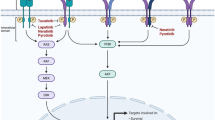
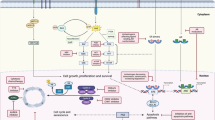
Abstract
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) refers to a heterogeneous group of tumors that do not express the estrogen/progesterone-receptor (ER/PR), and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2). TNBC is an aggressive histological subtype with limited treatment options and very poor prognosis following progression after standard chemotherapy regimens. There have been significant improvements in the outcome of other subtypes of breast cancer, including ER-positive/HER2 overexpressed tumors, attributed to the addition of targeted therapy, including hormonal agents and trastuzumab. However, no specific targeted agents are currently available for the treatment of TNBC. This review aims to collate and describe the most recent data on targeted therapies that have demonstrated efficacy in the management of metastatic TNBC. Targeted agents that have been investigated in the treatment of metastatic TNBC include inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, angiogenesis, mammalian target of rapamycin, epidermal growth factor receptor, HDAC, Jak2, and Src. Several of these agents have shown considerable promise.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gelmon KA et al (2010) Can we define tumors that will respond to PARP inhibitors? A phase II correlative study of olaparib in advanced serous ovarian cancer and triple-negative breast cancer. ASCO 2010. J Clin Oncol, Chicago, IL
Andre F, Job B, Dessen P, Tordai A, Michiels S, Liedtke C, Richon C, Yan K, Wang B, Vassal G, Delaloge S, Hortobagyi GN, Symmans WF, Lazar V, Pusztai L (2009) Molecular characterization of breast cancer with high-resolution oligonucleotide comparative genomic hybridization array. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 15:441–451. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1791
Barrios CH, Liu MC, Lee SC, Vanlemmens L, Ferrero JM, Tabei T, Pivot X, Iwata H, Aogi K, Lugo-Quintana R, Harbeck N, Brickman MJ, Zhang K, Kern KA, Martin M (2010) Phase III randomized trial of sunitinib versus capecitabine in patients with previously treated HER2-negative advanced breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 121:121–131. doi:10.1007/s10549-010-0788-0
Baselga J, Roché H et al (December 9–13, 2009) SOLTI-0701: a multinational double-blind, randomized phase 2b study evaluating the efficacy and safety of sorafenib compared to placebo when administered in combination with capecitabine in patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer (BC). 32nd Annual CTRC-AACR San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, San Antonio, TX
Baselga J, Albanell J, Ruiz A, Lluch A, Gascon P, Guillem V, Gonzalez S, Sauleda S, Marimon I, Tabernero JM, Koehler MT, Rojo F (2005) Phase II and tumor pharmacodynamic study of gefitinib in patients with advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 23:5323–5333. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.08.326
Baselga J, Stemmer S, Pego A et al (2010) Cetuximab + cisplatin in estrogen receptornegative, progesterone receptor-negative, HER2-negative (triple-negative) metastatic breast cancer: results of the randomized phase II BALI-1 trial. In: 33rd Annual CTRC-AACR San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, San Antonio, TX
Bergh J, Bondarenko IM, Lichinitser MR, Liljegren A, Greil R, Voytko NL, Makhson AN, Cortes J, Lortholary A, Bischoff J, Chan A, Delaloge S, Huang X, Kern KA, Giorgetti C (2012) First-line treatment of advanced breast cancer with sunitinib in combination with docetaxel versus docetaxel alone: results of a prospective, randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 30:921–929. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.35.7376
Bianchi G, Loibl S, Zamagni C, Salvagni S, Raab G, Siena S, Laferriere N, Pena C, Lathia C, Bergamini L, Gianni L (2009) Phase II multicenter, uncontrolled trial of sorafenib in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Anticancer Drugs 20:616–624
