Abstract
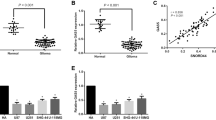
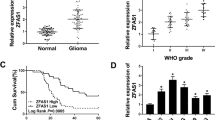
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 (hnRNP A2/B1) plays an important role in influence of pre-messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) processing and mRNA metabolism and transportation in cells. Increasing evidence indicates that hnRNP A2/B1 played an important role in development and progression of various human cancers. Forty cases of normal and human glioma tissue samples were analyzed using immunohistochemistry to reveal the expression of hnRNP A2/B1 protein in the samples. Then, knockdown of hnRNP A2/B1 expression induced by RNA interference (RNAi) method was used to analyze the role of hnRNP A2/B1 in glioblastoma cell viability, adhesion, migration, invasion, and chemoresistance for temozolomide (TMZ). The data showed that hnRNP A2/B1 protein was overexpressed in glioma tissue specimens and associated with advanced glioma grades. Knockdown of hnRNP A2/B1 could reduce glioblastoma cell viability, adhesion, migration, invasion, and chemoresistance for TMZ capacity, but induced tumor cells to apoptosis and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in glioma U251 and SHG44 cells. Molecularly, hnRNP A2/B1 knockdown reduced expression of phospho-STAT3 and MMP-2. Detection of hnRNP A2/B1 expression may be useful as a biomarker for prediction of glioma progression and knockdown of hnRNP A2/B1 expression as a novel strategy in future control of glioblastoma in clinic.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brat DJ, Prayson RA, Ryken TC, Olson JJ (2008) Diagnosis of malignant glioma: role of neuropathology. J Neurooncol 89(3):287–311
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A, Stommel JM et al (2007) Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev 21(21):2683–2710
Van Meir EG, Hadjipanayis CG, Norden AD, Shu HK, Wen PY et al (2010) Exciting new advances in neuro-oncology: the avenue to a cure for malignant glioma. CA Cancer J Clin 60(3):166–193
Giese A, Bjerkvig R, Berens ME, Westphal M (2003) Cost of migration: invasion of malignant gliomas and implications for treatment. J Clin Oncol 21(8):1624–1636
Prados MD, Levin V (2000) Biology and treatment of malignant glioma. Semin Oncol 27(3 Suppl 6):1–10
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B et al (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352(10):987–996
Ferla R, Haspinger E, Surmacz E (2012) Metformin inhibits leptin-induced growth and migration of glioblastoma cells. Oncol Lett 4(5):1077–1081
Dreyfuss G, Kim VN, Kataoka N (2002) Messenger-RNA-binding proteins and the messages they carry. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3(3):195–205
Krecic AM, Swanson MS (1999) hnRNP complexes: composition, structure, and function. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11(3):363–371
Kozu T, Henrich B, Schafer KP (1995) Structure and expression of the gene (HNRPA2B1) encoding the human hnRNP protein A2/B1. Genomics 25(2):365–371
He Y, Brown MA, Rothnagel JA, Saunders NA, Smith R (2005) Roles of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins A and B in cell proliferation. J Cell Sci 118(Pt 14):3173–3183
Fielding P, Turnbull L, Prime W, Walshaw M, Field JK (1999) Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 up-regulation in bronchial lavage specimens: a clinical marker of early lung cancer detection. Clin Cancer Res 5(12):4048–4052
Yan-Sanders Y, Hammons GJ, Lyn-Cook BD (2002) Increased expression of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 (hnRNP) in pancreatic tissue from smokers and pancreatic tumor cells. Cancer Lett 183(2):215–220
Patry C, Bouchard L, Labrecque P, Gendron D, Lemieux B et al (2003) Small interfering RNA-mediated reduction in heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoparticule A1/A2 proteins induces apoptosis in human cancer cells but not in normal mortal cell lines. Cancer Res 63(22):7679–7688
Garayoa M, Man YG, Martinez A, Cuttitta F, Mulshine JL (2003) Downregulation of hnRNP A2/B1 expression in tumor cells under prolonged hypoxia. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 28(1):80–85
Golan-Gerstl R, Cohen M, Shilo A, Suh SS, Bakacs A et al (2011) Splicing factor hnRNP A2/B1 regulates tumor suppressor gene splicing and is an oncogenic driver in glioblastoma. Cancer Res 71(13):4464–4472
Deng J, Huang Q, Wang F, Liu Y, Wang Z et al (2012) The role of caveolin-1 in blood–brain barrier disruption induced by focused ultrasound combined with microbubbles. J Mol Neurosci 46(3):677–687
Biamonti G, Ruggiu M, Saccone S, Della VG, Riva S (1994) Two homologous genes, originated by duplication, encode the human hnRNP proteins A2 and A1. Nucleic Acids Res 22(11):1996–2002
Burd CG, Swanson MS, Gorlach M, Dreyfuss G (1989) Primary structures of the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2, B1, and C2 proteins: a diversity of RNA binding proteins is generated by small peptide inserts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 86(24):9788–9792
