Abstract
Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease (PMD) and its allelic disorder, spastic paraplegia type 2 (SPG2), are among the best-characterized dysmyelinating leukodystrophies of the central nervous system (CNS). Both PMD and SPG2 are caused by mutations in the proteolipid protein 1 (PLP1) gene, which encodes a major component of CNS myelin proteins. Distinct types of mutations, including point mutations and genomic duplications and deletions, have been identified as causes of PMD/SPG2 that act through different molecular mechanisms. Studies of various PLP1 mutants in humans and animal models have shed light on the genomic, molecular, and cellular pathogeneses of PMD/SPG2. Recent discoveries include complex mutational mechanisms and associated disease phenotypes, novel cellular pathways that lead to the degeneration of oligodendrocytes, and genomic architectural features that result in unique chromosomal rearrangements. Here, I review the previous and current knowledge of the molecular pathogenesis of PMD/SPG2 and delineate future directions for PMD/SPG2 studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pelizaeus F (1885) Über eine eigentümliche Form spastischer Lähmung mit cerebral Erscheinungen auf hereditärer Grundlage (multiple Sklerose). Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr 16:698–710
Merzbacher L (1910) Eine eigenartige familiäre-hereditäre Erkrankungsform (Aplasia axialis extracorticalis congenita) Z Ges Neurol Psychiatr 3:1–138
Seitelberger F (1970) Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. In: Vinken P, Bruyn G (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology. Leucodystrophies and poliodystrophie. North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp 150–202
Willard HF, Riordan JR (1985) Assignment of the gene for myelin proteolipid protein to the X chromosome: implications for X-linked myelin disorders. Science 230:940–942
Hudson LD, Puckett C, Berndt J, Chan J, Gencic S (1989) Mutation of the proteolipid protein gene PLP in a human X chromosome-linked myelin disorder. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:8128–8131
Trofatter JA, Dlouhy SR, DeMyer W, Conneally PM, Hodes ME (1989) Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease: tight linkage to proteolipid protein gene exon variant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:9427–9430
Dautigny A, Mattei M-G, Morello D, Alliel PM, Pham-Dinh D, Amar L, Arnaud D, Simon D, Mattei JF, Guenet JL, Jollès P, Avner P (1986) The structural gene coding for myelin-associated proteolipid protein is mutated in jimpy mice. Nature 321:867–869
Nave KA, Lai C, Bloom F, Milner RJ (1989) Jimpy mutant mouse: a 74-base deletion in the mRNA for myelin proteolipid protein and evidence for a primary defect in mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:9264–9268
Schneider A, Montague P, Griffiths I, Fanarraga M, Kennedy P, Brophy P, Nave KA (1992) Uncoupling of hypomyelination and glial cell death by a mutation in the proteolipid protein gene. Nature 358:758–761
Gencic S, Hudson LD (1990) Conservative amino acid substitution in the myelin proteolipid protein of jimpymsd mice. J Neurosci 10:117–124
Boison D, Stoffel W (1989) Myelin-deficient rat: a point mutation in exon III (A→C, Thr 75→Pro) of myelin proteolipid protein causes dysmyelination and oligodendrocyte death. EMBO J 8:3295–3302
Nadon NL, Duncan ID, Hudson LD (1990) A point mutation in the proteolipid protein gene of the ‘shaking pup’ interrupts oligodendrocyte development. Development 110:529–537
Tosic M, Dolivo M, Domanska-Janik K, Matthieu JM (1994) Paralytic tremor (pt): a new allele of the proteolipid protein gene in rabbits. J Neurochem 63:2210–2216
Yool DA, Edgar JM, Montague P, Malcolm S (2000) The proteolipid protein gene and myelin disorders in man and animal models. Hum Mol Genet 9:987–992
Hudson LD (2001) Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease and the allelic disorder X-linked spastic paraplegia type 2. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds) The metabolic and molecular basis of inherited diseases. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 5789–5798
Garbern J, Cambi F, Shy M, Kamholz J (1999) The molecular pathogenesis of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Arch Neurol 56:1210–1214
Saugier-Veber P, Munnich A, Bonneau D, Rozet JM, Le Merrer M, Gil R, Boespflug-Tanguy O (1994) X-linked spastic paraplegia and Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease are allelic disorders at the proteolipid protein locus. Nat Genet 6:257–262
