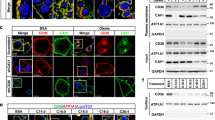
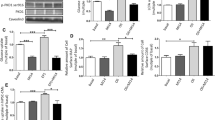
Abstract
Cardiac uptake of long-chain fatty acids (FA) is mediated predominantly by two membrane-associated proteins, the 43-kDa plasma membrane fatty acid-binding protein (FABPpm) and the 88-kDa fatty acid translocase/CD36 (FAT/CD36). While FABPpm is present constitutively in the sarcolemma, FAT/CD36 is recycled between an intracellular membrane compartment and the sarcolemma. Since the amount of sarcolemmal FAT/CD36 is a major determinant of cellular FA uptake, understanding of the regulation of its recycling is likely to provide new insights into altering substrate preference of the heart. FAT/CD36 recycling displays a remarkable similarity with that of the two glucose transporters (GLUT) in the heart, GLUT1 and GLUT4. Translocation of all three transporters is induced by insulin and by contraction, which stimuli activate distinct signalling cascades. The insulin pathway involves phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K) whilst the contraction pathway is dependent on AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). For the identification of additional protein components involved in the regulation of FAT/CD36 recycling, valuable lessons can be learned from GLUT1 and GLUT4 recycling. Especially GLUT4 recycling is an intensively studied process in which a number of signalling proteins, both upstream and downstream from PI3 K and AMPK, have been identified, as well as proteins that are part of the translocation machinery involving Rab GTPases and soluble N-ethylmaleimide attachment protein receptors (SNAREs). Comparison of the magnitude of the effects of insulin and contraction on substrate uptake and on transporter appearance in the sarcolemma have revealed that FAT/CD36 recycling resembles GLUT1 recycling more closely than that of GLUT4. This pinpoints the recycling compartment and excludes a pre-endosomal storage compartment as the intracellular storage site for FAT/CD36. Further research will probably establish whether FAT/CD36 translocation is (partly) coupled to that of one or both GLUTs or, alternatively, whether it is a distinct process that also can be induced independently of GLUT1 or GLUT4 movement. In the latter case, a unique set of proteins would be dedicated to FAT/CD36 recycling, which would then provide an attractive target for manipulating cardiac substrate preference.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AICAR :
-
5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxyamide-1-β-d-ribofuranoside, cell-permeable activator of AMPK
- AMPK :
-
AMP-activated protein kinase
- amrinone :
-
specific inhibitor of phosphodiesterase III
- CPT-I :
-
carnitine palmitoyl transferase I
- dibutyryl cyclic AMP :
-
cell-permeable analogue of cyclic AMP, mimics cyclic AMP-activated signalling
- DNP :
-
2,4-dinitrophenol, mitochondrial uncoupling agent
- ERK :
-
extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- etomoxir :
-
specific inhibitor of CPT-I
- FA :
-
long-chain fatty acid(s)
- FABPpm :
-
plasma membrane fatty acid-binding protein
- FAT/CD36 :
-
fatty acid translocase/CD36
- GTPγS :
-
guanosine 5′-O-(3-thiotriphosphate), non-hydrolysable GTP analogue, locks Rab proteins in a persistently active state
- IGF-II :
-
insulin-like growth factor II
- 5-iodotubercidin :
-
specific inhibitor of adenosine kinase, prevents conversion of AICAR into ZMP
- IRAP :
-
insulin-responsive aminopeptidase
- IRS :
-
insulin receptor substrate
- isoproterenol :
-
potent β-agonist
- myristoylated PKCζ pseudosubstrate :
-
cell-permeable, specific inhibitor of atypical PKCs
- oligomycin :
-
potent inhibitor of mitochondrial F1F0-ATPase
- PD98059 :
-
specific inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling
- PI3K :
-
phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase
- PKB (PKB/Akt):
-
protein kinase B
- PKC :
-
protein kinase C
- rotenone :
-
