Summary
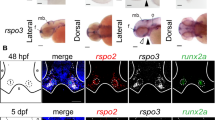
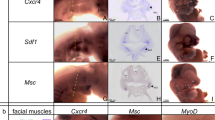
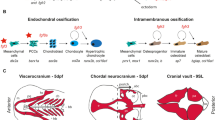
The Dickkopf family is important for embryogenesis and postnatal development and growth. Dkk1 is a strong head inducer and knockout of this gene leads to absence of anterior head structures, which are predominantly formed through neural crest migration. During early craniofacial development, Dkk1 to Dkk3 show developmentally regulated expression in a number of elements. However, their expression and roles in late times of craniofacial development are largely unknown. This study focuses on the expression profile of Dkk1-3 on late embryonic and early postnatal stages. It was found that Dkks were involved in a variety of craniofacial developmental processes, including facial outgrowth, myogenesis, osteogenesis, palatogenesis, olfactory epithelium and tooth development; and the expression persisted to postnatal stage in the muscles and bones. Their expression patterns suggest important roles in these processes; further study is warranted to elucidate these roles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anakwe K, Robson L, Hadley J, Buxton P, Church V, Allen S, Hartmann C, Harfe B, Nohno T, Brown AM, Evans DJ, Francis-West P (2003). Wnt signalling regulates myogenic differentiation in the developing avian wing. Development 130 (15): 3503–3514
Ang SJ, Stump RJ, Lovicu FJ, McAvoy JW (2004). Spatial and temporal expression of Wnt and Dickkopf genes during murine lens development. Gene Expr Patterns 4 (3): 289–295
Boyden LM, Mao J, Belsky J, Mitzner L, Farhi A, Mitnick MA, Wu D, Insogna K, Lifton RP (2002). High bone density due to a mutation in LDL-receptor-related protein (5). N Engl J Med 346 (20): 1513–1521
Byun T, Karimi M, Marsh JL, Milovanovic T, Lin F, Holcombe RF (2005). Expression of secreted Wnt antagonists in gastrointestinal tissues: potential role in stem cell homeostasis. J Clin Pathol 58 (5): 515–519
Davidson G, Mao B, del Barco Barrantes I, Niehrs C (2002). Kremen proteins interact with Dickkopf1 to regulate anteroposterior CNS patterning. Development 129 (24): 5587–5596
De Langhe SP, Sala FG, Del Moral PM, Fairbanks TJ, Yamada KM, Warburton D, Burns RC, Bellusci S (2005). Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) reveals that fibronectin is a major target of Wnt signaling in branching morphogenesis of the mouse embryonic lung. Dev Biol 277 (2): 316–331
Fjeld K, Kettunen P, Furmanek T, Kvinnsland IH, Luukko K (2005). Dynamic expression of Wnt signaling-related Dickkopf1, −2, and −3 mRNAs in the developing mouse tooth. Dev Dyn 233 (1): 161–166
Glinka A, Wu W, Delius H, Monaghan AP, Blumenstock C, Niehrs C. (1998). Dickkopf-1 is a member of a new family of secreted proteins and functions in head induction. Nature 391 (6665): 357–362
Gonzalez-Sancho JM, Aguilera O, Garcia JM, Pendas-Franco N, Pena C, Cal S, Garcia de Herreros A, Bonilla F, Munoz A (2005). The Wnt antagonist DICKKOPF-1 gene is a downstream target of beta-catenin/TCF and is downregulated in human colon cancer. Oncogene 24 (6): 1098–1103
Grotewold L, Ruther U (2002a). Bmp Fgf and Wnt signalling in programmed cell death and chondrogenesis during vertebrate limb development: the role of Dickkopf-(1). Int J Dev Biol 46 (7): 943–947
Grotewold L, Ruther U (2002b). The Wnt antagonist Dickkopf-1 is regulated by Bmp signaling and c-Jun and modulates programmed cell death. Embo J 21 (5): 966–975
Hashimoto H, Itoh M, Yamanaka Y, Yamashita S, Shimizu T, Solnica-Krezel L, Hibi M, Hirano T (2000). Zebrafish Dkk1 functions in forebrain specification and axial mesendoderm formation. Dev Biol 217(1): 138–152
Heller RS, Klein T, Ling Z, Heimberg H, Katoh M, Madsen OD, Serup P (2003). Expression of Wnt, Frizzled, sFRP, and DKK genes in adult human pancreas. Gene Expr 11(3–4): 141–147
Horwitz EM (2004). Dkk-1-mediated expansion of adult stem cells. Trends Biotechnol 22(8): 386–388
Kawano Y, Kypta R (2003). Secreted antagonists of the Wnt signalling pathway. J Cell Sci 116 (Pt 13): 2627–2634
Kazanskaya O, Glinka A, Niehrs C (2000). The role of Xenopus dickkopf1 in prechordal plate specification and neural patterning. Development 127(22): 4981–4992
