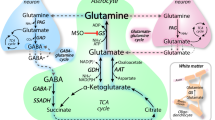
Abstract
Astrocyte cells require cysteine as a substrate for glutamate cysteine ligase (γ-glutamylcysteine synthase; EC 6.3.2.2) catalyst of the rate-limiting step of the γ-glutamylcycle leading to formation of glutathione (l-γ-glutamyl-l-cysteinyl-glycine; GSH). In both astrocytes and glioblastoma/astrocytoma cells, the majority of cysteine originates from reduction of cystine imported by the x −c cystine-glutamate exchanger. However, the transsulfuration pathway, which supplies cysteine from the indispensable amino acid, methionine, has recently been identified as a significant contributor to GSH synthesis in astrocytes. The purpose of this review is to evaluate the importance of the transsulfuration pathway in these cells, particularly in the context of a reserve pathway that channels methionine towards cysteine when the demand for glutathione is high, or under conditions in which the supply of cystine by the x −c exchanger may be compromised.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GSH:
-
l-γ-glutamyl-l-cysteinyl-glycine (glutathione)
- GSSG:
-
Oxidised form of glutathione
- DEM:
-
Diethylmaleate
- H2S:
-
Hydrogen sulfide
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- JNK:
-
c-Jun-N-terminal kinase
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factorκB
- SAPK:
-
Stress-activated protein kinase
- TNFα:
-
Tumour necrosis factorα
- xCT:
-
Subunit of the x −c cystine-glutamate exchanger
References
Aitken SM, Kirsch JF (2005) The enzymology of cystathionine biosynthesis: strategies for the control of substrate and reaction specificity. Arch Biochem Biophys 433:166–175
Banerjee R, Zou CG (2005) Redox regulation and reaction mechanism of human cystathionine-beta-synthase: a PLP-dependent hemesensor protein. Arch Biochem Biophys 433:144–156
Banjac A, Perisic T, Sato H, Seiler A, Bannai S, Weiss N et al (2008) The cystine/cysteine cycle: a redox cycle regulating susceptibility versus resistance to cell death. Oncogene 27:1618–1628
Bannai S (1984) Induction of cystine and glutamate transport activity in human fibroblasts by diethylmaleate and other electrophilic agents. J Biol Chem 259:2435–2440
Beatty PW, Reed DJ (1980) Involvement of the cystathionine pathway in the biosynthesis of glutathione by isolated rat hepatocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys 204:80–87
Benight N, Burrin DG, Stoll B (2009) Intestinal metabolism of sulfur amino acids. In: Masella R, Mazza G (eds) Glutathione and sulfur amino acids in human health and disease. Wiley, New Jersey, pp 47–72
Chiku T, Padovani D, Zhu W, Singh S, Vitvitsky V, Banerjee R (2009) H2S biogenesis by human cystathionine gamma-lyase leads to the novel sulfur metabolites lanthionine and homolanthionine and is responsive to the grade of hyperhomocysteinemia. J Biol Chem 284:11601–11612
Chung WJ, Sontheimer H (2009) Sulfasalazine inhibits the growth of primary brain tumors independent of nuclear factor-κB. J Neurochem 110:182–193
Conrad M, Sato H (2011) The oxidative stress-inducible cystine/glutamate antiporter, system xc−: cystine supplier and beyond. Amino Acids (this issue)
Diwakar L, Ravindranath V (2007) Inhibition of cystathionine-γ-lyase leads to loss of glutathione and aggravation of mitochondrial dysfunction mediated by excitatory amino acid in the CNS. Neurochem Int 50:418–426
Dringen R, Pfeiffer B, Hamprecht B (1999) Synthesis of the antioxidant glutathione in neurons: supply by astrocytes of CysGly as precursor for neuronal glutathione. J Neurosci 19:562–569
Dun Y, Mysona B, Van Ells T, Amarnath L, Shamsul OM, Ganapathy V et al (2006) Expression of the cystine-glutamate exchanger (xc−) in retinal ganglion cells and regulation by nitric oxide and oxidative stress. Cell Tissue Res 324:189–202
Frade J, Pope S, Schmidt M, Dringen R, Barbosa R, Pocock J et al (2008) Glutamate induces release of glutathione from cultured rat astrocytes—a possible neuroprotective mechanism. J Neurochem 105:1144–1152
Grange E, Gharib A, Lepetit P, Guillaud J, Sarda N, Bobillier P (1992) Brain protein synthesis in the conscious rat using l-[35S]methionine: relationship of methionine specific activity between plasma and precursor compartment and evaluation of methionine metabolic pathways. J Neurochem 59:1437–1443
Huang T, Wahlqvist ML, Li D (2010) Docosahexaenoic acid decreases plasma homocysteine via regulating enzyme activity and mRNA expression involved in methionine metabolism. Nutrition 26:112–119
Kandil S, Brennan L, McBean GJ (2010) Glutathione depletion causes a JNK and p38MAPK-mediated increase in expression of cystathionine-γ-lyase and upregulation of the transsulfuration pathway in C6 glioma cells. Neurochem Int 56:611–619
Karunakaran D, Diwakar L, Saeed U, Agarwal V, Ramikrishnan S, Iyengar S et al (2007) Activation of apoptosis signal regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) and translocation of death-associated protein, Daxx, in substantia nigra pars compacta in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: protection by alpha lipoic acid. FASEB J 21:2226–2236