Izaurralde E, Jarmolowski A, Beisel C, Mattaj IW, Dreyfuss G et al (1997) A role for the M9 transport signal of hnRNP A1 in mRNA nuclear export. J Cell Biol 137(1):27–35
Siomi H, Dreyfuss G (1995) A nuclear localization domain in the hnRNP A1 protein. J Cell Biol 129(3):551–560
He Y, Smith R (2009) Nuclear functions of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins A/B. Cell Mol Life Sci 66(7):1239–1256
Kamma H, Horiguchi H, Wan L, Matsui M, Fujiwara M et al (1999) Molecular characterization of the hnRNP A2/B1 proteins: tissue-specific expression and novel isoforms. Exp Cell Res 246(2):399–411
Cooper TA, Wan L, Dreyfuss G (2009) RNA and disease. Cell 136(4):777–793
Rao DD, Vorhies JS, Senzer N, Nemunaitis J (2009) siRNA vs. shRNA: similarities and differences. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61(9):746–759
Nakada M, Nakada S, Demuth T, Tran NL, Hoelzinger DB et al (2007) Molecular targets of glioma invasion. Cell Mol Life Sci 64(4):458–478
Ku BM, Lee YK, Ryu J, Jeong JY, Choi J et al (2011) CHI3L1 (YKL-40) is expressed in human gliomas and regulates the invasion, growth and survival of glioma cells. Int J Cancer 128(6):1316–1326
Sauvageot CM, Weatherbee JL, Kesari S, Winters SE, Barnes J et al (2009) Efficacy of the HSP90 inhibitor 17-AAG in human glioma cell lines and tumorigenic glioma stem cells. Neuro Oncol 11(2):109–121
Rahme GJ, Israel MA (2014) Id4 suppresses MMP2-mediated invasion of glioblastoma-derived cells by direct inactivation of Twist1 function. Oncogene.
Forsyth PA, Wong H, Laing TD et al (1999) Gelatinase-A (MMP-2), gelatinase-B (MMP-9) and membrane type matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MT1-MMP) are involved in different aspects of the pathophysiology of malignant gliomas. Br J Cancer 79(11–12):1828–1835
Rao JS (2003) Molecular mechanisms of glioma invasiveness: the role of proteases. Nat Rev Cancer 3(7):489–501
Choe G, Park JK, Jouben-Steele L et al (2002) Active matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression is associated with primary glioblastoma subtype. Clin Cancer Res 8(9):2894–2901
Kargiotis O, Chetty C, Gondi CS et al (2008) Adenovirus-mediated transfer of siRNA against MMP-2 mRNA results in impaired invasion and tumor-induced angiogenesis, induces apoptosis in vitro and inhibits tumor growth in vivo in glioblastoma. Oncogene 27(35):4830–4840
Wang M, Wang T, Liu S, Yoshida D, Teramoto A (2003) The expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in human gliomas of different pathological grades. Brain Tumor Pathol 20(2):65–72
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G et al (1999) Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell 98(3):295–303
Bowman T, Garcia R, Turkson J, Jove R (2000) STATs in oncogenesis. Oncogene 19(21):2474–2488
Sansone P, Bromberg J (2012) Targeting the interleukin-6/Jak/stat pathway in human malignancies. J Clin Oncol 30(9):1005–1014
Lo HW, Cao X, Zhu H, Ali-Osman F (2008) Constitutively activated STAT3 frequently coexpresses with epidermal growth factor receptor in high-grade gliomas and targeting STAT3 sensitizes them to Iressa and alkylators. Clin Cancer Res 14(19):6042–6054
Turkson J, Ryan D, Kim JS et al (2001) Phosphotyrosyl peptides block Stat3-mediated DNA binding activity, gene regulation, and cell transformation. J Biol Chem 276(48):45443–45455
Blaskovich MA, Sun J, Cantor A, Turkson J, Jove R, Sebti SM (2003) Discovery of JSI-124 (cucurbitacin I), a selective Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling pathway inhibitor with potent antitumor activity against human and murine cancer cells in mice. Cancer Res 63(6):1270–1279
Lai SY, Childs EE, Xi S et al (2005) Erythropoietin-mediated activation of JAK-STAT signaling contributes to cellular invasion in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 24(27):4442–4449
Rahaman SO, Vogelbaum MA, Haque SJ (2005) Aberrant Stat3 signaling by interleukin-4 in malignant glioma cells: involvement of IL-13Ralpha2. Cancer Res 65(7):2956–2963
Xie TX, Wei D, Liu M et al (2004) Stat3 activation regulates the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tumor invasion and metastasis. Oncogene 23(20):3550–3560
Zhou J, Nong L, Wloch M, Cantor A, Mulshine JL et al (2001) Expression of early lung cancer detection marker: hnRNP-A2/B1 and its relation to microsatellite alteration in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 34(3):341–350
Grant Support
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30870723 and 81201066) and Chongqing Natural Science Foundation Project (No. CSTC2013jcyjA10054).
Conflict of Interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, J., Chen, S., Wang, F. et al. Effects of hnRNP A2/B1 Knockdown on Inhibition of Glioblastoma Cell Invasion, Growth and Survival. Mol Neurobiol 53, 1132–1144 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-9080-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-9080-3