Brufsky A, Valero V, Tiangco B, Dakhil S, Brize A, Rugo HS, Rivera R, Duenne A, Bousfoul N, Yardley DA (2012) Second-line bevacizumab-containing therapy in patients with triple-negative breast cancer: subgroup analysis of the RIBBON-2 trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat 133:1067–1075. doi:10.1007/s10549-012-2008-6
Burstein HJ, Elias AD, Rugo HS, Cobleigh MA, Wolff AC, Eisenberg PD, Lehman M, Adams BJ, Bello CL, DePrimo SE, Baum CM, Miller KD (2008) Phase II study of sunitinib malate, an oral multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with metastatic breast cancer previously treated with an anthracycline and a taxane. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 26:1810–1816. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.14.5375
Cabezon T, Gromova I, Gromov P, Serizawa R, Timmermans Wielenga V, Kroman N, Celis JE, Moreira JM (2012) Proteomic profiling of triple-negative breast carcinomas in combination with a three-tier orthogonal technology approach identifies Mage-A4 as potential therapeutic target in estrogen receptor negative breast cancer. Molecular & cellular proteomics: MCP. doi:10.1074/mcp.M112.019786
Caldas-Lopes E, Cerchietti L, Ahn JH, Clement CC, Robles AI, Rodina A, Moulick K, Taldone T, Gozman A, Guo Y, Wu N, de Stanchina E, White J, Gross SS, Ma Y, Varticovski L, Melnick A, Chiosis G (2009) Hsp90 inhibitor PU-H71, a multimodal inhibitor of malignancy, induces complete responses in triple-negative breast cancer models. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:8368–8373. doi:10.1073/pnas.0903392106
Carey LA (2011) Directed therapy of subtypes of triple-negative breast cancer. Oncologist 16(Suppl 1):71–78. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2011-S1-71
Carey LA OSJ, Hoadley K et al (2009) Potential predictive markers of benefit from cetuximab in metastatic breast cancer: an analysis of two randomized phase 2 trials. 32nd Annual CTRC-AACR San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, San Antonio, TX
Carey LA, Rugo HS, Marcom PK, Mayer EL, Esteva FJ, Ma CX, Liu MC, Storniolo AM, Rimawi MF, Forero-Torres A, Wolff AC, Hobday TJ, Ivanova A, Chiu WK, Ferraro M, Burrows E, Bernard PS, Hoadley KA, Perou CM, Winer EP (2012) TBCRC 001: randomized phase II study of cetuximab in combination with carboplatin in stage IV triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 30:2615–2623. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.34.5579
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2000) Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 407:249–257. doi:10.1038/35025220
Carpenter D, Kesselheim AS, Joffe S (2011) Reputation and precedent in the bevacizumab decision. N Engl J Med 365:e3. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1107201
Corkery B, Crown J, Clynes M, O’Donovan N (2009) Epidermal growth factor receptor as a potential therapeutic target in triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol/ESMO 20:862–867. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdn710
Crown J, DierasV, Staroslawska E et al (2010) Phase III evaluation of sunitinib (SU) in combination with capecitabine (C) versus C in previously treated advanced breast cancer (ABC). J Clin Oncol
Curigliano GPX, Cortes J et al (2010) A randomized phase II study of sunitinib vs. standard of care for patients with previously treated advanced triple-negative breast cancer. SABCS 2010. Cancer Res, San Antonio, TX
Delaloge S, Tedesco K, Blum J et al (2009) Preliminary safety and activity results of trabectedin in a phase II trial dedicated to triple-negative (ER-, PR-, HER2-), HER2 + ++, or BRCA1/2 germline-mutated metastatic breast cancer (MBC) patients (pts). ASCO Annual Meeting. J Clin Oncol
Dickler MN, Rugo HS, Eberle CA, Brogi E, Caravelli JF, Panageas KS, Boyd J, Yeh B, Lake DE, Dang CT, Gilewski TA, Bromberg JF, Seidman AD, D’Andrea GM, Moasser MM, Melisko M, Park JW, Dancey J, Norton L, Hudis CA (2008) A phase II trial of erlotinib in combination with bevacizumab in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 14:7878–7883. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0141