Seitelberger F (1995) Neuropathology and genetics of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Brain Pathol 5:267–273
Miller MJ, Haxhiu MA, Georgiadis P, Gudz TI, Kangas CD, Macklin WB (2003) Proteolipid protein gene mutation induces altered ventilatory response to hypoxia in the myelin-deficient rat. J Neurosci 23:2265–2273
Boulloche J, Aicardi J (1986) Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease: clinical and nosological study. J Child Neurol 1:233–239
Cailloux F, Gauthier-Barichard F, Mimault C, Isabelle V, Courtois V, Giraud G, Dastugue B, Boespflug-Tanguy O Clinical European Network on Brain Dysmyelinating Disease (2000) Genotype–phenotype correlation in inherited brain myelination defects due to proteolipid protein gene mutations. Eur J Hum Genet 8:837–845
Fink JK (2003) The hereditary spastic paraplegias: nine genes and counting. Arch Neurol 60:1045–1049
Johnston AW, McKusick VA (1962) A sex-linked recessive form of spastic paraplegia. Am J Hum Genet 14:83–94
Osaka H, Kawanishi C, Inoue K, Uesugi H, Hiroshi K, Nishiyama K, Yamada Y, Suzuki K, Kimura S, Kosaka K (1995) Novel nonsense proteolipid protein gene mutation as a cause of X-linked spastic paraplegia in twin males. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 215:835–841
Cambi F, Tang XM, Cordray P, Fain PR, Keppen LD, Barker DF (1996) Refined genetic mapping and proteolipid protein mutation analysis in X-linked pure hereditary spastic paraplegia. Neurology 46:1112–1117
Knaap MS van der, Valk J (1995) Magnetic resonance of myelin, myelination, and myelin disorders. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 31–43
Barkovich AJ (2000) Concepts of myelin and myelination in neuroradiology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1099–1109
Barkovich AJ, Kjos BO, Jackson DE Jr, Norman D (1988) Normal maturation of the neonatal and infant brain: MR imaging at 1.5 T. Radiology 166:173–180
Sie LTL, van der Knaap MS, van Wezel-Meijler G, Valk J (1997) MRI assessment of myelination of motor and sensory pathways in the brain of preterm and term-born infants. Neuropediatrics 28:97–105
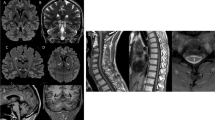
Takanashi J, Sugita K, Tanabe Y, Nagasawa K, Inoue K, Osaka H, Kohno Y (1999) MR-revealed myelination in the cerebral corticospinal tract as a marker for Pelizaeus-Merzbacher’s disease with proteolipid protein gene duplication. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1822–1828
Inoue K, Tanaka H, Scaglia F, Araki A, Shaffer LG, Lupski JR (2001) Compensating for central nervous system dysmyelination: females with a proteolipid protein gene duplication and sustained clinical improvement. Ann Neurol 50:747–754
Bonavita S, Schiffmann R, Moore DF, Frei K, Choi B, Patronas MN, Virta A, Boespflug-Tanguy O, Tedeschi G (2001) Evidence for neuroaxonal injury in patients with proteolipid protein gene mutations. Neurology 56:785–788
Garbern JY, Yool DA, Moore GJ, Wilds IB, Faulk MW, Klugmann M, Nave KA, Sistermans EA, van der Knaap MS, Bird TD, Shy ME, Kamholz JA, Griffiths IR (2002) Patients lacking the major CNS myelin protein, proteolipid protein 1, develop length-dependent axonal degeneration in the absence of demyelination and inflammation. Brain 125:551–561
Hobson GM, Huang Z, Sperle K, Stabley DL, Marks HG, Cambi F (2002) A PLP splicing abnormality is associated with an unusual presentation of PMD. Ann Neurol 52:477–488
Nezu A, Kimura S, Takeshita S, Osaka H, Kimura K, Inoue K (1998) An MRI and MRS study of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Pediatr Neurol 18:334–337
Pizzini F, Fatemi AS, Barker PB, Nagae-Poetscher LM, Horska A, Zimmerman AW, Moser HW, Bibat G, Naidu S (2003) Proton MR spectroscopic imaging in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1683–1689
Spalice A, Popolizio T, Parisi P, Scarabino T, Iannetti P (2000) Proton MR spectroscopy in connatal Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Pediatr Radiol 30:171–175
Takanashi J, Sugita K, Osaka H, Ishii M, Niimi H (1997) Proton MR spectroscopy in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:533–535
Takanashi J, Inoue K, Tomita M, Kurihara A, Morita F, Ikehira H, Tanada S, Yoshitome E, Kohno Y (2002) Brain N-acetylaspartate is elevated in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease with PLP1 duplication. Neurology 58:237–241
