Abstract.
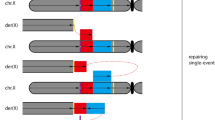
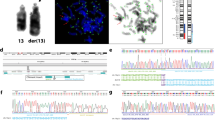
In five families with questionable chromosome rearrangements, we identified an interchromosomal insertion by fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH). In case 1 with a dir ins (5;11)(p14;q14q24) in three generations, the mentally retarded and microcephalic proband showed a 5p14→pter deletion. In case 2, a duplication (13)(q21.31→q31.2) combined with a deletion (11)(q14→q22) segregated from a reciprocal ins(11;13)(q14q122)(q21.32q31.2), causing a mixed phenotype with psychomotor retardation, caput quadratum, choanal atresia, and pes equinovarus. In case 3, a dir ins (18;5)(q21.3;p13.1p14) was associated with spontaneous abortions, in case 4, the proband with mental retardation, microcephaly, and a heart defect showed a pure trisomy of (12)(q13→q15), which had segregated from a carrier of an ins (18;12)(p11.3;q13q15). In case 5, a duplication of (10)(q26.3→q25.2) segregated from an inv ins(5;10)(q15;q26.3q25.2), which was passed on directly from a mother to her son,with mental retardation. In all families the elucidation of the insertional translocation (IT) considerably increased the associated genetic risks of carriers. For the review, we collected data from 81 articles on 87 IT probands on ascertainment, origin, familial transmittance, progeny, and genetic risks of IT carriers. We also discussed the recombinant chromosomes and complex rearrangements associated with ITs, and listed chromosome regions occurring solely as deletions, or solely as duplications, or as both to facilitate genotype/phenotype correlations. We conclude that ITs are rare chromosomal rearrangements with an 1:80,000 incidence, of which nearly 80% were referred because of congenital abnormalities and mental retardation. A maternal origin was seen in 59.5%, a paternal origin in 26.6%, and 13.9% were de novo. No notable difference in fertility between male and female IT carriers was noticed. Bias of ascertainment was excluded in 15 familial cases and led to an estimate of the genetic risks for IT carriers of 32.0–36.0%. The mean size of the inserted regions occurring solely as duplications (n=39) measures 0.96% of the haploid autosomal length (HAL), and of regions solely occurring as deletions (n=14) 0.47% HAL. In the families where both aneusomies occurred, the size of the insertions ranged between 0.22 and 1.21% HAL. Overall, the findings fit with the general idea that a surplus of genetic material is tolerated more easily than a deficiency.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Hemel, J., Eussen, H. Interchromosomal insertions. Hum Genet 107, 415–432 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390000398
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004390000398