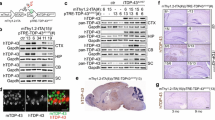
Abstract
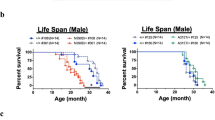
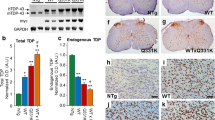
Accumulation of phosphorylated cytoplasmic TDP-43 inclusions accompanied by loss of normal nuclear TDP-43 in neurons and glia of the brain and spinal cord are the molecular hallmarks of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD-TDP). However, the role of cytoplasmic TDP-43 in the pathogenesis of these neurodegenerative TDP-43 proteinopathies remains unclear, due in part to a lack of valid mouse models. We therefore generated new mice with doxycycline (Dox)-suppressible expression of human TDP-43 (hTDP-43) harboring a defective nuclear localization signal (∆NLS) under the control of the neurofilament heavy chain promoter. Expression of hTDP-43∆NLS in these ‘regulatable NLS’ (rNLS) mice resulted in the accumulation of insoluble, phosphorylated cytoplasmic TDP-43 in brain and spinal cord, loss of endogenous nuclear mouse TDP-43 (mTDP-43), brain atrophy, muscle denervation, dramatic motor neuron loss, and progressive motor impairments leading to death. Notably, suppression of hTDP-43∆NLS expression by return of Dox to rNLS mice after disease onset caused a dramatic decrease in phosphorylated TDP-43 pathology, an increase in nuclear mTDP-43 to control levels, and the prevention of further motor neuron loss. rNLS mice back on Dox also showed a significant increase in muscle innervation, a rescue of motor impairments, and a dramatic extension of lifespan. Thus, the rNLS mice are new TDP-43 mouse models that delineate the timeline of pathology development, muscle denervation and neuron loss in ALS/FTLD-TDP. Importantly, even after neurodegeneration and onset of motor dysfunction, removal of cytoplasmic TDP-43 and the concomitant return of nuclear TDP-43 led to neuron preservation, muscle re-innervation and functional recovery.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfieri JA, Pino NS, Igaz LM (2014) Reversible Behavioral Phenotypes in a Conditional Mouse Model of TDP-43 Proteinopathies. J Neurosci 34:15244–15259. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.1918-14.2014
Arnold ES, Ling SC, Huelga SC, Lagier-Tourenne C, Polymenidou M, Ditsworth D et al (2013) ALS-linked TDP-43 mutations produce aberrant RNA splicing and adult-onset motor neuron disease without aggregation or loss of nuclear TDP-43. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110:E736–E745. doi:10.1073/pnas.1222809110
Ayala YM, De Conti L, Avendano-Vazquez SE, Dhir A, Romano M, D’Ambrogio A et al (2011) TDP-43 regulates its mRNA levels through a negative feedback loop. EMBO J 30:277–288. doi:10.1038/emboj.2010.310
Ayala YM, Zago P, D’Ambrogio A, Xu YF, Petrucelli L, Buratti E et al (2008) Structural determinants of the cellular localization and shuttling of TDP-43. J Cell Sci 121:3778–3785. doi:10.1242/jcs.038950
Balin BJ, Clark EA, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (1991) Neurofilament reassembly in vitro: biochemical, morphological and immuno-electron microscopic studies employing monoclonal antibodies to defined epitopes. Brain Res 556:181–195
Barmada SJ, Serio A, Arjun A, Bilican B, Daub A, Ando DM et al (2014) Autophagy induction enhances TDP43 turnover and survival in neuronal ALS models. Nat Chem Biol 10:677–685. doi:10.1038/nchembio.1563
Braak H, Brettschneider J, Ludolph AC, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Del Tredici K (2013) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis–a model of corticofugal axonal spread. Nat Rev Neurol 9:708–714. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2013.221
Brettschneider J, Del Tredici K, Irwin DJ, Grossman M, Robinson JL, Toledo JB et al (2014) Sequential distribution of pTDP-43 pathology in behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia (bvFTD). Acta Neuropathol 127:423–439. doi:10.1007/s00401-013-1238-y