Bjartmar C, Battistuta J, Terada N, Dupree E, Trapp BD (2002) N-acetylaspartate is an axon-specific marker of mature white matter in vivo: a biochemical and immunohistochemical study on the rat optic nerve. Ann Neurol 51:51–58
Nave KA, Lai C, Bloom FE, Milner RJ (1987) Splice site selection in the proteolipid protein (PLP) gene transcript and primary structure of the DM-20 protein of central nervous system myelin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:5665–5669
Weimbs T, Stoffel W (1992) Proteolipid protein (PLP) of CNS myelin: positions of free, disulfide-bonded, and fatty acid thioester-linked cysteine residues and implications for the membrane topology of PLP. Biochemistry 31:12289–12296
Gow A, Gragerov A, Gard A, Colman DR, Lazzarini RA (1997) Conservation of topology, but not conformation, of the proteolipid proteins of the myelin sheath. J Neurosci 17:181–189
Popot JL, Pham Dinh D, Dautigny A (1991) Major myelin proteolipid: the 4-alpha-helix topology. J Membr Biol 123:278
Bongarzone ER, Campagnoni CW, Kampf K, Jacobs EC, Handley VW, Schonmann V, Campagnoni AT (1999) Identification of a new exon in the myelin proteolipid protein gene encoding novel protein isoforms that are restricted to the somata of oligodendrocytes and neurons. J Neurosci 19:8349–8357
Jacobs EC, Bongarzone ER, Campagnoni CW, Kampf K, Campagnoni AT (2003) Soma-restricted products of the myelin proteolipid gene are expressed primarily in neurons in the developing mouse nervous system. Dev Neurosci 25:96–104
Nave KA, Lemke G (1991) Induction of the myelin proteolipid protein (PLP) gene in C6 glioblastoma cells: functional analysis of the PLP promotor. J Neurosci 11:3060–3069
Berndt JA, Kim JG, Hudson LD (1992) Identification of cis-regulatory elements in the myelin proteolipid protein (PLP) gene. J Biol Chem 267:14730–14737
Wight PA, Dobretsova A (2004) Where, when and how much: regulation of myelin proteolipid protein gene expression. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:810–821
Klugmann M, Schwab MH, Puhlhofer A, Schneider A, Zimmermann F, Griffiths IR, Nave KA (1997) Assembly of CNS myelin in the absence of proteolipid protein. Neuron 18:59–70
Boison D, Stoffel W (1994) Disruption of the compacted myelin sheath of axons of the central nervous system in proteolipid protein-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:11709–11713
Jurevics H, Hostettler J, Sammond DW, Nave KA, Toews AD, Morell P (2003) Normal metabolism but different physical properties of myelin from mice deficient in proteolipid protein. J Neurosci Res 71:826–834
Garbern JY, Cambi F, Tang X-M, Sima AA, Vallat JM, Bosch EP, Lewis R, Shy M, Sohi J, Kraft G, Chen KL, Joshi I, Leonard DG, Johnson W, Raskind W, Dlouhy SR, Pratt V, Hodes ME, Bird T, Kamholz J (1997) Proteolipid protein is necessary in peripheral as well as central myelin. Neuron 19:205–218
Boison D, Bussow H, D’Urso D, Muller HW, Stoffel W (1995) Adhesive properties of proteolipid protein are responsible for the compaction of CNS myelin sheaths. J Neurosci 15:5502–5513
Griffiths I, Klugmann M, Anderson T, Yool D, Thomson C, Schwab MH, Schneider A, Zimmermann F, McCulloch M, Nadon N, Nave KA (1998) Axonal swellings and degeneration in mice lacking the major proteolipid of myelin. Science 280:1610–1613
Ikenaka K, Kagawa T, Mikoshiba K (1992) Selective expression of DM-20, an alternatively spliced myelin proteolipid protein gene product, in developing nervous system and in nonglial cells. J Neurochem 58:2248–2253
Peyron F, Timsit S, Thomas JL, Kagawa T, Ikenaka K, Zalc B (1997) In situ expression of PLP/DM-20, MBP, and CNP during embryonic and postnatal development of the jimpy mutant and of transgenic mice overexpressing PLP. J Neurosci Res 50:190–201
Timsit S, Martinez S, Allinquant B, Peyron F, Puelles L, Zalc B (1995) Oligodendrocytes originate in a restricted zone of the embryonic ventral neural tube defined by DM-20 mRNA expression. J Neurosci 15:1012–1024
Yu WP, Collarini EJ, Pringle NP, Richardson WD (1994) Embryonic expression of myelin genes: evidence for a focal source of oligodendrocyte precursors in the ventricular zone of the neural tube. Neuron 12:1353–1362
Nery S, Wichterle H, Fishell G (2001) Sonic hedgehog contributes to oligodendrocyte specification in the mammalian forebrain. Development 128:527–540
Zhou Q, Wang S, Anderson D.J (2000) Identification of a novel family of oligodendrocyte lineage-specific basic helix–loop–helix transcription factors. Neuron 25:331–343