inhibitor of electron transfer in mitochondria
- SCAMP :
-
secretory carrier membrane protein
- SNAP23 :
-
synaptosomal-associated protein (23 kDa)
- SNARE :
-
soluble N-ethylmaleimide attachment protein receptor
- SSO :
-
sulpho-N-succinimidyloleate, specific inhibitor of transport function of FAT/CD36
- VAMP2 (-3):
-
vesicle-associated membrane protein-2 (-3)
- VAP33 :
-
vesicle-associated protein 33
- wortmannin :
-
inhibitor of PI3K
- ZMP :
-
5′-monophosphate of AICAR
References
Abumrad NA, el-Maghrabi MR, Amri EZ, Lopez E, Grimaldi PA (1993) Cloning of a rat adipocyte membrane protein implicated in binding or transport of long-chain fatty acids that is induced during preadipocyte differentiation. Homology with human CD36. J Biol Chem 268:17665–17668
Aledo JC, Lavoie L, Volchuk A, Keller SR, Klip A, Hundal HS (1997) Identification and characterization of two distinct intracellular GLUT4 pools in rat skeletal muscle: evidence for an endosomal and an insulin-sensitive GLUT4 compartment. Biochem J 325:727–732
Baldini G, Hohman R, Charron MJ, Lodish HF (1991) Insulin and nonhydrolyzable GTP analogs induce translocation of GLUT 4 to the plasma membrane in alpha-toxin-permeabilized rat adipose cells. J Biol Chem 266:4037–4040
Becker C, Sevilla L, Tomas E, Palacin M, Zorzano A, Fischer Y (2001) The endosomal compartment is an insulin-sensitive recruitment site for GLUT4 and GLUT1 glucose transporters in cardiac myocytes. Endocrinology 142:5267–5276
Bergemann C, Loken C, Becker C, Graf B, Hamidizadeh M, Fischer Y (2001) Inhibition of glucose transport by cyclic GMP in cardiomyocytes. Life Sci 69:1391–1406
Bonen A, Luiken JJFP, Arumugam Y, Glatz JFC, Tandon NN (2000) Acute regulation of fatty acid uptake involves the cellular redistribution of fatty acid translocase. J Biol Chem 275:14501–14508
Bonen A, Luiken JJ, Glatz JFC (2002) Regulation of fatty acid transport and membrane transporters in health and disease. Mol Cell Biochem 239:181–192
Brooks CC, Scherer PE, Cleveland K, Whittemore JL, Lodish HF, Cheatham B (2000) Pantophysin is a phosphoprotein component of adipocyte transport vesicles and associates with GLUT4-containing vesicles. J Biol Chem 275:2029–2036
Bryant NJ, Govers R, James DE (2002) Regulated transport of the glucose transporter GLUT4. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:267–277
Bucci C, Parton RG, Mather IH, Stunnenberg H, Simons K, Hoflack B, Zerial M (1992) The small GTPase rab5 functions as a regulatory factor in the early endocytic pathway. Cell 70:715–728
Calera MR, Martinez C, Liu H, Jack AK, Birnbaum MJ, Pilch PF (1998) Insulin increases the association of Akt-2 with Glut4-containing vesicles. J Biol Chem 273:7201–7204
Chavrier P, Parton RG, Hauri HP, Simons K, Zerial M (1990) Localization of low molecular weight GTP binding proteins to exocytic and endocytic compartments. Cell 62:317–329
Cheatham B (2000) GLUT4 and company: SNAREing roles in insulin-regulated glucose uptake. Trends Endocrinol Metab 11:356–361
Chen HC, Bandyopadhyay G, Sajan MP, Kanoh Y, Standaert M, Farese RV Jr, Farese RV (2002) Activation of the ERK pathway and atypical protein kinase C isoforms in exercise- and aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-d-riboside (AICAR)-stimulated glucose transport. J Biol Chem 277:23554–23562
Coderre L, Kandror KV, Vallega G, Pilch PF (1995) Identification and characterization of an exercise-sensitive pool of glucose transporters in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 270:27584–27588
Coe NR, Smith AJ, Frohnert BI, Watkins PA, Bernlohr DA (1999) The fatty acid transport protein (FATP1) is a very long chain acyl-CoA synthetase. J Biol Chem 274:36300–36304
Coort SLM, Willems J, Coumans WA, van der Vusse GJ, Bonen A, Glatz JFC, Luiken JJFP (????) Sulfo-N-succinimidyl esters of long chain fatty acids specifically inhibit fatty acid translocase (FAT/CD36)-mediated cellular fatty acid uptake. Mol Cell Biochem 239:213–219