Kurose K, Sakaguchi M, Nasu Y, Ebara S, Kaku H, Kariyama R, Arao Y, Miyazaki M, Tsushima T, Namba M, Kumon H, Huh NH (2004). Decreased expression of REIC/Dkk-3 in human renal clear cell carcinoma. J Urol 171(3): 1314–1318
Lee AY, He B, You L, Xu Z, Mazieres J, Reguart N, Mikami I, Batra S, Jablons DM (2004). Dickkopf-1 antagonizes Wnt signaling independent of beta-catenin in human mesothelioma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 323(4): 1246–1250
Li X, Liu P, Liu W, Maye P, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Hurley M, Guo C, Boskey A, Sun L, Harris SE, Rowe DW, Ke HZ, Wu D (2005) Dkk2 has a role in terminal osteoblast differentiation and mineralized matrix formation. Nat Genet 37(9): 945–952
Little RD, Carulli JP, Del Mastro RG, Dupuis J, Osborne M, Folz C, Manning SP, Swain PM, Zhao SC, Eustace B, Lappe MM, Spitzer L, Zweier S, Braunschweiger K, Benchekroun Y, Hu X, Adair R, Chee L, FitzGerald MG, Tulig C, Caruso A, Tzellas N, Bawa A, Franklin B, McGuire S, Nogues X, Gong G, Allen KM, Anisowicz A, Morales AJ, Lomedico PT, Recker SM, Van Eerdewegh P, Recker RR, Johnson ML (2002). A mutation in the LDL receptor-related protein 5 gene results in the autosomal dominant high-bone-mass trait. Am J Hum Genet 70(1): 11–19
Mao B, Niehrs C (2003). Kremen2 modulates Dickkopf2 activity during Wnt/LRP6 signaling. Gene 302(1–2): 179–183
Mao B, Wu W, Davidson G, Marhold J, Li M, Mechler BM, Delius H, Hoppe D, Stannek P, Walter C, Glinka A, Niehrs C (2002). Kremen proteins are Dickkopf receptors that regulate Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. Nature 417(6889): 664–667
Mao B, Wu W, Li Y, Hoppe D, Stannek P, Glinka A, Niehrs C(2001). LDL-receptor-related protein 6 is a receptor for Dickkopf proteins. Nature 411(6835): 321–325
Monaghan AP, Kioschis P, Wu W, Zuniga A, Bock D, Poustka A, Delius H, Niehrs C (1999). Dickkopf genes are co-ordinately expressed in mesodermal lineages. Mech Dev 87 (1–2): 45–56
Mukhopadhyay M, Shtrom S, Rodriguez-Esteban C, Chen L, Tsukui T, Gomer L, Dorward DW, Glinka A, Grinberg A, Huang SP, Niehrs C, Belmonte JC, Westphal H (2001). Dickkopf1 is required for embryonic head induction and limb morphogenesis in the mouse. Dev Cell 1(3): 423–434
Murrell W, Feron F, Wetzig A, Cameron N, Splatt K, Bellette B, Bianco J, Perry C, Lee G, Mackay-Sim A (2005). Multipotent stem cells from adult olfactory mucosa. Dev Dyn 233(2): 496–515
Nie X (2005) Apoptosis proliferation and gene expression patterns in mouse developing tongue. Anat Embryol (DOI (10).1007/s00429-005-0009-5) Sep 6: 1–8
Semenov MV, Tamai K, Brott BK, Kuhl M, Sokol S, He X (2001). Head inducer Dickkopf-1 is a ligand for Wnt coreceptor LRP6. Curr Biol 11(12): 951–961
Shinya M, Eschbach C, Clark M, Lehrach H, Furutani-Seiki M (2000). Zebrafish Dkk1, induced by the pre-MBT Wnt signaling, is secreted from the prechordal plate and patterns the anterior neural plate. Mech Dev 98(1–2): 3–17
Shuler CF, Dalrymple KR (2001). Molecular regulation of tongue and craniofacial muscle differentiation. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 12(1): 3–17
Tian E, Zhan F, Walker R, Rasmussen E, Ma Y, Barlogie B, Shaughnessy JD, Jr (2003). The role of the Wnt-signaling antagonist DKK1 in the development of osteolytic lesions in multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 349(26): 2483–2494
Tzahor E, Kempf H, Mootoosamy RC, Poon AC, Abzhanov A, Tabin CJ, Dietrich S, Lassar AB (2003). Antagonists of Wnt and BMP signaling promote the formation of vertebrate head muscle. Genes Dev 17(24): 3087–3099
Wirths O, Waha A, Weggen S, Schirmacher P, Kuhne T, Goodyer CG, Albrecht S, Von Schweinitz D, Pietsch T (2003). Overexpression of human Dickkopf-1, an antagonist of wingless/WNT signaling, in human hepatoblastomas and Wilms’ tumors. Lab Invest 83(3): 429–434
Acknowledgements
This work was carried out in the Department of Biomedicine and financed by Faculty of Dentistry, University of Bergen. I thank the faculties for the financial support and excellent facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, X. Dkk1, -2, and -3 expression in mouse craniofacial development. J Mol Hist 36, 367–372 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-005-9008-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-005-9008-3