Abstract
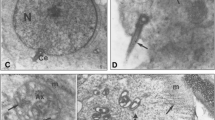
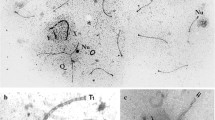
The localization of vasa homolog protein in the spermatogenic cells of mice, rats, and guinea pigs was studied by immunofluorescence and electron microscopies with the antibody against mouse vasa homolog (MVH) protein. By immunofluorescence microscopy, four types of granular staining patterns were identified: (1) fine particles observed in diplotene and meiotic cells, (2) small granules associated with a mitochondrial marker and appearing in pachytene spermatocytes after stage V, (3) strands lacking the mitochondrial marker in late spermatocytes, and (4) large irregularly shaped granules in round spermatids. Immunoelectron microscopy defined the ultrastructural profiles of these MVH protein-positive granules: the first type consisted of small dense particles, the second had intermitochondrial cement (IMC), the third type, consisting of strands, had loose aggregates of either material dissociated from IMC or 70–90-nm particles, and the fourth had typical chromatoid bodies (CBs). The results suggest that MVH proteins function in these components of nuage. MVH protein-positive structures other than CBs disappeared during meiosis and CB appeared first in early spermatids. The results suggest that the formation of nuage is discontinued between spermatocytes and spermatids. The formation of nuage in spermatocytes and of CB in spermatids is discussed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benda C (1891) Neue Mitteilungen über die Entwicklung der Genitaldrüsen und die Metamorphose der Samenzellen (Histogenese der Spermatozoen). Verhandlungen der Berliner Physiologischen Gesellschaft. Arch Anat Physiol Physiol Abt, pp 549–552
Carrera P, Johnstone O, Nakamura A, Casanova J, Jackle H, Lasko P (2000) VASA mediates translation through interaction with a Drosophila yIF2 homolog. Mol Cell 5:181–187
Chuma S, Hiyoshi M, Yamamoto A, Hosokawa M, Takamune K, Nakatsuji N (2003) Mouse tudor repeat-1(MTR-1) is a novel component of chromatoid bodies/nuages in male germ cells and forms a complex with snRNPs. Mech Dev 120:979–990
Chuma S, Hosokawa M, Kitamura K, Kasai S, Fujioka M, Hiyoshi M, Takamune K, Noce T, Nakatsuji N (2006) Tdrd1/Mtr-1, a tudor-related gene, is essential for male germ-cell differentiation and nuage/germinal granule formation in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:15894–15899
Chuma S, Hosokawa M, Tanaka T, Nakatsuji N (2009) Ultrastructual characterization of spermatogenesis and its evolutionary conservation in the germline: germinal granules in mammals. Mol Cell Endocrinol 306:17–23
Clermont Y, Oko R, Hermo L (1990) Immunocytochemical localization of proteins utilized in the formation of outer dense fibers and fibrous sheath in rat spermatids. An electron microscope study. Anat Rec 227:447–457
Clermont Y, Oko R, Hermo L (1993) Cell biology of mammalian spermiogenesis. In: Desjardins C, Ewing LL (eds) Cell and molecular biology of the testis. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 332–376
Daoust R, Clermont Y (1955) Distribution of nucleic acids in germ cells during the cycle of the somniferous epithelium in the rat. Am J Anat 96:255–283
De Roe C, Courtoy PJ, Baudhuin P (1987) A model of protein–colloidal gold interactions. J Histochem Cytochem 35:1191–1198
Eddy EM (1974) Fine structural observations on the form and distribution of nuage in germ cells of rat. Anat Rec 178:731–758
Eddy EM (1975) Germplasm and the differentiation of germ cell line. Int Rev Cytol 43:229–280
Fasten N (1914) Spermatogenesis of the American grayfish, Cambarus virilis and Cambrarus immunis (?), with special reference to synapsis and the chromatoid bodies. J Morphol 25:587–649
Fawcett DW, Eddy EM, Phillips DM (1970) Observations on the fine structure and relationships of the chromatoid body in mammalian spermatogenesis. Biol Reprod 2:129–153
Figueroa J, Burzio LO (1998) Polysome-like structures in the chromatoid body of rat spermatids. Cell Tissue Res 291:575–579
Fujiwara Y, Komiya T, Kawabata H, Sato M, Fujimoto H, Furusawa M, Noce T (1994) Isolation of a DEAD-family protein gene that encodes a murine homolog of drosophila VASA and its specific expression in germ cell lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:12258–12262
Gavis ER, Lunsford L, Bergsten SE, Lehmann R (1996) A conserved 90-nucleotide element mediates translational repression of nanos RNA. Development 122:2791–2800
Haraguchi CM, Mabuchi T, Hirata S, Shoda T, Hoshi K, Akasaki K, Yokota S (2000) Chromatoid bodies: aggresome-like characteristics and degradation sites for organelles of spermiogenic cells. J Histochem Cytochem 53:455–465
Hay B, Jan LY, Jan YN (1988) A protein component of Drosophila polar granules is encoded by vasa and has extensive sequence similarity to ATP-dependent helicase. Cell 55:577–587
Hosokawa M, Shoji M, Kitamura K, Tanaka T, Noce T, Chuma S, Nakatsuji N (2007) Tudor-related proteins TDRD1/MTR-1, TDRD6 and TDRD7/TRAP: domain composition, intracellular localization, and function in male germ cells in mice. Dev Biol 301:38–52