Cormont M, Tanti JF, Zahraoui A, Van Obberghen E, Tavitian A, Le Marchand-Brustel Y (1993) Insulin and okadaic acid induce Rab4 redistribution in adipocytes. J Biol Chem 268:19491–19497
Derave W, Ai H, Ihlemann J, Witters LA, Kristiansen S, Richter EA, Ploug T (2000) Dissociation of AMP-activated protein kinase activation and glucose transport in contracting slow-twitch muscle. Diabetes 49:1281–1287
Donthi RV, Huisamen B, Lochner A (2000) Effect of vanadate and insulin on glucose transport in isolated adult rat cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 14:463–470
Dransfeld O, Uphues I, Sasson S, Schurmann A, Joost HG, Eckel J (2000) Regulation of subcellular distribution of GLUT4 in cardiomyocytes: Rab4A reduces basal glucose transport and augments insulin responsiveness. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 108:26–36
Dyck DJ, Steinberg G, Bonen A (????) Insulin increases FA uptake and esterification but reduces lipid utilization in isolated contracting muscle. Am J Physiol 281:E600–E607
Egert S, Nguyen N, Schwaiger M (1999) Myocardial glucose transporter GLUT1: translocation induced by insulin and ischemia. J Mol Cell Cardiol 31:1337–1344
Elsing C, Kassner A, Gajdzik L, Graf J, Stremmel W (1998) Electrogenicity of hepatocellular fatty acid uptake. Eur J Med Res 3:393–396
Farese RV (2002) Function and dysfunction of aPKC isoforms for glucose transport in insulin-sensitive and insulin-resistant states. Am J Physiol 283:E1–E11
Feron O, Zhao YY, Kelly RA (1999) The ins and outs of caveolar signaling. m2 muscarinic cholinergic receptors and eNOS activation versus neuregulin and ErbB4 signaling in cardiac myocytes. Ann NY Acad Sci 874:11–19
Fischer Y, Rose H, Kammermeier H (1991) Highly insulin-responsive isolated rat heart muscle cells yielded by a modified isolation method. Life Sci 49:1679–1688
Fischer Y, Kamp J, Thomas J, Popping S, Rose H, Carpene C, Kammermeier H (1996) Signals mediating stimulation of cardiomyocyte glucose transport by the alpha-adrenergic agonist phenylephrine. Am J Physiol 270:C1211–C1220
Fischer Y, Thomas J, Sevilla L, Munoz P, Becker C, Holman G, Kozka IJ, Palacin M, Testar X, Kammermeier H, Zorzano A (1997) Insulin-induced recruitment of glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) and GLUT1 in isolated rat cardiac myocytes. Evidence of the existence of different intracellular GLUT4 vesicle populations. J Biol Chem 272:7085–7092
Foster LJ, Weir ML, Lim DY, Liu Z, Trimble WS, Klip A (2000) A functional role for VAP-33 in insulin-stimulated GLUT4 traffic. Traffic 1:512–521
Fryer LG, Hajduch E, Rencurel F, Salt IP, Hundal HS, Hardie DG, Carling D (2000) Activation of glucose transport by AMP-activated protein kinase via stimulation of nitric oxide synthase. Diabetes 49:1978–1985
Gao J, Ren J, Gulve EA, Holloszy JO (1994) Additive effect of contractions and insulin on GLUT-4 translocation into the sarcolemma. J Appl Physiol 77:1597–1601
Gervois P, Torra IP, Fruchart JC, Staels B (2000) Regulation of lipid and lipoprotein metabolism by PPAR activators. Clin Chem Lab Med 38:3–11
Gimeno RE, Ortegon AM, Patel S, Punreddy S, Ge P, Sun Y, Lodish HF, Stahl A (2003) Characterization of a heart-specific fatty acid transport protein. J Biol Chem 278:16039–16044
Glatz JF, van der Vusse GJ (1989) Intracellular transport of lipids. Mol Cell Biochem 88:37–44
Glatz JF, Luiken JJ, Bonen A (2001) Involvement of membrane-associated proteins in the acute regulation of cellular fatty acid uptake. J Mol Neurosci 16:123–132
Groen AK, Wanders RJ, Westerhoff HV, van der Meer R, Tager JM (1982) Quantification of the contribution of various steps to the control of mitochondrial respiration. J Biol Chem 257:2754–2757
Hamilton JA (1998) Fatty acid transport: difficult or easy? J Lipid Res 39:467–481
Hamilton JA, Kamp F (1999) How are free fatty acids transported in membranes? Is it by proteins or by free diffusion through the lipids? Diabetes 48:2255–2269