Doane AS, Danso M, Lal P, Donaton M, Zhang L, Hudis C, Gerald WL (2006) An estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer subset characterized by a hormonally regulated transcriptional program and response to androgen. Oncogene 25:3994–4008. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209415
Ellard SLCM, Gelmon KA et al (2009) Randomised phase II study comparing two schedules of everolimus in patients with recurrent/metastatic breast cancer: NCIC Clinical Trials Group IND.163. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 27:4536–4541
Finn RS, Dering J, Ginther C, Wilson CA, Glaspy P, Tchekmedyian N, Slamon DJ (2007) Dasatinib, an orally active small molecule inhibitor of both the src and abl kinases, selectively inhibits growth of basal-type/“triple-negative” breast cancer cell lines growing in vitro. Breast Cancer Res Treat 105:319–326. doi:10.1007/s10549-006-9463-x
Finn RS, Press MF, Dering J, Arbushites M, Koehler M, Oliva C, Williams LS, Di Leo A (2009) Estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), and epidermal growth factor receptor expression and benefit from lapatinib in a randomized trial of paclitaxel with lapatinib or placebo as first-line treatment in HER2-negative or unknown metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 27:3908–3915. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.18.1925
Finn RS, Bengala C, Ibrahim N, Roche H, Sparano J, Strauss LC, Fairchild J, Sy O, Goldstein LJ (2011) Dasatinib as a single agent in triple-negative breast cancer: results of an open-label phase 2 study. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 17:6905–6913. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0288
Fornier MN, Morris PG, Abbruzzi A, D’Andrea G, Gilewski T, Bromberg J, Dang C, Dickler M, Modi S, Seidman AD, Sklarin N, Chang J, Norton L, Hudis CA (2011) A phase I study of dasatinib and weekly paclitaxel for metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol/ESMO 22:2575–2581. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdr018
Foulkes WD, Stefansson IM, Chappuis PO, Begin LR, Goffin JR, Wong N, Trudel M, Akslen LA (2003) Germline BRCA1 mutations and a basal epithelial phenotype in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:1482–1485
Gluck S, Ross JS, Royce M, McKenna EF Jr, Perou CM, Avisar E, Wu L (2012) TP53 genomics predict higher clinical and pathologic tumor response in operable early-stage breast cancer treated with docetaxel-capecitabine ± trastuzumab. Breast Cancer Res Treat 132:781–791. doi:10.1007/s10549-011-1412-7
Gradishar WJ, Kaklamani V, Sahoo TP, Lokanatha D, Raina V, Bondarde S, Jain M, Ro SK, Lokker NA, Schwartzberg L (2012) A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2b study evaluating sorafenib in combination with paclitaxel as a first-line therapy in patients with HER2-negative advanced breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2012.08.005
Greenberg S, Rugo HS (2010) Triple-negative breast cancer: role of antiangiogenic agents. Cancer J 16:33–38. doi:10.1097/PPO.0b013e3181d38514
Hastak K, Alli E, Ford JM (2010) Synergistic chemosensitivity of triple-negative breast cancer cell lines to poly(ADP-Ribose) polymerase inhibition, gemcitabine, and cisplatin. Cancer Res 70:7970–7980. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4521
Helleday T, Petermann E, Lundin C, Hodgson B, Sharma RA (2008) DNA repair pathways as targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 8:193–204. doi:10.1038/nrc2342
Herschkowitz JI, Simin K, Weigman VJ, Mikaelian I, Usary J, Hu Z, Rasmussen KE, Jones LP, Assefnia S, Chandrasekharan S, Backlund MG, Yin Y, Khramtsov AI, Bastein R, Quackenbush J, Glazer RI, Brown PH, Green JE, Kopelovich L, Furth PA, Palazzo JP, Olopade OI, Bernard PS, Churchill GA, Van Dyke T, Perou CM (2007) Identification of conserved gene expression features between murine mammary carcinoma models and human breast tumors. Genome Biol 8:R76. doi:10.1186/gb-2007-8-5-r76
Hobday TJ SP, Fitch TR et al (2008) N0436: a phase II trial of irinotecan plus cetuximab in patients with metastatic breast cancer and prior anthracycline and/or taxane-containing therapy. ASCO Annual Meeting. J Clin Oncol
