Abstract
Background
The discovery of circulating microRNAs (miRNAs), as potential noninvasive diagnostic biomarkers, has opened new avenues of research for identifying patients with chronic failure in renal transplantation. The present study aimed to investigate the expression levels of four immune-related miRNAs (miR-21, miR-31, miR-142-3p and miR-155) in plasma samples of renal recipients.
Methods
The plasma expression levels of the miRNAs were evaluated by quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) in 53 renal recipients with long-term stable allograft function, SGF (N = 27), and with biopsy-proven interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (IFTA) (N = 26) and also healthy controls (N = 15). The possible correlation between clinical parameters and the circulating miRNAs and the receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) analysis were performed.
Results
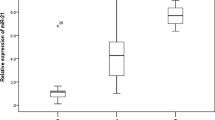
Our results showed that expression of miR-21 (p = 0.023), miR-142-3p (p = 0.048) and miR-155 (p = 0.005) was significantly upregulated in plasma samples of recipients with IFTA in comparison with SGF and healthy control groups. Concentration of miR-21 (∆Ct value) in plasma was negatively correlated with creatinine (r = −0.432, p = 0.028) and positively correlated with eGFR (r = 0.423, p = 0.031). The multivariate ROC curve analysis indicated that miR-21, miR-142-3p and miR-155 in plasma samples could discriminate almost most of the IFTA patients (area under curve = 0.802, sensitivity = 81%, specificity = 92%).
Conclusion
Our data suggested that altered expression of miR-21, miR-142-3p and miR-155 in plasma samples may be associated with renal dysfunction and can be used for graft monitoring.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arias M, Serón D, Moreso F, Bestard O, Praga M (2011) Chronic renal allograft damage: existing challenges. Transplantation 91(9S):S4–S25
Chapman JR, O’Connell PJ, Nankivell BJ (2005) Chronic renal allograft dysfunction. J Am Soc Nephrol 16(10):3015–3026
Abedini S, Holme I, März W, Weihrauch G, Fellström B, Jardine A, Cole E, Maes B, Neumayer H-H, Grønhagen-Riska C (2009) Inflammation in renal transplantation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4(7):1246–1254
Jelencsics K, Oberbauer R (2015) Microrna and kidney transplantation. Adv Exp Med Biol 888:271–290. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-22671-2_14
Moreso F, Ibernon M, Goma M, Carrera M, Fulladosa X, Hueso M, Gil-Vernet S, Cruzado J, Torras J, Grinyo J (2006) Subclinical rejection associated with chronic allograft nephropathy in protocol biopsies as a risk factor for late graft loss. Am J Transplant 6(4):747–752
Lu J, Clark AG (2012) Impact of microRNA regulation on variation in human gene expression. Genome Res 22(7):1243–1254. doi:10.1101/gr.132514.111
Kang K, Peng X, Luo J, Gou D (2012) Identification of circulating miRNA biomarkers based on global quantitative real-time PCR profiling. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 3(1):4. doi:10.1186/2049-1891-3-4
Trionfini P, Benigni A, Remuzzi G (2015) MicroRNAs in kidney physiology and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 11(1):23–33. doi:10.1038/nrneph.2014.202
Anglicheau D, Sharma VK, Ding R, Hummel A, Snopkowski C, Dadhania D, Seshan SV, Suthanthiran M (2009) MicroRNA expression profiles predictive of human renal allograft status. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(13):5330–5335. doi:10.1073/pnas.0813121106
Danger R, Paul C, Giral M, Lavault A, Foucher Y, Degauque N, Pallier A, Durand M, Castagnet S, Duong Van Huyen JP, Delahousse M, Renaudin K, Soulillou JP, Brouard S (2013) Expression of miR-142-5p in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from renal transplant patients with chronic antibody-mediated rejection. PLoS ONE 8(4):e60702. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0060702