Hardie DG, Carling D (1997) The AMP-activated protein kinase--fuel gauge of the mammalian cell? Eur J Biochem 246:259–273
Hayashi T, Wojtaszewski JF, Goodyear LJ (1997) Exercise regulation of glucose transport in skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol 273:E1039–E1051
Hayashi T, Hirshman MF, Kurth EJ, Winder WW, Goodyear LJ (1998) Evidence for 5’ AMP-activated protein kinase mediation of the effect of muscle contraction on glucose transport. Diabetes 47:1369–1373
Heller-Harrison RA, Morin M, Guilherme A, Czech MP (1996) Insulin-mediated targeting of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to GLUT4-containing vesicles. J Biol Chem 271:10200–10204
Holman GD, Lo Leggio L, Cushman SW (1994) Insulin-stimulated GLUT4 glucose transporter recycling. A problem in membrane protein subcellular trafficking through multiple pools. J Biol Chem 269:17516–17524
Huang J, Imamura T, Olefsky JM (2001) Insulin can regulate GLUT4 internalization by signaling to Rab5 and the motor protein dynein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13084–13089
Hyde R, Peyrollier K, Hundal HS (2002) Insulin promotes the cell surface recruitment of the SAT2/ATA2 system A amino acid transporter from an endosomal compartment in skeletal muscle cells. J Biol Chem 277:13628–13634
Ibrahimi A, Sfeir Z, Magharaie H, Amri EZ, Grimaldi P, Abumrad NA (1996) Expression of the CD36 homolog (FAT) in fibroblast cells: effects on fatty acid transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:2646–2651
Isola LM, Zhou SL, Kiang CL, Stump DD, Bradbury MW, Berk PD (1995) 3T3 fibroblasts transfected with a cDNA for mitochondrial aspartate aminotransferase express plasma membrane fatty acid-binding protein and saturable fatty acid uptake. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:9866–9870
Jiang H, Li J, Katz EB, Charron MJ (2001) GLUT4 ablation in mice results in redistribution of IRAP to the plasma membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 284:519–525
Johannsson E, Nagelhus EA, McCullagh KJ, Sejersted OM, Blackstad TW, Bonen A, Ottersen OP (1997) Cellular and subcellular expression of the monocarboxylate transporter MCT1 in rat heart. A high-resolution immunogold analysis. Circ Res 80:400–407
Joost HG, Bell GI, Best JD, Birnbaum MJ, Charron MJ, Chen YT, Doege H, James DE, Lodish HF, Moley KH, Moley JF, Mueckler M, Rogers S, Schurmann A, Seino S, Thorens B (2002) Nomenclature of the GLUT/SLC2A family of sugar/polyol transport facilitators. Am J Physiol 282:E974–E976
Kagaya Y, Kanno Y, Takeyama D, Ishide N, Maruyama Y, Takahashi T, Ido T, Takishima T (1990) Effects of long-term pressure overload on regional myocardial glucose and free fatty acid uptake in rats. A quantitative autoradiographic study. Circulation 81:1353–1361
Kandror KV, Pilch PF (1994) gp160, a tissue-specific marker for insulin-activated glucose transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:8017–8021
Kandror KV, Pilch PF (1996) Compartmentalization of protein traffic in insulin-sensitive cells. Am J Physiol 271:E1–E14
Karlsson M, Thorn H, Parpal S, Stralfors P, Gustavsson J (2002) Insulin induces translocation of glucose transporter GLUT4 to plasma membrane caveolae in adipocytes. FASEB J 16:249–251
Karnieli E, Hissin PJ, Simpson IA, Salans LB, Cushman SW (1981) A possible mechanism of insulin resistance in the rat adipose cell in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. Depletion of intracellular glucose transport systems. J Clin Invest 68:811–814
Kessler A, Tomas E, Immler D, Meyer HE, Zorzano A, Eckel J (2000) Rab11 is associated with GLUT4-containing vesicles and redistributes in response to insulin. Diabetologia 43:1518–1527
Kessler A, Uphues I, Ouwens DM, Till M, Eckel J (2001) Diversification of cardiac insulin signaling involves the p85 alpha/beta subunits of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Am J Physiol 280:E65–E74