http://www.incyte.com/drugs_product_pipeline.html (27 November 2012, date last accessed)
Hudis C TK, Hermann RC et al (2011) Sorafenib (SOR) plus chemotherapy (CRx) for patients (pts) with advanced (adv) breast cancer (BC) previously treated with bevacizumab (BEV). In: ASCO Annual Meeting. J Clin Oncol, Chicago, IL
Hudis CA, Gianni L (2011) Triple-negative breast cancer: an unmet medical need. Oncologist 16(Suppl 1):1–11. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2011-S1-01
Isakoff SJ, Overmoyer B, Tung NM, Gelman RS et al (2010) A phase II trial of the PARP inhibitor veliparib (ABT888) and temozolomide for metastatic breast cancer. ASCO 2010. J Clin Oncol, Chicago, IL
Jain RK, Duda DG, Clark JW, Loeffler JS (2006) Lessons from phase III clinical trials on anti-VEGF therapy for cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 3:24–40. doi:10.1038/ncponc0403
Jassem J, Carroll C, Ward SE, Simpson E, Hind D (2009) The clinical efficacy of cytotoxic agents in locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer patients pretreated with an anthracycline and a taxane: a systematic review. Eur J Cancer 45:2749–2758. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2009.05.035
Jones A, O’Brien M, Sommer H, Nowara E, Welt A, Pienkowski T, Rolski J, Pham ML, Perraud K, Trillet-Lenoir V (2010) Phase II study of oral vinorelbine in combination with capecitabine as second line chemotherapy in metastatic breast cancer patients previously treated with anthracyclines and taxanes. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 65:755–763. doi:10.1007/s00280-009-1081-y
Kassam F, Enright K, Dent R, Dranitsaris G, Myers J, Flynn C, Fralick M, Kumar R, Clemons M (2009) Survival outcomes for patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: implications for clinical practice and trial design. Clin Breast Cancer 9:29–33. doi:10.3816/CBC.2009.n.005
Kobune M, Takimoto R, Murase K, Iyama S, Sato T, Kikuchi S, Kawano Y, Miyanishi K, Sato Y, Niitsu Y, Kato J (2009) Drug resistance is dramatically restored by hedgehog inhibitors in CD34+ leukemic cells. Cancer Sci 100:948–955. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01111.x
Kummar S, Ji J, Morgan R, Lenz HJ, Puhalla SL, Belani CP, Gandara DR, Allen D, Kiesel B, Beumer JH, Newman EM, Rubinstein L, Chen A, Zhang Y, Wang L, Kinders RJ, Parchment RE, Tomaszewski JE, Doroshow JH (2012) A phase I study of veliparib in combination with metronomic cyclophosphamide in adults with refractory solid tumors and lymphomas. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 18:1726–1734. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2821
Lakhani SR, Reis-Filho JS, Fulford L, Penault-Llorca F, van der Vijver M, Parry S, Bishop T, Benitez J, Rivas C, Bignon YJ, Chang-Claude J, Hamann U, Cornelisse CJ, Devilee P, Beckmann MW, Nestle-Kramling C, Daly PA, Haites N, Varley J, Lalloo F, Evans G, Maugard C, Meijers-Heijboer H, Klijn JG, Olah E, Gusterson BA, Pilotti S, Radice P, Scherneck S, Sobol H, Jacquemier J, Wagner T, Peto J, Stratton MR, McGuffog L, Easton DF (2005) Prediction of BRCA1 status in patients with breast cancer using estrogen receptor and basal phenotype. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 11:5175–5180. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2424
Lee J AC, Minasian LM et al (2011) Phase I study of the PARP inhibitor olaparib (O) in combination with carboplatin (C) in BRCA1/2 mutation carriers with breast (Br) or ovarian (Ov) cancer (Ca). In: ASCO 2011. J Clin Oncol, Chicago, IL
Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, Andre F, Tordai A, Mejia JA, Symmans WF, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hennessy B, Green M, Cristofanilli M, Hortobagyi GN, Pusztai L (2008) Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 26:1275–1281. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.14.4147
Liu J, Fleming G, Tolaney SM et al (2011) A phase I trial of the PARP inhibitor olaparib (AZD2281) in combination with the antiangiogenic cediranib (AZD2171) in recurrent ovarian or triple-negative breast cancer. ASCO 2011. J Clin Oncol, Chicago, IL