Brettschneider J, Del Tredici K, Toledo JB, Robinson JL, Irwin DJ, Grossman M et al (2013) Stages of pTDP-43 pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 74:20–38. doi:10.1002/ana.23937
Chen-Plotkin AS, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2010) TAR DNA-binding protein 43 in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol 6:211–220. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2010.18
Chiang PM, Ling J, Jeong YH, Price DL, Aja SM, Wong PC (2010) Deletion of TDP-43 down-regulates Tbc1d1, a gene linked to obesity, and alters body fat metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:16320–16324. doi:10.1073/pnas.1002176107
Geser F, Brandmeir NJ, Kwong LK, Martinez-Lage M, Elman L, McCluskey L et al (2008) Evidence of multisystem disorder in whole-brain map of pathological TDP-43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arch Neurol 65:636–641. doi:10.1001/archneur.65.5.636
Geser F, Martinez-Lage M, Robinson J, Uryu K, Neumann M, Brandmeir NJ et al (2009) Clinical and pathological continuum of multisystem TDP-43 proteinopathies. Arch Neurol 66:180–189. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2008.558
Gordon PH, Meininger V (2011) How can we improve clinical trials in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis? Nat Rev Neurol 7:650–654. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2011.147
Guo JL, Covell DJ, Daniels JP, Iba M, Stieber A, Zhang B et al (2013) Distinct alpha-synuclein strains differentially promote tau inclusions in neurons. Cell 154:103–117. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.057
Guo JL, Lee VM (2014) Cell-to-cell transmission of pathogenic proteins in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Med 20:130–138. doi:10.1038/nm.3457
Gurney ME, Pu H, Chiu AY, Dal Canto MC, Polchow CY, Alexander DD et al (1994) Motor neuron degeneration in mice that express a human Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase mutation. Science 264:1772–1775
Hirasawa M, Cho A, Sreenath T, Sauer B, Julien JP, Kulkarni AB (2001) Neuron-specific expression of Cre recombinase during the late phase of brain development. Neurosci Res 40:125–132
Holmes BB, Furman JL, Mahan TE, Yamasaki TR, Mirbaha H, Eades WC et al (2014) Proteopathic tau seeding predicts tauopathy in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111:E4376–E4385. doi:10.1073/pnas.1411649111
Huang C, Tong J, Bi F, Zhou H, Xia XG (2012) Mutant TDP-43 in motor neurons promotes the onset and progression of ALS in rats. J Clin Invest 122:107–118. doi:10.1172/jci59130
Iba M, Guo JL, McBride JD, Zhang B, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2013) Synthetic tau fibrils mediate transmission of neurofibrillary tangles in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s-like tauopathy. J Neurosci 33:1024–1037. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.2642-12.2013
Igaz LM, Kwong LK, Lee EB, Chen-Plotkin A, Swanson E, Unger T et al (2011) Dysregulation of the ALS-associated gene TDP-43 leads to neuronal death and degeneration in mice. J Clin Invest 121:726–738. doi:10.1172/jci44867
Igaz LM, Kwong LK, Xu Y, Truax AC, Uryu K, Neumann M et al (2008) Enrichment of C-terminal fragments in TAR DNA-binding protein-43 cytoplasmic inclusions in brain but not in spinal cord of frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Am J Pathol 173:182–194. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2008.080003
Kraemer BC, Schuck T, Wheeler JM, Robinson LC, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM et al (2010) Loss of murine TDP-43 disrupts motor function and plays an essential role in embryogenesis. Acta Neuropathol 119:409–419. doi:10.1007/s00401-010-0659-0
Kwong LK, Irwin DJ, Walker AK, Xu Y, Riddle DM, Trojanowski JQ et al (2014) Novel monoclonal antibodies to normal and pathologically altered human TDP-43 proteins. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2:33. doi:10.1186/2051-5960-2-33
Lee EB, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ (2012) Gains or losses: molecular mechanisms of TDP43-mediated neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci 13:38–50. doi:10.1038/nrn3121