Khan AH, Pessin JE (2002) Insulin regulation of glucose uptake: a complex interplay of intracellular signalling pathways. Diabetologia 45:1475–1483
Kono T (1982) Recycling of the insulin-sensitive glucose transport mechanism in fat-cells. Biochem Soc Trans 10:9–10
Koonen DPY, Coumans WA, Arumugam Y, Bonen A, Glatz JFC, Luiken JJFP (2002) Giant membrane vesicles as a model to study cellular substrate uptake dissected from metabolism. Mol Cell Biochem 239:121–130
Kupriyanova TA, Kandror KV (1999) Akt-2 binds to Glut4-containing vesicles and phosphorylates their component proteins in response to insulin. J Biol Chem 274:1458–1464
Lango R, Smolenski RT, Narkiewicz M, Suchorzewska J, Lysiak-Szydlowska W (2001) Influence of L-carnitine and its derivatives on myocardial metabolism and function in ischemic heart disease and during cardiopulmonary bypass. Cardiovasc Res 51:21–29
Lasley RD, Smart EJ (2001) Cardiac myocyte adenosine receptors and caveolae. Trends Cardiovasc Med 11:259–263
Lopaschuk GD (2001) Malonyl CoA control of fatty acid oxidation in the diabetic rat heart. Adv Exp Med Biol 498:155–165
Lopaschuk GD (2002) Metabolic abnormalities in the diabetic heart. Heart Fail Rev 7:149–159
Luiken JJFP, van Nieuwenhoven FA, America G, van der Vusse GJ, Glatz JFC (1997) Uptake and metabolism of palmitate by isolated cardiac myocytes from adult rats: involvement of sarcolemmal proteins. J Lipid Res 38:745–758
Luiken JJFP, Turcotte LP, Bonen A (1999) Protein-mediated palmitate uptake and expression of fatty acid transport proteins in heart giant vesicles. J Lipid Res 40:1007–1016
Luiken JJFP, Arumugam Y, Dyck DJ, Bell RC, Pelsers MM, Turcotte LP, Tandon NN, Glatz JFC, Bonen A (2001) Increased rates of fatty acid uptake and plasmalemmal fatty acid transporters in obese Zucker rats. J Biol Chem 276:40567–40573
Luiken JJFP, Willems J, van der Vusse GJ, Glatz JFC (2001) Electrostimulation enhances FAT/CD36-mediated long-chain fatty acid uptake by isolated rat cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol 281:E704–E712
Luiken JJFP, Dyck DJ, Han XX, Tandon NN, Arumugam Y, Glatz JFC, Bonen A (2002) Insulin induces the translocation of the fatty acid transporter FAT/CD36 to the plasma membrane. Am J Physiol 282:E491–E495
Luiken JJFP, Koonen DP, Willems J, Zorzano A, Becker C, Fischer Y, Tandon NN, Van Der Vusse GJ, Bonen A, Glatz JFC (2002) Insulin stimulates long-chain fatty acid utilization by rat cardiac myocytes through cellular redistribution of FAT/CD36. Diabetes 51:3113–3119
Luiken JJFP, Willems J, Coort SLM, Coumans WA, Bonen A, Van Der Vusse GJ, Glatz JFC (2002) Effects of cAMP modulators on long-chain fatty-acid uptake and utilization by electrically stimulated rat cardiac myocytes. Biochem J 367:881–887
Luiken JJFP, Coort SLM, Willems J, Coumans WA, Bonen A, van der Vusse GJ, Glatz JFC (2003) Contraction-induced FAT/CD36 translocation in rat cardiac myocytes is mediated through AMP-activated protein kinase signaling. Diabetes 52:1627–1634
Lund S, Holman GD, Schmitz O, Pedersen O (1995) Contraction stimulates translocation of glucose transporter GLUT4 in skeletal muscle through a mechanism distinct from that of insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:5817–5821
Malide D, Ramm G, Cushman SW, Slot JW (2000) Immunoelectron microscopic evidence that GLUT4 translocation explains the stimulation of glucose transport in isolated rat white adipose cells. J Cell Sci 113:4203–4210
Martin LB, Shewan A, Millar CA, Gould GW, James DE (1998) Vesicle-associated membrane protein 2 plays a specific role in the insulin-dependent trafficking of the facilitative glucose transporter GLUT4 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem 273:1444–1452
Martinez O, Antony C, Pehau-Arnaudet G, Berger EG, Salamero J, Goud B (1997) GTP-bound forms of rab6 induce the redistribution of Golgi proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:1828–1833