Kato S, Ishita S, Suguwara K, Mawatari K (1993) Cystine/glutamate antiporter expression in retinal Müller glial cells: implications for DL-alpha-aminoadipate toxicity. Neuroscience 57:473–482
Kato T, Shinoda J, Oka N, Miwa K, Nakayama N, Yano H et al (2008) Analysis of 11C-methionine uptake in low-grade gliomas and correlation with proliferative activity. Am J Neuroradiol 29:1867–1871
Kimura H (2010) Hydrogen sulfide: its production, release and functions. Amino Acids. doi:10.1007/s00726-010-0510-x
Kranich O, Dringen R, Sandberg M, Hamprecht B (1998) Utilization of cysteine and cysteine precursors for the synthesis of glutathione in astroglial cultures: preference for cystine. Glia 22:11–18
Krejsa CM, Franklin CC, White CC, Ledbetter JA, Schieven GL, Kavanagh TJ (2010) Rapid activation of glutamate cysteine ligase following oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 285:16116–16124
Kyriakas JM, Avruch J (1996) Sounding the alarm: protein kinase cascades activated by stress and inflammation. J Biol Chem 271:24313–24316
Lee M, Schwab C, Yu S, McGeer E, McGeer PL (2009) Astrocytes produce the antiinflammatory and neuroprotective agent, hydrogen sulfide. Neurobiol Aging 30:1523–1534
Lee SW, Hu YS, Hu LF, Lu Q, Dawe GS, Moore PK et al (2006) Hydrogen sulphide regulates calcium homeostasis in microglial cells. Glia 54:116–124
Lewerenz J, Maher P, Methner A (2011) Regulation of xCT expression and system xc− function in neuronal cells. Amino Acids (this issue)
Li L, Hsu A, Moore PK (2009) Actions and interactions of nitric oxide, carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulfide in the cardiovascular system and in inflammation—a tale of three gases! Pharmacol Ther 123:386–400
Lo M, Wang YZ, Gout PW (2008) The x(c)− cystine/glutamate antiporter: a potential target for therapy of cancer and other diseases. J Cell Physiol 215:593–602
Martín JA, Pereda J, Martínez-López I, Escrig R, Miralles V, Pallardó FV, et al (2007) Oxidative stress as a signal to up-regulate gamma cystathionase in the fetal-to-neonatal transition in rats. Cell Mol Biol 53(Suppl):OL1010–OL1014
Matsumaru K, Cheng J, Kaplowitz N (2003) Mechanisms for sensitization to TNF-induced apoptosis by acute glutathione depletion in murine hepatocytes. Hepatology 37:1425–1434
McBean GJ (2002) Cerebral cystine uptake: a tale of two transporters. Trends Pharmacol Sci 23:299–302
Mosharov E, Cranford MR, Banerjee R (2000) The quantitatively important relationship between homocysteine metabolism and glutathione synthesis by the transsulfuration pathway and its regulation by redox changes. Biochemistry 39:13005–13011
Mysona B, Dun Y, Duplantier J, Ganapathy V, Smith SB (2009) Effects of hyperglycaemia and oxidative stress on the glutamate transporters GLAST and system xc− in mouse retinal Müller glial cells. Cell Tissue Res 335:477–488
Opere CA, Monjok EM, Kulkarni KH, Njie YF, Ohia SE (2009) Regulation of [3H]D-aspartate release from mammalian isolated retinase by hydrogen sulfide. Neurochem Res 34:1962–1968
Pong WW, Stouracova R, Frank N, Kraus JP, Eldred WD (2007) Comparative localization of cystathionine beta-synthase and cystathionine gamma-lyase in retina: differences between amphibians and mammals. J Comp Neurol 505:158–165
Rosado JO, Salvador M, Bonatto D (2007) Importance of the trans-sulfuration pathway in cancer prevention and promotion. Mol Cell Biochem 301:1–12
Ruiz E, Siow RCM, Bartlett SR, Jenner AM, Sato H, Bannai S et al (2003) Vitamin C inhibits diethylmaleate-induced l-cystine transport in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Free Radic Biol Med 34:103–110
Sato H, Tamba M, Kuriyama-Matsumura K, Okuno S, Bannai S (2000) Molecular cloning and expression of human xCT, the light chain of amino acid transport system xc−. Antioxid Redox Signal 2:665–671
Savaskan NE, Heckl A, Hahnen E, Engelhorn T, Doerfler A, Gansladt O et al (2008) Small interfering RNA-mediated xCT silencing in gliomas inhibits neurodegeneration and alleviates brain edema. Nat Med 15:629–632
Singh S, Padovani D, Leslie RA, Chiku T, Banerjee R (2009) Relative contributions of cystathionine beta-synthase and gamma-cystathionase to H2S biogenesis via alternative trans-sulfuration reactions. J Biol Chem 284:22457–22466
Sontheimer H (2008) A role for glutamate in growth and invasion of primary brain tumors. J Neurochem 105:287–295
Tripatara P, Patel NS, Brancaleone V, Renshaw D, Rocha J, Sepodes B et al (2009) Characterisation of cystathionine gamma-lyase/hydrogen sulphide pathway in ischaemia/reperfusion injury: an in vivo study. Eur J Pharmacol 606:205–209
Vitvitsky V, Thomas M, Ghorpade A, Gendleman HE, Banerjee R (2006) A functional transulfuration pathway in the brain links to glutathione homeostasis. J Biol Chem 281:35785–35793
Acknowledgments
The author’s research in this area is supported by Science Foundation Ireland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McBean, G.J. The transsulfuration pathway: a source of cysteine for glutathione in astrocytes. Amino Acids 42, 199–205 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0864-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0864-8