Soltaninejad E, Nicknam MH, Nafar M, Ahmadpoor P, Pourrezagholi F, Sharbafi MH, Hosseinzadeh M, Foroughi F, Yekaninejad MS, Bahrami T, Sharif-Paghaleh E, Amirzargar A (2015) Differential expression of microRNAs in renal transplant patients with acute T-cell mediated rejection. Transpl Immunol 33(1):1–6. doi:10.1016/j.trim.2015.05.002
Sui W, Dai Y, Huang Y, Lan H, Yan Q, Huang H (2008) Microarray analysis of MicroRNA expression in acute rejection after renal transplantation. Transpl Immunol 19(1):81–85. doi:10.1016/j.trim.2008.01.007
Danger R, Pallier A, Giral M, Martinez-Llordella M, Lozano JJ, Degauque N, Sanchez-Fueyo A, Soulillou JP, Brouard S (2012) Upregulation of miR-142-3p in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of operationally tolerant patients with a renal transplant. J Am Soc Nephrol 23(4):597–606. doi:10.1681/asn.2011060543
Zununi Vahed S, Omidi Y, Ardalan MR, Samadi N (2017) Dysregulation of urinary miR-21 and miR-200b associated with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (IFTA) in renal transplant recipients. Clin Biochem 50(1–2):32–39. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2016.08.007
Maluf DG, Dumur CI, Suh JL, Scian MJ, King AL, Cathro H, Lee JK, Gehrau RC, Brayman KL, Gallon L, Mas VR (2014) The urine microRNA profile may help monitor post-transplant renal graft function. Kidney Int 85(2):439–449. doi:10.1038/ki.2013.338
Ben-Dov IZ, Muthukumar T, Morozov P, Mueller FB, Tuschl T, Suthanthiran M (2012) MicroRNA sequence profiles of human kidney allografts with or without tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Transplantation 94(11):1086–1094. doi:10.1097/TP.0b013e3182751efd
Glowacki F, Savary G, Gnemmi V, Buob D, Van der Hauwaert C, Lo-Guidice JM, Bouye S, Hazzan M, Pottier N, Perrais M, Aubert S, Cauffiez C (2013) Increased circulating miR-21 levels are associated with kidney fibrosis. PLoS ONE 8(2):e58014. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0058014
Scian MJ, Maluf DG, David KG, Archer KJ, Suh JL, Wolen AR, Mba MU, Massey HD, King AL, Gehr T, Cotterell A, Posner M, Mas V (2011) MicroRNA profiles in allograft tissues and paired urines associate with chronic allograft dysfunction with IF/TA. Am J Transplant 11(10):2110–2122. doi:10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03666.x
Soltaninejad E, Nicknam MH, Nafar M, Sharbafi MH, Shahbaz SK, Barabadi M, Yekaninejad MS, Bahrami T, Ahmadpoor P, Amirzargar A (2015) Altered expression of microRNAs following chronic allograft dysfunction with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol 14(6):615–623
Zununi Vahed S, Poursadegh Zonouzi A, Mahmoodpoor F, Samadi N, Ardalan MR, Omidi Y (2017) Circulating miR-150, miR-192, miR-200b, and miR-423-3p as non-invasive biomarkers of chronic allograft dysfunction. Arch Med Res 48(1):82–90
Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D (1999) A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. Ann Intern Med 130(6):461–470
Zununi Vahed S, Ardalan M, Samadi N, Omidi Y (2015) Pharmacogenetics and drug-induced nephrotoxicity in renal transplant recipients. Bioimpacts 5(1):45–54. doi:10.15171/bi.2015.12
Zununi Vahed S, Samadi N, Mostafidi E, Ardalan MR, Omidi Y (2016) Genetics and epigenetics of chronic allograft dysfunction in kidney transplants. Iran J Kidney Dis 10(1):1–9
Zununi Vahed S, Nikasa P, Ardalan M (2013) Klotho and renal fibrosis. Nephrourol Mon 5(5):946–948. doi:10.5812/numonthly.16179
Torres IB, Moreso F, Sarro E, Meseguer A (2014) The interplay between inflammation and fibrosis in kidney transplantation. Biomed Res Int 2014(2014):1–9. doi:10.1155/2014/750602
Zununi S, Ardalan M (2013) MicroRNA and renal allograft monitoring. Nephrourol Mon 5(3):783–786. doi:10.5812/numonthly.12722
Zununi Vahed S, Samadi N, Ardalan M (2014) Diagnosis of interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy in kidney allograft: implementation of microRNAs. Iran J Kidney Dis 8(1):4–12