Merrill GF, Kurth EJ, Hardie DG, Winder WW (1997) AICA riboside increases AMP-activated protein kinase, fatty acid oxidation, and glucose uptake in rat muscle. Am J Physiol 273:E1107–E1112
Min J, Okada S, Kanzaki M, Elmendorf JS, Coker KJ, Ceresa BP, Syu LJ, Noda Y, Saltiel AR, Pessin JE (1999) Synip: a novel insulin-regulated syntaxin 4-binding protein mediating GLUT4 translocation in adipocytes. Mol Cell 3:751–760
Mu J, Brozinick JT Jr, Valladares O, Bucan M, Birnbaum MJ (2001) A role for AMP-activated protein kinase in contraction- and hypoxia-regulated glucose transport in skeletal muscle. Mol Cell 7:1085–1094
Mueckler M (1994) Facilitative glucose transporters. Eur J Biochem 219:713–725
Muller H, Deckers K, Eckel J (2002) The fatty acid translocase (FAT)/CD36 and the glucose transporter GLUT4 are localized in different cellular compartments in rat cardiac muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 293:665–669
Munoz P, Mora S, Sevilla L, Kaliman P, Tomas E, Guma A, Testar X, Palacin M, Zorzano A (1996) Expression and insulin-regulated distribution of caveolin in skeletal muscle. Caveolin does not colocalize with GLUT4 in intracellular membranes. J Biol Chem 271:8133–8139
Muoio DM, Dohm GL, Tapscott EB, Coleman RA (1999) Leptin opposes insulin’s effects on fatty acid partitioning in muscles isolated from obese ob/ob mice. Am J Physiol 276:E913–E921
Oram JF, Wenger JI, Neely JR (1975) Regulation of long chain fatty acid activation in heart muscle. J Biol Chem 250:73–78
Pearce SF, Wu J, Silverstein RL (1994) A carboxyl terminal truncation mutant of CD36 is secreted and binds thrombospondin: evidence for a single transmembrane domain. Blood 84:384–389
Ploug T, van Deurs B, Ai H, Cushman SW, Ralston E (1998) Analysis of GLUT4 distribution in whole skeletal muscle fibers: identification of distinct storage compartments that are recruited by insulin and muscle contractions. J Cell Biol 142:1429–1446
Plutner H, Cox AD, Pind S, Khosravi-Far R, Bourne JR, Schwaninger R, Der CJ, Balch WE (1991) Rab1b regulates vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and successive Golgi compartments. J Cell Biol 115:31–43
Pohl J, Ring A, Stremmel W (2002) Uptake of long-chain fatty acids in HepG2 cells involves caveolae: analysis of a novel pathway. J Lipid Res 43:1390–1399
Ponticos M, Lu QL, Morgan JE, Hardie DG, Partridge TA, Carling D (1998) Dual regulation of the AMP-activated protein kinase provides a novel mechanism for the control of creatine kinase in skeletal muscle. EMBO J 17:1688–1699
Ralston E, Ploug T (1999) Caveolin-3 is associated with the T-tubules of mature skeletal muscle fibers. Exp Cell Res 246:510–515
Ramrath S, Tritschler HJ, Eckel J (1999) Stimulation of cardiac glucose transport by thioctic acid and insulin. Horm Metab Res 31:632–635
Randle PJ, Garland PB, Newsholme EA, Hales CN (1965) The glucose fatty acid cycle in obesity and maturity onset diabetes mellitus. Ann NY Acad Sci 131:324–333
Rett K, Wicklmayr M, Dietze GJ, Haring HU (1996) Insulin-induced glucose transporter (GLUT1 and GLUT4) translocation in cardiac muscle tissue is mimicked by bradykinin. Diabetes 45:S66–S69
Rodrigues B, Cam MC, McNeill JH (1998) Metabolic disturbances in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Mol Cell Biochem 180:53–57
Ros-Baro A, Lopez-Iglesias C, Peiro S, Bellido D, Palacin M, Zorzano A, Camps M (2001) Lipid rafts are required for GLUT4 internalization in adipose cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12050–12055
Rose H, Hennecke T, Kammermeier H (1990) Sarcolemmal fatty acid transfer in isolated cardiomyocytes governed by albumin/membrane-lipid partition. J Mol Cell Cardiol 22:883–892
Saltis J, Habberfield AD, Egan JJ, Londos C, Simpson IA, Cushman SW (1991) Role of protein kinase C in the regulation of glucose transport in the rat adipose cell. Translocation of glucose transporters without stimulation of glucose transport activity. J Biol Chem 266:261–267