Lu QR, Yuk D, Alberta JA, Zhu Z, Pawlitzky I, Chan J, McMahon AP, Stiles CD, Rowitch DH (2000) Sonic hedgehog-regulated oligodendrocyte lineage genes encoding bHLH proteins in the mammalian central nervous system. Neuron 25:317–329
Chandran S, Kato H, Gerreli D, Compston A, Svendsen CN, Allen ND (2003) FGF-dependent generation of oligodendrocytes by a hedgehog-independent pathway. Development 130:6599–6609
Griffiths IR, Dickinson P, Montague P (1995) Expression of the proteolipid protein gene in glial cells of the post-natal peripheral nervous system of rodents. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 21:97–110
Richardson WD, Pringle NP, Yu WP, Hall AC (1997) Origins of spinal cord oligodendrocytes: possible developmental and evolutionary relationships with motor neurons. Dev Neurosci 19:58–68
Jacobs EC, Bongarzone ER, Campagnoni CW, Campagnoni AT (2004) Embryonic expression of the soma-restricted products of the myelin proteolipid gene in motor neurons and muscle. Neurochem Res 29:997–1002
Campagnoni CW, Garbay B, Micevych P, Pribyl T, Kampf K, Handley VW, Campagnoni AT (1992) DM 20 mRNA splice product of the myelin proteolipid protein gene is expressed in the murine heart. J Neurosci Res 33:148–155
Feng JM, Fernandes AO, Bongarzone ER, Campagnoni CW, Kampf K, Campagnoni AT (2003) Expression of soma-restricted proteolipid/DM 20 proteins in lymphoid cells. J Neuroimmunol 144:9–15
Pribyl TM, Campagnoni CW, Kampf K, Kashima T, Handley VW, McMahon J, Campagnoni AT (1996) Expression of the myelin proteolipid protein gene in the human fetal thymus. J Neuroimmunol 67:125–130
Bruno R, Sabater L, Sospedra M, Ferrer-Francesch X, Escudero D, Martinez-Caceres E, Pujol-Borrell R (2002) Multiple sclerosis candidate autoantigens except myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein are transcribed in human thymus. Eur J Immunol 32:2737–2747
Shy ME, Hobson G, Jain M, Boespflug-Tanguy O, Garbern J, Sperle K, Li W, Gow A, Rodriguez D, Bertini E, Mancias P, Krajewski K, Lewis R, Kamholz J (2003) Schwann cell expression of PLP1 but not DM 20 is necessary to prevent neuropathy. Ann Neurol 53:354–365
Kitagawa K, Sinoway MP, Yang C, Gould RM, Colman DR (1993) A proteolipid protein gene family: expression in sharks and rays and possible evolution from an ancestral gene encoding a pore-forming polypeptide. Neuron 11:433–448
Yoshida M, Colman DR (1996) Parallel evolution and coexpression of the proteolipid proteins and protein zero in vertebrate myelin. Neuron 16:1115–1126
Yan Y, Lagenaur C, Narayanan C. (1993) Molecular cloning of M6: identification of a PLP/DM 20 gene family. Neuron 11:423–431
Stecca B, Southwood CM, Gragerov A, Kelley KA, Friedrich VL Jr, Gow A (2000) The evolution of lipophilin genes from invertebrates to tetrapods: DM-20 cannot replace proteolipid protein in CNS myelin. J Neurosci 20:4002–4010
Boucher SE, Cypher MA, Carlock LR, Skoff RP (2002) Proteolipid protein gene modulates viability and phenotype of neurons. J Neurosci 22:1772–1783
Ye P, Bagnell R, D’Ercole AJ (2003) Mouse NG2+ oligodendrocyte precursors express mRNA for proteolipid protein but not its DM-20 variant: a study of laser microdissection-captured NG2+ cells. J Neurosci 23:4401–4405
Yamaguchi Y, Ikenaka K, Niinobe M, Yamada H, Mikoshiba K (1996) Myelin proteolipid protein (PLP), but not DM-20, is an inositol hexakisphosphate-binding protein. J Biol Chem 271:27838–27846
Gudz TI, Schneider TE, Haas TA, Macklin WB (2002) Myelin proteolipid protein forms a complex with integrins and may participate in integrin receptor signaling in oligodendrocytes. J Neurosci 22:7398–7407
Sivakumar K, Sambuughin N, Selenge B, Nagle JW, Baasanjav D, Hudson LD, Goldfarb LG (1999) Novel exon 3B proteolipid protein gene mutation causing late-onset spastic paraplegia type 2 with variable penetrance in female family members. Ann Neurol 45:680–683
Bond C, Si X, Crisp M, Wong P, Paulson GW, Boesel CP, Dlouhy SR, Hodes ME (1997) Family with Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease/X-linked spastic paraplegia and a nonsense mutation in exon 6 of the proteolipid protein gene. Am J Med Genet 71:357–360
Inoue K, Khajavi M, Ohyama T, Hirabayashi S, Wilson J, Reggin JD, Mancias P, Butler IJ, Wilkinson MF, Wegner M, Lupski JR (2004) Molecular mechanism for distinct neurological phenotypes conveyed by allelic truncating mutations. Nat Genet 36:361–369
Gow A, Lazzarini RA (1996) A cellular mechanism governing the severity of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Nat Genet 13:422–428
