., et al. (2000). Development of methods to detect “norwalk-like viruses” (NLVs) and hepatitis A virus in delicatessen foods: Application to a food-borne NLV outbreak. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 66(1), 213–218.
Stals, A., Baert, L., Jasson, V., van Coillie, E., & Uyttendaele, M. (2011a). Screening of fruit products for norovirus and the difficulty of interpreting positive PCR results. Journal of Food Protection, 74(3), 425–431.
Stals, A., Baert, L., van Coillie, E., & Uyttendaele, M. (2011b). Evaluation of a norovirus detection methodology for soft red fruits. Food Microbiology, 28, 52–58.
Stals, A., Baert, L., van Coillie, E., & Uyttendaele, M. (2012). Extraction of food-borne viruses from food samples: A review. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 153, 1–9.
Stals, A., Uyttendaele, M., Baert, L., & van Coillie, E. (2013). Norovirus transfer between foods and food contact materials. Journal of Food Protection, 76(7), 1202–1209.
Summa, M., von Bonsdorff, C.-H., & Maunula, L. (2012a). Evaluation of four virus recovery methods for detecting noroviruses on fresh lettuce, sliced ham, and frozen raspberries. Journal of Virological Methods, 183, 154–160.
Summa, M., von Bonsdorff, C.-H., & Maunula, L. (2012b). Pet dogs—A transmission route for human noroviruses? Journal of Clinical Virology, 53, 244–247.
Teunis, P., Moe, C., Liu, P., Miller, S., Lindesmith, L., Baric, R., et al. (2008). Norwalk virus: How infectious is it? Journal of Medical Virology, 80, 1468–1476.
Tuladhar, E., Hazeleger, W., Koopmans, M., Zwietering, M., Duizer, E., & Beumer, R. (2013). Transfer of noroviruses between fingers and fomites and food products. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 167, 346–352.
Verhaelen, K., Bouwknegt, M., Carratala, A., Lodder-Verschoor, F., Diez-Valcarce, M., Rodriguez-Lazaro, D., et al. (2013). Virus transfer proportions between gloved fingertips, soft berries, and lettuce, an associated health risks. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 166, 419–425.
White, P. (2014). Evolution of norovirus. Clinical Microbiology & Infection, 20, 741–745.
Wilson, I. G. (1997). Inhibition and facilitation of nucleic acid amplification. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 63(10), 3741–3751.
Zheng, D.-U., Ando, T., Fankhauser, R., Beard, R., Glass, R., & Monroe, S. (2006). Norovirus classification and proposed strain nomenclature. Virology, 346, 312–323.
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Söderberg for her valuable contribution during the method design and C.H. von Bonsdorff for his specialist advice when proceeding this study.
Funding
The work was funded by the Academy of Finland (Grant Number 1122782), the Walter Ehrström Foundation and the Finnish Foundation of Veterinary Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Summa, M., Maunula, L. Rapid Detection of Human Norovirus in Frozen Raspberries. Food Environ Virol 10, 51–60 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-017-9321-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12560-017-9321-5