Liu T, Yacoub R, Taliaferro-Smith LD, Sun SY, Graham TR, Dolan R, Lobo C, Tighiouart M, Yang L, Adams A, O’Regan RM (2011) Combinatorial effects of lapatinib and rapamycin in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 10:1460–1469. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0925
Lobo C, Lopes G, Baez O, Castrellon A, Ferrell A, Higgins C, Hurley E, Hurley J, Reis I, Richman S, Seo P, Silva O, Slingerland J, Tukia K, Welsh C, Gluck S (2010) Final results of a phase II study of nab-paclitaxel, bevacizumab, and gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 123:427–435. doi:10.1007/s10549-010-1002-0
Longley DB, Johnston PG (2005) Molecular mechanisms of drug resistance. J Pathol 205:275–292. doi:10.1002/path.1706
Lu D, Shen J, Vil MD, Zhang H, Jimenez X, Bohlen P, Witte L, Zhu Z (2003) Tailoring in vitro selection for a picomolar affinity human antibody directed against vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 for enhanced neutralizing activity. J Biol Chem 278:43496–43507. doi:10.1074/jbc.M307742200
Marotta LL, Almendro V, Marusyk A, Shipitsin M, Schemme J, Walker SR, Bloushtain-Qimron N, Kim JJ, Choudhury SA, Maruyama R, Wu Z, Gonen M, Mulvey LA, Bessarabova MO, Huh SJ, Silver SJ, Kim SY, Park SY, Lee HE, Anderson KS, Richardson AL, Nikolskaya T, Nikolsky Y, Liu XS, Root DE, Hahn WC, Frank DA, Polyak K (2011) The JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway is required for growth of CD44(+)CD24(-) stem cell-like breast cancer cells in human tumors. J Clin Investig 121:2723–2735. doi:10.1172/JCI44745
McCabe N, Turner NC, Lord CJ, Kluzek K, Bialkowska A, Swift S, Giavara S, O’Connor MJ, Tutt AN, Zdzienicka MZ, Smith GC, Ashworth A (2006) Deficiency in the repair of DNA damage by homologous recombination and sensitivity to poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition. Cancer Res 66:8109–8115. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0140
Miller K, Wang M, Gralow J, Dickler M, Cobleigh M, Perez EA, Shenkier T, Cella D, Davidson NE (2007) Paclitaxel plus bevacizumab versus paclitaxel alone for metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med 357:2666–2676. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa072113
Montagna E, Cancello G, Bagnardi V, Pastrello D, Dellapasqua S, Perri G, Viale G, Veronesi P, Luini A, Intra M, Calleri A, Rampinelli C, Goldhirsch A, Bertolini F, Colleoni M (2012) Metronomic chemotherapy combined with bevacizumab and erlotinib in patients with metastatic HER2-negative breast cancer: clinical and biological activity. Clin Breast Cancer 12:207–214. doi:10.1016/j.clbc.2012.03.008
Moulder S MM, Bradley C, Rocha C, Harris L (2010) A phase 1b study to assess the safety and tolerability of the PARP inhibitor iniparib (BSI-201) in combination with irinotecan for the treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer. San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, San Antonio, TX
Moulder S, Yan K, Huang F, Hess KR, Liedtke C, Lin F, Hatzis C, Hortobagyi GN, Symmans WF, Pusztai L (2010) Development of candidate genomic markers to select breast cancer patients for dasatinib therapy. Mol Cancer Ther 9:1120–1127. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-1117
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology; Breast Cancer. V2. 2012. Available at: http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/breast.pdf (25 November 2012, date last accessed)
Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, Cheang M, Karaca G, Hu Z, Hernandez-Boussard T, Livasy C, Cowan D, Dressler L, Akslen LA, Ragaz J, Gown AM, Gilks CB, van de Rijn M, Perou CM (2004) Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 10:5367–5374. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0220
Niemeier LA, Dabbs DJ, Beriwal S, Striebel JM, Bhargava R (2010) Androgen receptor in breast cancer: expression in estrogen receptor-positive tumors and in estrogen receptor-negative tumors with apocrine differentiation. Modern Pathol Off J US Can Acad Pathol Inc 23:205–212. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2009.159