Raskind WH, Williams CA, Hudson LD, Bird TD (1991) Complete deletion of the proteolipid protein gene (PLP) in a family with X-linked Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Am J Hum Genet 49:1355–1360
Sistermans EA, de Wijs IJ, de Coo RFM, Smit LM, Menko FH, van Oost BA (1996) A (G-to-A) mutation in the initiation codon of the proteolipid protein gene causing a relatively mild form of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease in a Dutch family. Hum Genet 97:337–339
Inoue K, Osaka H, Thurston VC, Clarke JTR, Yoneyama A, Rosenbarker L, Bird TD, Hodes ME, Shaffer LG, Lupski JR (2002) Genomic rearrangements resulting in PLP1 deletion occur by non-homologous end-joining and cause different dysmyelinating phenotypes in males and females. Am J Hum Genet 71:838–853
Griffiths I, Klugmann M, Anderson T, Thomson C, Vouyiouklis D, Nave KA (1998) Current concepts of PLP and its role in the nervous system. Microsc Res Tech 41:344–358
Knapp PE, Skoff RP, Redstone DW (1986) Oligodendroglial cell death in jimpy mice: an explanation for the myelin deficit. J Neurosci 6:2813–2822
Gow A, Southwood CM, Lazzarini RA (1998) Disrupted proteolipid protein trafficking results in oligodendrocyte apoptosis in an animal model of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. J Cell Biol 140:925–934
Knapp PE, Bartlett WP, Williams LA, Yamada M, Ikenaka K, Skoff RP (1999) Programmed cell death without DNA fragmentation in the jimpy mouse: secreted factors can enhance survival. Cell Death Differ 6:136–145
Schneider AM, Griffiths IR, Readhead C, Nave KA (1995) Dominant-negative action of the jimpy mutation in mice complemented with an autosomal transgene for myelin proteolipid protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:4447–4451
Nadon NL, Arnheiter H, Hudson LD (1994) A combination of PLP and DM 20 transgenes promotes partial myelination in the jimpy mouse. J Neurochem 63:822–833
Southwood C, Gow A (2001) Molecular pathways of oligodendrocyte apoptosis revealed by mutations in the proteolipid protein gene. Microsc Res Tech 52:700–708
Swanton E, High S, Woodman P (2003) Role of calnexin in the glycan-independent quality control of proteolipid protein. EMBO J 22:2948–2958
Southwood CM, Garbern J, Jiang W, Gow A (2002) The unfolded protein response modulates disease severity in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Neuron 36:585–596
Gow A, Sharma R (2003) The unfolded protein response in protein aggregating diseases. Neuromolecular Med 4:73–94
Forman MS, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2003) “Unfolding” pathways in neurodegenerative disease. Trends Neurosci 26:407–410
Osaka H, Kawanishi C, Inoue K, Onishi H, Kobayashi T, Sugiyama N, Kosaka K, Nezu A, Fujii K, Sugita K, Kodama K, Murayama K, Murayama S, Kanazawa I, Kimura S (1999) Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease: three novel mutations and implication for locus heterogeneity. Ann Neurol 45:59–64
Vaurs-Barriere C, Wong K, Weibel TD, Abu-Asab M, Weiss MD, Kaneski CR, Mixon TH, Bonavita S, Creveaux I, Heiss JD, Tsokos M, Goldin E, Quarles RH, Boespflug-Tanguy O, Schiffmann R (2003) Insertion of mutant proteolipid protein results in missorting of myelin proteins. Ann Neurol 54:769–780
Aoyagi Y, Kobayashi H, Tanaka K, Ozawa T, Nitta H, Tsuji S (1999) A de novo splice donor site mutation causes in-frame deletion of 14 amino acids in the proteolipid protein in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Ann Neurol 46:112–115
Hobson GM, Davis AP, Stowell NC, Kolodny EH, Sistermans EA, de Coo IF, Funanage VL, Marks HG (2000) Mutations in noncoding regions of the proteolipid protein gene in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Neurology 55:1089–1096
Inoue K, Osaka H, Imaizumi K, Nezu A, Takanashi J, Arii J, Murayama K, Ono J, Kikawa Y, Mito T, Shaffer LG, Lupski JR (1999) Proteolipid protein gene duplications causing Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease: molecular mechanism and phenotypic manifestations. Ann Neurol 45:624–632
Sistermans EA, de Coo RFM, De Wijs IJ, Van Oost BA (1998) Duplication of the proteolipid protein gene is the major cause of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Neurology 50:1749–1754
Mimault C, Giraud G, Courtois V, Cailloux F, Boire JY, Dastugue B, Boespflug-Tanguy O (1999) Proteolipoprotein gene analysis in 82 patients with sporadic Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease: duplications, the major cause of the disease, originate more frequently in male germ cells, but point mutations do not. Am J Hum Genet 65:360–369