Lee VM, Carden MJ, Schlaepfer WW, Trojanowski JQ (1987) Monoclonal antibodies distinguish several differentially phosphorylated states of the two largest rat neurofilament subunits (NF-H and NF-M) and demonstrate their existence in the normal nervous system of adult rats. J Neurosci 7:3474–3488
Lee VM, Page CD, Wu HL, Schlaepfer WW (1984) Monoclonal antibodies to gel-excised glial filament protein and their reactivities with other intermediate filament proteins. J Neurochem 42:25–32
Ling SC, Polymenidou M, Cleveland DW (2013) Converging mechanisms in ALS and FTD: disrupted RNA and protein homeostasis. Neuron 79:416–438. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2013.07.033
Neumann M, Kwong LK, Lee EB, Kremmer E, Flatley A, Xu Y et al (2009) Phosphorylation of S409/410 of TDP-43 is a consistent feature in all sporadic and familial forms of TDP-43 proteinopathies. Acta Neuropathol 117:137–149. doi:10.1007/s00401-008-0477-9
Neumann M, Sampathu DM, Kwong LK, Truax AC, Micsenyi MC, Chou TT et al (2006) Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314:130–133. doi:10.1126/science.1134108
Nonaka T, Masuda-Suzukake M, Arai T, Hasegawa Y, Akatsu H, Obi T et al (2013) Prion-like properties of pathological TDP-43 aggregates from diseased brains. Cell Rep 4:124–134. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2013.06.007
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2001) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Pesiridis GS, Tripathy K, Tanik S, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2011) A “two-hit” hypothesis for inclusion formation by carboxyl-terminal fragments of TDP-43 protein linked to RNA depletion and impaired microtubule-dependent transport. J Biol Chem 286:18845–18855. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.231118
Polymenidou M, Lagier-Tourenne C, Hutt KR, Huelga SC, Moran J, Liang TY et al (2011) Long pre-mRNA depletion and RNA missplicing contribute to neuronal vulnerability from loss of TDP-43. Nat Neurosci 14:459–468. doi:10.1038/nn.2779
Robertson J, Sanelli T, Xiao S, Yang W, Horne P, Hammond R et al (2007) Lack of TDP-43 abnormalities in mutant SOD1 transgenic mice shows disparity with ALS. Neurosci Lett 420:128–132. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2007.03.066
Sampathu DM, Neumann M, Kwong LK, Chou TT, Micsenyi M, Truax A et al (2006) Pathological heterogeneity of frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin-positive inclusions delineated by ubiquitin immunohistochemistry and novel monoclonal antibodies. Am J Pathol 169:1343–1352. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2006.060438
Sanders DW, Kaufman SK, DeVos SL, Sharma AM, Mirbaha H, Li A et al (2014) Distinct tau prion strains propagate in cells and mice and define different tauopathies. Neuron 82:1271–1288. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2014.04.047
Scotter EL, Vance C, Nishimura AL, Lee YB, Chen HJ, Urwin H et al (2014) Differential roles of the ubiquitin proteasome system and autophagy in the clearance of soluble and aggregated TDP-43 species. J Cell Sci 127:1263–1278. doi:10.1242/jcs.140087
Sephton CF, Good SK, Atkin S, Dewey CM, Mayer P 3rd, Herz J et al (2010) TDP-43 is a developmentally regulated protein essential for early embryonic development. J Biol Chem 285:6826–6834. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.061846
Shan X, Vocadlo D, Krieger C (2009) Mislocalization of TDP-43 in the G93A mutant SOD1 transgenic mouse model of ALS. Neurosci Lett 458:70–74. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2009.04.031
Sobue G, Hashizume Y, Yasuda T, Mukai E, Kumagai T, Mitsuma T et al (1990) Phosphorylated high molecular weight neurofilament protein in lower motor neurons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and other neurodegenerative diseases involving ventral horn cells. Acta Neuropathol 79:402–408