Nogi H, Kobayashi T, Suzuki M, Tabei I, Kawase K, Toriumi Y, Fukushima H, Uchida K (2009) EGFR as paradoxical predictor of chemosensitivity and outcome among triple-negative breast cancer. Oncol Rep 21:413–417
O’Shaughnessy J WD, Vukelja S et al (2007) Preliminary results of a randomized phase II study of weekly irinotecan/carboplatin with or without cetuximab in patients with metastatic breast cancer. 30th Annual CTRC-AACR San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, San Antonio, TX
O’Shaughnessy J MD, Gray RJ et al (2010) A meta-analysis of overall survival data from three randomized trials of bevacizumab (BV) and first-line chemotherapy as treatment for patients with metastatic breast cancer (MBC). ASCO Annual Meeting, J Clin Oncol, Chicago, IL
O’Driscoll L, Clynes M (2006) Biomarkers and multiple drug resistance in breast cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 6:365–384
Ordentlich P, Tee L, Huynh Y, Mee S, et al (2009) Ex-vivo analysis of the isoform selective histone deacetylase inhibitor entinostat in triple-negative breast cancer tumors.. In: ASCO Annual Meeting. J Clin Oncol
O’Shaughnessy J, Schwartzberg S, Danso MA et al (2011) A randomized phase III study of iniparib (BSI-201) in combination with gemcitabine/carboplatin (G/C) in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). In: ASCO Annual Meeting. J Clin Oncol, Chicago, IL
O’Shaughnessy J, Osborne C, Pippen JE, Yoffe M, Patt D, Rocha C, Koo IC, Sherman BM, Bradley C (2011) Iniparib plus chemotherapy in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med 364:205–214. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1011418
Peng Y (2012) Potential prognostic tumor biomarkers in triple-negative breast carcinoma. Beijing da xue xue bao. Yi xue ban = Journal of Peking University. Health Sci 44:666–672
Perou CM (2011) Molecular stratification of triple-negative breast cancers. Oncologist 16(Suppl 1):61–70. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2011-S1-61
Pivot X, Schneeweiss A, Verma S, Thomssen C, Passos-Coelho JL, Benedetti G, Ciruelos E, von Moos R, Chang HT, Duenne AA, Miles DW (2011) Efficacy and safety of bevacizumab in combination with docetaxel for the first-line treatment of elderly patients with locally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer: results from AVADO. Eur J Cancer 47:2387–2395. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2011.06.018
Ponzo MG, Lesurf R, Petkiewicz S, O’Malley FP, Pinnaduwage D, Andrulis IL, Bull SB, Chughtai N, Zuo D, Souleimanova M, Germain D, Omeroglu A, Cardiff RD, Hallett M, Park M (2009) Met induces mammary tumors with diverse histologies and is associated with poor outcome and human basal breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:12903–12908. doi:10.1073/pnas.0810402106
Prat A, Perou CM (2011) Deconstructing the molecular portraits of breast cancer. Mol Oncol 5:5–23. doi:10.1016/j.molonc.2010.11.003
Questions and answers on the review of Avastin (bevacizumab) in the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Medicine_QA/2010/12/WC500099939.pdf (25 November 2012, date last accessed)
Rios J, Puhalla S (2011) PARP inhibitors in breast cancer: BRCA and beyond. Oncology (Williston Park) 25:1014–1025
Robert NJ, Dieras V, Glaspy J, Brufsky AM, Bondarenko I, Lipatov ON, Perez EA, Yardley DA, Chan SY, Zhou X, Phan SC, O’Shaughnessy J (2011) RIBBON-1: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial of chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for first-line treatment of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative, locally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol 29:1252–1260. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.28.0982
Rouzier R, Perou CM, Symmans WF, Ibrahim N, Cristofanilli M, Anderson K, Hess KR, Stec J, Ayers M, Wagner P, Morandi P, Fan C, Rabiul I, Ross JS, Hortobagyi GN, Pusztai L (2005) Breast cancer molecular subtypes respond differently to preoperative chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 11:5678–5685. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2421