Woodward K, Kendall E, Vetrie D, Malcolm S. (1998) Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease: identification of Xq22 proteolipid-protein duplications and characterization of breakpoints by interphase FISH. Am J Hum Genet 63:207–217
Inoue K, Osaka H, Sugiyama N, Kawanishi C, Onishi H, Nezu A, Kimura K, Kimura S, Yamada Y, Kosaka K (1996) A duplicated PLP gene causing Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease detected by comparative multiplex PCR. Am J Hum Genet 59:32–39
Ellis D, Malcolm S (1994) Proteolipid protein gene dosage effect in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Nat Genet 6:333–334
Lupski JR (1998) Genomic disorders: structural features of the genome can lead to DNA rearrangements and human disease traits. Trends Genet 14:417–422
Inoue K, Lupski JR (2002) Molecular mechanisms for genomic disorders. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 3:199–242
Stankiewicz P, Lupski JR (2002) Genome architecture, rearrangements and genomic disorders. Trends Genet 18:74–82
Woodward K, Palmer R, Rao K, Malcolm S. (1999) Prenatal diagnosis by FISH in a family with Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease caused by duplication of PLP gene. Prenat Diagn 19:266–268
Inoue K, Kanai M, Tanabe Y, Kubota T, Kashork CD, Wakui K, Fukushima Y, Lupski JR, Shaffer LG (2001) Prenatal interphase FISH diagnosis of PLP1 duplication associated with Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Prenat Diagn 21:1133–1136
Garbern J, Hobson G. (2002) Prenatal diagnosis of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Prenat Diagn 22:1033–1035
Shiraishi K, Itoh M, Sano K, Takashima S, Kubota T (2003) Myelination of a fetus with Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease: immunopathological study. Ann Neurol 54:259–262
Kagawa T, Ikenaka K, Inoue Y, Kuriyama S, Tsujii T, Nakao J, Nakajima K, Aruga J, Okano H, Mikoshiba K (1994) Glial cell degeneration and hypomyelination caused by overexpression of myelin proteolipid protein gene. Neuron 13:427–442
Readhead C, Schneider A, Griffiths I, Nave KA (1994) Premature arrest of myelin formation in transgenic mice with increased proteolipid protein gene dosage. Neuron 12:583–595
Anderson TJ, Schneider A, Barrie JA, Klugmann M, McCulloch MC, Kirkham D, Kyriakides E, Nave KA, Griffiths IR (1998) Late-onset neurodegeneration in mice with increased dosage of the proteolipid protein gene. J Comp Neurol 394:506–519
Inoue Y, Kagawa T, Matsumura Y, Ikenaka K, Mikoshiba K (1996) Cell death of oligodendrocytes or demyelination induced by overexpression of proteolipid protein depending on expressed gene dosage. Neurosci Res 25:161–172
Simons M, Kramer EM, Macchi P, Rathke-Hartlieb S, Trotter J, Nave KA, Schulz JB (2002) Overexpression of the myelin proteolipid protein leads to accumulation of cholesterol and proteolipid protein in endosomes/lysosomes: implications for Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. J Cell Biol 157:327–336
Cerghet M, Bessert DA, Nave KA, Skoff RP (2001) Differential expression of apoptotic markers in jimpy and in Plp overexpressors: evidence for different apoptotic pathways. J Neurocytol 30:841–855
Simons M, Kramer EM, Thiele C, Stoffel W, Trotter J (2000) Assembly of myelin by association of proteolipid protein with cholesterol- and galactosylceramide-rich membrane domains. J Cell Biol 151:143–154
Shaw CJ, Lupski JR (2004) Implications of human genome architecture for rearrangement-based disorders: the genomic basis of disease. Hum Mol Genet 13:R57–64
Hodes ME, Woodward K, Spinner NB, Emanuel BS, Enrico-Simon A, Kamholz J, Stambolian D, Zackai EH, Pratt VM, Thomas IT, Crandall K, Dlouhy SR, Malcolm S. (2000) Additional copies of the proteolipid protein gene causing Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease arise by separate integration into the X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet 67:14–22
Ida T, Miharu N, Hayashitani M, Shimokawa O, Harada N, Samura O, Kubota T, Niikawa N, Matsumoto N. (2003) Functional disomy for Xq22-q23 in a girl with complex rearrangements of chromosomes 3 and X. Am J Med Genet 120A:557–561
Woodward K, Cundall M, Palmer R, Surtees R, Winter RM, Malcolm S (2003) Complex chromosomal rearrangement and associated counseling issues in a family with Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Am J Med Genet 118A:15–24
