Abstract
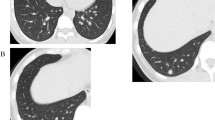
The aim of this study was to demonstrate the characteristic CT findings of leukemic pulmonary infiltration based on the pathologic findings. The CT findings of 11 leukemic patients with leukemic pulmonary infiltration were compared with those of 22 leukemic patients with other diseases as a control group. Evaluated pulmonary parenchymal CT findings included thickening of bronchovascular bundles and interlobular septa, prominence of peripheral pulmonary arteries, ground-glass opacities, air-space consolidation, and nodules. The CT-pathologic correlations for leukemic infiltration were evaluated in 7 patients. Frequent parenchymal CT findings were thickening of bronchovascular bundles (81.8%), prominence of peripheral pulmonary arteries (81.8%), and non-lobular and non-segmental ground-glass opacities (90.9%). The first two findings were significantly more frequently observed in leukemic infiltration than in the control group, had good interobserver agreement, and corresponded pathologically to leukemic cell infiltration around the pulmonary arteries, bronchi, or bronchioles. Non-lobular and non-segmental ground-glass opacity corresponded to leukemic cell infiltration within alveolar spaces and septa adjacent to the pulmonary arteries or bronchi and also corresponded to hemorrhage, edema, or diffuse alveolar damage. Thickening of bronchovascular bundles and prominence of peripheral pulmonary arteries are CT findings suggestive for leukemic infiltration and correspond to peribronchovascular tumor extension.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, N., Matsumoto, T., Miura, G. et al. CT findings of leukemic pulmonary infiltration with pathologic correlation. Eur Radiol 12, 166–174 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003300101013
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003300101013