Schneider BP, Winer EP, Foulkes WD, Garber J, Perou CM, Richardson A, Sledge GW, Carey LA (2008) Triple-negative breast cancer: risk factors to potential targets. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 14:8010–8018. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1208
Seitz S SA, Gluck S et al (2009) Effective treatment of triple-negative breast cancer with targeted cytotoxic somatostatin analogue AN-162 (AEZS-124). In: ASCO Annual Meeting. J Clin Oncol
Somlo G, Sparano JA, Cigler T et al (2012) ABT-888 (veliparib) in combination with carboplatin in patients with stage IV BRCA-associated breast cancer. A California Cancer Consortium Trial. In: J Clin Oncol
Sutton LM, Han JS, Molberg KH, Sarode VR, Cao D, Rakheja D, Sailors J, Peng Y (2010) Intratumoral expression level of epidermal growth factor receptor and cytokeratin 5/6 is significantly associated with nodal and distant metastases in patients with basal-like triple-negative breast carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol 134:782–787. doi:10.1309/AJCPRMD3ARUO5WPN
Tan AR, Toppmeyer D, Stein MN et al (2011) Phase I trial of veliparib, (ABT-888), a poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor, in combination with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide in breast cancer and other solid tumors. ASCO 2011. J Clin Oncol, Chicago, IL
Thomssen C, Pierga JY, Pritchard KI, Biganzoli L, Cortes-Funes H, Petrakova K, Kaufman B, Duenne A, Smith I (2012) First-line bevacizumab-containing therapy for triple-negative breast cancer: analysis of 585 patients treated in the ATHENA study. Oncology 82:218–227. doi:10.1159/000336892
Tryfonopoulos D, Walsh S, Collins DM, Flanagan L, Quinn C, Corkery B, McDermott EW, Evoy D, Pierce A, O’Donovan N, Crown J, Duffy MJ (2011) Src: a potential target for the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol/ESMO 22:2234–2240. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdq757
Turner NC, Reis-Filho JS, Russell AM, Springall RJ, Ryder K, Steele D, Savage K, Gillett CE, Schmitt FC, Ashworth A, Tutt AN (2007) BRCA1 dysfunction in sporadic basal-like breast cancer. Oncogene 26:2126–2132. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210014
Turner N, Lambros MB, Horlings HM, Pearson A, Sharpe R, Natrajan R, Geyer FC, van Kouwenhove M, Kreike B, Mackay A, Ashworth A, van de Vijver MJ, Reis-Filho JS (2010) Integrative molecular profiling of triple negative breast cancers identifies amplicon drivers and potential therapeutic targets. Oncogene 29:2013–2023. doi:10.1038/onc.2009.489
Tutt A, Robson M, Garber JE, Domchek SM, Audeh MW, Weitzel JN, Friedlander M, Arun B, Loman N, Schmutzler RK, Wardley A, Mitchell G, Earl H, Wickens M, Carmichael J (2010) Oral poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor olaparib in patients with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations and advanced breast cancer: a proof-of-concept trial. Lancet 376:235–244. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60892-6
Whitesell L, Mimnaugh EG, De Costa B, Myers CE, Neckers LM (1994) Inhibition of heat shock protein HSP90-pp 60v-src heteroprotein complex formation by benzoquinone ansamycins: essential role for stress proteins in oncogenic transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:8324–8328
Wildiers H, Fontaine C, Vuylsteke P, Martens M, Canon JL, Wynendaele W, Focan C, De Greve J, Squifflet P, Paridaens R (2010) Multicenter phase II randomized trial evaluating antiangiogenic therapy with sunitinib as consolidation after objective response to taxane chemotherapy in women with HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 123:463–469. doi:10.1007/s10549-010-1066-x
Disclosures
The manuscript has never been published and is not under consideration for publication elsewhere. Authors have no financial interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bayraktar, S., Glück, S. Molecularly targeted therapies for metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 138, 21–35 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2421-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2421-5