Kotaja N, Sassone-Corsi P (2007) The chromatoid body: a germ-cell-specific RNA-processing centre. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:85–90
Kotaja N, Bhattacharyya SN, Jaskiewicz L, Kimmins S, Parvinen M, Filipowicz W, Sassone-Corsi P (2006a) The chromatoid body of male germ cells: similarity with processing bodies and presence of dicer and microRNA pathway components. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:2647–2652
Kotaja N, Lin H, Parvinen M, Sassone-Corsi P (2006b) Interplay of PIWI/Argonaute protein MIWI and kinesin KIF17b in chromatoid bodies of male germ cells. J Cell Sci 119:2819–2825
Lasko PE, Ashburner M (1988) The product of the Drosophila gene vasa is very similar to eukaryotic initiation factor-4A. Nature 335:611–617
Liang L, Diehl-Jones W, Lasko P (1994) Localization of vasa protein to the Drosophila pole plasm is independent of its RNA-binding and helicase activities. Development 120:1201–1211
Meinhardt A, Wilhelm B, Seitz J (1999) New aspects of spermatogenesis. Hum Reprod Update 5:108–119
Niessing C (1897) Die Beteiligung von Centralkörper und Sphäre am Aufbau des Samenfadens bei Säugetieren. Arch Mikroskop Anat 48:111–142
Noce T, Okamoto-Ito S, Tsunekawa N (2001) Vasa homolog genes in mammalian germ cell development. Cell Struct Funct 26:131–136
Pan J, Goodheart M, Chuma S, Nakatsuji N, Page DC, Wang PJ (2005) RNF17, a component of the mammalian germ cell nuage, is essential for spermatogenesis. Development 132:4029–4039
Raz E (2000) The function and regulation of vasa-like genes in germ-cell development. Genome Biol 1:1017.1–1017.6
Regaud C (1910) Etudes sur la structure des tubes seminiferes et sur la spermatogenese chez les mammiferes. Arch Anat Micr Morphol Exp 4:101–156
Russell L, Frank B (1978) Ultrastructural characterization of nuage in spermatocytes of the rat testis. Anat Rec 190:79–98
Russell LD, Ettlin RA, Hikim APS, Clegg ED (1990) Histological and histopathological evaluation of the testis. Cache River Press, Florida
Schreiner A, Schreiner KE (1905) Über die Entwickelung der männlichen Geschlechtszellen von Myxine glutinosa (L). Arch Biol 21:183–355
Sheth U, Parker R (2003) Decapping and decay of messenger RNA occur in cytoplasmic processing bodies. Science 300:805–808
Sönderström KO (1978) Formation of chromatoid body during rat spermatogenesis. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch 92:417–430
Sönderström KO (1981) The relationship between the nuage and the chromatoid body during spermatogenesis in the rat. Cell Tissue Res 215:425–430
Soper SF, van der Heijden GW, Hardiman TC, Gooheart M, Martin SL, de Boer P, Bortvin A (2008) Mouse maelstrom, a component of nuage, is essential for spermatogenesis and transposon repression in meiosis. Dev Cell 15:285–297
Styhler S, Nakamura A, Swan A, Suter B, Lasko P (1998) vasa is required for GURKEN accumulation in the oocyte, and is involved in oocyte differentiation and germline cyst development. Development 125:1569–1578
Sud B (1961) Morphological and histochemical studies of the chromatoid body in the grass-snake, Natrix natrix. Q J Microsc Sci 102:51–58
Susi FR, Clermont Y (1970) Fine structural modifications of the rat chromatoid body during spermatogenesis. Am J Anat 129:177–192
Tanaka SS, Toyooka Y, Akasu R, Katoh-Fukui Y, Nakahara Y, Suzuki R, Yokoyama M, Noce T (2000) The mouse homolog of Drosophila vasa is required for the development of male germ cells. Genes Dev 14:841–853
Tomancak P, Guichet A, Zavorszky P, Ephrussi A (1998) Oocyte polarity depends on regulation of gurken by Vasa. Development 125:1723–1732
Toyooka Y, Tsunekawa N, Takahashi Y, Matsui Y, Satoh M, Noce T (2000) Expression and intracellular localization of mouse Vasa-homologue during germ cell development. Mech Dev 93:139–149
Tsai-Morris CH, Sheng Y, Lee E, Lei KJ, Dufau ML (2004) Gonadotropin-regulated testicular RNA helicase (GRTH/Ddx25) is essential for spermatid development and completion of spermatogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:6373–6378
von Brunn A (1876) Beiträge zur Entwicklungsgeschichte der Samenkörper. Arch Mikroscop Anat 12:528–536
von Korff K (1902) Zur Histogenese der Spermien von Phalangista vulpine. Arch Mikr Anat 60:232–260
Wilson EB (1913) A chromatoid body simulating an accessory chromosome in pentatoma. Biol Bull 24:392–411
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a university research fund and in part by a Grant-in-Aid (17570158) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Culture and Sport to S.Y.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onohara, Y., Fujiwara, T., Yasukochi, T. et al. Localization of mouse vasa homolog protein in chromatoid body and related nuage structures of mammalian spermatogenic cells during spermatogenesis. Histochem Cell Biol 133, 627–639 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-010-0699-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-010-0699-5