Schaffer JE, Lodish HF (1994) Expression cloning and characterization of a novel adipocyte long chain fatty acid transport protein. Cell 79:427–436
Sevilla L, Tomas E, Munoz P, Guma A, Fischer Y, Thomas J, Ruiz-Montasell B, Testar X, Palacin M, Blasi J, Zorzano A (1997) Characterization of two distinct intracellular GLUT4 membrane populations in muscle fiber. Differential protein composition and sensitivity to insulin. Endocrinology 138:3006–3015
Shulman GI (2000) Cellular mechanisms of insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 106:171–176
Slot JW, Geuze HJ, Gigengack S, James DE, Lienhard GE (1991) Translocation of the glucose transporter GLUT4 in cardiac myocytes of the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:7815–7819
Sogaard M, Tani K, Ye RR, Geromanos S, Tempst P, Kirchhausen T, Rothman JE, Sollner T (1994) A rab protein is required for the assembly of SNARE complexes in the docking of transport vesicles. Cell 78:937–948
Song KS, Scherer PE, Tang Z, Okamoto T, Li S, Chafel M, Chu C, Kohtz DS, Lisanti MP (1996) Expression of caveolin-3 in skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle cells. Caveolin-3 is a component of the sarcolemma and co-fractionates with dystrophin and dystrophin-associated glycoproteins. J Biol Chem 271:15160–15165
Sonnichsen B, De Renzis S, Nielsen E, Rietdorf J, Zerial M (2000) Distinct membrane domains on endosomes in the recycling pathway visualized by multicolor imaging of Rab4, Rab5, and Rab11. J Cell Biol 149:901–914
St.Denis JF, Cushman SW (1998) Role of SNAREs in the GLUT4 translocation response to insulin in adipose cells and muscle. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 9:153–165
Stagsted J, Olsson L, Holman GD, Cushman SW, Satoh S (1993) Inhibition of internalization of glucose transporters and IGF-II receptors. Mechanism of action of MHC class I-derived peptides which augment the insulin response in rat adipose cells. J Biol Chem 268:22809–22813
Stahl A, Evans JG, Pattel S, Hirsch D, Lodish HF (2002) Insulin causes fatty acid transport protein translocation and enhanced fatty acid uptake in adipocytes. Dev Cell 2:477–488
Stremmel W (1988) Fatty acid uptake by isolated rat heart myocytes represents a carrier-mediated transport process. J Clin Invest 81:844–852
Stuart Wood I, Trayhurn P (2003) Glucose transporters (GLUT and SGLT): expanded families of sugar transport proteins. Br J Nutr 89:3–9
Stump DD, Zhou SL, Berk PD (1993) Comparison of plasma membrane FABP and mitochondrial isoform of aspartate aminotransferase from rat liver. Am J Physiol 265:G894–G902
Taegtmeyer H, Goodwin GW, Doenst T, Frazier OH (1997) Substrate metabolism as a determinant for postischemic functional recovery of the heart. Am J Cardiol 80:3A–10A
Tomas E, Sevilla L, Palacin M, Zorzano A (2001) The insulin-sensitive GLUT4 storage compartment is a postendocytic and heterogeneous population recruited by acute exercise. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 284:490–495
Trischler M, Stoorvogel W, Ullrich O (1999) Biochemical analysis of distinct Rab5- and Rab11-positive endosomes along the transferrin pathway. J Cell Sci112:4773–4783
Tsakiridis T, Vranic M, Klip A (1995) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and the actin network are not required for the stimulation of glucose transport caused by mitochondrial uncoupling: comparison with insulin action. Biochem J 309:1–5
Ullrich O, Reinsch S, Urbe S, Zerial M, Parton RG (1996) Rab11 regulates recycling through the pericentriolar recycling endosome. J Cell Biol 135:913–924
Unger RH, Orci L (2001) Diseases of liporegulation: new perspective on obesity and related disorders. FASEB J 15:312–321
Uphues I, Kolter T, Goud B, Eckel J (1994) Insulin-induced translocation of the glucose transporter GLUT4 in cardiac muscle: studies on the role of small-molecular-mass GTP-binding proteins. Biochem J 301:177–182