Saito-Ohara F, Fukuda Y, Ito M, Agarwala KL, Hayashi M, Matsuo M, Imoto I, Yamakawa K, Nakamura Y, Inazawa J (2002) The Xq22 inversion breakpoint interrupted a novel Ras-like GTPase gene in a patient with Duchenne muscular dystrophy and profound mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet 71:637–645
Lazzarini A, Schwarz KO, Jiang S, Stenroos ES, Lehner T, Johnson WG, (1997) Pelizaeus-Merzbacher-like disease: exclusion of the proteolipid protein locus and documentation of a new locus on Xq. Neurology 49:824–832
Uhlenberg B, Schuelke M, Rüschendorf F, Ruf N, Kaindl AM, Henneke M, Thiele H, Stoltenburg-Didinger G, Aksu F, Topaloglu H, Nürnberg P, Hübner C, Weschke B, Gärtner J (2004) Mutations in the gene encoding gap junction protein α12 (connexin 46.6) cause Pelizaeus-Merzbacher-like disease. Am J Hum Genet 75:251–260
Kuhlbrodt K, Herbarth B, Sock E, Hermans-Borgmeyer I, Wegner M (1998) Sox10, a novel transcriptional modulator in glial cells. J Neurosci 18:237–250
Stolt CC, Rehberg S, Ader M, Lommes P, Riethmacher D, Schachner M, Bartsch U, Wegner M (2002) Terminal differentiation of myelin-forming oligodendrocytes depends on the transcription factor Sox10. Genes Dev 16:165–170
Inoue K, Tanabe Y, Lupski J (1999) Myelin deficiencies in both the central and peripheral nervous system associated with a SOX10 mutation. Ann Neurol 46:313–318
Inoue K, Shilo K, Boerkoel CF, Crowe C, Sawady J, Lupski JR, Agamanolis DP (2002) Congenital hypomyelinating neuropathy, central dysmyelination, and Waardenburg-Hirschsprung disease: phenotypes linked by SOX10 mutation. Ann Neurol 52:836–842
Pingault V, Girard M, Bondurand N, Dorkins H, Van Maldergem L, Mowat D, Shimotake T, Verma I, Baumann C, Goossens M (2002) SOX10 mutations in chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction suggest a complex physiopathological mechanism. Hum Genet 111:198–206
Touraine RL, Attie-Bitach T, Manceau E, Korsch E, Sarda P, Pingault V, Encha-Razavi F, Pelet A, Auge J, Nivelon-Chevallier A, Holschneider AM, Munnes M, Doerfler W, Goossens M, Munnich A, Vekemans M, Lyonnet S (2000) Neurological phenotype in Waardenburg syndrome type 4 correlates with novel SOX10 truncating mutations and expression in developing brain. Am J Hum Genet 66:1496–1503
Toki F, Suzuki N, Inoue K, Suzuki M, Hirakata K, Nagai K, Kuroiwa M, Lupski JR, Tsuchida Y (2003) Intestinal aganglionosis associated with the Waardenburg syndrome: report of two cases and review of the literature. Pediatr Surg Int 19:725–728
Pingault V, Bondurand N, Le Caignec C, Tardieu S, Lemort N, Dubourg O, Le Guern E, Goossens M, Boespflug-Tanguy O (2001) The SOX10 transcription factor: evaluation as a candidate gene for central and peripheral hereditary myelin disorders. J Neurol 248:496–499
Nance MA, Boyadjiev S, Pratt VM, Taylor S, Hodes ME, Dlouhy S. R (1996) Adult-onset neurodegenerative disorder due to proteolipid protein gene mutation in the mother of a man with Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Neurology 47:1333–1335
Hodes ME, Blank CA, Pratt VM, Morales J, Napier J, Dlouhy SR (1997) Nonsense mutation in exon 3 of the proteolipid protein gene (PLP) in a family with an unusual form of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Am J Med Genet 69:121–125
Hodes ME, DeMyer WE, Pratt VM, Edwards MK, Dlouhy SR (1995) Girl with signs of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease heterozygous for a mutation in exon 2 of the proteolipid protein gene. Am J Med Genet 55:397–401
Bartlett WP, Skoff RP (1986) Expression of the jimpy gene in the spinal cords of heterozygous female mice. I. An early myelin deficit followed by compensation. J Neurosci 6:2802–2812
Bartlett WP, Skoff RP (1989) Expression of the jimpy gene in the spinal cords of heterozygous female mice. 2. Oligodendroglial and endothelial cell hyperplasia. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 47:1–11
Kagawa T, Nakao J, Yamada M, Shimizu K, Hayakawa T, Mikoshiba K, Ikenaka K (1994) Fate of jimpy-type oligodendrocytes in jimpy heterozygote. J Neurochem 62:1887–1893
Fanarraga ML, Griffiths IR, McCulloch MC, Barrie JA, Cattanach BM, Brophy PJ, Kennedy PG (1991) Rumpshaker: an X-linked mutation affecting CNS myelination. A study of the female heterozygote. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 17:323–334
Cuddon PA, Lipsitz D, Duncan ID (1998) Myelin mosaicism and brain plasticity in heterozygous females of a canine X-linked trait. Ann Neurol 44:771–779