Aguado-Fraile E, Ramos E, Conde E, Rodriguez M, Liano F, Garcia-Bermejo ML (2013) MicroRNAs in the kidney: novel biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Nefrologia 33(6):826–834. doi:10.3265/Nefrologia.pre2013.Aug.12198
Li YF, Jing Y, Hao J, Frankfort NC, Zhou X, Shen B, Liu X, Wang L, Li R (2013) MicroRNA-21 in the pathogenesis of acute kidney injury. Protein Cell 4(11):813–819. doi:10.1007/s13238-013-3085-y
Sheedy FJ (2015) Turning 21: induction of miR-21 as a key switch in the inflammatory response. Front Immunol 6:19. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2015.00019
Zhong X, Chung AC, Chen HY, Meng XM, Lan HY (2011) Smad3-mediated upregulation of miR-21 promotes renal fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 22(9):1668–1681. doi:10.1681/asn.2010111168
Huang B, Zhao J, Lei Z, Shen S, Li D, Shen GX, Zhang GM, Feng ZH (2009) miR-142-3p restricts cAMP production in CD4+ CD25− T cells and CD4+ CD25+ TREG cells by targeting AC9 mRNA. EMBO Rep 10(2):180–185. doi:10.1038/embor.2008.224
Bunnag S, Allanach K, Jhangri GS, Sis B, Einecke G, Mengel M, Mueller TF, Halloran PF (2008) FOXP3 expression in human kidney transplant biopsies is associated with rejection and time post transplant but not with favorable outcomes. Am J Transplant 8(7):1423–1433. doi:10.1111/j.1600-6143.2008.02268.x
Chen CZ, Li L, Lodish HF, Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 303(5654):83–86. doi:10.1126/science.1091903
Harris A, Krams SM, Martinez OM (2010) MicroRNAs as immune regulators: implications for transplantation. Am J Transplant 10(4):713–719. doi:10.1111/j.1600-6143.2010.03032.x
Huang Y, Liu Y, Li L, Su B, Yang L, Fan W, Yin Q, Chen L, Cui T, Zhang J, Lu Y, Cheng J, Fu P, Liu F (2014) Involvement of inflammation-related miR-155 and miR-146a in diabetic nephropathy: implications for glomerular endothelial injury. BMC Nephrol 15:142. doi:10.1186/1471-2369-15-142
Mengel M, Chang J, Kayser D, Gwinner W, Schwarz A, Einecke G, Broecker V, Famulski K, de Freitas DG, Guembes-Hidalgo L, Sis B, Haller H, Halloran PF (2011) The molecular phenotype of 6-week protocol biopsies from human renal allografts: reflections of prior injury but not future course. Am J Transplant 11(4):708–718. doi:10.1111/j.1600-6143.2010.03339.x
Park WD, Griffin MD, Cornell LD, Cosio FG, Stegall MD (2010) Fibrosis with inflammation at one year predicts transplant functional decline. J Am Soc Nephrol 21(11):1987–1997. doi:10.1681/asn.2010010049
Mannon RB, Matas AJ, Grande J, Leduc R, Connett J, Kasiske B, Cecka JM, Gaston RS, Cosio F, Gourishankar S, Halloran PF, Hunsicker L, Rush D (2010) Inflammation in areas of tubular atrophy in kidney allograft biopsies: a potent predictor of allograft failure. Am J Transplant 10(9):2066–2073. doi:10.1111/j.1600-6143.2010.03240.x
Ortiz F, Gelpi R, Helantera I, Melilli E, Honkanen E, Bestard O, Grinyo JM, Cruzado JM (2016) Decreased kidney graft survival in low immunological risk patients showing inflammation in normal protocol biopsies. PLoS ONE 11(8):e0159717. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0159717
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Kidney Research Center of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences. The authors gratefully acknowledge Research Center for Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, for technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
The study was approved by the Committee of Clinical Research Ethics in Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Iran (Ethical code: TBZMED.REC.1394.932), and written informed consent was obtained from all the study subjects.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zununi Vahed, S., Poursadegh Zonouzi, A., Ghanbarian, H. et al. Differential expression of circulating miR-21, miR-142-3p and miR-155 in renal transplant recipients with impaired graft function. Int Urol Nephrol 49, 1681–1689 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1602-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1602-2