Uphues I, Chern Y, Eckel J (1995) Insulin-dependent translocation of the small GTP-binding protein rab3C in cardiac muscle: studies on insulin-resistant Zucker rats. FEBS Lett 377:109–112
Van der Vusse GJ, Coumans WA, Van der Veen E, Drake AJ, Flameng W, Suy R (1984) ATP, creatine phosphate and glycogen content in human myocardial biopsies: markers for the efficacy of cardioprotection during aorto-coronary bypass surgery. Vasc Surg 18:127–134
Van der Vusse GJ, Glatz JF, Stam HC, Reneman RS (1992) Fatty acid homeostasis in the normoxic and ischemic heart. Physiol Rev 72:881–940
Van der Vusse GJ, van Bilsen M, Glatz JFC (2000) Cardiac fatty acid uptake and transport in health and disease. Cardiovasc Res 45:279–293
Van Nieuwenhoven FA, Willemsen PHM, Van der Vusse GJ, Glatz JFC (1999) Co-expression in rat heart and skeletal muscle of four genes coding for proteins implicated in long-chain fatty acid uptake. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 31:489–498
Watson RT, Pessin JE (2001) Subcellular compartmentalization and trafficking of the insulin-responsive glucose transporter, GLUT4. Exp Cell Res 271:75–83
Weisiger RA, Fitz JG, Scharschmidt BF (1989) Hepatic oleate uptake. Electrochemical driving forces in intact rat liver. J Clin Invest 83:411–420
Wheeler TJ, Fell RD, Hauck MA (1994) Translocation of two glucose transporters in heart: effects of rotenone, uncouplers, workload, palmitate, insulin and anoxia. Biochim Biophys Acta 1196:191–200
Wu G, Yussman MG, Barrett TJ, Hahn HS, Osinska H, Hilliard GM, Wang X, Toyokawa T, Yatani A, Lynch RA, Robbins J, Dorn GW 2nd (2001) Increased myocardial Rab GTPase expression: a consequence and cause of cardiomyopathy. Circ Res 89:1130–1137
Yeh JI, Gulve EA, Rameh L, Birnbaum MJ (1995) The effects of wortmannin on rat skeletal muscle. Dissociation of signaling pathways for insulin- and contraction-activated hexose transport. J Biol Chem 270:2107–2111
Ylitalo K, Ala-Rami A, Vuorinen K, Peuhkurinen K, Lepojarvi M, Kaukoranta P, Kiviluoma K, Hassinen I (2001) Reversible ischemic inhibition of F1F0-ATPase in rat and human myocardium. Biochim Biophys Acta 1504:329–339
Young LH, Renfu Y, Russell R, Hu X, Caplan M, Ren J, Shulman GI, Sinusas AJ (1997) Low-flow ischemia leads to translocation of canine heart GLUT-4 and GLUT-1 glucose transporters to the sarcolemma in vivo. Circulation 95:415–422
Zerial M, Stenmark H (1993) Rab GTPases in vesicular transport. Curr Opin Cell Biol 5:613–620
Zhou SL, Potter BJ, Stump D, Sorrentino D, Berk PD (1990) Quantitation of plasma membrane fatty acid-binding protein by enzyme dilution and monoclonal antibody based immunoassay. Mol Cell Biochem 98:183–189
Zhou M, Sevilla L, Vallega G, Chen P, Palacin M, Zorzano A, Pilch PF, Kandror KV (1998) Insulin-dependent protein trafficking in skeletal muscle cells. Am J Physiol 275:E187–E196
Zorzano A, Sevilla L, Camps M, Becker C, Meyer J, Kammermeier H, Munoz P, Guma A, Testar X, Palacin M, Blasi J, Fischer Y (1997) Regulation of glucose transport, and glucose transporters expression and trafficking in the heart: studies in cardiac myocytes. Am J Cardiol 80:65A–76A
Acknowledgements
Work in the authors’ laboratories is supported by the Netherlands Heart Foundation, grant 2000.156, and by the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Ontario. Joost Luiken is the recipient of a VIDI-Innovational Research grant from the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO-ZonMw grant No. 016.036.305). Arend Bonen is a Canada Research Chair in Metabolism and Health. Jan Glatz is Netherlands Heart Foundation Professor of Cardiac Metabolism.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luiken, J.J.F.P., Coort, S.L.M., Koonen, D.P.Y. et al. Regulation of cardiac long-chain fatty acid and glucose uptake by translocation of substrate transporters. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 448, 1–15 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-003-1199-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-003-1199-4