Woodward K, Kirtland K, Dlouhy S, Raskind W, Bird T, Malcolm S, Abeliovich D (2000) X-inactivation phenotype in carriers of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease: skewed in carriers of a duplication and random in carriers of point mutations. Eur J Hum Genet 8:449–454
Edgar JM, Anderson TJ, Dickinson PJ, Barrie JA, McCulloch MC, Nave KA, Griffiths IR (2002) Survival of, and competition between, oligodendrocytes expressing different alleles of the Plp gene. J Cell Biol 158:719–729
Filbin MT (2003) Myelin-associated inhibitors of axonal regeneration in the adult mammalian CNS. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:703–713
Popko B (2003) Notch signaling: a rheostat regulating oligodendrocyte differentiation? Dev Cell 5:668–669
Frost EE, Buttery PC, Milner R, ffrench-Constant C (1999) Integrins mediate a neuronal survival signal for oligodendrocytes. Curr Biol 9:1251–1254
Colello RJ, Pott U (1997) Signals that initiate myelination in the developing mammalian nervous system. Mol Neurobiol 15:83–100
Rosenfeld J, Freidrich VL Jr (1983) Axonal swellings in jimpy mice: does lack of myelin cause neuronal abnormalities? Neuroscience 10:959–966
Edgar JM, McLaughlin M, Yool D, Zhang SC, Fowler JH, Montague P, Barrie JA, McCulloch MC, Duncan ID, Garbern J, Nave KA, Griffiths IR (2004) Oligodendroglial modulation of fast axonal transport in a mouse model of hereditary spastic paraplegia. J Cell Biol 166:121–131
Lappe-Siefke C, Goebbels S, Gravel M, Nicksch E, Lee J, Braun PE, Griffiths IR, Nave KA (2003) Disruption of Cnp1 uncouples oligodendroglial functions in axonal support and myelination. Nat Genet 33:366–374
Helynck G, Luu B, Nussbaum JL, Picken D, Skalidis G, Trifilieff E, Van Dorsselaer A, Seta P, Sandeaux R, Gavach C, Heitz F, Simon D, Spach D (1983) Brain proteolipids. Isolation, purification and effect on ionic permeability of membranes. Eur J Biochem 133:689–695
Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN, Anderson KC, Glimcher LH (2003) Proteasome inhibitors disrupt the unfolded protein response in myeloma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:9946–9951
Passage E, Norreel JC, Noack-Fraissignes P, Sanguedolce V, Pizant J, Thirion X, Robaglia-Schlupp A, Pellissier JF, Fontés M (2004) Ascorbic acid treatment corrects the phenotype of a mouse model of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Nat Med 10:396–401
Sereda MW, Meyer zu Horste G, Suter U, Uzma N, Nave KA (2003) Therapeutic administration of progesterone antagonist in a model of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT-1A). Nat Med 9:1533–1537
Brüstle O, Jones KN, Learish RD, Karram K, Choudhary K, Wiestler OD, Duncan ID, McKay RD (1999) Embryonic stem cell-derived glial precursors: a source of myelinating transplants. Science 285:754–756
Liu S, Qu Y, Stewart TJ, Howard MJ, Chakrabortty S, Holekamp TF, McDonald JW (2000) Embryonic stem cells differentiate into oligodendrocytes and myelinate in culture and after spinal cord transplantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6126–6131
Mitome M, Low HP, van den Pol A, Nunnari JJ, Wolf MK, Billings-Gagliardi S, Schwartz WJ (2001) Towards the reconstruction of central nervous system white matter using neural precursor cells. Brain 124:2147–2161
Pluchino S, Quattrini A, Brambilla E, Gritti A, Salani G, Dina G, Galli R, Del Carro U, Amadio S, Bergami A, Furlan R, Comi G, Vescovi AL, Martino G (2003) Injection of adult neurospheres induces recovery in a chronic model of multiple sclerosis. Nature 422:688–694
Acknowledgements
I would like to acknowledge Dr. James R. Lupski for his advice and support. I also thank Drs. Hitoshi Osaka, Kimiko Deguchi, Pawel Stankiewicz, and Ms. Jennifer Lee for their critical review. This work is supported in part by Muscular Dystrophy Association Developmental Grant and The Research Grant (16B-1) for Nervous and Mental Disorders from Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan. Information about the Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Disease Foundation is available online (http://www.pmdfoundation.org).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, K. PLP1-related inherited dysmyelinating disorders: Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease and spastic paraplegia type 2. Neurogenetics 6, 1–16 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-004-0207-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-004-0207-y