Toledo JB, Van Deerlin VM, Lee EB, Suh E, Baek Y, Robinson JL et al (2014) A platform for discovery: the University of Pennsylvania Integrated Neurodegenerative Disease Biobank. Alzheimers Dement 10(477–484):e471. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2013.06.003
Tsai KJ, Yang CH, Fang YH, Cho KH, Chien WL, Wang WT et al (2010) Elevated expression of TDP-43 in the forebrain of mice is sufficient to cause neurological and pathological phenotypes mimicking FTLD-U. J Exp Med 207:1661–1673. doi:10.1084/jem.20092164
Turner BJ, Baumer D, Parkinson NJ, Scaber J, Ansorge O, Talbot K (2008) TDP-43 expression in mouse models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and spinal muscular atrophy. BMC Neurosci 9:104. doi:10.1186/1471-2202-9-104
Wang IF, Guo BS, Liu YC, Wu CC, Yang CH, Tsai KJ et al (2012) Autophagy activators rescue and alleviate pathogenesis of a mouse model with proteinopathies of the TAR DNA-binding protein 43. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:15024–15029. doi:10.1073/pnas.1206362109
Wang IF, Reddy NM, Shen CK (2002) Higher order arrangement of the eukaryotic nuclear bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:13583–13588. doi:10.1073/pnas.212483099
Wegorzewska I, Bell S, Cairns NJ, Miller TM, Baloh RH (2009) TDP-43 mutant transgenic mice develop features of ALS and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:18809–18814. doi:10.1073/pnas.0908767106
Wils H, Kleinberger G, Janssens J, Pereson S, Joris G, Cuijt I et al (2010) TDP-43 transgenic mice develop spastic paralysis and neuronal inclusions characteristic of ALS and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:3858–3863. doi:10.1073/pnas.0912417107
Wu LS, Cheng WC, Hou SC, Yan YT, Jiang ST, Shen CK (2010) TDP-43, a neuro-pathosignature factor, is essential for early mouse embryogenesis. Genesis 48:56–62. doi:10.1002/dvg.20584
Wu LS, Cheng WC, Shen CK (2012) Targeted depletion of TDP-43 expression in the spinal cord motor neurons leads to the development of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-like phenotypes in mice. J Biol Chem 287:27335–27344. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.359000
Yoshiyama Y, Higuchi M, Zhang B, Huang SM, Iwata N, Saido TC et al (2007) Synapse loss and microglial activation precede tangles in a P301S tauopathy mouse model. Neuron 53:337–351. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2007.01.010
Zhang YJ, Gendron TF, Xu YF, Ko LW, Yen SH, Petrucelli L (2010) Phosphorylation regulates proteasomal-mediated degradation and solubility of TAR DNA binding protein-43 C-terminal fragments. Mol Neurodegener 5:33. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-5-33
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Todd Cohen, Edward B. Lee, Sílvia Porta and Kurt Brunden for helpful discussion and input on the manuscript, Chi Li and Clark Restrepo for technical assistance, Drs. Manuela Neumann and Elizabeth Kremmer for providing the phosphorylation specific TDP-43 rat monoclonal antibody TAR5P-1D3, Dr. Xu-Gang Xia, Thomas Jefferson University for the NEFH-tTA construct, Dr. Chris Henderson, Columbia University for the VAChT antibody, and Dr. Jean Richa of the University of Pennsylvania Transgenic and Chimeric Mouse Facility for transgenic mouse production. This work was supported by NIH/NIA AG032953 and AG17586, and by Australian National Health & Medical Research Council C.J. Martin Biomedical Early Career Fellowship 1036835 (to A.W.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution at which the studies were conducted.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 2 (MP4 10923 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walker, A.K., Spiller, K.J., Ge, G. et al. Functional recovery in new mouse models of ALS/FTLD after clearance of pathological cytoplasmic TDP-43. Acta Neuropathol 130, 643–660 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1460-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-015-1460-x